Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (6): 627-645.DOI: 10.6023/A23030063 Previous Articles Next Articles
Special Issue: 庆祝《化学学报》创刊90周年合辑
Review
曾少娟, 孙雪琦, 白银鸽, 白璐, 郑爽, 张香平, 张锁江*( )
)
投稿日期:2023-03-03
发布日期:2023-04-26
作者简介: |
曾少娟, 2007年在东华大学获硕士学位, 同年进入中国科学院过程工程研究所工作, 2016年获中国科学院过程工程研究所博士学位, 现为中国科学院过程工程研究所研究员. 主要研究方向: 离子液体构效关系、功能离子液体/材料设计合成和气体分离应用. |
 |
张锁江, 1986年获河南大学学士学位; 1994年获浙江大学博士学位, 之后进入北京化工大学做博士后; 1995年获得日本文部省奖学金在日本留学; 2001年回国进入中国科学院过程工程研究所工作, 2010年任中国科学院过程工程研究所所长, 2015年当选为中国科学院院士. 主要研究方向: 离子液体与绿色过程, 包括离子液体的分子设计、规模制备和清洁工艺. |
基金资助:
Shaojuan Zeng, Xueqi Sun, Yinge Bai, Lu Bai, Shuang Zheng, Xiangping Zhang, Suojiang Zhang( )
)
Received:2023-03-03
Published:2023-04-26
Contact:
* E-mail: sjzhang@ipe.ac.cn
About author:Supported by:Share
Shaojuan Zeng, Xueqi Sun, Yinge Bai, Lu Bai, Shuang Zheng, Xiangping Zhang, Suojiang Zhang. Research Progress of CO2 Capture and Separation by Functionalized Ionic Liquids and Materials★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 627-645.
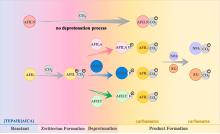

| [1] |
(a) Mohammad, A.; Kibum, K.; Cong, L.; Addepalli, A. Science 2016, 353, 467.
doi: 10.1126/science.aaf4767 pmid: 27471300 |
|
(b) Hirunsit, P.; Soodsawang, W.; Limtrakul, J. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 8238.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b01574 pmid: 27471300 |
|
|
(c) Alvarez-Guerra, M.; Albo, J.; Alvarez-Guerra, E.; Irabien, A. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2574.
doi: 10.1039/C5EE01486G pmid: 27471300 |
|
|
(d) Rosen, B.; Salehi-Khojin, A.; Thorson, M.; Zhu, W.; Whipple, D.; Kenis, P.; Masel, R. Science 2011, 334, 643.
doi: 10.1126/science.1209786 pmid: 27471300 |
|
| [2] |
(a) Zeng, S.; Dong, H.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Green Chem. Eng. 2020, 1, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.gce.2020.10.004 |
|
(b) Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Mumford, K.; Stevens, G.; Fei, W.; Wang, Y. Green Chem. Eng. 2020, 1, 16.
doi: 10.1016/j.gce.2020.09.005 |
|
|
(c) Li, B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Green Energy Environ. 2021, 6, 253.
doi: 10.1016/j.gee.2020.04.009 |
|
| [3] |
(a) Wu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Mumford, K.; Stevens, G.; Fei, W. Green Energy Environ. 2021, 6, 291.
doi: 10.1016/j.gee.2020.04.016 |
|
(b) Liu, Y.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Ji, X. Green Energy Environ. 2021, 6, 314.
doi: 10.1016/j.gee.2020.11.024 |
|
|
(c) Zhang, S.; He, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; Tian, Y. Green Chem. Eng. 2022, 3, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.gce.2021.11.008 |
|
| [4] |
Blanchard, L.; Hancu, D.; Beckman, E.; Brennecke, J. Nature 1999, 399, 28.
|
| [5] |
Eleanor, D.; Bates, R.; Ioanna, N.; James, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 926.
pmid: 11829599 |
| [6] |
Luo, X.; Guo, Y.; Ding, F.; Zhao, H.; Cui, G.; Li, H.; Wang, C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7053.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201400957 |
| [7] |
Huang, Y.; Cui, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Dai, S.; Wang, J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 13293.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201706280 |
| [8] |
Bates, E. D.; Mayton, R. D.; Ntai, I.; Davis, J. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 124, 926.
doi: 10.1021/ja017593d |
| [9] |
Zareiekordshouli, F.; Lashani-zadehgan, A.; Darvishi, P. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Con. 2016, 53, 328.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2016.08.022 |
| [10] |
Pan, L.; Shi, W.; Li, B.; Wei, X. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 30, 1780.
doi: 10.1007/s11630-021-1504-6 |
| [11] |
Huang, K.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Wu, Y. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 14060.
doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b03049 |
| [12] |
Zhang, J.; Jia, C.; Dong, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 5835.
doi: 10.1021/ie4001629 |
| [13] |
Simons, T.; Verheyen, T.; Izgorodina, E. I.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Young, S.; Pearson, A.; Pas, S.; MacFarlane, D. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 1140.
doi: 10.1039/C5CP05200A |
| [14] |
Shi, G.; Zhao, H.; Chen, K.; Lin, W.; Li, H.; Wang, C. AIChE J. 2019, 66, 1.
|
| [15] |
Tiwari, S.; Pant, K.; Upadhyayula, S. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 45, 101416.
|
| [16] |
Gurkan, B.; de la Fuente, J.; Mindrup, E.; Ficke, L.; Goodrich, B.; Price, E.; Schneider, W. F.; Brennecke, J. F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2116.
doi: 10.1021/ja909305t pmid: 20121150 |
| [17] |
Brett, F.; Juan, C.; Burcu, E.; David, J.; Erica, A.; Huang, Y.; Brennecke, J. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 111.
doi: 10.1021/ie101688a |
| [18] |
(a) Luo, X.; Ding, F.; Lin, W.; Qi, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, C. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 381.
|
|
(b) Luo, X.; Fan, X.; Shi, G.; Li, H.; Wang, C. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 2807.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.5b10553 |
|
| [19] |
(a) Saravanamurugan, S.; Kunov-Kruse, A.; Fehrmann, R.; Riisager, A. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 897.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.201300691 pmid: 24677784 |
|
(b) Sistla, Y.; Khanna, A. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 268.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.09.043 pmid: 24677784 |
|
|
(c) Chen, F.; Huang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zhu, X.; Tao, D.; Jiang, D.; Dai, S. CIESC J. 2016, 55, 7166.
pmid: 24677784 |
|
| [20] |
Goodrich, B. F.; de la Fuente, J.; Gurkan, B.; Lopez, Z.; Price, E.; Huang, Y.; Brennecke, J. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 9140.
doi: 10.1021/jp2015534 |
| [21] |
Firaha, D.; Kirchner, B. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 1591.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.201600126 |
| [22] |
Yang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Bao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Q.; Xing, H.; Dai, S. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 806.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.201501691 |
| [23] |
Rezaeian, M.; Izadyar, M.; Nakhaei Pour, A. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 5721.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.8b03152 pmid: 29893557 |
| [24] |
Luo, X.; Lv, X.; Shi, G.; Meng, Q.; Li, H. R.; Wang, C. AIChE J. 2019, 65, 230.
doi: 10.1002/aic.v65.1 |
| [25] |
Onofri, S.; Bodo, E. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 5611.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.1c02945 |
| [26] |
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Fan, W.; Zhang, X. Chemistry 2009, 15, 3003.
|
| [27] |
Kasahara, S.; Kamio, E.; Shaikh, A. R.; Matsuki, T.; Matsuyama, H. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 503, 148.
doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2016.01.007 |
| [28] |
Shaikh, A.; Karkhanechi, H.; Kamio, E.; Yoshioka, T.; Matsuyama, H. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 27734.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b07305 |
| [29] |
(a) Zhou, X.; Jing, G.; Liu, F.; Lv, B.; Zhou, Z. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 1793.
doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b02963 |
|
(b) Zhou, Z.; Zhou, X.; Jing, G.; Lv, B. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 7489.
doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b00692 |
|
| [30] |
Jing, G.; Qian, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lv, B.; Zhou, Z. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2017, 6, 1182.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03467 |
| [31] |
Zeng, S.; Wang, J.; Bai, L.; Wang, B.; Gao, H.; Shang, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 6039.
doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b01274 |
| [32] |
Zhou, L.; Fan, J.; Shang, X.; Wang, J. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2013, 59, 28.
doi: 10.1016/j.jct.2012.11.030 |
| [33] |
(a) Kanakubo, M.; Makino, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Nokami, T.; Itoh, T. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 525.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00960 |
|
(b) Makino, T.; Kanakubo, M.; Masuda, Y.; Umecky, T.; Suzuki, A. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2014, 362, 300.
doi: 10.1016/j.fluid.2013.10.031 |
|
| [34] |
Wang, C.; Luo, H.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Yu, B.; Dai, S. Chemistry 2012, 18, 2153.
|
| [35] |
Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.; Tu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 268, 617.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2018.07.096 |
| [36] |
Chen, K.; Mei, K.; Li, H.; Wang, C. CIESC J. 2016, 67, 623.
|
| [37] |
Lin, W.; Cai, Z.; Lv, X.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, K.; Li, H.; Wang, C. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 16894.
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b02872 |
| [38] |
Wang, C.; Luo, H.; Jiang, D.; Li, H.; Dai, S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4918.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v50.21 |
| [39] |
Wang, C.; Luo, H.; Jiang, D.; Li, H.; Dai, S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 5978.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201002641 |
| [40] |
Oh, S.; Morales-Collazo, O.; Keller, A. N.; Brennecke, J. F. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 8877.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c06374 |
| [41] |
Seo, S.; DeSilva, M. A.; Brennecke, J. F. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 14870.
doi: 10.1021/jp509583c |
| [42] |
Baj, S.; Krawczyk, T.; Dabrowska, A.; Siewniak, A.; Sobolewski, A. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 2295.
doi: 10.1007/s11814-015-0082-2 |
| [43] |
Mei, K.; He, X.; Chen, K.; Zhou, X.; Li, H.; Wang, C. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 8066.
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.7b01001 |
| [44] |
Zhang, X.; Xiong, W.; Peng, L.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X. AIChE J. 2020, 66, 103319.
|
| [45] |
Huang, Y.; Cui, G.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 28, 299.
|
| [46] |
(a) Qiao, Y.; Ma, W.; Theyssen, N.; Chen, C.; Hou, Z. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6881.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00652 pmid: 29675708 |
|
(b) Nobuoka, K.; Kitaoka, S.; Yamauchi, T.; Harran, T.; Ishikawa, Y. Chem. Lett. 2016, 45, 433.
doi: 10.1246/cl.160048 pmid: 29675708 |
|
|
(c) Shi, Y.; Xiong, D.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J. Langmuir 2016, 32, 6895.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b01167 pmid: 29675708 |
|
|
(d) Fiorentini, E.; Escudero, L.; Wuilloud, R. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4715.
doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-1050-6 pmid: 29675708 |
|
| [47] |
Lin, W.; Pan, M.; Xiao, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, C. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 3346.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b01023 |
| [48] |
Zhang, F.; Gao, Y.; Wu, X.; Ma, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 371.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.03.005 |
| [49] |
Hasib-ur-Rahman, M.; Larachi, F. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11443.
doi: 10.1021/es302513j pmid: 22963662 |
| [50] |
(a) Dean, C.; Jason, E.; Douglas, L.; Noble, R. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 8496.
doi: 10.1021/ie801002m |
|
(b) Ahmady, A.; Hashim, M.; Aroua, M. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 763.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.06.059 |
|
|
(c) Taib, M.; Murugesan, T. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 181, 56.
|
|
|
(d) Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, S.; Zhou, Q.; Dong, H.; Tian, X.; Zhang, S. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 3513.
doi: 10.1021/je100078w |
|
|
(e) Ahmady, A.; Hashim, M.; Aroua, M. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2011, 309, 76.
doi: 10.1016/j.fluid.2011.06.029 |
|
|
(f) Aziz, N.; Yusoff, R.; Aroua, M. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2012, 322, 120.
|
|
|
(g) Gao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Huang, K.; Ma, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Con. 2013, 19, 379.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2013.09.019 |
|
| [51] |
Romanos, G.; Zubeir, L.; Likodimos, V.; Falaras, P.; Kroon, M.; Iliev, B.; Adamova, G.; Schubert, T. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 12234.
doi: 10.1021/jp407364e |
| [52] |
Aparicio, S.; Atilhan, M. Chem. Phys. 2012, 400, 118.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemphys.2012.03.008 |
| [53] |
Li, T.; Chen, B.; Piao, X. CIESC J. 2013, 64, 600. (in Chinese)
|
|
(李天成, 陈郴, 朴香兰, 化工学报, 2013, 64, 600.)
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2013.02.026 |
|
| [54] |
Zhang, Y.; Yu, P.; Luo, Y. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 214, 355.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.10.080 |
| [55] |
Simon, N.; Zanatta, M.; Dos Santos, F.; Corvo, M.; Cabrita, E.; Dupont, J. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 4927.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.201701044 |
| [56] |
Zheng, W.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 243, 169.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2017.08.035 |
| [57] |
Li, F.; Bai, Y.; Zeng, S.; Liang, X.; Wang, H.; Huo, F.; Zhang, X. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Con. 2019, 90, 102801.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2019.102801 |
| [58] |
Wei, L.; Guo, R.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Xu, Y. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 239, 116531.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116531 |
| [59] |
Shohrat, A.; Zhang, M.; Hu, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Huang, H. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Con. 2022, 119, 103709.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2022.103709 |
| [60] |
Li, W.; Wen, S.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.; Li, S. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 10813.
doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b02612 |
| [61] |
Wang, K.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zeng, S.; Ren, B.; Zhang, X.; Dong, H. Chin. J. Proc. Eng. 2022, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.4541.TQ.20220622.1123.004.html in Chinese)
|
|
(王凯旋, 李涛, 李玉, 白银鸽, 曾少娟, 任保增, 张香平, 董海峰, 过程工程学报, 2022, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.4541.TQ.20220622.1123.004.html
|
|
| [62] |
Ma, D.; Zhu, C.; Fu, T.; Ma, Y.; Yuan, X. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129302.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129302 |
| [63] |
Zheng, W.; Huang, K.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X. AIChE J. 2018, 64, 209.
doi: 10.1002/aic.v64.1 |
| [64] |
(a) Sun, X.; Waters, K. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1910.
doi: 10.1021/sc500255n |
|
(b) Zhang, Z.; Hu, S.; Song, J.; Li, W.; Yang, G.; Han, B. ChemSusChem 2009, 2, 234.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.v2:3 |
|
| [65] |
Xiao, M.; Liu, H.; Gao, H.; Olson, W.; Liang, Z. Appl. Energ. 2019, 235, 311.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.10.103 |
| [66] |
Zhang, J.; Peng, H.; Liu, Y.; Tao, D.; Wu, P.; Fan, J.; Huang, K. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 9369.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b00530 |
| [67] |
Li, C.; Zhao, T.; Yang, A.; Liu, F. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 34027.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c05416 |
| [68] |
Li, J.; Dai, Z.; Usman, M.; Qi, Z.; Deng, L. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Con. 2016, 45, 207.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2015.12.027 |
| [69] |
Liu, F.; Shen, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, W. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 275, 119123.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119123 |
| [70] |
Li, F.; Zeng, S.; Bai, Y.; Dong, H.; Wang, H.; Ji, X.; Zhang, X. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 8526.
doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c00728 |
| [71] |
Shaahmadi, F.; Hashemi Shahraki, B.; Farhadi, A. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 584.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jced.8b00784 |
| [72] |
Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Pang, X. Molecules 2020, 25, 1.
doi: 10.3390/molecules25010001 |
| [73] |
Cui, G.; Lv, M.; Yang, D. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 1426.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC10085C |
| [74] |
Yan, H.; Zhao, L.; Bai, Y.; Li, F.; Dong, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, S. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 2523.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b07128 |
| [75] |
Cheng, J.; Wu, C.; Gao, W.; Li, H.; Ma, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, D. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1893.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23031893 |
| [76] |
Haider, M.; Kumar, R. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117055.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117055 |
| [77] |
Zhang, N.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, L. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 13321.
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b02041 |
| [78] |
Lian, S.; Song, C.; Liu, Q.; Duan, E.; Ren, H.; Kitamura, Y. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 99, 281.
doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2020.06.034 |
| [79] |
Xu, M.; Wang, S. CIESC J. 2018, 69, 1. (in Chinese)
|
|
(许咪咪, 王淑娟, 化工学报, 2018, 69, 1.)
|
|
| [80] |
Chen, Y.; Hu, H. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 5363.
doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b00268 |
| [81] |
Huang, Q.; Jing, G.; Zhou, X.; Lv, B.; Zhou, Z. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 25, 22.
|
| [82] |
Jiang, W.; Wu, F.; Gao, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Luo, C. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129897.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129897 |
| [83] |
Seo, S.; Simoni, L. D.; Ma, M.; DeSilva, M.; Huang, Y.; Stadtherr, M.; Brennecke, J. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 5968.
doi: 10.1021/ef501374x |
| [84] |
Han, G.; Yu, N.; Liu, D.; Yu, G.; Chen, X.; Zhong, C. AIChE J. 2020, 67, 1.
doi: 10.1002/aic.v67.4 |
| [85] |
Zhang, W.; Gao, E.; Li, Y.; Bernards, M. T.; He, Y.; Shi, Y. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 34, 606.
|
| [86] |
Mohamedali, M.; Ibrahim, H.; Henni, A. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 817.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.104 |
| [87] |
Karousos, D.; Vangeli, O.; Athanasekou, C.; Sapalidis, A.; Kouvelos, E.; Romanos, G.; Kanellopoulos, N. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 146.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.07.040 |
| [88] |
Reed, D.; Dowson, G.; Styring, P. Front. Energy Res. 2017, 5, 1.
|
| [89] |
Raja Shahrom, M.; Nordin, A.; Wilfred, C. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103319.
doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2019.103319 |
| [90] |
Zheng, S.; Zeng, S.; Li, G.; Yao, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138736.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.138736 |
| [91] |
(a) Erto, A.; Silvestre-Albero, A.; Silvestre-Albero, J.; Rodriguez- Reinoso, F.; Balsamo, M.; Lancia, A.; Montagnaro, F. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2015, 448, 41.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2015.01.089 |
|
(b) Xu, W.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, N.; Li, Z.; Lan, H.; Jiang, W.; Huang, K.; Peng, H.; Du, J. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 125, 115.
doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2021.05.053 |
|
|
(c) Huang, Z.; Karami, D.; Mahinpey, N. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 167, 198.
doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2021.01.016 |
|
|
(d) Hiremath, V.; Jadhav, A.; Lee, H.; Kwon, S.; Seo, J. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 602.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.11.075 |
|
| [92] |
Yuan, J.; Fan, M.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Y.; Tang, H.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 903.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.02.035 |
| [93] |
Sun, L.; Yin, M.; Tang, S. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105829.
doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105829 |
| [94] |
He, X.; Mei, K.; Dao, R.; Cai, J.; Lin, W.; Kong, X.; Wang, C. AIChE J. 2017, 63, 3008.
doi: 10.1002/aic.15647 |
| [95] |
Santiago, R.; Lemus, J.; Moya, C.; Moreno, D.; Alonso-Morales, N.; Palomar, J. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 14178.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b02797 |
| [96] |
Mohamedali, M.; Ibrahim, H.; Henni, A. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 294, 109916.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109916 |
| [97] |
Lee, Y.; Edgehouse, K.; Klemm, A.; Mao, H.; Pentzer, E.; Gurkan, B. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 12, 19184.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c01622 |
| [98] |
Zhao, X.; Yuan, Y.; Li, P.; Song, Z.; Ma, C.; Pan, D.; Wu, S.; Ding, T.; Guo, Z.; Wang, N. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 13179.
doi: 10.1039/C9CC07243H |
| [99] |
(a) Friess, K.; Izak, P.; Karaszova, M.; Pasichnyk, M.; Lanc, M.; Nikolaeva, D.; Luis, P.; Jansen, J. Membranes 2021, 11, 1.
doi: 10.3390/membranes11010001 |
|
(b) Shafie, S.; Md Nordin, N.; Racha, S.; Bilad, M.; Othman, M.; Misdan, N.; Jaafar, J.; Putra, Z.; Wirzal, M. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 358, 119192.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2022.119192 |
|
| [100] |
Gao, H.; Bai, L.; Han, J.; Yang, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 12671.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC07348A |
| [101] |
Dai, Z.; Bai, L.; Hval, K. N.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Deng, L. Sci. China: Chem. 2016, 59, 538.
|
| [102] |
Moghadam, F.; Kamio, E.; Matsuyama, H. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 525, 290.
doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2016.12.002 |
| [103] |
Jiang, H.; Bai, L.; Yang, B.; Zeng, S.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 43, 169.
doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2022.02.006 |
| [104] |
Pishva, S.; Hassanajili, S. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 107, 180.
doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2021.11.046 |
| [105] |
Ahmad, N.; Leo, C.; Mohammad, A.; Shaari, N.; Ang, W. Int. J. Energ. Res. 2021, 45, 9800.
doi: 10.1002/er.v45.7 |
| [106] |
Han, J.; Bai, L.; Jiang, H.; Zeng, S.; Yang, B.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, X. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 60, 593.
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.0c04830 |
| [107] |
Hu, L.; Cheng, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 410, 249.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.045 |
| [108] |
Ilyas, A.; Muhammad, N.; Gilani, M.; Vankelecom, I.; Khan, A. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 205, 176.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.05.040 |
| [109] |
Ma, J.; Ying, Y.; Guo, X.; Huang, H.; Liu, D.; Zhong, C. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 7281.
doi: 10.1039/C6TA02611G |
| [1] | Wen He, Bo Wang, Hanjun Feng, Xiangru Kong, Tao Li, Rui Xiao. Research Progress of CO2 Capture and Membrane Separation by Pebax Based Materials [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 226-241. |
| [2] | Hangqing Lin, Ruoru Ma, Yilan Jiang, Murong Xu, Yangpeng Lin, Kezhao Du. Research Progress of Materials Used for Elemental Halogen Capture [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(1): 62-74. |
| [3] | Yuchun Han, Yilin Wang. Retrospect and Prospect of Long-lasting Antibacterial Materials★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(9): 1196-1201. |
| [4] | Ziqi Li, Liwei Liu, Chenghui Mao, Changkai Zhou, Minqi Xia, Zhen Shen, Yue Guo, Qiang Wu, Xizhang Wang, Lijun Yang, Zheng Hu. Cobalt-Substituted Polyoxometalates as Soluble Mediators to Boost the Lithium-Sulfur Battery Performance [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 620-626. |
| [5] | Kaiqing Wang, Shuo Yuan, Wangdong Xu, Dan Huo, Qiulin Yang, Qingxi Hou, Dehai Yu. Preparation and Adsorption Properties of ZIF-8@B-CNF Composite Aerogel [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 604-612. |
| [6] | Zhao Zhenxin, Yao Yikun, Chen Jiajun, Niu Rong, Wang Xiaomin. A High-entropy Phosphate Cathode Host towards High-stability Lithium-sulfur Batteries [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(5): 496-501. |
| [7] | Jiangmin Jiang, Xinran Zheng, Yating Meng, Wenjie He, Yaxin Chen, Quanchao Zhuang, Jiaren Yuan, Zhicheng Ju, Xiaogang Zhang. Research on the Preparation and Potassium Storage Performance of F, N Co-doped Porous Carbon Nanosheets [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(4): 319-327. |
| [8] | Wanhong Li, Mingyue Yu, Lili Wang, Dehuang Zhu, Suhong Peng, Hui Wang, Haiyang Liu. Sovlent Influence on the Femtosecond Transient Absorption Spectra of Tetraphenylporphyrin Manganese(III) Chloride [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(4): 345-350. |
| [9] | Wentao Wang, Xinting Lai, Shiquan Yan, Lei Zhu, Yuyuan Yao, Liming Ding. Synergistic Treatment of Dye Wastewater by the Adsorption-Degradation of a Bifunctional Aerogel [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(3): 222-230. |
| [10] | Liangmeng Hao, Weigang Zhu. Research Progress on Organic Cocrystals Nonlinear Optics Materials and Applications [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(2): 191-206. |
| [11] | Bing Zheng, Zhe Wang, Jing He, Jiao Zhang, Wenbo Qi, Mengyuan Zhang, Haitao Yu. Structure and Work Function of Alkaline (Earth) Metal-Bilayer α-Borophene Nanocomposite: A Theoretical Study [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(10): 1357-1370. |
| [12] | Jing Zheng, Jinkun Liu, Chunyi Luo, Guochao Zeng, Guanglei Wu, Xu Hou. Research Progress of Active Colloidal Motors and Their Application Perspective in Electromagnetic Wave Absorption★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(10): 1394-1401. |
| [13] | Ke Zhao, Xiayu Cheng, Xuexue Ma, Minghui Geng. Mechanism of Two-photon Absorption Enhancement for a Piperazine-based Zinc Ion Probe [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(10): 1371-1378. |
| [14] | Fang Liu, Tingting Pan, Xiurong Ren, Weiren Bao, Jiancheng Wang, Jiangliang Hu. Research on Preparation and Benzene Adsorption Performance of HCDs@MIL-100(Fe) Adsorbents [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 879-887. |
| [15] | Xiaoqian Li, Jing Zhang, Fangfang Su, Dechao Wang, Dongdong Yao, Yaping Zheng. Construction and Application of Porous Ionic Liquids [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(6): 848-860. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||