

德国小蠊性信息素类似物的设计与合成
收稿日期: 2012-07-28
修回日期: 2012-09-18
网络出版日期: 2012-09-21
Design and Synthesis of German Cockroach (Blattella germanica) Sex Pheromone Analogues
Received date: 2012-07-28
Revised date: 2012-09-18
Online published: 2012-09-21
王晓波 , 张钟宁 , 杨新玲 . 德国小蠊性信息素类似物的设计与合成[J]. 有机化学, 2013 , 33(01) : 178 -183 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201207045
As one of the most important sanitation pests worldwide, German cockroach (Blattella germanica L.) is difficult to control. Insect sex pheromones are safe and efficient attractants used in integrated pest management. The sex pheromone of German cockroach had been identified as blattellaquinone. The instability hampered the application of this compound. In order to find new and stable structures, a number of analogues were designed and synthesized by modification of the quinone ring (A), aliphatic terminal (B) and ester group (C) of blattellaquinone. The structures were confirmed by 1H NMR, IR spectra and HRMS analysis.
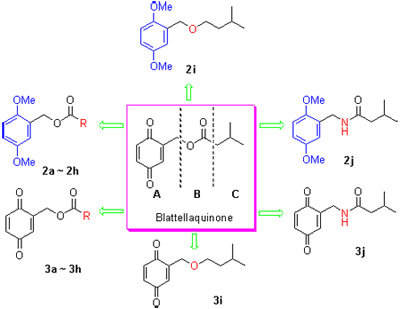
Key words: Blattella germanica; blattellaquinone; sex pheromone analogues; synthesis
[1] Fakoorziba, M. R.; Eghbal, F.; Hassanzadeh, J.; Moemenbellah- Fard, M. D. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2010, 104, 521.
[2] Londres, M. I.; Sarinho, F. W.; Miranda, P. J.; Solé, D.; Sarinho, E. Clin. Lab. 2011, 57, 969.
[3] Wen, Z.; Scott, J. G. Pestic. Sci. 1997, 49, 367.
[4] Wu, D.; Scharf, M. E.; Neal, J. J.; Suiter, D. R.; Bennett, G. W. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 1998, 61, 53.
[5] Wei, Y.; Appel, A.; Moar, W. J.; Liu, N. Pest. Manage. Sci. 2001, 57, 1055.
[6] Morrison, G.; Barile, J.; Macom, T. E. Pest Control Technol. 2004, 32(2), 62.
[7] Wang, C. L.; Scharf, M. E.; Bennett, G. W. J. Econ. Entomol. 2004, 97, 2067.
[8] Nojima, S.; Schal, C.; Webster, F. C.; Santangelo, R. G.; Roelofs, W. L. Science 2005, 307, 1104.
[9] Liang, D.; Schal, C. Experientia 1993, 49, 324.
[10] Abed, D.; Tokro, P.; Farine, J. P.; Brossut, R. Chemoecology 1993, 4, 46.
[11] Kostikov, A. P.; Popik, V. V. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 9190.
[12] Barbosa, L. C. A.; Alvarenga, E. S.; Demuner, A. J.; Virtuoso, L. S.; Silva, A. A. Chem. Biodiverity 2006, 3, 553.
[13] Williamson, D. A.; Bowler, B. E. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 12357.
[14] Kumar, S. K.; Amador, M.; Hidalgo, M.; Bhat, S. V.; Khan, S. R. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 2873.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |