化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (2): 152-159.DOI: 10.6023/A23100459 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
刘洋a,*( ), 高丰琴a, 马占营a, 张引莉a, 李午戊a, 侯磊b,*(
), 高丰琴a, 马占营a, 张引莉a, 李午戊a, 侯磊b,*( ), 张小娟a, 王尧宇b
), 张小娟a, 王尧宇b
投稿日期:2023-10-20
发布日期:2024-01-05
基金资助:
Yang Liua( ), Fengqin Gaoa, Zhanying Maa, Yinli Zhanga, Wuwu Lia, Lei Houb(
), Fengqin Gaoa, Zhanying Maa, Yinli Zhanga, Wuwu Lia, Lei Houb( ), Xiaojuan Zhanga, Yaoyu Wangb
), Xiaojuan Zhanga, Yaoyu Wangb
Received:2023-10-20
Published:2024-01-05
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:文章分享

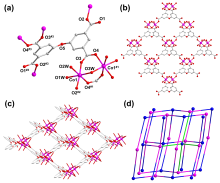
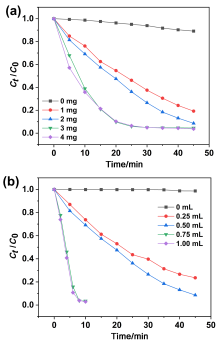
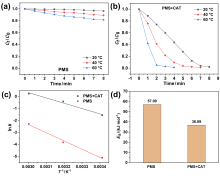
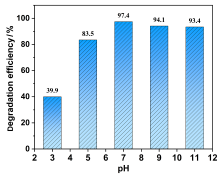
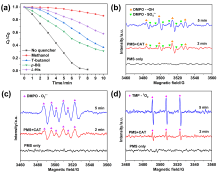
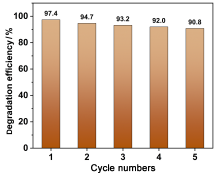
在水净化领域, 基于硫酸根自由基(SO4•-)的高级氧化工艺因其高选择性和氧化优势应用潜力巨大. 开发高性能过氧单硫酸盐(PMS)催化剂是染料废水处理的研究热点. 此工作中, 选用5,5'-二苯醚间苯二甲酸(H4odip)和Co2+离子通过溶剂热法合成得到一例新的钴基金属有机框架化合物Co(μ6-odip)0.5(μ2-OH2)0.5(H2O)2•1.5H2O (1). 该化合物水稳定性和热稳定性优良且具有一定的耐酸碱性. 通过X-射线单晶和粉末衍射、热重分析、元素分析和红外光谱表征了该化合物的结构及组成. 化合物1属于单斜晶系C2/c空间群, 晶胞参数为a=1.6101(9) nm, b=1.5508(10) nm, c=0.9660(6) nm, α=90°, β=112.70(2)°, γ=90°. 通过紫外-可见分光光度计对1活化过氧单硫酸盐降解水中亚甲基蓝(MB)的性能进行测试, 系统研究了1的负载量、过氧单硫酸盐的浓度、反应温度和溶液pH对染料降解性能的影响. 综合化学淬灭实验和电子顺磁共振证明在1/PMS反应体系中催化降解MB的主要活性氧物种(ROS)有SO4•-, •OH和1O2, 但O2•-对MB的催化降解也起到一定促进作用. 实验结果表明该化合物在催化PMS过程中可作为一种高效且可重复使用的新型多相催化剂用于染料废水的修复处理.
刘洋, 高丰琴, 马占营, 张引莉, 李午戊, 侯磊, 张小娟, 王尧宇. 一例钴基金属有机框架化合物活化过氧单硫酸盐高效降解水中亚甲基蓝研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 152-159.
Yang Liu, Fengqin Gao, Zhanying Ma, Yinli Zhang, Wuwu Li, Lei Hou, Xiaojuan Zhang, Yaoyu Wang. Co-based Metal-organic Framework for High-efficiency Degradation of Methylene Blue in Water by Peroxymonosulfate Activation[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 152-159.


| Catalysts | Pollutants/ (mg•L-1) | Time/ min | Degradation rate/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Me2NH2/Sr | MB, 10 | 22 | 99 | [ |
| MIL-101(Fe) | MB, 10 | 25 | 90 | [ |
| Zn-MOF | MB, 10 | 28 | 98 | [ |
| CoFe2O4/ZIF-8 | MB, 20 | 60 | 97.9 | [ |
| Co3/NTB/DPE | MB, 20 | 110 | 93.8 | [ |
| 1 | MB, 20 | 8 | 97.39 | this work |
| Catalysts | Pollutants/ (mg•L-1) | Time/ min | Degradation rate/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Me2NH2/Sr | MB, 10 | 22 | 99 | [ |
| MIL-101(Fe) | MB, 10 | 25 | 90 | [ |
| Zn-MOF | MB, 10 | 28 | 98 | [ |
| CoFe2O4/ZIF-8 | MB, 20 | 60 | 97.9 | [ |
| Co3/NTB/DPE | MB, 20 | 110 | 93.8 | [ |
| 1 | MB, 20 | 8 | 97.39 | this work |

| cMB/(mg•L-1) | VPMS/mL | m1/mg | T/℃ | k/min-1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 0.5 | 1 | 20 | 0.0362 | 0.9897 |
| 20 | 0.5 | 2 | 20 | 0.0534 | 0.9710 |
| 20 | 0.5 | 3 | 20 | 0.1047 | 0.9905 |
| 20 | 0.5 | 4 | 20 | 0.1095 | 0.9810 |
| 20 | 0.25 | 3 | 20 | 0.0328 | 0.9975 |
| 20 | 0.75 | 3 | 20 | 0.2101 | 0.9538 |
| 20 | 0.10 | 3 | 20 | 0.2023 | 0.9112 |
| 20 | 0.75 | 3 | 40 | 0.6652 | 0.9792 |
| 20 | 0.75 | 3 | 60 | 1.2851 | 0.9325 |
| 20 | 0.75 | 0 | 20 | 0.0061 | 0.9334 |
| 20 | 0.75 | 0 | 40 | 0.0211 | 0.9913 |
| 20 | 0.75 | 0 | 60 | 0.1028 | 0.9862 |
| cMB/(mg•L-1) | VPMS/mL | m1/mg | T/℃ | k/min-1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 0.5 | 1 | 20 | 0.0362 | 0.9897 |
| 20 | 0.5 | 2 | 20 | 0.0534 | 0.9710 |
| 20 | 0.5 | 3 | 20 | 0.1047 | 0.9905 |
| 20 | 0.5 | 4 | 20 | 0.1095 | 0.9810 |
| 20 | 0.25 | 3 | 20 | 0.0328 | 0.9975 |
| 20 | 0.75 | 3 | 20 | 0.2101 | 0.9538 |
| 20 | 0.10 | 3 | 20 | 0.2023 | 0.9112 |
| 20 | 0.75 | 3 | 40 | 0.6652 | 0.9792 |
| 20 | 0.75 | 3 | 60 | 1.2851 | 0.9325 |
| 20 | 0.75 | 0 | 20 | 0.0061 | 0.9334 |
| 20 | 0.75 | 0 | 40 | 0.0211 | 0.9913 |
| 20 | 0.75 | 0 | 60 | 0.1028 | 0.9862 |



| [1] |
Sriram, G.; Bendre, A.; Mariappan, E.; Altalhi, T.; Kigga, M.; Ching, Y. C.; Jung, H. Y.; Bhaduri, B.; Kurkuri, M. Sustainable Mater. Technol. 2022, 31, e00378.
|
| [2] |
Tambat, S. N.; Sane, P. K.; Suresh, S.; Varadan, N.; Pandit, A. B.; Sontakke, S. M. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 11, 2626.
|
| [3] |
Deng, Y. C.; Tang, L.; Zeng, G. M.; Feng, C. Y.; Dong, H. R.; Wang, J. J.; Feng, H. P.; Liu, Y. N.; Zhou, Y. Y.; Pang, Y. Environ. Sci.: Nano 2017, 4, 1494.
doi: 10.1039/C7EN00237H |
| [4] |
Jiang, L. B.; Yuan, X. Z.; Zeng, G. M.; Wu, Z. B.; Liang, J.; Chen, X. H.; Leng, L. J.; Wang, H.; Wang, H. Appl. Catal., B 2018, 221, 715.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.09.059 |
| [5] |
Xiao, X.; Tu, S. H.; Lu, M. L.; Zhong, H.; Zheng, C. X.; Zuo, X. X.; Nan, J. M. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2016, 198, 124.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.05.042 |
| [6] |
Wang, W. T.; Lai, X. T.; Yan, S. Q.; Zhu, L.; Yao, Y. Y.; Ding, L. M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 222. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A23010009 |
|
(王文涛, 赖欣婷, 闫士全, 朱雷, 姚玉元, 丁黎明, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 222.)
|
|
| [7] |
Miyata, M.; Ihara, I.; Yoshid, G.; Toyod, K.; Umetsu, K. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 456.
doi: 10.2166/wst.2011.243 pmid: 21278467 |
| [8] |
Miklos, D. B.; Remy, C.; Jekel, M.; Linden, K. G.; Drewes, J. E.; Hubner, U. Water Research 2018, 139, 118.
doi: S0043-1354(18)30238-0 pmid: 29631187 |
| [9] |
Giannakis, S.; Lin, K. Y. A.; Ghanbari, F. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 127083.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127083 |
| [10] |
Huang, X.; Zhang, S. T.; Tang, Y. J.; Zhang, X. Y.; Bai, Y.; Pang, H. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 449, 214216.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2021.214216 |
| [11] |
Huang, D. L.; Zhang, G. X.; Yi, J.; Cheng, M.; Lai, C.; Xu, P.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, C. Y.; Xue, W. J.; Wang, R. Z.; Li, Z. H.; Chen, S. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127672.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127672 |
| [12] |
Yang, Q. J.; Choi, H.; Al-Abed, S. R.; Dionysiou, D. D. Appl. Catal., B 2009, 88, 462.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.10.013 |
| [13] |
Huang, G. X.; Wang, C. Y.; Yang, C. W.; Guo, P. C.; Yu, H. Q. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12611.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b03007 |
| [14] |
Oh, W. D.; Dong, Z. L.; Lim, T. T. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 194, 169.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.04.003 |
| [15] |
Li, J. L.; Zhu, W. H.; Gao, Y.; Lin, P.; Liu, J. W.; Zhang, J. F.; Huang, T. L. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 285, 120362.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120362 |
| [16] |
Wang, C. H.; Kim, J.; Malgras, V.; Na, J.; Lin, J. J.; You, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, J. S.; Yamauchi, Y. Small 2019, 15, 1900744.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v15.16 |
| [17] |
Rojas, S.; Horcajada, P. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8378.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00797 pmid: 32023043 |
| [18] |
Zhu, W. K.; Han, M. S.; Kim, D.; Zhang, Y.; Kwon, G.; You, J.; Jia, C.; Kim, J. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112417.
doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112417 |
| [19] |
Sun, K.; Qian, Y. Y.; Jiang, H. L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202217565.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v62.15 |
| [20] |
Jiao, L.; Jiang, H. L. Chin. J. Catal. 2023, 45, 1.
doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(22)64193-7 |
| [21] |
Anipsitakis, G. P.; Dionysiou, D. D. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 3705.
doi: 10.1021/es035121o |
| [22] |
Zhao, J. Y.; Zhang, Y. B.; Quan, X.; Chen, S. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 71, 302.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2009.12.010 |
| [23] |
Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, X. L.; Su, Z. M. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 289, 121443.
doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2020.121443 |
| [24] |
Sun, H. Q.; Zhou, G. L.; Liu, S. Z.; Ang, H. M.; Tadé, M. O.; Wang, S. B. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6235.
doi: 10.1021/am301829u |
| [25] |
Tang, D.; Zhang, G. K.; Guo, S. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 454, 44.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2015.05.009 |
| [26] |
Xu, L. L.; Liu, W. P.; Li, X. F.; Rashid, S.; Shen, C.; Wen, Y. Z. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 12248.
doi: 10.1039/C4RA13329C |
| [27] |
Yang, Y.; Fu, P.; Li, X.; Su, Z. M.; Xu, N.; Wang, X. L. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 122, 108282.27
doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2020.108282 |
| [28] |
Zhu, M. P.; Yang, J. C. E.; Duan, X. G.; Zhang, D. D.; Wang, S. B.; Yuan, B. L.; Fu, M. L. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125339.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125339 |
| [29] |
Klu, P. K.; Khan, M. A. N.; Wang, C. H.; Qi, J. E.; Sun, X. Y.; Li, J. S. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112148.
doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112148 |
| [30] |
Tuan, D. D.; Nguyen, N. H.; Quang, N. V.; Park, Y. K.; Lin, C. H.; Ghotekar, S.; Wang, H. T.; Chen, W. H.; Yee, Y. F.; Lin, K. Y. A. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110789.
doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.110789 |
| [31] |
Qi, M. Y.; Lin, P.; Shi, Q. Y.; Bai, H. L.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, W. H. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 171, 847.
doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2023.01.069 |
| [32] |
Xie, F. S.; Shi, Q. Y.; Bai, H. L.; Liu, M. Y.; Zhang, J. B.; Qi, M. Y.; Zhang, J. F.; Li, Z. H.; Zhu, W. H. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137384.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137384 |
| [33] |
Feng, Y. Z.; Liu, M. Y.; Shi, Q. Y.; Song, Y. N.; Yang, L. N.; Zhang, J. F.; Li, Z. H.; Zhu, W. H. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111365.
doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.111365 |
| [34] |
Zhao, H.; Sun, H. J.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 1307. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A15030190 |
|
(赵华, 孙宏建, 王麟, 李晓燕, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 1307.)
doi: 10.6023/A15030190 |
|
| [35] |
Liu, Y.; Shi, W. J.; Lu, Y. K.; Liu, G.; Hou, L.; Wang, Y. Y. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 16743.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b02889 |
| [36] |
Liu, H. T.; Ding, L.; Zhou, C. C.; Zou, H. Q.; Lu, J.; Wang, S. N.; Li, Y. W. Chinese J. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 39, 596. (in Chinese)
|
|
(刘厚亭, 丁利, 周传聪, 邹会琪, 卢静, 王素娜, 李允伍, 无机化学学报, 2023, 39, 596.)
|
|
| [37] |
Chen, X. H.; Zhang, Y. S.; Li, W. B.; Guan, X. W.; Ye, J. W.; Chen, L.; Wang, H. P.; Bai, J.; Mo, Z. W.; Chen, X. M. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 2328.
doi: 10.1039/D2QI00091A |
| [38] |
Xiao, Z. Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, L.; Wang, Y. X.; Li, L. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 589, 298.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.12.123 |
| [39] |
Zhang, K.; Sun, D.; Ma, C.; Wang, G. L.; Dong, X. L.; Zhang, X. X. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125021.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125021 |
| [40] |
Luo, X. S.; Bai, L. M.; Xing, J. J.; Zhu, X. W.; Xu, D. L.; Xie, B. H.; Gan, Z. D.; Li, G. B.; Liang, H. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 35720.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b11322 |
| [41] |
Buxton, G. V.; Greenstock, C. L.; Helman, W. P.; Ross, A. B. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 513.
doi: 10.1063/1.555805 |
| [42] |
Li, X. H.; Guo, W. L.; Liu, Z. H.; Wang, R. Q.; Liu, H. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 369, 130.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.02.037 |
| [43] |
Luo, X.; Liang, H.; Qu, F.; Ding, A.; Cheng, X.; Tang, C. Y.; Li, G. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 237.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.113 |
| [1] | 刘嘉文, 林玮璜, 王惟嘉, 郭学益, 杨英. Cu1.94S-SnS纳米异质结的合成及其光催化降解研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 725-734. |
| [2] | 孙博, 琚雯雯, 王涛, 孙晓军, 赵婷, 卢晓梅, 陆峰, 范曲立. 高分散共轭聚合物-金属有机框架纳米立方体的制备及抗肿瘤应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 757-762. |
| [3] | 齐学平, 王飞, 张健. 后合成法构筑钛基金属有机框架及其应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 548-558. |
| [4] | 殷政, 赵英博, 曾明华. 动态化学与材料和非晶物理新关联——金属有机框架玻璃的挑战、进展与新机遇[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(3): 246-252. |
| [5] | 陈俊畅, 张明星, 王殳凹. 晶态多孔材料合成方法的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 146-157. |
| [6] | 程敏, 王诗慧, 罗磊, 周利, 毕可鑫, 戴一阳, 吉旭. 面向乙烷/乙烯分离的金属有机框架膜的大规模计算筛选[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1277-1288. |
| [7] | 闫续, 屈贺幂, 常烨, 段学欣. 金属有机框架在气体预富集、预分离及检测中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1183-1202. |
| [8] | 闫绍兵, 焦龙, 何传新, 江海龙. ZIF-67/石墨烯复合物衍生的氮掺杂碳限域Co纳米颗粒用于高效电催化氧还原[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1084-1090. |
| [9] | 谢晨帆, 徐玉平, 高明亮, 徐忠宁, 江海龙. MOF基Pd单位点催化CO酯化制碳酸二甲酯[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 867-873. |
| [10] | 何家伟, 焦柳, 程雪怡, 陈光海, 吴强, 王喜章, 杨立军, 胡征. 金属有机框架衍生的空心碳纳米笼的结构调控与锂硫电池性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 896-902. |
| [11] | 曹琳安, 魏敏. 电子导电金属有机框架薄膜的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 1042-1056. |
| [12] | 耿元昊, 林小秋, 孙亚昕, 李惠雨, 秦悦, 李从举. 双金属导电金属有机框架材料Ni/Co-CAT的制备及其氧还原催化性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 748-755. |
| [13] | 王诗慧, 薛小雨, 程敏, 陈少臣, 刘冲, 周利, 毕可鑫, 吉旭. 机器学习与分子模拟协同的CH4/H2分离金属有机框架高通量计算筛选[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(5): 614-624. |
| [14] | 吕天天, 马文, 詹冬笋, 邹燕敏, 李继龙, 冯美玲, 黄小荥. 两例新的镧系金属-有机框架化合物高效去除Cs+离子研究※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(5): 640-646. |
| [15] | 赵锦旭, 张铭枢, 陈文发, 姜小明, 刘彬文, 郭国聪. KAg3Ga8S14: 一种高激光损伤阈值的中远红外非线性光学材料※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(3): 259-264. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||