

含不同烷基链四苯基丁二烯衍生物的聚集诱导发光及力致变色性能
收稿日期: 2021-12-12
网络出版日期: 2022-01-24
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(21374010)
Aggregation-Induced Emission and Mechanochromism of the Tetraphenylbutadiene Derivatives Containing Different Alkyl Chains
Received date: 2021-12-12
Online published: 2022-01-24
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(21374010)
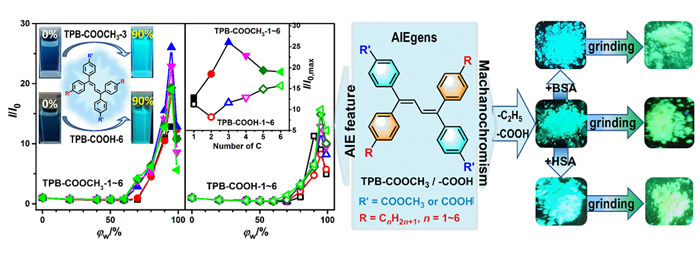
设计合成了带有不同长度烷基链、不同极性取代基的四苯基丁二烯(TPB)衍生物TPB-COOCH3-1~6和TPB-COOH-1~6, 目标化合物均具有显著的聚集诱导发光(AIE)特性及较高的固态荧光量子效率. 烷基链长及取代基极性都会影响目标化合物在聚集时分子排列及分子运动的受限程度, 从而调控其AIE行为. 带有羧酸甲酯的TPB-COOCH3-1~6中, 丙基取代的TPB-COOCH3-3在四氢呋喃/水(THF/H2O)体系中荧光发射增强最为显著; 而羧基取代的TPB-COOH-1~6中, 因亲水性增加, 己基取代的TPB-COOH-6荧光强度增加的倍数最大; 并且, TPB-COOH系列化合物荧光增强的倍数明显低于相同烷基取代的甲酯衍生物TPB-COOCH3. 此外, 牛血清白蛋白、人血清白蛋白和带有羧基的AIE化合物掺杂时明显影响其固态时的发光及其力致变色性质, 尤其是研磨后会明显提高其荧光强度.
张璐璐 , 王媛媛 , 朱贵楠 , 戴文博 , 赵紫璇 , 赵盈 , 支俊格 , 董宇平 . 含不同烷基链四苯基丁二烯衍生物的聚集诱导发光及力致变色性能[J]. 化学学报, 2022 , 80(3) : 282 -290 . DOI: 10.6023/A21120556
Series of 1,1,4,4-tetraphenylbuta-1,3-diene (TPB) derivatives, named TPB-COOCH3-1~6 and TPB-COOH-1~6 containing different alkyl chains and polar substituents, were designed and synthesized by terminal alkyne dimerization and Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling, etc. The target compounds were characterized by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance, 13C nuclear magnetic resonance, mass spectrum, Fourier transform infrared, from which satisfactory results to their molecular structures were obtained. They all have good thermal stabilities with high decomposition temperatures above 310 ℃ based on thermogravimetric analysis. Investigation of the photophysical properties indicated that the target compounds exhibited significant aggregation-induced emission (AIE) features with higher αAIE (αAIE=ΦPL,solid/ΦPL,solu) values of 20.5~49.6 for TPB-COOCH3-1~6 and 14.4~26.3 for TPB-COOH-1~6, and their photoluminescence quantum yields in solid state (ΦPL,solid) were determined as high as 71.3%~89.1% and 34.5%~73.2% for TPB-COOCH3-1~6 and TPB-COOH-1~6, respectively. The different lengths of alkyl chains and the polarity of the other substituent had obvious effect on the regular molecular stacking of the target compounds when they were forced to aggregate or precipitate, which affects the intermolecular interaction and the restriction degree of the rotators, consequently influenced their AIE behavior in the tetrahydrofuran (THF)/H2O mixtures. For the compounds TPB-COOCH3-1~6 containing methyl esters and different alkyl chains, TPB-COOCH3-3, which is with n-propyl, exhibited the most significant fluorescence enhancement (I/I0=26.0) in the THF/H2O mixtures. While, for TPB-COOH-1~6 containing -COOH and alkyl chains, TPB-COOH-6, which is with n-hexyl, had the maximum I/I0 (I/I0=15.7) due to the increase of hydrophilicity. Careful comparison revealed that the I/I0 and ΦPL,solid values of TPB-COOCH3-1~6 were higher than those of TPB-COOH-1~6 containing same alkyl chains under the same measuring condition, mainly attributing to the interaction between the -COOH groups or between -COOH and the polar solvent molecules, which increasing the nonradiative energy decay and weakening fluorescence emission. Furthermore, the incorporation of bovine serum albumin (BSA) and human serum albumin (HSA) into TPB-COOH significantly enhanced the solid-state fluorescence emission, and the BSA and HSA also influenced the mechanochromic properties of the AIEgens containing -COOH. Especially, the fluorescence intensity increased obviously after grinding the doped system of TPB-COOH-2 and BSA, mainly because the existence and steric hindrance of BSA molecules weakened the π-π interaction of the planarized TPB-COOH-2 molecules, which effectively inhibiting the intramolecular rotation of benzene ring and reducing the nonradia tive energy loss.

| [1] | Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Cheng, L.; Tang, B. Z.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H. S.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D. Chem. Commun. 2001, (18), 1740. |
| [2] | Chen, Y.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Liu, B.; Tang, B. Z. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 428. |
| [3] | Zhang, Y.; Mao, H.; Xu, W.; Shi, J.; Cai, Z.; Tong, B.; Dong, Y. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 15965. |
| [4] | Yuan, Y.; Zhang, C.-J.; Xu, S.; Liu, B. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1862. |
| [5] | Gao, H.; Jiao, D.; Ou, H.; Zhang, J.; Ding, D. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 319. (in Chinese) |
| [5] | (高贺麟, 焦迪, 欧翰林, 章经天, 丁丹, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 319.) |
| [6] | Shao, L.; Sun, J.; Hua, B.; Huang, F. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 4866. |
| [7] | Han, T.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X.; Lin, Z.; Tong, B.; Shi, J.; Zhi, J.; Dong, Y. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7049. |
| [8] | Zhang, Y.; Han, T.; Gu, S.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, C.; Guo, Y.; Feng, X.; Tong, B.; Bing, J.; Shi, J.; Zhi, J.; Dong, Y. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 8856. |
| [9] | Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Cai, Z.; Tong, B.; Shi, J.; Dong, Y. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2018, 267, 351. |
| [10] | Guo, Y.; Feng, X.; Han, T.; Wang, S.; Lin, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wang, B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15485. |
| [11] | Chen, J.; Xia, J.; Gao, W.-J.; Yu, H.-J.; Zhong, J.-X.; Jia, C.; Qin, Y.-S.; She, Z.; Kuang, D.-B.; Shao, G. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 21088. |
| [12] | Guo, Y.; Gu, S.; Feng, X.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Han, T.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, X.; James, T. D.; Wang, B. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 4388. |
| [13] | He, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhang, S.; Yan, J.; Wang, M.; Cai, Z.; Wang, J.; Dong, Y. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3834. |
| [14] | Liu, P.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X.; Li, H.; Shi, J.; Tong, B.; Dong, Y. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 536. |
| [15] | Bera, M. K.; Chakraborty, C.; Malik, S. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 6872. |
| [16] | Xu, Z.; Gu, J.; Qiao, X.; Qin, A.; Tang, B. Z.; Ma, D. ACS Photonics 2019, 6, 767. |
| [17] | Zheng, K.; Ni, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, C.; Yang, C. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9972. |
| [18] | Huang, G.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, B. S.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900516. |
| [19] | Li, W.; Huang, Q.; Mao, Z.; Li, Q.; Jiang, L.; Xie, Z.; Xu, R.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Aldred, M. P.; Chi, Z. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12727. |
| [20] | Liu, M.; Wu, Q.; Shi, H.; An, Z.; Huang, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 246. (in Chinese) |
| [20] | (刘明丽, 吴琪, 史慧芳, 安众福, 黄维, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 246.) |
| [21] | Hu, M.; Feng, H.-T.; Yuan, Y.-X.; Zheng, Y.-S.; Tang, B. Z. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2020, 416, 213329. |
| [22] | Huang, Y.; You, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Gui, S.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, D. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10042. |
| [23] | Wang, J.; Chai, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Han, M.; Liao, Q.; Huang, A.; Lin, P.; Li, C.; Li, Q.; Li, Z. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17297. |
| [24] | Li, Q.; Li, Z. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 962. |
| [25] | Wang, J.; Li, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 575. (in Chinese) |
| [25] | (王金凤, 李振, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 575.) |
| [26] | Zhou, T.; Qian, Y.; Wang, H.; Feng, Q.; Xie, L.; Huang, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 557. (in Chinese) |
| [26] | (周涛, 钱越, 王宏健, 冯全友, 解令海, 黄维, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 557.) |
| [27] | Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Ji, S.; Liu, Q.; Ding, D.; Zhao, D.; Liu, B. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 2782. |
| [28] | Qu, J.; Ren, F.; Shi, J.; Tong, B.; Cai, Z.; Dong, Y. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 14947. |
| [29] | Li, N.; Liu, Y. Y.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, J. B.; Cui, R. R.; Gong, Q.; Zhao, N.; Tang, B. Z. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24249. |
| [30] | Qiu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Chen, W.-C.; Xing, L.; Hu, S.; Ji, S.; Yang, Q.; Cai, N.; Ouyang, X.; Huo, Y. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 4139. |
| [31] | Li, J.-H.; Liang, Y.; Xie, Y.-X. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 8125. |
| [32] | Li, Y.; Lei, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhi, J.; Shi, J.; Tong, B.; Dong, Y. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 573. |
| [33] | Yu, H.-X.; Zhi, J.; Wang, J.-L. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 3882. |
| [34] | Zhang, L.; Liang, K.; Dong, L.; Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhi, J.; Shi, J.; Tong, B.; Dong, Y. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 8877. |
| [35] | Dong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, A.; Gong, J.; He, B.; Xu, S.; Yin, J.; Liu, S. H.; Tang, B. Z. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 894. |
| [36] | Xia, Z.; Shao, A.; Li, Q.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 351. (in Chinese) |
| [36] | (夏志清, 邵安东, 李强, 朱世琴, 朱为宏, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 351.) |
| [37] | Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Quan, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Ye, S. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 439. |
| [38] | Peng, Z.; Ji, Y.; Huang, Z.; Tong, B.; Shi, J.; Dong, Y. Mater. Chem. Front. 2018, 2, 1175. |
| [39] | Feng, X.; Tong, B.; Shen, J.; Shi, J.; Han, T.; Chen, L.; Zhi, J.; Lu, P.; Ma, Y.; Dong, Y. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 16731. |
| [40] | Gao, H.; Xu, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Han, A.; Wang, Y. Dyes Pigments 2018, 150, 165. |
| [41] | Lei, Y.; Lai, Y.; Dong, L.; Shang, G.; Cai, Z.; Shi, J.; Zhi, J.; Li, P.; Huang, X.; Tong, B.; Dong, Y. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 434. |
| [42] | Song, W.; Zhi, J.; Wang, T.; Li, B.; Ni, S.; Ye, Y.; Wang, J. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 3875. |
| [43] | Ràfols, C.; Amézqueta, S.; Fuguet, E.; Bosch, E. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 150, 452. |
| [44] | Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Chem. J. Chinese Univ. 2021, 42, 731. (in Chinese) |
| [44] | (李梦硕, 张静, 刘丹, 朱亚先, 张勇, 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42, 731.) |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |