

2H-吡咯的简易合成方法:金催化与路易斯酸催化的组合应用
收稿日期: 2015-09-01
网络出版日期: 2015-10-12
基金资助
项目受国家自然科学基金(No. 21272191)、福建省杰出青年科学基金(No. 2015J06003)、国家基础科学人才培养基金(No. J1310024)资助.
Facile Synthesis of 2H-Pyrroles: Combination of Gold Catalysis and Lewis Acid Catalysis
Received date: 2015-09-01
Online published: 2015-10-12
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21272191), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 2015J06003), and National Found for Fostering Talents of Basic Science (No. J1310024).
李新玲 , 王佳琪 , 李龙 , 尹应武 , 叶龙武 . 2H-吡咯的简易合成方法:金催化与路易斯酸催化的组合应用[J]. 化学学报, 2016 , 74(1) : 49 -53 . DOI: 10.6023/A15090573
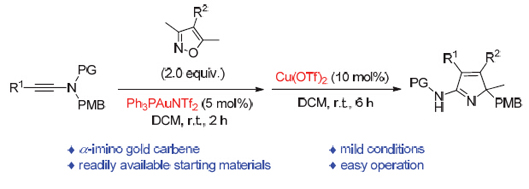
A two-step synthesis of 5-amino 2H-pyrroles using gold and copper catalysis was presented. Firstly, 5-amino 3H-pyrroles were synthesized by gold-catalyzed formal [3+2] cycloaddition between ynamides and isoxazoles via α-imino gold carbene intermediate. The following Lewis acid-triggered decarbonylation and group migration results in the formation of 5-amino 2H-pyrroles. Other notable features of this method include the simple procedure, the mild reaction conditions and compatibility with a broad range of functional groups. Thus, this protocol provides a practical and general solution for the synthesis of 5-amino 2H-pyrroles. Accordingly, isoxazole 2 (2.0 equiv., 0.6 mmol) and Ph3PAuNTf2 (5 mol%) were added to a suspension of the ynamide 1 (1.0 equiv., 0.3 mmol) in DCM (3.0 mL) at room temperature. The reaction mixture was then stirred at r.t. and the progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC. The reaction typically took 2 h. Upon completion, the mixture was quenched with pyridine, concentrated and purified by chromatography on silica gel, using an eluent of petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (5/1, V/V), to afford 3H-pyrrole 3. Then, 3H-pyrrole 3 and Cu(OTf)2 (10 mol%) were dissolved in DCM (3 mL) and stirred at room temperature for 6 h. The residue was purified by column chromatography on silica gel, using an eluent of petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (3/1, V/V), to afford the desired 2H-pyrrole 4. Under this condition, a variety of differently substituted ynamides 1 and isoxazoles 2 work well to provide the corresponding 2H-pyrroles 4a~4l in moderate to good overall yields. But N-(4-methoxybenzyl)-N-(phenylethynyl)methanesulfonamide 1a reacts with 4-(3-bromophenyl)-3,5- dimethylisoxazole 2d poorly under this condition, affording product 4h in only 33% yield. These results indicate that this method has certain universality, but the reaction is influenced by the substituents to some extent. Notably, the scalability and preparative utility of the developed methodology was exemplified by the fact that the desired product 4a was obtained without a significant loss in yield when the reaction was scaled up to 5 mmol. Also a plausible mechanism is proposed and we tend to believe that the reaction is featured by an α-imino gold carbene intermediate.
Key words: pyrrole; gold catalysis; copper catalysis; α-imino gold carbene; [3+2] cycloaddition
[1] For recent reviews, see: (a) Estévez, V.; Villacampa, M.; Menéndez, J. C. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4633.
(b) Rane, R.; Sahu, N.; Shah, C.; Karpoormath, R. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 253.
(c) Young, I. S.; Thornton, P. D.; Thompson, A. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 1801.
(d) Thirumalairajan, S.; Pearce, B. M.; Thompson, A. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 1797.
(e) Fan, H.; Peng, J.; Hamann, M. T.; Hu, J.-F. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 264.
(f) Weinreb, S. M. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 931.
[2] (a) Roos, K.; Viklund, J.; Meuller, J.; Kaspersson, K.; Svensson, M. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 818.
(b) Minidis, A.; Rahm, F.; Viklund, J. PCT Int. Appl. WO 2013054108A1, 2013.
(c) Chow, K.; Gil, D. W.; Donello, J. E.; Wang, L.; Corpuz, E. G.; Fang, W. K.; Sinha, S. C.; Dibas, M. I. PCT Int. Appl. WO 2011044229A1, 2011.
(d) Saito, S.; Takaaki, K.; Kobayashi, J. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 5693.
[3] For recent examples on the synthesis of 2H-pyrroles, see: (a) Zhuo, C.-X.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, W.-B.; Zhao, Q.; You, S.-L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8475.
(b) Zhou, Y.; Zhuo, C.-X.; Gu, Q.; You, S.-L. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2015, 357, 912.
(c) Zhuo, C.-X.; Zhou, Y.; You, S.-L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6590.
(d) Lin, J.; Cheng, Y.; Kang, T.; He, L.; Liu, Q. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 34, 735. (林敬, 程宇, 康泰然, 何龙, 刘全忠, 有机化学, 2014, 34, 735).
(e) Zhuo, C.-X.; Liu, W.-B.; Wu, Q.-F.; You, S.-L. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 205.
(f) Ghavtadze, N.; Fröhlich, R.; Würthwein, E.-U. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 3656.
(g) Cai, C.-J.; Hu, B.-C.; Lu, C.-X. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 25, 1311. (蔡超君, 胡炳成, 吕春绪, 有机化学, 2005, 25, 1311).
[4] For recent reviews on ynamide reactivity, see: (a) Wang, X.-N.; Yeom, H.-S.; Fang, L.-C.; He, S.; Ma, Z.-X.; Kedrowski, B. L.; Hsung, R. P. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 560.
(b) DeKorver, K. A.; Li, H.; Lohse, A. G.; Hayashi, R.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hsung, R. P. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 5064.
(c) Evano, G.; Coste, A.; Jouvin, K. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2840.
[5] For our recent study on the ynamide chemistry, see: (a) Shen, C.-H.; Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.-F.; Wang, Z.-S.; He, W.; Li, T.; Ye, L.-W. J. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 795, 63.
(b) Shu, C.; Wang, Y.-H.; Zhou, B.; Li, X.-L.; Ping, Y.-F.; Lu, X.; Ye, L.-W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 9567.
(c) Li, L.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Y.-H.; Shu, C.; Pan, Y.-F.; Lu, X.; Ye, L.-W. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8245.
(d) Li, L.; Zhou, B.; Ye, L.-W. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 35, 655. (李龙, 周波, 叶龙武, 有机化学, 2015, 35, 655).
(e) Li, L.; Shu, C.; Zhou, B.; Yu, Y.-F.; Xiao, X.-Y.; Ye, L.-W. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 4057.
(f) Pan, F.; Liu, S.; Shu, C.; Lin, R.-K.; Yu, Y.-F.; Zhou, J.-M.; Ye, L.-W. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 10726.
(g) Shen, C.-H.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, S.; Shu, C.; Xie, Y.-E.; Yu, Y.-F.; Ye, L.-W. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 9313.
[6] (a) Xiao, X.-Y.; Zhou, A.-H.; Shu, C.; Pan, F.; Li, T.; Ye, L.-W. Chem. Asian J. 2015, 10, 1854.
(b) Zhou, A.-H.; He, Q.; Shu, C.; Yu, Y.-F.; Liu, S.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X.; Ye, L.-W. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 1265.
[7] For recent selected reviews on gold carbene chemistry, see: (a) Qian, D.; Zhang, J. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 677.
(b) Wang, Y.; Muratore, M. E.; Echavarren, A. M. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 7332.
(c) Yeom, H.-S.; Shin, S. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 966.
(d) Fensterbank, L.; Malacria, M. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 953.
(e) Obradors, C.; Echavarren, A. M. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 902.
(f) Zhang, L. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 877.
(g) Hashmi, A. S. K. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 864.
(h) Obradors, C.; Echavarren, A. M. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 16.
(i) Zhang, Y.; Luo, S.; Zhu, C. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 32, 2073. (张艳, 罗莎, 朱成建, 有机化学,2012, 32, 2073).
(j) Xiao, J.; Li, X. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7226.
(k) Hashmi, A. S. K. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 5232.
(l) Luo, P.; Tang, R.; Zhong, P.; Li, J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 29, 1924. (罗培松, 汤日元, 钟平, 李金恒, 有机化学, 2009, 29, 1924).
[8] For selected examples on the generation of α-imino gold carbenes, see: (a) Li, N.; Wang, T.-Y.; Gong, L.-Z.; Zhang, L. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 3585.
(b) Zhu, L.; Yu, Y.; Mao, Z.; Huang, X. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 30.
(c) Prechter, A.; Henrion, G.; dit Bel, P. F.; Gagosz, F. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 4959.
(d) Garzón, M.; Davies, P. W. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 4850.
(e) Tokimizu, Y.; Oishi, S.; Fujii, N.; Ohno, H. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 3138.
(f) Gronnier, C.; Boissonnat, G.; Gagosz, F. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 4234.
(g) Chatzopoulou, E.; Davies, P. W.; Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8617.
(h) Yan, Z.-Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8624.
(i) Xiao, Y.; Zhang, L. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4662.
(j) Davies, P. W.; Cremonesi, A.; Dumitrescu, L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8931.
(k) Lu, B.; Luo, Y.; Liu, L.; Ye, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8358.
(l) Wetzel, A.; Gagosz, F. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7354.
(m) Li, C.; Zhang, L. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 1738.
(n) Gorin, D. J.; Davis, N. R.; Toste, F. D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 11260.
[9] For a review on the combination of Au/acid catalysis, see: Zhang, S.; Wei, F.; Song, C.; Jia, J.; Xu, Z. Chin. J. Chem. 2014, 32, 937.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |