有机化学 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 1341-1364.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202209007 上一篇 下一篇
综述与进展
收稿日期:2022-09-05
修回日期:2022-10-17
发布日期:2022-11-21
通讯作者:
姚佳琪
Received:2022-09-05
Revised:2022-10-17
Published:2022-11-21
Contact:
Jiaqi Yao
文章分享

芳香腈是有机合成中普遍存在的原料之一, 也是一类重要的合成中间体, 可广泛应用于药物、农用化学品、染料、香料以及功能材料等领域, 但由于C—CN键热力学稳定性较高, 很少被认为是一个有价值的反应位点. 因此, 开发简便、高效的方法催化芳香腈C—CN键转化成为近年研究热点之一. 综述了近十年来基于C—CN键断裂的芳香腈转化反应研究进展, 并按照不同反应原理分类, 主要包括过渡金属介导/催化的C—CN的转化、自由基介导的C—CN的转化、Lewis酸、碱或Brønsted酸介导的C—CN的转化, 详细讨论了反应底物普适性、反应机理和应用, 并对该领域的发展前景和局限性进行了总结.
缪存静, 姚佳琪. 基于C—CN键断裂的芳香腈转化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(4): 1341-1364.
Cunjing Miao, Jiaqi Yao. Recent Advances in the Transformation Reactions of Aromatic Nitriles via C—CN Bond Cleavage[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(4): 1341-1364.
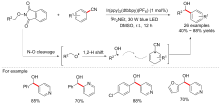
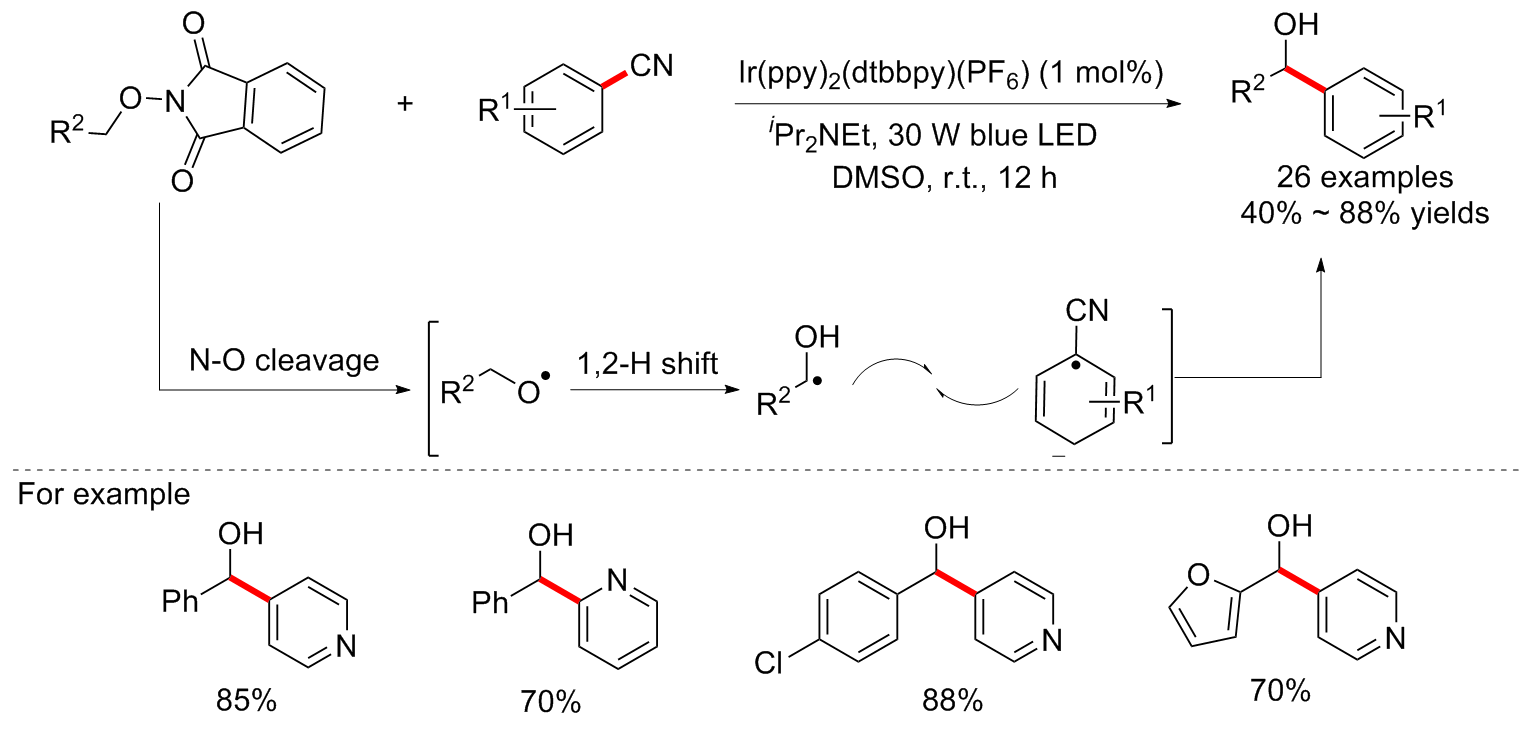
| [1] |
Anbarasan, P.; Schareina, T.; Beller, M. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5049.
doi: 10.1039/c1cs15004a |
| [2] |
(a) Trivedi, B. K.; Holmes, A.; Stoeber, T. L.; Blankley, C. J.; Roark, W. H.; Picard, J. A.; Shaw, M. K.; Essenburg, A. D.; Stanfield, R. L.; Krause, B. R. J. Med. Chem. 1993, 36, 3300.
pmid: 8230120 |
|
(b) Weiberth, F. J.; Hall, S. S. J. Org. Chem. 1987, 52, 3901.
doi: 10.1021/jo00226a033 pmid: 8230120 |
|
|
(c) Miller, J. S.; Manson, J. L. Acc. Chem. Res. 2001, 34, 563.
doi: 10.1021/ar0000354 pmid: 8230120 |
|
| [3] |
(a) Takagi, K.; Okamoto, T.; Sakakibara, Y.; Oka, S. Chem. Lett. 1973, 471.
|
|
(b) Zanon, J.; Klapars, A.; Buchwald, S. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 2890.
doi: 10.1021/ja0299708 |
|
|
(c) Sundermeier, M.; Zapf, A.; Beller, M. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 3513.
|
|
|
(d) Zhou, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Jiao, N. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 2888.
doi: 10.1021/ol101094u |
|
| [4] |
(a) So, Y.-H.; Miller, L. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 7119.
doi: 10.1021/ja00543a047 |
|
(b) Dohi, T.; Morimoto, K.; Kiyono, Y.; Tohma, H.; Kita, Y. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 537.
doi: 10.1021/ol0476826 |
|
|
(c) Zhou, W.; Zhang, L.; Jiao, N. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7094.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v48:38 |
|
|
(d) Qin, C.; Jiao, N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15893.
doi: 10.1021/ja1070202 |
|
|
(e) Pimparkar, S.; Koodan, A.; Maiti, S.; Ahmed, N. S.; Mostafa, M. M. M.; Maiti, D. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 2210.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC07783F |
|
| [5] |
(a) Magano, J.; Dunetz, J. R. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2177.
doi: 10.1021/cr100346g |
|
(b) Bunnett, J. F.; Zahler, R. E. Chem. Rev. 1951, 49, 273.
doi: 10.1021/cr60153a002 |
|
| [6] |
Nakazawa, H.; Kamata, K.; Itazaki, M. Chem. Commun. 2005, 4004.
|
| [7] |
Nakazawa, H.; Itazaki, M.; Kamata, K.; Ueda, K. Chem. Asian J. 2007, 2, 882.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1861-471X |
| [8] |
(a) Tobisu, M.; Nakamura, R.; Kita, Y.; Chatani, N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3174.
doi: 10.1021/ja810142v |
|
(b) Tobisu, M.; Nakamura, R.; Kita, Y.; Chatani, N. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 582.
|
|
| [9] |
Patra, T.; Agasti, S.; Akanksha; Maiti, D. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 69.
doi: 10.1039/c2cc36883h |
| [10] |
Patra, T.; Agasti, S.; Modak, A.; Maiti, D. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8362.
doi: 10.1039/c3cc44562c |
| [11] |
Weidauer, M.; Someya, C. I.; Irran, E.; Enthaler, S. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2, 150.
doi: 10.1002/ajoc.v2.2 |
| [12] |
Enthaler, S.; Weidauer, M.; Irran, E.; Epping, J. D.; Kretschmer, R.; Someya, C. I. J. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 745-746, 262.
doi: 10.1016/j.jorganchem.2013.07.068 |
| [13] |
Hünig, S.; Schaller, R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1982, 21, 36.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3773 |
| [14] |
(a) Nakao, Y. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 327.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00301 |
|
(b) Wen, Q.; Lu, P.; Wang, Y. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 47806.
doi: 10.1039/C4RA08675A |
|
|
(c) Kou, X.; Fan, J.; Tong, X.; Shen, Z. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 33, 1407. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201212033 |
|
|
(寇学振, 范佳骏, 童晓峰, 沈增明, 有机化学, 2013, 33, 1407.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201212033 |
|
|
(d) Paul, N.; Patra, T.; Maiti, D. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2022, 11, e202100591.
|
|
| [15] |
Sun, M.; Zhang, H. Y.; Han, Q.; Yang, K.; Yang, S. D. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 9566.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v17.35 |
| [16] |
Liu, N.; Wang, Z.-X. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2012, 354, 1641.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.201200369 |
| [17] |
Miller, J. A.; Dankwardt, J. W. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 1907.
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(03)00075-3 |
| [18] |
Yada, A.; Ebata, S.; Idei, H.; Zhang, D.; Nakao, Y.; Hiyama, T. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn 2010, 83, 1170.
doi: 10.1246/bcsj.20100068 |
| [19] |
(a) Nakao, Y.; Oda, S.; Hiyama, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13904.
doi: 10.1021/ja0448723 |
|
(b) Nakao, Y.; Yukawa, T.; Hirata, Y.; Oda, S.; Satoh, J.; Hiyama, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7116.
doi: 10.1021/ja060519g |
|
|
(c) Nakao, Y.; Yada, A.; Ebata, S.; Hiyama, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 2428.
doi: 10.1021/ja067364x |
|
|
(d) Ohnishi, Y.-Y.; Nakao, Y.; Sato, H.; Nakao, Y.; Hiyama, T.; Sakaki, S. Organometallics 2009, 28, 2583.
doi: 10.1021/om8008525 |
|
| [20] |
Nakai, K.; Kurahashi, T.; Matsubara, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11066.
doi: 10.1021/ja203829j |
| [21] |
Nakai, K.; Kurahashi, T.; Matsubara, S. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 856.
doi: 10.1021/ol303546p |
| [22] |
Fang, X.; Yu, P.; Prina Cerai, G.; Morandi, B. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 15629.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201604061 |
| [23] |
Munjanja, L.; Torres-López, C.; Brennessel, W. W.; Jones, W. D. Organometallics 2016, 35, 2010.
doi: 10.1021/acs.organomet.6b00304 |
| [24] |
Zhang, T.; Luan, Y. X.; Zheng, S. J.; Peng, Q.; Ye, M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7439.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.19 |
| [25] |
Wu, K.; Rong, Q.; Sun, N.; Hu, B.; Shen, Z.; Jin, L.; Hu, X. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2021, 363, 4708.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.v363.20 |
| [26] |
Delcaillau, T.; Morandi, B. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 11823.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v27.46 |
| [27] |
Beletskaya, I. P.; Cheprakov, A. V. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 3009.
pmid: 11749313 |
| [28] |
Kita, Y.; Tobisu, M.; Chatani, N. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 1864.
doi: 10.1021/ol100481h |
| [29] |
(a) Chatani, N.; Tobisu, M.; Kinuta, H.; Kita, Y.; Rémond, E. Synthesis 2012, 44, 2999.
doi: 10.1055/s-00000084 |
|
(b) Tobisu, M.; Kinuta, H.; Kita, Y.; Remond, E.; Chatani, N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 115.
doi: 10.1021/ja2095975 |
|
| [30] |
Jiang, Y.-Y.; Yu, H.-Z.; Fu, Y. Organometallics 2013, 32, 926.
doi: 10.1021/om301263s |
| [31] |
Esteruelas, M. A.; Oliván, M.; Vélez, A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 12321.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b07357 pmid: 26339861 |
| [32] |
Wang, C.-S.; Yu, Y.; Sunada, Y.; Wang, C.; Yoshikai, N. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 4054.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.2c00181 |
| [33] |
(a) McNally, A.; Prier, C. K.; MacMillan, D. W. C. Science 2011, 334, 1114.
doi: 10.1126/science.1213920 pmid: 22116882 |
|
(b) Zuo, Z.; MacMillan, D. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5257.
doi: 10.1021/ja501621q pmid: 22116882 |
|
| [34] |
(a) Dixon, I. M.; Collin, J.-P.; Sauvage, J.-P.; Flamigni, L.; Encinas, S.; Barigelletti, F. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2000, 29, 385.
doi: 10.1039/b000704h |
|
(b) Mori, Y.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Hayashi, H. J. Phys. Chem. 2000, 104, 4896.
doi: 10.1021/jp0007437 |
|
| [35] |
Panteleeva, E. V.; Vaganova, T. A.; Shteingarts, V. D.; Bilkis, I. I. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 8465.
doi: 10.1016/0040-4039(95)01685-B |
| [36] |
(a) Lewis, J. R. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2001, 18, 95.
pmid: 7932582 |
|
(b) Lin, N.-H.; Carrera, G. M.; Anderson, D. J. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 3542.
pmid: 7932582 |
|
| [37] |
(a) Seel, S.; Thaler, T.; Takatsu, K.; Zhang, C.; Zipse, H.; Straub, B. F.; Mayer, P.; Knochel, P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 4774.
doi: 10.1021/ja201008e pmid: 16536525 |
|
(b) Beng, T. K.; Gawley, R. E. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 394.
doi: 10.1021/ol102682r pmid: 16536525 |
|
|
(c) Campos, K. R.; Klapars, A.; Waldman, J. H.; Dormer, P. G.; Chen, C.-y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3538.
pmid: 16536525 |
|
| [38] |
Vega, J. A.; Alonso, J. M.; Mendez, G.; Ciordia, M.; Delgado, F.; Trabanco, A. A. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 938.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b00117 |
| [39] |
Yan, C.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 4686.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b02326 |
| [40] |
Ide, T.; Barham, J. P.; Fujita, M.; Kawato, Y.; Egami, H.; Hamashima, Y. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 8453.
doi: 10.1039/C8SC02965B |
| [41] |
Vorobév, A. Y. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2019, 55, 90.
doi: 10.1007/s10593-019-02423-7 |
| [42] |
Campos, K.; Coleman, P.; Alvarez, J.; Dreher, S.; Garbaccio, R.; Terrett, N.; Tillyer, R.; Truppo, M.; Parmee, E. Science 2019, 363, eaat0805.
|
| [43] |
Nicastri, M. C.; Lehnherr, D.; Lam, Y. H.; DiRocco, D. A.; Rovis, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 987.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b10871 pmid: 31904228 |
| [44] |
Liu, Z.; Nan, X.; Lei, T.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, B.; Tung, C.; Wu, L. Chin. J. Catal. 2018, 39, 487.
doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(17)62896-1 |
| [45] |
Zhong, L. J.; Wang, H. Y.; Ouyang, X. H.; Li, J. H.; An, D. L. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 8671.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC03619F |
| [46] |
(a) Shahid, M.; Banakar, V. B.; Prabhakar Ganesh, P. S. K.; Gopinath, P. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2022, 11, e202200184.
|
|
(b) Ni, S.-F.; Huang, G.; Chen, Y.; Wright, J. S.; Li, M.; Dang, L. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 455, 214255.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2021.214255 |
|
|
(c) Liu, B.; Romine, A. M.; Rubel, C. Z.; Engle, K. M.; Shi, B. F. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 14957.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00519 |
|
| [47] |
Pirnot, M. T.; Rankic, D. A.; Martin, D. B. C.; MacMillan, D. W. C. Science 2013, 339, 1593.
doi: 10.1126/science.1232993 |
| [48] |
Cuthbertson, J. D.; MacMillan, D. W. Nature 2015, 519, 74.
doi: 10.1038/nature14255 |
| [49] |
Chen, J.; Zhu, S.; Qin, J.; Chu, L. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 2336.
doi: 10.1039/C9CC00241C |
| [50] |
Hoshikawa, T.; Inoue, M. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 3118.
doi: 10.1039/c3sc51080h |
| [51] |
Lipp, B.; Nauth, A. M.; Opatz, T. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 6875.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.6b01215 |
| [52] |
Nauth, A. M.; Lipp, A.; Lipp, B.; Opatz, T. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2017, 2099.
|
| [53] |
Chen, Y.; Lu, P.; Wang, Y. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 2130.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b00443 |
| [54] |
Shi, J.; Yuan, T.; Zheng, M.; Wang, X. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 3040.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c05211 |
| [55] |
(a) Liu, B.; Lim, C.-H.; Miyake, G. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13616.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b07390 |
|
(b) Li, G.; Yan, Q.; Gan, Z.; Li, Q.; Dou, X.; Yang, D. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 7938.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b02921 |
|
| [56] |
Kobayashi, F.; Fujita, M.; Ide, T.; Ito, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Egami, H.; Hamashima, Y. ACS Catal. 2020, 11, 82.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c04722 |
| [57] |
Lipp, B.; Lipp, A.; Detert, H.; Opatz, T. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 2054.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b00652 |
| [58] |
Betori, R. C.; Scheidt, K. A. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 10350.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b03608 |
| [59] |
Chen, D.; Xu, L.; Long, T.; Zhu, S.; Yang, J.; Chu, L. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 9012.
doi: 10.1039/c8sc03493a pmid: 30647893 |
| [60] |
Wang, F.; Qin, J.; Zhu, S.; Chu, L. RSC Adv. 2020, 11, 142.
doi: 10.1039/D0RA10180J |
| [61] |
Yu, J. M.; Zhu, L. W.; Hong, X. Y.; Gao, H.; Chen, T. T. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 5642.
doi: 10.1039/D1OB00498K |
| [62] |
Ma, C.-H.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, J.; He, X.; Zhang, S.-T.; Jiang, Y.-Q.; Yu, B. Chin. J. Catal. 2022, 43, 571.
doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(21)63917-7 |
| [63] |
(a) Blakemore, D. C.; Castro, L.; Churcher, I.; Rees, D. C.; Thomas, A. W.; Wilson, D. M.; Wood, A. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 383.
doi: 10.1038/s41557-018-0021-z pmid: 29568051 |
|
(b) Liu, J.; Qiu, X.; Huang, X.; Luo, X.; Zhang, C.; Wei, J.; Pan, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, Q.; Song, S.; Jiao, N. Nat. Chem. 2019, 11, 71.
doi: 10.1038/s41557-018-0156-y pmid: 29568051 |
|
| [64] |
(a) Ruiz-Castillo, P.; Buchwald, S. L. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12564.
pmid: 27689804 |
|
(b) Chen, B.; Wu, L.-Z.; Tung, C.-H. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2512.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00267 pmid: 27689804 |
|
| [65] |
Miller, J. A.; Dankwardt, J. W.; Penney, J. M. Synthesis 2003, 1643.
|
| [66] |
Zhou, C.; Lei, T.; Wei, X. Z.; Ye, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, B.; Tung, C. H.; Wu, L. Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 16805.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c07600 |
| [67] |
Condon, S.; Dupré, D.; Lachaise, I.; Nédélec, J.-Y. Synthesis 2002, 1752.
|
| [68] |
(a) Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Nie, F.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Z. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 16204.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c01526 pmid: 35385272 |
|
(b) Yang, J.; Ma, J.; Yan, K.; Tian, L.; Li, B.; Wen, J. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2021, 364, 845.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.v364.4 pmid: 35385272 |
|
|
(c) Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, K.; Li, G.; Findlater, M. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 3570.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c01014 pmid: 35385272 |
|
|
(d) Zhou, H. J.; Huang, J. M. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 5328.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.2c00177 pmid: 35385272 |
|
| [69] |
Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Gao, H.; Wang, L.; Guo, L.; Xia, W. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 3472.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c00920 pmid: 33861088 |
| [70] |
Lehnherr, D.; Lam, Y. H.; Nicastri, M. C.; Liu, J.; Newman, J. A.; Regalado, E. L.; DiRocco, D. A.; Rovis, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 468.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b10870 pmid: 31849221 |
| [71] |
Wen, J.; Yang, X.; Yan, K.; Qin, H.; Ma, J.; Sun, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, H. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 1081.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c04296 |
| [72] |
Thompson, A. D.; Huestis, M. P. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 762.
doi: 10.1021/jo302307y |
| [73] |
Quinio, P.; Roman, D. S.; Leon, T.; William, S.; Karaghiosoff, K.; Knochel, P. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 4396.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5b02380 |
| [74] |
Chen, Q.; Leon, T.; Knochel, P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 8746.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201400750 |
| [75] |
(a) Li, M.; Gutierrez, O.; Berritt, S.; Pascual-Escudero, A.; Yesilcimen, A.; Yang, X.; Adrio, J.; Huang, G.; Nakamaru-Ogiso, E.; Kozlowski, M. C.; Walsh, P. J. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 997.
doi: 10.1038/nchem.2760 |
|
(b) Li, M.; Berritt, S.; Matuszewski, L.; Deng, G.; Pascual-Escudero, A.; Panetti, G. B.; Poznik, M.; Yang, X.; Chruma, J. J.; Walsh, P. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16327.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b09394 |
|
|
(c) Wang, Q.; Poznik, M.; Li, M.; Walsh, P. J.; Chruma, J. J. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 360, 2854.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.v360.15 |
|
| [76] |
Zou, D.; Gan, L.; Yang, F.; Wang, H.; Pu, Y.; Li, J.; Walsh, P. J. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7060.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26767-x |
| [77] |
Shelp, R. A.; Walsh, P. J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15857.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.48 |
| [78] |
Lei, Y.; Yang, J.; Qi, R.; Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Xu, Z. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 11881.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC06408C |
| [79] |
Takeda, M.; Nagao, K.; Ohmiya, H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 22460.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.50 |
| [80] |
(a) Sato, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Sumida, Y.; Hashizume, D.; Hosoya, T.; Ohmiya, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 9938;
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c04456 |
|
(b) Buzzetti, L.; Prieto, A.; Roy, S. R.; Melchiorre, P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15039.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201709571 |
|
| [81] |
Reidl, T. W.; Bandar, J. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 11939.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c05764 |
| [82] |
Gao, L.; Wang, G.; Cao, J.; Chen, H.; Gu, Y.; Liu, X.; Cheng, X.; Ma, J.; Li, S. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 10142.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b03798 |
| [83] |
Wang, G.; Cao, J.; Gao, L.; Chen, W.; Huang, W.; Cheng, X.; Li, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3904.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b00823 |
| [84] |
Tang, L.; Jiang, S.; Huang, X.; Song, Z.; Wang, J. B.; Ma, M.; Chen, B.; Ma, Y. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 3232.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.2c01027 |
| [85] |
Cao, J.; Wang, G.; Gao, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Cheng, X.; Li, S. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 2767.
doi: 10.1039/C8SC05237A |
| [86] |
Gao, L.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Chen, S.; Cao, J.; Wang, G.; Li, S. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 5698.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.2c02074 |
| [1] | 杨俊娟, 史大昕, 刘明星, 张立军, 张奇, 李加荣. 邻氨基芳香腈与羰基化合物的反应机理及其产物的骨架结构[J]. 有机化学, 2014, 34(12): 2424-2437. |
| [2] | 刘长娥, 于琪瑶, 唐健红, 李加荣. 碱性条件下4(3H)-喹唑啉酮的一锅合成[J]. 有机化学, 2012, (03): 532-537. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
