Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (4): 423-427.DOI: 10.6023/A22010001 Previous Articles Next Articles
Special Issue: 中国科学院青年创新促进会合辑
Communication
刘若湄a,b, 冯艳辉a,b, 李卓b, 卢珊a,b,*( ), 关天用b, 李幸俊b, 刘䶮b, 陈卓b, 陈学元a,b,*(
), 关天用b, 李幸俊b, 刘䶮b, 陈卓b, 陈学元a,b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2022-01-01
发布日期:2022-04-28
通讯作者:
卢珊, 陈学元
作者简介:基金资助:
Ruomei Liua,b, Yanhui Fenga,b, Zhuo Lib, Shan Lua,b( ), Tianyong Guanb, Xingjun Lib, Yan Liub, Zhuo Chenb, Xueyuan Chena,b(
), Tianyong Guanb, Xingjun Lib, Yan Liub, Zhuo Chenb, Xueyuan Chena,b( )
)
Received:2022-01-01
Published:2022-04-28
Contact:
Shan Lu, Xueyuan Chen
About author:Supported by:Share
Ruomei Liu, Yanhui Feng, Zhuo Li, Shan Lu, Tianyong Guan, Xingjun Li, Yan Liu, Zhuo Chen, Xueyuan Chen. A Novel Near-infrared Responsive Lanthanide Upconversion Nanoplatform for Drug Delivery Based on Photocleavage of Cypate※[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(4): 423-427.



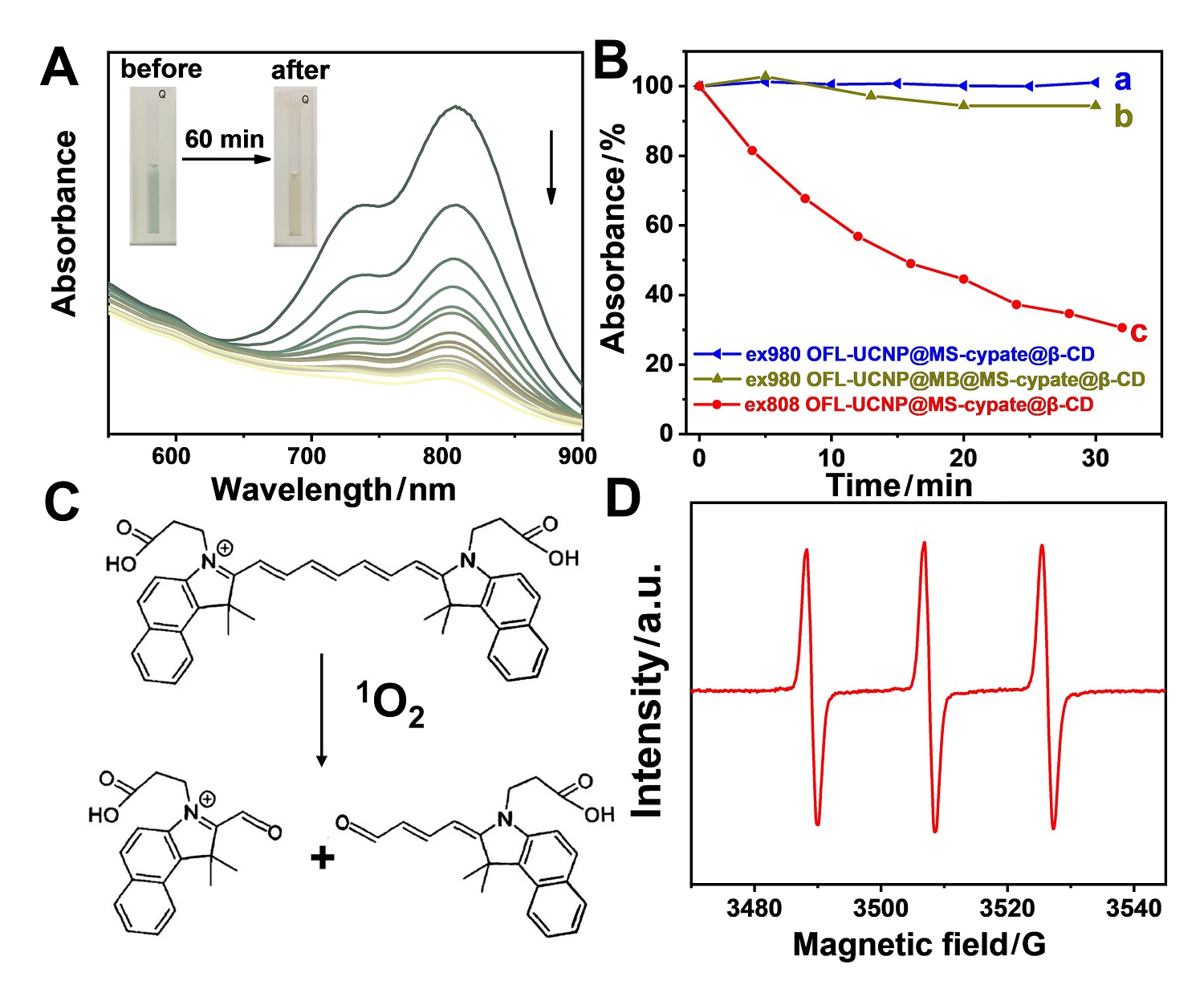
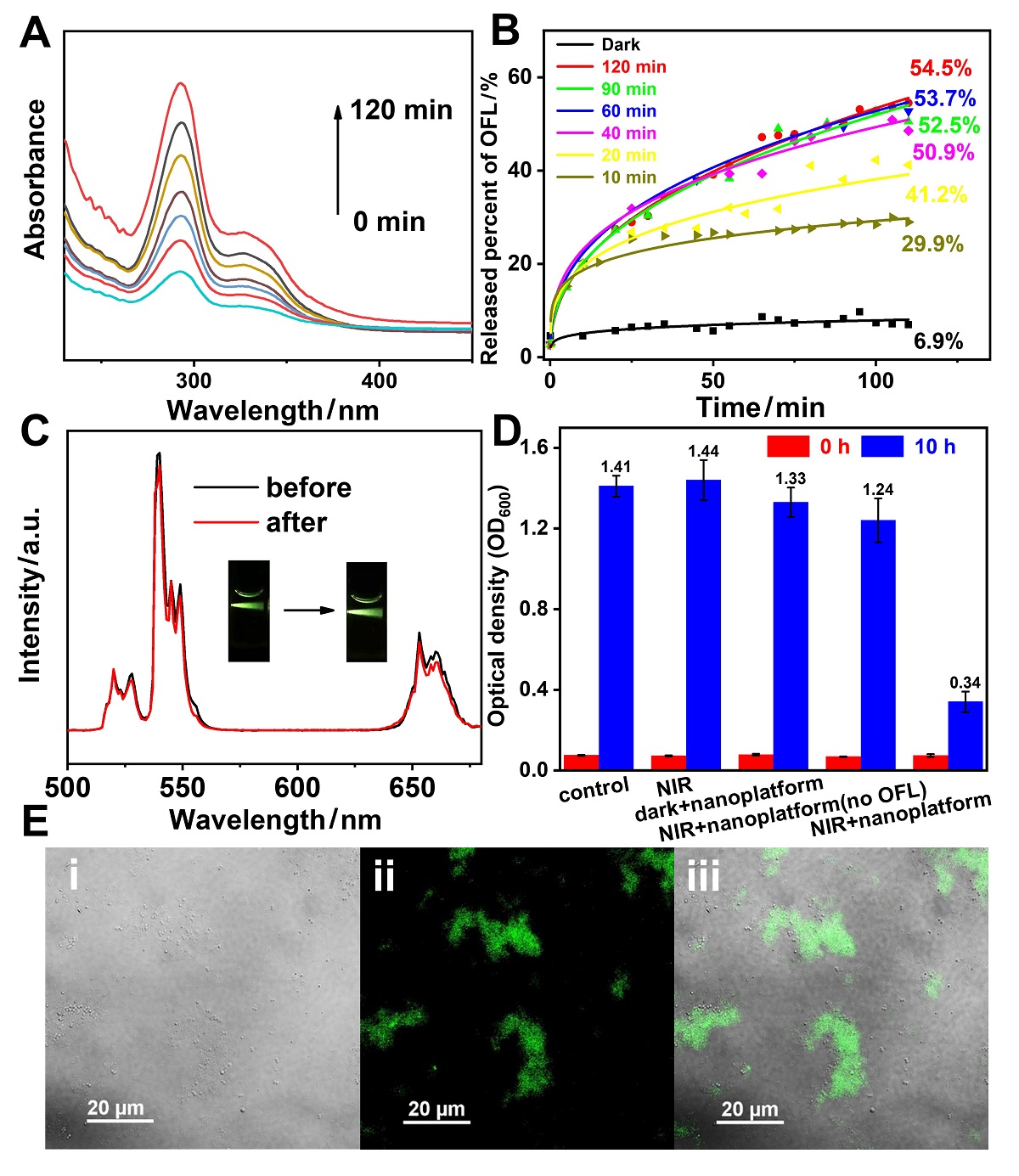
| [1] |
Lakkadwala, S.; Dos Santos Rodrigues, B.; Sun, C.; Singh, J. J. Control. Release 2019, 307, 247.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.06.033 |
| [2] |
Lu, S.; Tu, D.; Li, X.; Li, R.; Chen, X. Nano Res. 2015, 9, 187.
doi: 10.1007/s12274-015-0979-4 |
| [3] |
Luther, D. C.; Huang, R.; Jeon, T.; Zhang, X.; Lee, Y. W.; Nagaraj, H.; Rotello, V. M. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 156, 188.
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.06.020 |
| [4] |
Wang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, H.; Peng, K.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X. Biomaterials 2017, 122, 10.
doi: S0142-9612(17)30016-9 pmid: 28107661 |
| [5] |
Yadav, S.; van Vlerken, L. E.; Little, S. R.; Amiji, M. M. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2009, 63, 711.
doi: 10.1007/s00280-008-0790-y |
| [6] |
Zhang, M.; Song, R.; Liu, Y.; Yi, Z.; Meng, X.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Z.; Yao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Bu, W. Chem 2019, 5, 2171.
doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2019.06.003 |
| [7] |
Cai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 481. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20120583 |
|
(蔡政, 张颖雯, 姜立萍, 朱俊杰, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 481.)
doi: 10.6023/A20120583 |
|
| [8] |
Han, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Sui, X.; Qian, M.; Chen, Q.; Wang, J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79. 794.. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21030090 |
|
(韩旭, 张留伟, 张强, 睢晞航, 钱明, 陈麒先, 王静云, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 794.)
doi: 10.6023/A21030090 |
|
| [9] |
Liu, G.; Liu, W.; Dong, C. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 3431.
doi: 10.1039/c3py21121e |
| [10] |
Shi, B.; Ren, N.; Gu, L.; Xu, G.; Wang, R.; Zhu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, C.; Zhao, C.; Tian, H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 16826.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201909883 |
| [11] |
Li, Z.; Lu, S.; Liu, W.; Dai, T.; Ke, J.; Li, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 19201.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202103943 |
| [12] |
Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1049. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21050194 |
|
(黄菊, 李贞, 刘志洪, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1049.)
doi: 10.6023/A21050194 |
|
| [13] |
Xu, J.; Shi, R.; Chen, G.; Dong, S.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Niu, N.; Gai, S.; He, F.; Fu, Y.; Lin, J. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 9613.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c00082 |
| [14] |
Xu, J.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, P.; Lin, J. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 415, 213328.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213328 |
| [15] |
Zheng, W.; Huang, P.; Tu, D.; Ma, E.; Zhu, H.; Chen, X. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1379.
doi: 10.1039/c4cs00178h pmid: 25093303 |
| [16] |
Cui, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Q.; Lin, H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, T.; Tong, R.; An, N.; Qu, F. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7046.
doi: 10.1039/C5TB00709G |
| [17] |
Liu, J.; Bu, W.; Pan, L.; Shi, J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4375.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201300183 |
| [18] |
Yan, B.; Boyer, J. C.; Branda, N. R.; Zhao, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19714.
doi: 10.1021/ja209793b |
| [19] |
Yan, B.; Boyer, J. C.; Habault, D.; Branda, N. R.; Zhao, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16558.
doi: 10.1021/ja308876j |
| [20] |
Yao, C.; Wang, P.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Hou, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9341.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201503799 |
| [21] |
Zhao, L.; Peng, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, C.; Chen, M.; Sun, Y.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, L.; Li, F. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 363.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201302133 |
| [22] |
Bao, G.; Wen, S.; Lin, G.; Yuan, J.; Lin, J.; Wong, K.-L.; Bünzli, J.-C. G.; Jin, D. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 429, 213642.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213642 |
| [23] |
Chen, D.; Zhang, G.; Li, R.; Guan, M.; Wang, X.; Zou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Shu, C.; Hong, H.; Wan, L. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7373.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b12025 |
| [24] |
Wang, H.; Han, R. L.; Yang, L. M.; Shi, J. H.; Liu, Z. J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S. J.; Gan, Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4416.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b11197 |
| [25] |
Wang, X.; Meng, G.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29911.
doi: 10.1038/srep29911 |
| [26] |
Yang, G.; Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Feng, L.; Liu, Z. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 4722.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201600722 |
| [27] |
Zhang, T.; Lin, H.; Cui, L.; An, N.; Tong, R.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Qu, F. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 2016, 1206.
doi: 10.1002/ejic.201501320 |
| [28] |
Li, N.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. M.; Yang, Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, J. T.; Liu, Y. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4164.
doi: 10.1038/srep04164 |
| [29] |
Cuggino, J. C.; Contreras, C. B.; Jimenez-Kairuz, A.; Maletto, B. A.; Alvarez Igarzabal, C. I. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 2239.
doi: 10.1021/mp400615n |
| [30] |
Li, J.; Li, S.; He, Z. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 71, 999.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.11.015 |
| [31] |
Sezer, A. D.; Akbuga, J. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2012, 17, 118.
doi: 10.3109/10837450.2010.529145 |
| [32] |
Xie, J.; Wang, C.; Ning, Q.; Gao, Q.; Gao, C.; Gou, Z.; Ye, J. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2017, 255, 2173.
doi: 10.1007/s00417-017-3755-1 |
| [33] |
You, W.; Tu, D.; Zheng, W.; Shang, X.; Song, X.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Chen, X. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 11477.
doi: 10.1039/C8NR03252A |
| [34] |
Li, C.; Liu, J.; Alonso, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 6065.
doi: 10.1039/c2nr31570j |
| [35] |
Zhang, Y. M.; Liu, Y. H.; Liu, Y. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1806158.
|
| [36] |
James, N. S.; Cheruku, R. R.; Missert, J. R.; Sunar, U.; Pandey, R. K. Molecules 2018, 23, 1842.
doi: 10.3390/molecules23081842 |
| [1] | Zhiliang Gao, Mengqi Li, Jingcheng Hao, Jiwei Cui. Tuning the Mechanical Properties of Colloid Particles for Drug Delivery [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 1010-1020. |
| [2] | Ju Huang, Zhen Li, Zhihong Liu. Functionalized Upconversion Nanoparticles for Disassembly of β‑Amyloid Aggregation with Near-Infrared Excitation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(8): 1049-1057. |
| [3] | Zheng Cai, Yingwen Zhang, Liping Jiang, Junjie Zhu. The Construction and Application of Mn3O4/DOX@Lip Nano-drug Delivery System Based on Fenton-Like Reaction [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(4): 481-489. |
| [4] | Hua Yue, Guanghui Ma. Advances in Functionalized Carriers Based on Graphene's Unique Biological Interface Effect [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(10): 1244-1256. |
| [5] | Wang Peipei, Liang Tao, Zuo Miaomiao, Li Zhen, Liu Zhihong. A Ratiometric Upconversion Nanoprobe for Detection of HNO Based on Luminescence Resonance Energy Transfer [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(8): 797-804. |
| [6] | Zhang Liuwei, Chen Qixian, Wang Jingyun. Advances in Reactive Oxygen Species Responsive Anti-cancer Prodrugs [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(7): 642-656. |
| [7] | Qi Ye, Ren Shuangsong, Che Ying, Ye Junwei, Ning Guiling. Research Progress of Metal-Organic Frameworks Based Antibacterial Materials [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(7): 613-624. |
| [8] | Yan Tao, Liu Zhenhua, Song Xinyue, Zhang Shusheng. Construction and Development of Tumor Microenvironment Stimulus-Responsive Upconversion Photodynamic Diagnosis and Treatment System [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(7): 657-669. |
| [9] | Zeng Jinyue, Wang Xiaoshuang, Zhang Xianzheng, Zhuo Renxi. Research Progress in Functional Metal-Organic Frameworks for Tumor Therapy [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2019, 77(11): 1156-1163. |
| [10] | Zhang Bei, Chang Baisong, Sun Taolei. Synthesis and Study of Hypoxia-Responsive Micelles Based on Hyaluronic Acid [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2018, 76(1): 35-42. |
| [11] | Zhang Liuwei, Qian Ming, Wang Jingyun. Progress in Research of Photo-controlled Drug Delivery Systems [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2017, 75(8): 770-782. |
| [12] | Peng Kaimei, Ding Wei, Tu Weiping, Hu Jianqing, Liu Chao, Yang Jian. Construction of Guanidinium-rich Polymers and Their Applications [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2016, 74(9): 713-725. |
| [13] | Zhang Shaofei, Yang Jiandong, Liu Mingzhu, Lü Shaoyu, Gao Chunmei, Wu Can, Zhu Zhaoyan. Synthesis of Peptide Dendrimers and Their Application in the Drug Delivery System [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2016, 74(5): 401-409. |
| [14] | Chen Meihua, Pan Zheng, Yin Yuefeng, Liu Jie, Liu Mengyuan, Jia Zijun, Liang Guijie. Panchromatic and High-efficient Energy Transfer Assembly Based on Type I Core-shell Quantum Dots [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2016, 74(4): 330-334. |
| [15] | Wang Xin, Tan Lili, Yang Yingwei. Controlled Drug Release Systems Based on Mesoporous Silica Capped by Gold Nanoparticles [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2016, 74(4): 303-311. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||