化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (6): 579-587.DOI: 10.6023/A24120380 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
于千水a, 戚聪b, 顾顺心a, 杨欣达c, 姜琴a,*( ), 魏荣斌b,*(
), 魏荣斌b,*( ), 施鹏飞a,*(
), 施鹏飞a,*( )
)
投稿日期:2024-12-25
发布日期:2025-03-28
基金资助:
Qianshui Yua, Cong Qib, Shunxin Gua, Xinda Yangc, Qin Jianga,*( ), Rongbin Weib,*(
), Rongbin Weib,*( ), Pengfei Shia,*(
), Pengfei Shia,*( )
)
Received:2024-12-25
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
*E-mail: jiangqin@jou.edu.cn; rbwei@jou.edu.cn; shipf@jou.edu.cn
Supported by:文章分享
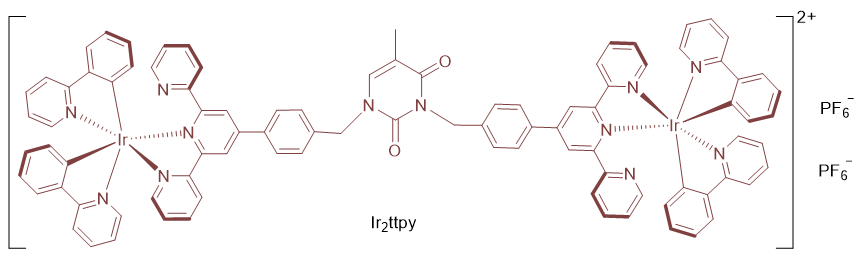
环金属铱配合物因其优秀的发光性能和良好的光毒性, 在双光子光动力疗法(PDT)光敏剂研究领域备受关注. 多联吡啶衍生物常被选作铱配合物的配体, 考虑到胸腺嘧啶分子拥有两个便于修饰的酰胺基团, 将其引入配体有可能会提升生物相容性. 将2,2':6',2''-三联吡啶基团与胸腺嘧啶相连接以制备多联吡啶衍生物ttpy, 进而制备出含有正二价配位阳离子的双核铱配合物Ir2ttpy. Ir2ttpy在250~350 nm呈现出强配体内电荷转移(ILCT)吸收峰, 400~550 nm处呈现弱的金属到配体的荷移跃迁(MLCT)吸收肩峰. Ir2ttpy表现出双重荧光发射, 350 nm处发射峰源自tpy基团3LC激发态, 而600 nm处的发射则来自配位中心3MLCT激发态. 配合物在680~800 nm飞秒激光激发下表现出一定的双光子荧光效应, 吸收截面约为24 GM. 配合物Ir2ttpy针对4T1乳腺癌细胞表现出一定的光毒性, 光毒性指数(PI)值约为18. UV-Vis滴定实验表明配合物Ir2ttpy与DNA有一定的相互结合作用, Autodock模拟显示配合物Ir2ttpy嵌入DNA大沟, 并以氢键与DNA的碱基DA-17以及DC-9结合. 体外滴定实验表明配合物Ir2ttpy在可见光照射下生成1O2和$\text{O}_{2}^{\centerdot }$, 能够光催化氧化烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸(NADH). 细胞成像结果也显示配合物Ir2ttpy能在光照下生成活性氧物种(ROS). 配合物Ir2ttpy的抗肿瘤活性与其诱导生成ROS以及与DNA相互结合有关, 二者协同作用而导致肿瘤细胞死亡.
于千水, 戚聪, 顾顺心, 杨欣达, 姜琴, 魏荣斌, 施鹏飞. 基于胸腺嘧啶三联吡啶的双核铱配合物的发光及抗肿瘤活性研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(6): 579-587.
Qianshui Yu, Cong Qi, Shunxin Gu, Xinda Yang, Qin Jiang, Rongbin Wei, Pengfei Shi. Study on the Luminescent and Antitumor Activities of Binuclear Iridium Complex Based on Thymidyl-Terpyridine[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(6): 579-587.


















| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1039/d4sc01214c pmid: 38725496 |
| [15] |
|
|
(顾顺心, 姜琴, 施鹏飞, 化学进展, 2022, 34, 1957.)
doi: 10.7536/PC211129 |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] | |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1039/d1dt04148g pmid: 35266928 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c13137 pmid: 35171598 |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00203 pmid: 34278794 |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01978 pmid: 38141031 |
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.3390/ijms150610334 pmid: 24918290 |
| [39] |
|
| [1] | 李帅, 刘亚婷, 仰大勇. 外泌体分离技术研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(4): 428-438. |
| [2] | 王丹钰, 郭子涵, 郭梦珂, 易桦, 黄梦雨, 段捷, 张开翔. DNA纳米花生物医学研究进展概述[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(6): 677-689. |
| [3] | 李兰英, 陶晴, 闻艳丽, 王乐乐, 郭瑞妍, 刘刚, 左小磊. 多聚腺嘌呤DNA探针及其生物传感应用★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 681-690. |
| [4] | 郭宜君, 魏冰, 周翔, 姚东宝, 梁好均. DNA步行器调控的纳米粒子超晶格[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 192-199. |
| [5] | 朱青青, 宋晓君, 邓兆祥. 金/铜纳米异质界面的电荷转移等离激元调控[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(7): 675-679. |
| [6] | 李海梅, 罗华健, 肖琦, 杨立云, 黄珊, 刘义. 手性石墨烯量子点与DNA相互作用及其机制研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(6): 577-586. |
| [7] | 刘启雁, 蔡戴宏, 戚永育, 乐学义. 司帕沙星及均三嗪衍生物铜(II)配合物与DNA作用及其抗肿瘤活性[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(3): 263-270. |
| [8] | 赵丽东, 左鹏, 尹斌成, 洪成林, 叶邦策. 细胞膜锚定DNA四面体传感器实时监测外泌体的分泌[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(10): 1076-1081. |
| [9] | 迟景元, 李晶, 任少康, 苏邵, 汪联辉. DNA-二维纳米片层材料传感平台的构建及其应用[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(12): 1230-1238. |
| [10] | 邵昱, 李闯, 周旭, 陈平, 杨忠强, 李志波, 刘冬生. 基于G-四联体的聚多肽-DNA水凝胶响应性研究[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(8): 815-818. |
| [11] | 龙飒然, 宛岩, 夏安东. 水溶性共轭聚合物PFP/DNA/卟啉复合物光谱性质的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(7): 723-728. |
| [12] | 李来才, 张明, 毛双, 杨春, 田安民. B掺杂SWCNT表面吸附DNA碱基的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(2): 143-150. |
| [13] | 张佳佳, 代佩卿, 李超, 李南忘, 程圭芳, 何品刚, 方禹之. 基于磁纳米颗粒的二段对称分裂式G-四分体DNA酶生物传感器用于Hg2+的快速检测[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(9): 1029-1035. |
| [14] | 蔺超, 宫贺, 范楼珍, 李晓宏. DNA/银纳米簇荧光探针在检测Pb2+中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(6): 704-708. |
| [15] | 刘莹, 陈小曼, 张朗棋, 孙冬冬, 周艳晖, 陈兰美, 刘杰. 钌配合物稳定端粒DNA的作用及其诱导细胞凋亡分子机制的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(4): 473-480. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||