

荞麦地鼠尾草根中的二萜类成分
收稿日期: 2017-03-02
修回日期: 2017-05-22
网络出版日期: 2017-06-02
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(No.31100143)资助项目.
Diterpenes from the Roots of Salvia kiaometiensis Lévl
Received date: 2017-03-02
Revised date: 2017-05-22
Online published: 2017-06-02
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.31100143).
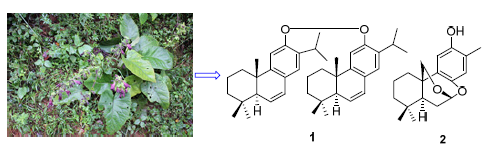
对民间丹参代用品荞麦地丹参(Salvia kiaometiensis Lévl.)乙醇提取物进行化学成分研究,通过现代多种色谱技术和波谱技术,从中分离并鉴定16个二萜类化合物,分别是6,8,11,13-abietatetraen-12-ol dimer(1),kiaometin(2),miltirone(3),tanshinone ⅡA(4),crypotanshione(5),tanshindiol C(6),ferruginol(7),2-isopropyl-8-methylphenanthrene-3,4-dione(8),tanshinone I(9),trijuganone B(10),dihydrotanshinone I(11),grandifolias C(12),przewalskin(13),tanshinlactone(14),6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-1,6,6-trimethylfuro[3,2-c]naphtha[2,1-e]oxepine-10,12-dione(15),almilalbanone(16).其中,化合物1为新的松香烷型二萜的二聚体,2为新的降松香烷型二萜化合物,其B环7,8位开环后又通过醚桥连接起来.所有化合物均为首次从该种植物中得到.
夏光惠 , 李元平 , 毕德文 , 张兰军 , 李宏哲 , 高林花 , 王利勤 . 荞麦地鼠尾草根中的二萜类成分[J]. 有机化学, 2017 , 37(10) : 2772 -2775 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201703007
Through a variety of chromatographic techniques and spectroscopic methods, sixteen diterpenes were isolated and identified from the ethanol extraction of the roots of Salvia kiaometiensis Lévl. Their structures were identified to be 6,8,11,13-abietatetraen-12-ol dimer (1), kiaometin (2), miltirone (3), tanshinone ⅡA (4), crypotanshione (5), tanshindiol C (6), ferruginol (7), 2-isopropyl-8-methylphenanthrene-3,4-dione (8), tanshinone I (9), trijuganone B (10), dihydrotanshinone I (11), grandifolias C (12), przewalskin (13), tanshinlactone (14), 6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-1,6,6-trimethylfuro[3,2-c]naphtha[2,1-e]oxepine-10,12-dione (15), and salmilalbanone (16). Compound 1 is a new abietane diterpenes dimer, and compound 2 is a new 7,8:7,20-diepoxy-nor-abietane diterpenes. All of the diterpenes were isolated from this plant for the first time.

Key words: Salvia kiaometiensis; Salvia; Lamiaceae; abietane diterpenes
[1] Delectis Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae Edita Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae, Vol. 66, Science Press, Beijing, 1977, pp. 129~130(in Chinese). (中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会编, 中国植物志, 第66卷,科学出版社, 北京, 1977, pp. 129~130.)
[2] Editorial Board of Chinese Materia Medica Chinese Materia Medica, Vol. 19, Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai, 1999, p. 168(in Chinese). (国家中医药管理局《中华本草》编委会, 中华本草, 第19卷, 上海科学技术出版社, 上海, 1999, p. 168.)
[3] Cao, C. Q.; Sun, L. R.; Lou, H. X.; Ji, M. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2009, 20, 636(in Chinese). (曹春泉, 孙隆儒, 娄红祥, 季梅, 时珍国医国药, 2009, 20, 636.)
[4] Zhu, L. P.; Xiang, C.; Zhuang, W. T.; He, J.; Li, P.; Li, B. C. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2013, 25, 785(in Chinese). (朱路平, 向诚, 庄文婷, 何静, 李鹏, 李宝才, 天然产物研究与开发, 2013, 25, 785.)
[5] Cao, C. Q.; Sun, L. R.; Wang, X. N. Chin. Trad. Herb. Drugs 2009, 40, 173(in Chinese). (曹春泉, 孙隆儒, 王小宁, 中草药, 2009, 40, 173.)
[6] Hasegawa, S.; Hirose, Y. Phytochemistry 1982, 21, 643.
[7] Onitsuka, M.; Fujiu, M.; Shinma, N.; Maruyama H. B. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1983, 31, 1670.
[8] Lan, T. F.; Yu, Z. Y.; Wang, D. J.; Wang, X.; Guan, R. J. Chin. Trad. Herb. Drugs 2011, 42, 466(in Chinese). (蓝天凤, 于宗渊, 王岱杰, 王晓, 管仁军, 中草药, 2011, 42, 466.)
[9] Kang, J.; Li L.; Wang, D. D.; Wang, H. Q.; Liu, C.; Li, B. M.; Yan, Y.; Fang, L. H.; Du, G. H.; Chen, R. Y. Phytochemistry 2015, 116, 337.
[10] Li, B.; Niu, F. D.; Lin, Z. W.; Zhang, H. J.; Wang, D. Z.; Sun, H. D. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 3815.
[11] Mak, T. C. W.; Wong, N. C.; Chang, H. M.; Choang, T. F.; Chui, K. Y.; Hon, P. M.; Lee, C. M. J. Chem. Res. 1990, 877.
[12] Guillen, M. D.; Manzanos, M. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 3016.
[13] Han, G. H.; Li, Z. L.; Sun, L.; Hua, H. L. J. Shengyang Pharm. Univ. 2009, 26, 896(in Chinese). (韩国华, 李占林, 孙琳, 华会明, 沈阳药科大学学报, 2009, 26, 896.)
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |