

一种新型科罗索酸衍生物的生物催化合成
收稿日期: 2016-05-09
修回日期: 2016-06-04
网络出版日期: 2016-07-13
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(No.21462057)、教育部春晖计划(No.Z2014091)、贵州省科技厅、遵义医学院、遵义市科技局联合基金(No.QKHLH-2014-7555)资助项目.
Biocatalytic Synthesis of a Novel Corosolic Acid Derivative
Received date: 2016-05-09
Revised date: 2016-06-04
Online published: 2016-07-13
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No.21462057),the Program of Ministry of Education "Chunhui Plan" (No.Z2014091),and the United Fund of Guizhou Province,Zunyi Medical University and Zunyi City (No.QKHLH-2014-7555).
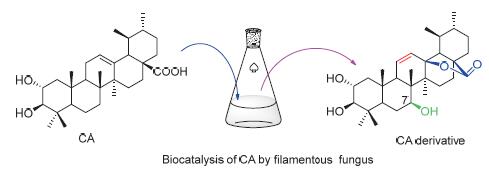
科罗索酸是一种五环三萜酸,因其显著的抗糖尿病活性而备受关注.通过生物催化的方法对其进行结构修饰和改造,增加科罗索酸结构多样性,为筛选结构新颖或活性更强衍生物奠定基础.使用一株植物内生真菌Umbelopsis is-abellina催化合成一个新的科罗索酸衍生物,命名为2α,3β,7β-三羟基-乌苏-11-烯-28,13-内酯(2).其结构通过高分辨质谱、核磁共振等波谱技术确定.
关键词: 科罗索酸; 生物催化; 羟基化; 2α,3β,7β-三羟基-乌苏-11-烯-28,13-内酯
付少彬 , 孟庆峰 , 辛庆 , 肖世基 . 一种新型科罗索酸衍生物的生物催化合成[J]. 有机化学, 2016 , 36(11) : 2743 -2745 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201605011
Corosolic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene acid, attracted more and more attention because of the significant anti-diabetes activity. Biocatalysis was applied to modify the structure of corosolic acid to increase the structural diversity of corosolic acid and lay the foundation for screening derivatives with novel structure or better activity. A novel corosolic acid derivative was synthesized by endophytic fungus Umbelopsis isabellina. The structure of the new compound was established by HR-ESIMS and NMR spectrum.

[1] Lin, G.-R.; Shen, G.-Y.; Wu, J.-C. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2014, 28, 133 (in Chinese). (林国荣, 沈高扬, 吴锦程, 中国农学通报, 2014, 28, 133.)
[2] He, J.-R.; Liu, J.; Bai, Z.-L.; Huang, R.-Q.; Wang, Z.-L. J. Southern Med. Univ. 2010, 11, 2533 (in Chinese). (贺建荣, 刘欠, 白志龙, 黄仁权, 王增禄, 南方医科大学学报, 2010, 11, 2533.)
[3] Sung, B.; Kang, Y. J.; Kim, D. H.; Hwang, S. Y.; Lee, Y.; Kim, M.; Yoon, J.-H.; Kim, C. M.; Chung, H. Y.; Kim, N. D. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 943.
[4] Kim, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Song, G.-Y.; Kim, D.-E.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Liu, K.-H.; Chung, Y.-H.; Oh, S. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 67, 87.
[5] Aguirre, M. C.; Delporte, C.; Backhouse, N.; Erazo, S.; Letelier, M. E.; Cassels, B. K.; Silva, X.; Alegría, S.; Negrete, R. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 5673.
[6] Xu, Y.-F.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Xu, Y.-L.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, G.-Q.; Chen, Y.-X.; Sun, F.-Y.; Wang, J.-Y.; Yu, Y.-C. Cell Signal 2016, 29, 209.
[7] Ren, X.-H.; Lu, X.-F. Prog. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 3, 129 (in Chi-nese). (任新凤, 陆雪芬, 药学进展, 2011, 3, 129.)
[8] Park, C.; Lee, J.-S. Biomed. Res. 2013, 24, 164.
[9] Giampapa, V. C.; Falls, L. WO 2006127779, 2006[Chem. Abstr. 2005, 145, 511747].
[10] Deng, J.-J.; Lu, C.-H.. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 30, 1
[11] Feng, X.; Li, D.-P.; Chu, Z.-Y. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 1.
[12] Li, D.-P.; Feng, X.; Chu, Z.-Y.; Guo, F.-F.; Zhang, Z.-S. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 15, 789.
[13] Fu, S.-B.; Yang, J.-S.; Cui, J.-L.; Feng, X.; Sun, D.-A. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 59, 1180.
[14] Fu, S.-B.; Yang, J.-S.; Cui, J.-L.; Sun, D.-A. Fitoterapia 2013, 86, 123.
[15] Feng, X.; Lu, Y.-H.; Liu, Z.; Li, D.-P.; Zou, Y.-X.; Fang, Y.-Q.; Chu, Z.-Y. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 1.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |