Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (8): 887-893.DOI: 10.6023/A24040148 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
张登朝a, 贾吉慧a,*( ), 梁栋b,c, 蔡显宝d, 赵雨晴d, 胡祥龙a, 江钰冰a, 卢灿忠b,c,*(
), 梁栋b,c, 蔡显宝d, 赵雨晴d, 胡祥龙a, 江钰冰a, 卢灿忠b,c,*( )
)
投稿日期:2024-04-30
发布日期:2024-06-12
基金资助:
Dengchao Zhanga, Jihui Jiaa,*( ), Dong Liangb,c, Xianbao Caid, Yuqing Zhaod, Xianglong Hua, Yubing Jianga, Canzhong Lub,c,*(
), Dong Liangb,c, Xianbao Caid, Yuqing Zhaod, Xianglong Hua, Yubing Jianga, Canzhong Lub,c,*( )
)
Received:2024-04-30
Published:2024-06-12
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:Share
Dengchao Zhang, Jihui Jia, Dong Liang, Xianbao Cai, Yuqing Zhao, Xianglong Hu, Yubing Jiang, Canzhong Lu. Design, Synthesis and Properties of Cu(I) Complexes with a Nitrogen-containing Spirocycle Ligand for Delayed Fluorescence Materials[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(8): 887-893.


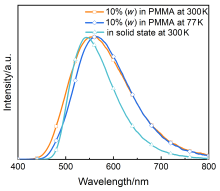
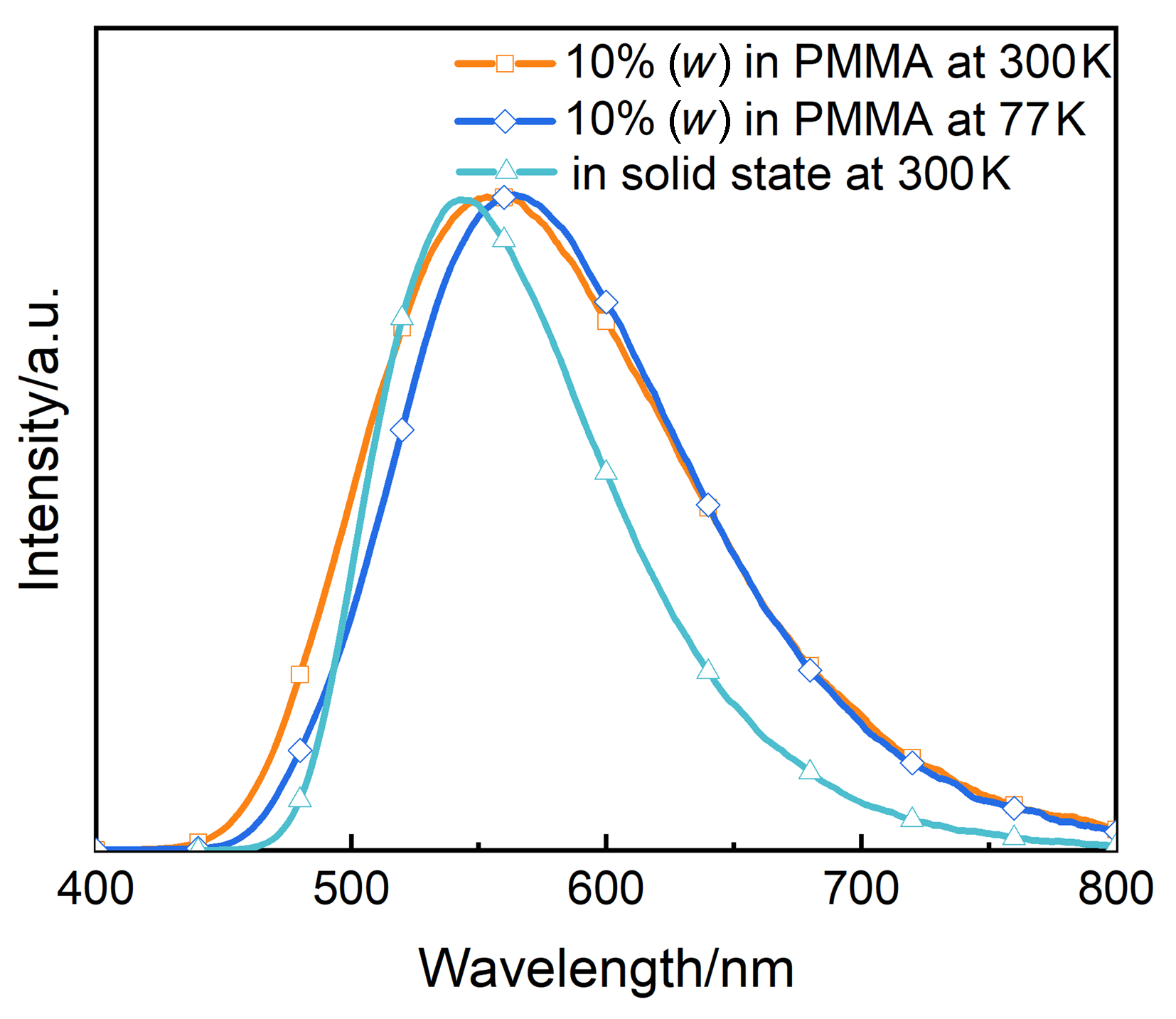
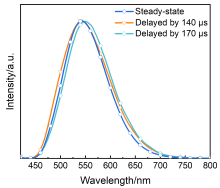
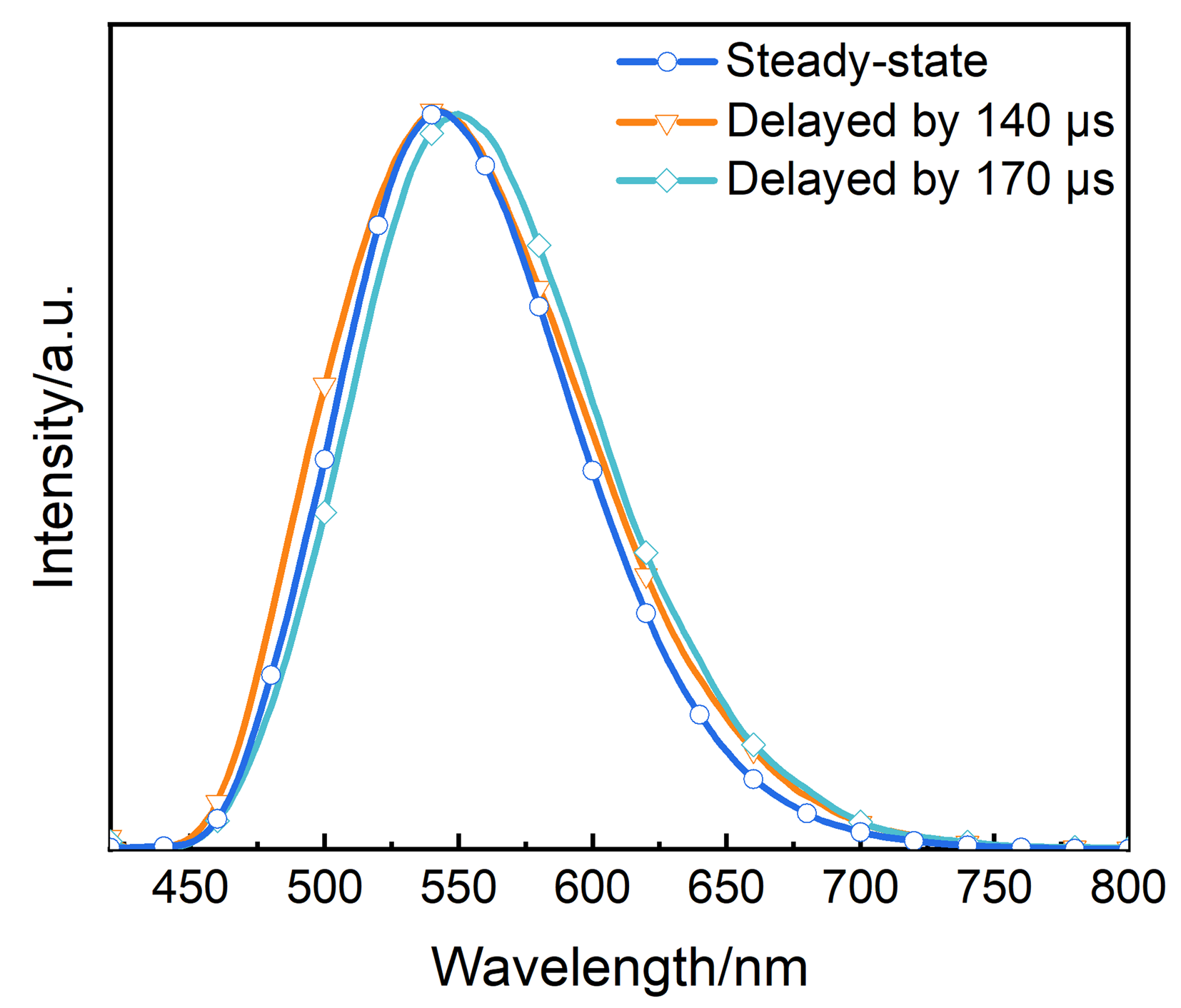
| [1] |
Arias-Rotondo, D. M.; McCusker, J. K. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5803.
pmid: 27711624 |
| [2] |
Ma, D.; Tsuboi, T.; Qiu, Y.; Duan, L. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603253.
|
| [3] |
Hong, G.; Gan, X.; Leonhardt, C.; Zhang, Z.; Seibert, J.; Busch, J. M.; Bräse, S. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005630.
|
| [4] |
Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z. Chem. Asian J. 2021, 16, 2817.
|
| [5] |
Ge, F.; Zhang, K.; Cao, Q.; Xu, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, W.; Ban, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Zhu, P. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 1157 (in Chinese).
|
|
(葛凤洁, 张开志, 曹清鹏, 徐慧, 周涛, 张文浩, 班鑫鑫, 张晓波, 李娜, 朱鹏, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1157.)
doi: 10.6023/A23020051 |
|
| [6] |
Tao, P.; Zheng, X.; Wang, G.; Sheng, X.; Jiang, H.; Li, W.; Jin, J.; Wong, S.-H.; Miao, Y.; Wang, H.; Wong, W.-Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 891 (in Chinese).
|
|
(陶鹏, 郑小康, 王国良, 盛星浩, 姜贺, 李文桃, 靳继彪, 王瑞鸿, 苗艳勤, 王华, 黄维扬, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 891.)
doi: 10.6023/A23040187 |
|
| [7] |
Kalinowski, J.; Fattori, V.; Cocchi, M.; Williams, J. A. G. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 2401.
|
| [8] |
Yersin, H.; Rausch, A. F.; Czerwieniec, R.; Hofbeck, T.; Fischer, T. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 2622.
|
| [9] |
Lee, J.; Chen, H. F.; Batagoda, T.; Coburn, C.; Djurovich, P. I.; Thompson, M. E.; Forrest, S. R. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 92.
|
| [10] |
Ren, B.-Y.; Yi, J.-C.; Zhong, D.-K.; Zhao, Y.-Z.; Guo, R.-D.; Sheng, Y.-G.; Sun, Y.-G.; Xie, L.-H.; Huang, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 56 (in Chinese).
|
|
(任保轶, 依建成, 钟道昆, 赵玉志, 郭闰达, 盛永刚, 孙亚光, 解令海, 黄维, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 56.)
doi: 10.6023/A19110406 |
|
| [11] |
Zhu, S.; Huang, X.; Han, X.; Liu, S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 1066 (in Chinese).
|
|
(朱诗敏, 黄鑫, 韩勰, 刘思敏, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 1066.)
doi: 10.6023/A22020078 |
|
| [12] |
Cao, L.; Yang, X.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Tan, H. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 42, 1831 (in Chinese).
|
|
(曹丽琴, 杨小琴, 李茂秋, 刘琳, 于俊婷, 谭华, 有机化学, 2022, 42, 1831.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202111017 |
|
| [13] |
Czerwieniec, R.; Leitl, M. J.; Homeier, H. H. H.; Yersin, H. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2016, 325, 2.
|
| [14] |
Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, X.; Li, P.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Q. H.; Bian, Z.; Lu, Z. H.; Huang, C. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 3262.
|
| [15] |
Mohankumar, M.; Holler, M.; Meichsner, E.; Nierengarten, J. F.; Niess, F.; Sauvage, J. P.; Delavaux-Nicot, B.; Leoni, E.; Monti, F.; Malicka, J. M.; Cocchi, M.; Bandini, E.; Armaroli, N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2336.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b12671 pmid: 29298047 |
| [16] |
Hamze, R.; Peltier, J. L.; Sylvinson, D.; Jung, M.; Cardenas, J.; Haiges, R.; Soleilhavoup, M.; Jazzar, R.; Djurovich, P. I.; Bertrand, G.; Thompson, M. E. Science 2019, 363, 601.
|
| [17] |
Jia, J. H.; Zhang, D. C.; Liang, D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z. Q.; Zhang, L.; Lu, C. Z. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2024, 12, 2303053.
|
| [18] |
Armaroli, N.; Accorsi, G.; Cardinali, F.; Listorti, A. Photochemistry and Photophysics of Coordination Compounds: Copper, Eds.: Balzani, V.; Campagna, S., Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, 2007, pp. 69-115.
|
| [19] |
Osawa, M.; Kawata, I.; Ishii, R.; Igawa, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Hoshino, M. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 4375.
|
| [20] |
Klein, M.; Rau, N.; Wende, M.; Sundermeyer, J.; Cheng, G.; Che, C.-M.; Schinabeck, A.; Yersin, H. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 10365.
|
| [21] |
Shafikov, M. Z.; Suleymanova, A. F.; Czerwieniec, R.; Yersin, H. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 13274.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b02002 pmid: 29053269 |
| [22] |
Volz, D.; Chen, Y.; Wallesch, M.; Liu, R.; Flechon, C.; Zink, D. M.; Friedrichs, J.; Flugge, H.; Steininger, R.; Gottlicher, J.; Heske, C.; Weinhardt, L.; Brase, S.; So, F.; Baumann, T. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2538.
|
| [23] |
Jia, J.-H.; Liang, D.; Yu, R.; Chen, X.-L.; Meng, L.; Chang, J.-F.; Liao, J.-Z.; Yang, M.; Li, X.-N.; Lu, C.-Z. Chem. Mater. 2019, 32, 620.
|
| [24] |
Cai, X. B.; Liang, D.; Yang, M.; Wu, X. Y.; Lu, C. Z.; Yu, R. Chem. Commun. (Camb). 2022, 58, 8970.
|
| [25] |
Liang, D.; Jia, J.-H.; Cai, X.-B.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Lu, C.-Z. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 6561.
|
| [26] |
Liang, D.; Jia, J. H.; Yang, M.; Cai, X. B.; Yu, R.; Lu, C. Z. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2201130.
|
| [27] |
Adamo, C.; Barone, V. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 6158.
|
| [28] |
Perdew, J. P.; Ernzerhof, M.; Burke, K. J. Chem. Phys. 1996, 105, 9982.
|
| [29] |
Cances, E.; Mennucci, B.; Tomasi, J. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 3032.
|
| [30] |
Mennucci, B.; Cances, E.; Tomasi, J. J. Phys. Chem. 1997, 101, 10506.
|
| [31] |
Miertuš, S.; Scrocco, E.; Tomasi, J. Chem. Phys. 1981, 55, 117.
|
| [32] |
Roy, L. E.; Hay, P. J.; Martin, R. L. J. Chem. Theory. Comput. 2008, 4, 1029.
|
| [33] |
Hariharan, P. C.; Pople, J. A. Mol. Phys. 1974, 27, 209.
|
| [34] |
Czerwieniec, R.; Kowalski, K.; Yersin, H. Dalton. T. 2013, 42, 9826.
|
| [35] |
Volz, D.; Wallesch, M.; Grage, S. L.; Gottlicher, J.; Steininger, R.; Batchelor, D.; Vitova, T.; Ulrich, A. S.; Heske, C.; Weinhardt, L.; Baumann, T.; Brase, S. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 7837.
|
| [36] |
Endo, A.; Sato, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Kai, T.; Kawada, A.; Miyazaki, H.; Adachi, C. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 083302.
|
| [37] |
Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Shizu, K.; Huang, S.; Hirata, S.; Miyazaki, H.; Adachi, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 14706.
|
| [38] |
Yersin, H.; Czerwieniec, R.; Hupfer, A. Organic Photonics V. 2012, 8435, 843508.
|
| [1] | Yuqing Zhao, Dong Liang, Jihui Jia, Rongmin Yu, Can-Zhong Lu. Synthesis and Characterization of an Emissive Ag(I) Complex with a D-A Type Ligand Containing Two Electron-withdrawing Groups [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(5): 486-492. |
| [2] | Yinuo Wang, Shiyang Shao, Lixiang Wang. Recent Advances in Multiple Resonance Organic/Polymer Fluorescent Materials with Narrowband Emission★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(9): 1202-1214. |
| [3] | Zhenyu Liu, Junfeng Rao, Shoujia Zhu, Bingyang Wang, Fan Yu, Quanyou Feng, Linghai Xie. Research Progress of Solution-Processed Self-Host Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Materials [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(7): 820-835. |
| [4] | Yinfeng Wang, Meng Li, Chuanfeng Chen. Chiral Triptycene-Based Red Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Polymers and Their Organic Light-Emitting Diodes★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 588-594. |
| [5] | Shaoqin Zhang, Meiqing Li, Zhongjun Zhou, Zexing Qu. Theoretical Study on the Multiple Resonance Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Process [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(2): 124-130. |
| [6] | Lu Zhou, Jia-Xiong Chen, Shaomin Ji, Wen-Cheng Chen, Yanping Huo. Research Progress of Red Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescent Materials Based on Quinoxaline [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 359-372. |
| [7] | Tao Zhou, Yue Qian, Hongjian Wang, Quanyou Feng, Linghai Xie, Wei Huang. Recent Advances in Substituent Effects of Blue Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Small Molecules [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(5): 557-574. |
| [8] | Cao Hongtao, Li Bo, Wan Jun, Yu Tao, Xie Linghai, Sun Chen, Liu Yuyu, Wang Jin, Huang Wei. Cyano-substituted Spiro[fluorine-9,9'-xanthene] Derivatives: Exciplex Emission and Property Manipulation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(7): 680-687. |
| [9] | Wang Zhiqiang, Bai Meidan, Zhang Ming, Zhang Zhiqiang, Feng Xun, Zheng Caijun. Synthesis and Properties of Two Novel Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Materials with 1,3,5-Tribenzoylbenzene as Electron-Acceptor [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(2): 140-146. |
| [10] | Wang Zhiqiang, Cai Jialin, Zhang Ming, Zheng Caijun, Ji Baoming. A Novel Yellow Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Emitter For Highly Efficient Organic Light-Emitting Diodes [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2019, 77(3): 263-268. |
| [11] | Wu Youxiong, Ren Hongyang, Wu Yifang, Wang Bingxi. Theoretical Study of Energy Gaps for Naphthalimide-based Charge Transfer Compounds [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2015, 73(1): 53-59. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||