Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (6): 765-771.DOI: 10.6023/A21120567 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
贺续发a, 贾康乐b,*( ), 余龙飞b,*(
), 余龙飞b,*( ), 刘明杰b, 郑小珊b, 李欢玲b, 辛锦兰b, 黄淋佳b,*(
), 刘明杰b, 郑小珊b, 李欢玲b, 辛锦兰b, 黄淋佳b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2021-12-16
发布日期:2022-07-07
通讯作者:
贾康乐, 余龙飞, 黄淋佳
基金资助:
Xufa Hea, Kangle Jiab( ), Longfei Yub(
), Longfei Yub( ), Mingjie Liub, Xiaoshan Zhengb, Huanling Lib, Jinlan Xinb, Linjia Huangb(
), Mingjie Liub, Xiaoshan Zhengb, Huanling Lib, Jinlan Xinb, Linjia Huangb( )
)
Received:2021-12-16
Published:2022-07-07
Contact:
Kangle Jia, Longfei Yu, Linjia Huang
Supported by:Share
Xufa He, Kangle Jia, Longfei Yu, Mingjie Liu, Xiaoshan Zheng, Huanling Li, Jinlan Xin, Linjia Huang. pH-Responsive Pickering Emulsions Synergistically Stabilized by Maleopimaric Acid and Alumina Nanoparticles[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(6): 765-771.
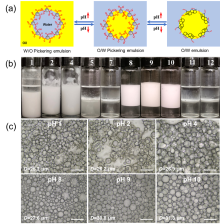



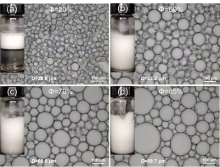

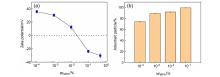
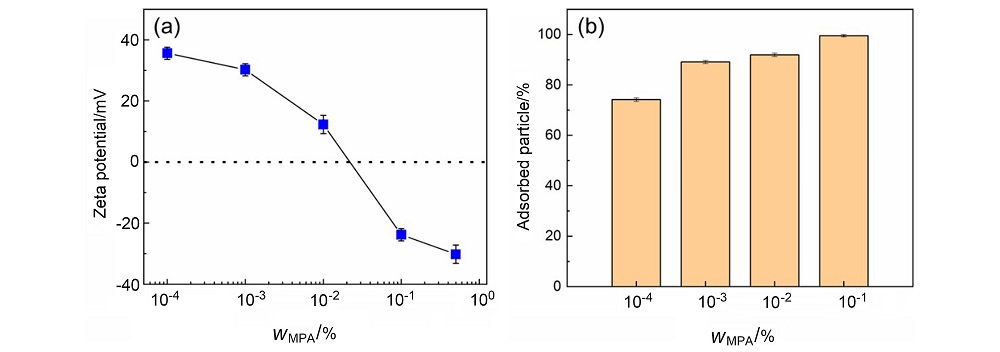

| [1] |
Wu, J.; Ma, G. H. Small 2016, 12, 4582.
doi: 10.1002/smll.201670169 |
| [2] |
Ortiz, D. G.; Pochat-Bohatier, C.; Cambedouzou, J.; Bechelany, M.; Miele, P. Engineering 2020, 6, 468.
doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2019.08.017 |
| [3] |
Zhang, X.; Jia, K. L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. J.; Dai, Y. Q.; Yu, L. F.; Wen, W.; Mai, Y. L. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 313, 113505.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113505 |
| [4] |
Kaz, D. M.; McGorty, R.; Mani, M.; Brenner, M. P.; Manoharan, V. N. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 138.
doi: 10.1038/nmat3190 |
| [5] |
Aveyard, R. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 5233.
doi: 10.1039/c2sm07230k |
| [6] |
Xu, M. D.; Xu, L. F.; Ling, Q.; Pei, X. M.; Jiang, J. Z.; Zhu, H. Y.; Cui, Z. G.; Binks, B. P. Langmuir 2019, 38, 4068.
|
| [7] |
Yang, Y. Q.; Fang, Z. W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W. W.; Xie, Y. M.; Chen, Y. H.; Liu, Z. G.; Yuan, W. E. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 287.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00287 |
| [8] |
Chevalier, Y.; Bolzinger, M. A. Colloid. Surface. A 2013, 439, 23.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.02.054 |
| [9] |
Dupont, H.; Maingret, V.; Schmitt, V.; Heroguez, V. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 4945.
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.1c00225 |
| [10] |
Berton-Carabin, C. C.; Schroen, K. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. T. 2015, 6, 263.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-081114-110822 pmid: 25705932 |
| [11] |
Venkataramani, D.; Tsulaia, A.; Amin, S. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 283, 102234.
doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2020.102234 |
| [12] |
Harman, C. L. G.; Patel, M. A.; Guldin, S.; Davies, G. L. Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2019, 39, 173.
doi: 10.1016/j.cocis.2019.01.017 |
| [13] |
Zheng, Y.; Luo, J.; Wei, W.; Liu, X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 391. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A16110624 |
|
(郑媛, 罗静, 魏玮, 刘晓亚, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 391.)
doi: 10.6023/A16110624 |
|
| [14] |
Wang, C.; Ning, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tong, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 1721. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A12040163 |
|
(王朝阳, 宁印, 陈云华, 童真, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 1721.)
doi: 10.6023/A12040163 |
|
| [15] |
Arab, D.; Kantzas, A.; Bryant, S. L. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 163, 217.
doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.12.091 |
| [16] |
Shi, Y. L.; Xiong, D. Z.; Li, Z. Y.; Wang, H. Y.; Pei, Y. C.; Chen, Y. K.; Wang, J. J. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 15383.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03808 |
| [17] |
Pi, G.; Li, Y. M.; Bao, M. T.; Mao, L. L.; Gong, H. Y.; Wang, Z. N. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3095.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00063 |
| [18] |
Jiang, J. Z.; Ma, Y. X.; Cui, Z. G.; Binks, B. P. Langmuir 2016, 32, 8668.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b01475 |
| [19] |
Liu, K. H.; Jiang, J. Z.; Cui, Z. G.; Binks, B. P. Langmuir 2017, 33, 2296.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b04459 |
| [20] |
Zhu, Y.; Fu, T.; Liu, K. H.; Ling, Q.; Pei, X. M.; Jiang, J. Z.; Cui, Z. G.; Binks, B. P. Langmuir 2017, 33, 5724.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b00273 |
| [21] |
Yu, S. J.; Zhang, H. J.; Jiang, J. Z.; Cui, Z. G.; Xia, W. S.; Binks, B. P. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5470.
doi: 10.1039/D0GC02016H |
| [22] |
Yu, S. J.; Lv, M.; Lu, G. P.; Cai, C.; Jiang, J. Z.; Cui, Z. G. Langmuir 2021, 37, 10683.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c01179 |
| [23] |
Tao, S. N.; Guan, X.; Li, Y. X.; Jiang, H.; Gong, S. J.; Ngai, T. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 1491.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.09.056 |
| [24] |
Tao, S. N.; Jiang, H.; Wang, R. J.; Yang, C.; Li, Y. X.; Ngai, T. ChemComm 2020, 56, 14011.
|
| [25] |
Wei, Z. J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, C. Y. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 3230.
doi: 10.1039/c2gc36278c |
| [26] |
Liu, F.; Tang, C. H. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5133.
doi: 10.1021/jf404930c |
| [27] |
Tong, Q. L.; Yi, Z.; Ran, Y. Q.; Chen, X. Y.; Chen, G. C.; Li, X. D. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 4076.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c08633 |
| [28] |
Moustafa, H.; El Kissi, N.; Abou-Kandil, A. I.; Abdel-Aziz, M.S.; Dufresne, A. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 20132.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b05557 |
| [29] |
Binks, B. P.; Philip, J.; Rodrigues, J. A. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3296.
doi: 10.1021/la046915z |
| [30] |
Huang, C. L.; Sun, Z. W.; Cui, M. M.; Liu, F.; Helms, B. A.; Russell, T. P. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6612.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201600691 |
| [31] |
Li, Y. A.; Liu, X. B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, S. J.; Tian, G. F.; Zheng, J. K.; Wang, D.; Shi, S. W.; Russell, T. P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 13560.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201808888 |
| [32] |
Zou, S.; Wang, C.; Wei, Z.; Liu, H.; Tong, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 133. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A1106281 |
|
(邹声文, 王朝阳, 魏增江, 刘浩, 童真, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 133.)
doi: 10.6023/A1106281 |
|
| [33] |
Vignati, E.; Piazza, R. Langmuir 2003, 19, 6650.
doi: 10.1021/la034264l |
| [1] | Yuqing Shi, Mingzhu Chu, Bo Han, Haojie Ma, Ran Li, Xueyan Hou, Yuqi Zhang, Ji-Jiang Wang. Smart Two-dimensional Photonic Crystal Hydrogel for Accurate Detection of Hg2+ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(1): 9-15. |
| [2] | Chen Jian, Cai Zhuoer, Jiao Shulin, Zhang Xiang, Hu Jinzhong, Liu Min, Sun Baiwang, Hua Xiuni. A Thermally Responsive Dielectric Switchable Zero-Dimensional Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Material: (C3H6NH2)2CoCl4 [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(5): 480-485. |
| [3] | Yumiao Lu, Wei Chen, Yanlei Wang, Feng Huo, Yihui Dong, Li Wei, Hongyan He. Research Progress on the Preparation and Properties of Two Dimensional Structure of Ionic Liquids [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(4): 443-458. |
| [4] | Aodi Shi, Si Chen, Songsheng Zheng, Zhaolin Wang. Correlation between the Pseudo-Capacitance Behavior and the Second-Order Phase Transition in the Li+ Insertion/Desertion in Cu3Si [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(12): 1511-1517. |
| [5] | Zhao Jiongpeng, Wang Weiwei, Han Songde, Li Quanwen, Li Na, Liu Fuchen, Bu Xianhe. Construction, Magnetic and Dielectric Properties of Mixed-Valence Iron Formate with Methylammonium Guest [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(11): 1223-1228. |
| [6] | Hu Chengyu, Yan Wenfu, Xu Ruren. Phase Transition Behavior of Zeolite Y under Hydrothermal Conditions [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2017, 75(7): 679-685. |
| [7] | Zhang Guobin, Xiong Tengfei, Pan Xuelei, Yan Mengyu, Han Chunhua, Mai Liqiang. In Situ Observation and Mechanism Investigation of Lattice Breathing in Vanadium Oxide Cathode [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2016, 74(7): 582-586. |
| [8] | Yang Jing, Sun Runguang, Hao Changchun, Qiao Jinjing, He Guangxiao. A Monolayer Study on the Interfacial Behavior of DPPC with β-sitosterol and Stigmasterol [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013, 71(9): 1293-1300. |
| [9] | Yu Han, Huang Qingming, Cao Wenbing, Zhang Xinqi, Yu Jianchang. Phase Transition Induction and Upconversion Luminescence Enhancement of NaY0.95-x Yb0.03Er0.02F4 by In3+ Codoping [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013, 71(12): 1639-1646. |
| [10] | Zhao Bin, Lin Lin, Chen Chao, Chai Yuchao, He Dannong. Research on the Phase Transition and Morphological Evolution Behaviors of Titania/Titanate Nanomaterials by Calcination Treatment [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013, 71(01): 93-101. |
| [11] | Wang Chaoyang, Ning Yin, Chen Yunhua, Tong Zhen. Preparation of Colloidosome Microcapsules Based on Particle Stabilized Photo-Crosslinkable Pickering Emulsions [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2012, 70(16): 1721-1724. |
| [12] | Lu Dongfei, Di Youying, Dou Jianmin. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Low-temperature Heat Capacities of Bis(n-undecylammonium)tetrachlorocadmiumate [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2012, 70(07): 889-896 . |
| [13] | LIN Song-Bai, YUAN Cong-Hui, KE Ai-Ru, LI Yun-Long, OUYang-Na . Synthesis and Properties of PVA Enhanced P(AAEA-co-AA) Temperature Sensitive Hydrogels [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2011, 69(22): 2710-2716. |
| [14] | SUN Hong-Juan, PENG Tong-Jiang, CHEN Yan-Cui, GU Chao-Jian. Interlayer in-situ Reaction Process and Preparation of TiO2/montmorillonite Composites [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2011, 69(17): 2003-2008. |
| [15] | LI Meng, YU Jian-Chang. Synthesis and Phase Transition of Ordered Mesoporous Carbon [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2011, 69(02): 226-230. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||