Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (3): 229-236.DOI: 10.6023/A24120364 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
胡国伟, 王晓欢*( ), 原志鹏, 新巴雅尔, 乌力吉贺希格*(
), 原志鹏, 新巴雅尔, 乌力吉贺希格*( )
)
投稿日期:2024-12-04
发布日期:2025-02-14
基金资助:
Guowei Hu, Xiaohuan Wang( ), Zhipeng Yuan, Yaer Xinba, Hexige Wuliji(
), Zhipeng Yuan, Yaer Xinba, Hexige Wuliji( )
)
Received:2024-12-04
Published:2025-02-14
Contact:
*E-mail: wangxiaohuan@imut.edu.cn; wljhxg@imut.edu.cn
Supported by:Share
Guowei Hu, Xiaohuan Wang, Zhipeng Yuan, Yaer Xinba, Hexige Wuliji. Effect of Ag Doping on the Photocatalytic Performance of Bismuth Ferrite-based Compounds[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(3): 229-236.










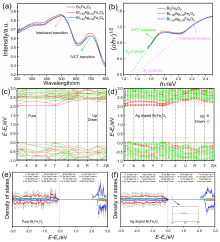

| [1] |
Xia, X. L.; Yang, X. Y.; Huang, W.; Xia, X. X.; Yan, D. Y. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 33.
|
| [2] |
Sun. P. F.; Lin, M. C.; Chen, G. S.; Jiang, M. Sci. China Chem. 2016, 59, 1616.
|
| [3] |
Zhang, J. P.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L. A.; Zhou, J. P.; Lu, A. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 8.
|
| [4] |
Wang, B.; Tang, W.; Zhao, H.-X.; Long, L.-S; Zheng, L.-S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 119 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A20080397 |
|
(王宾, 唐雯, 赵海霞, 龙腊生, 郑兰荪, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 119.)
doi: 10.6023/A20080397 |
|
| [5] |
Xie, M.-S.; Wu, X.-X.; Wang, G.; Lin, L.-L; Feng, X.-M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2014, 72, 856 (in Chinese).
|
|
(谢明胜, 武晓霞, 王刚, 林丽丽, 冯小明, 化学学报, 2014, 72, 856.)
doi: 10.6023/A13121253 |
|
| [6] |
Zhang, C. Y.; Song, A.; Huang, Q. R.; Cao, Y. H.; Zhong, Z. Y.; Liang, Y. C.; Zhang, K.; Liu, C. C.; Huang, F.; Cao, Y. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 140.
|
| [7] |
Zhou, L.; Shao, M. F.; Wei, M.; Duan, X. J. Energy Chem. 2017, 26, 1094.
|
| [8] |
Peng, K.; Fan, Z. Y.; Wang, Y. Q.; Xie, Y.; Ling, Y. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 60, 835.
|
| [9] |
Reddy, P. A. K.; Reddy, P. V. L.; Kwon, E.; Kim, K. H.; Akter, T.; Kalagara, S. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 94.
|
| [10] |
Saad, A. M.; Abukhadra, M. R.; Ahme, S. A. K.; Elzanaty, A. M.; Mady, A. H.; Betiha, M. A.; Shim, J. J.; Rabie, A. M. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 258, 110043.
|
| [11] |
Hu, L. X.; Chen, F. Y.; Hu, P. F.; Zou, L. P.; Hu, X. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 411, 203.
|
| [12] |
Botta, S. G.; Navı́o, J. A.; Hidalgo, M. C.; Restrepo, G. M.; Litter, M. I. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 1999, 129, 89.
|
| [13] |
Tavker, N.; Sharma, M. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 255, 109906.
|
| [14] |
Das, S.; Jayaraman, V. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 66, 112.
|
| [15] |
Zhang, J. j.; Qi, P.; Li, J.; Zheng, X. C.; Liu, P.; Guan, X. X.; Zheng, G. P. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 61, 407.
|
| [16] |
Ran, J. R.; Yu, J. G.; Jaroniec, M. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2708.
|
| [17] |
Tahmasebi, N.; Mirzavand, S.; Hakimyfard, A.; Barzegar, S. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 30, 257.
|
| [18] |
Patial, S.; Hasija, V.; Raizada, P.; Singh, P.; Singh, A. A. P. K.; Asiri, A. M. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103791.
|
| [19] |
Malathi, A.; Madhanvan, J.; Ashokkumar, M.; Arunachalam, P. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2018, 555, 47.
|
| [20] |
Karamian, E.; Sharifnia, S. MSEB 2018, 238-239, 142.
|
| [21] |
Haroonabadi, L.; Sharifnia, S. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 82, 1263.
|
| [22] |
Lee, J. H.; Lee, H.; Kang, M. Mater. Lett. 2016, 178, 316.
|
| [23] |
Song, Y. K.; Bao, Z. Q.; Ge, X. L.; Hu, S. H.; Meng, M. F.; Gu, Y. Y. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 671, 160676.
|
| [24] |
Zhu, Q. Q.; Shi, X. Y.; Zhang, X. J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Z.; Wang, C. C. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 997, 174887.
|
| [25] |
Liu, Y. J.; Xing, C. C.; Yao, Z. F.; Deng, Q. C.; Liang, T.; Zhang, S. M.; Pan, J. H.; Yu, Z. B.; Xie, T.; Li, R.; Hou, Y. P. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 677, 1095.
|
| [26] |
Fang, Y. Z.; Kong, X. J.; Wang, D. T.; Liu, J. H.; Cui, S. X. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 127, 107.
|
| [27] |
Cheng, B. J.; Li, X. Q.; Li, H. B.; Zhang, W. Z.; Han, R. Q.; Zhang, Y. M.; Xiang, J. J. Energy Storage. 2024, 79, 110137.
|
| [28] |
Wu, Z. Z.; Shi, J.; Deng, H. P. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 349, 127779.
|
| [29] |
Zhang, C. M.; Wang, R. X.; Zhang, X. C.; Dong, Z. Y.; Wu, W. S.; Xue, J. B.; Fan, C. M. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 342, 127087.
|
| [30] |
Lomanova, N. A.; Pleshakov, I. V.; Volkov, M. P.; Yastrebov, S. G.; Kenges, K.; Ugolkov, V. L.; Osipov, A. V.; Siyuan, T.; Buryanenko, I. V.; Semenov, V. G. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 161, 112109.
|
| [31] |
Qi, S. Y.; Guan, L.; Zhang, R. Y.; Wu, S. Q.; Zhang, K. Y. Opt. Mater. 2023, 142, 114112.
|
| [32] |
Wang, L. L.; Meng, S. A.; Chen, G. L.; Yang, X. D.; Yan, Y.; Chen, R. Micro Nano Lett. 2020, 15, 713.
|
| [33] |
Rao, K. S.; Kamath, S. M.; Kumar, R. R.; Kavitha, G.; MeherAbhinav, E.; Shri, S. S.; Induja, S.; Gopalakrishnan, C. Mater. Lett. 2021, 297, 129960.
|
| [34] |
Wang, G. M.; Yan, S. H.; Sun, J.; Wang, S. G.; Deng, Q. R. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. El. 2017, 28, 4371.
|
| [35] |
Wang, K.; Xu, X. G.; Lu, L. Y.; Li, A.; Han, X. D.; Wu, Y.; Miao, J.; Jiang, Y. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2019, 715, 129.
doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2018.11.021 |
| [36] |
Wang, G. M.; Cheng, D.; He, T. C.; Hu, Y. Y.; Deng, Q. R.; Mao, Y. W.; Wang, S. G. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 10923.
|
| [37] |
Li, S. J.; Hu, S. W.; Xu, K. B.; Jiang, W.; Hu, J. Q.; Liu, J. S. Mater. Lett. 2017, 188, 368.
|
| [38] |
Wang, Y. Y.; Yang, J. H.; Zhang, Z. X.; Zhao, P. J.; Chen, Y. Q.; Guo, Y.; Luo, X. G. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 269, 131885.
|
| [39] |
Fan, T.; Chen, C. C.; Tang, Z. H. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 9994.
|
| [40] |
Singh, A.; Singh, D.; Ahmed, B.; Ojha, A. K. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 277, 125531.
|
| [41] |
Khalid, N. R.; Mazia, U.; Tahir, M. B.; Noaz, N. A.; Javid, M. A. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 313, 113522.
|
| [42] |
Ersoz, E.; Yildirim, O. A. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2022, 59, 655.
|
| [43] |
Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Zhai, B. Y.; Liang, Y. N. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 568, 429.
|
| [44] |
Sundararajan, M.; Bonisha, B.; Ubaidullah, M.; Shaikh, S. M. F.; Revathi, S.; Thiripurasundari, D.; Dhiwahar, A. T.; Pandit, B.; Dash, C. S.; Shahazad, M. Mater. Res. Bull. 2022, 154, 111911.
|
| [45] |
Sultana, R.; Liba, S. I.; Rahman, M. A.; Yeachin, N.; Syed, I. M.; Bhuiyan, M. A. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 42 (Part A), 103302.
|
| [46] |
Phuruangrat, A.; Buapoon, S.; Bunluesak, T.; Suebsom, P.; Wannapop, S.; Thongtem, T.; Thongtem, S. Solid State Sci. 2022, 128, 106881.
|
| [47] |
Sundararajan, M.; Sailaja, V.; Kennedy, J. L.; Vijaya, J. J. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 540.
|
| [48] |
Zhang, L.; He, Y. M.; Wu, Y.; Wu, T. H. MSEB 2011, 176, 1497.
|
| [49] |
Zhang, Y. Y.; Guo, Y. P.; Duan, H. N.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, P.; Sun, C. Y.; Xu, B. Y.; Liu, H. Z. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 28209.
|
| [50] |
Wang, T. T.; Deng, H. M.; Zhou, W. L.; Meng, X. K.; Yang, P. X.; Chu, J. H. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 6453.
|
| [51] |
Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15.
|
| [52] |
Jiang, H.; Gomez-Abal, R. I.; Rinke, P.; Scheffler, M. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 045108.
|
| [53] |
Wuliji, H. X. G.; Zhao, K. P.; Cai, X. M.; Jing, H. R.; Wang, Y. W.; Huang, H. R.; Wei, T. R.; Zhu, H.; Shi, X. Mater. Today Phys. 2023, 35, 101129.
|
| [1] | Guokai Li, Binfeng Zhu, Tao Hu, Ruifeng Fan, Weiqing Sun, Zhenxiu He, Jingchao Chen, Baomin Fan. Photoredox Dealkylative Acylation of Tertiary Amines [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(3): 199-205. |
| [2] | Jihong Liu, Jiapeng Zhu, Xu Zhang, Jiyang Zhang, Chaoyang Huang, Guixiao Jia, Shengli An. Strain Mechanism Study on Li-rich Layered Cathode Materials Li-Ni-Mn-O for Li-ion Batteries [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(2): 101-109. |
| [3] | Jian Kang, Zixuan Shi, Jingmei Li. Preparation of Highly Antimicrobial Composites and Study of Photocatalytic Antimicrobial Properties Driven by LED Light [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(9): 962-970. |
| [4] | Kangkui Li, Xianyang Long, Yue Huang, Shifa Zhu. Recent Advances in Visible Light Induced Radical 1,2-Functionalization of Alkynes [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(6): 658-676. |
| [5] | Guangzheng Huang, Kunwei Li, Yannan Luo, Qiang Zhang, Yuanlong Pan, Honglin Gao. Hydrothermal Treatment for Constructing K Doping and Surface Defects in g-C3N4 Nanosheets Promote Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(3): 314-322. |
| [6] | Jianqiang Chen, Gangguo Zhu, Jie Wu. Recent Advances in Nickel-Catalyzed Ring Opening Cross-Coupling of Aziridines [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 190-212. |
| [7] | Cui Xin, Jun Jiang, Zi-Wei Deng, Li-Juan Ou, Wei-Min He. Photoinduced FeCl3‑catalyzed Cross-Dehydrogenative Alkylation of Benzoxazin-2-ones with Alkanes [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(11): 1109-1113. |
| [8] | Yuhan Wu, Dongdong Zhang, Hongyu Yin, Zhengnan Chen, Wen Zhao, Yuhua Chi. Density Functional Theory Study of Janus In2S2X Photocatalytic Reduction of CO2 under “Double Carbon” Target [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(9): 1148-1156. |
| [9] | Kai Zhang, Xiaojun Wu. Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism in Two-Dimensional Janus Titanium Chalcogenides★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(9): 1142-1147. |
| [10] | Yuying Zhang, Xiao Cai, Weigang Hu, Guangjun Li, Yan Zhu. Pd and Hg Atoms Co-doped HgPdAu23(PET)18 Nanocluster★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(7): 703-708. |
| [11] | Minghui He, Ziqiu Ye, Guiqing Lin, Sheng Yin, Xinyi Huang, Xu Zhou, Ying Yin, Bo Gui, Cheng Wang. Research Progress of Porphyrin-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks in Photocatalysis★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(7): 784-792. |
| [12] | Jiawen Liu, Weihuang Lin, Weijia Wang, Xueyi Guo, Ying Yang. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Degradation of Cu1.94S-SnS Nano-heterojunction [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(7): 725-734. |
| [13] | Li Liu, Gang Zheng, Guoqiang Fan, Hongguang Du, Jiajing Tan. Research Progress in Organic Reactions Involving 4-Acyl/Carbamoyl/Alkoxycarbonyl Substituted Hantzsch Esters [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 657-668. |
| [14] | Fei Li, Huili Ding, Chaozhong Li. Hydrotrifluoromethylation of Alkenes with a Fluoroform-Derived Trifluoromethylboron Complex [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 577-581. |
| [15] | Xueping Qi, Fei Wang, Jian Zhang. A Post-Synthetic Method for the Construction of Titanium-Based Metal Organic Frameworks and Their Applications [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(5): 548-558. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||