Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1644-1668.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202406018 Previous Articles Next Articles
REVIEWS
收稿日期:2024-06-12
修回日期:2024-08-08
发布日期:2024-09-18
基金资助:Received:2024-06-12
Revised:2024-08-08
Published:2024-09-18
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:Share
Sicheng Zhou, Yunkui Liu. Recent Progresses in P/N-Heteroleptic Cu(I)-Photocatalyst-Mediated Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalytic Reactions[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(5): 1644-1668.
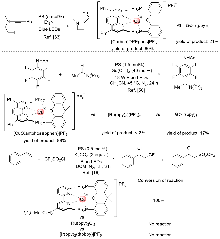






| [1] |
(a)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
(b)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1039/b913880n pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(d)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(e)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(f)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(李康葵, 龙先扬, 黄岳, 祝诗发, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 658.)
doi: 10.6023/A24030090 pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(g)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(何明慧, 叶子秋, 林桂庆, 尹晟, 黄心翊, 周旭, 尹颖, 桂波, 汪成, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 784.)
doi: 10.6023/A23040178 pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(h)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(吕鑫, 吴仪, 张勃然, 郭炜, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 359.)
doi: 10.6023/A22120487 pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(i)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(闫英红, 梁平兆, 邹杨, 袁林, 彭孝军, 樊江莉, 张晓兵, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1642.)
doi: 10.6023/A23050243 pmid: 20532341 |
|
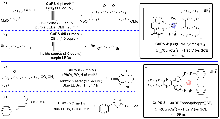
| [2] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
|
(c)
|
|
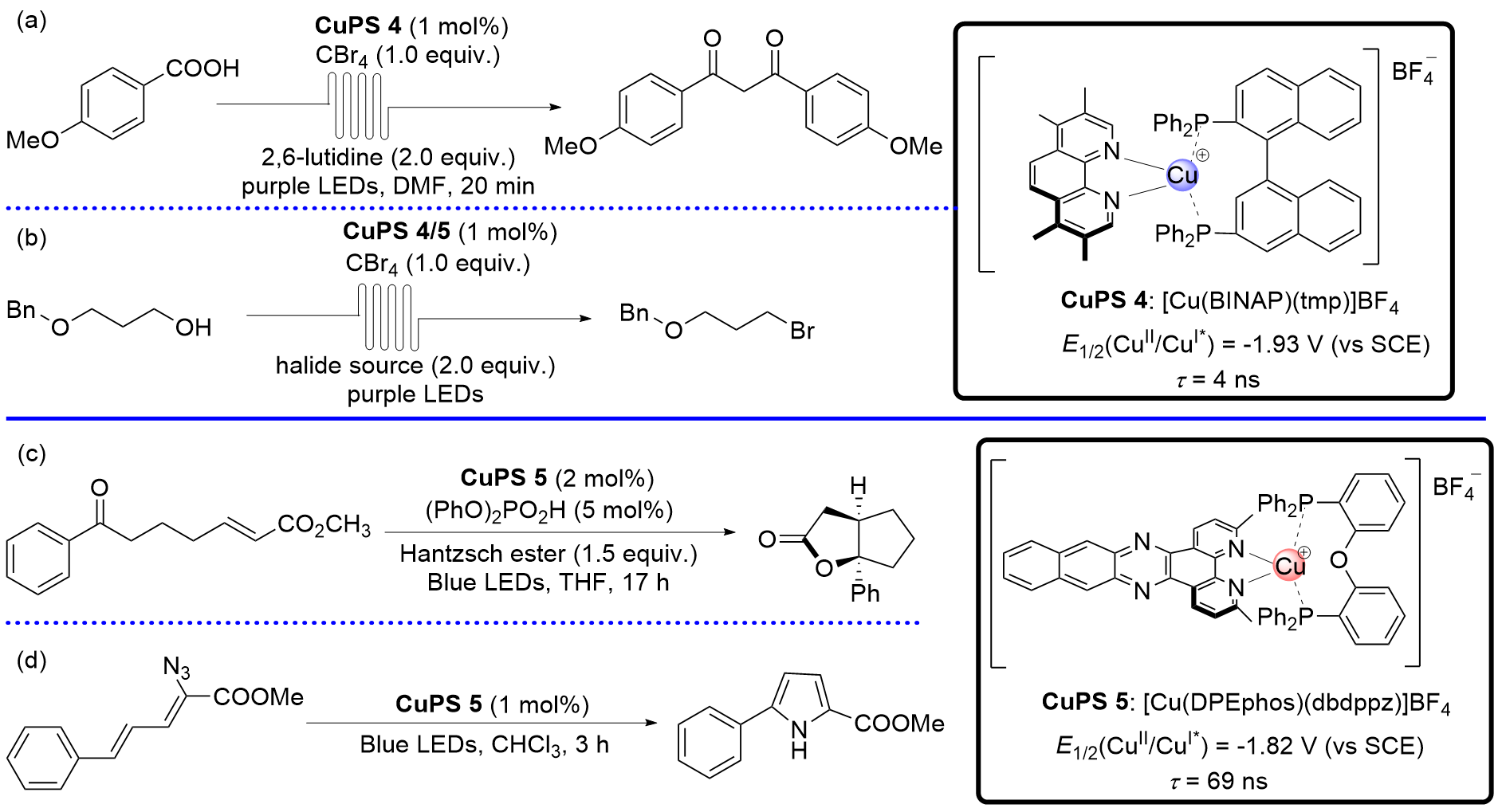
| [3] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
| [4] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
|
(c)
|
|
|
(d)
|
|
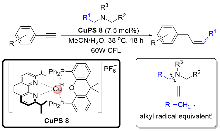
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1021/ol300983b pmid: 22642645 |
| [8] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.1002/chem.201405356 pmid: 25413572 |
| [10] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b01518 pmid: 28598630 |
|
(b)
pmid: 28598630 |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.4c00793 pmid: 38587936 |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
(a) Hydrogen Transfer Reactions: Reductions and Beyond, Eds.: Guillena, G.; Ramón, D. J. Topics in Current Chemistry Collections, Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2016.
|
|
(b)
|
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
(a)
pmid: 30088504 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1039/c8cs00054a pmid: 30088504 |
|
|
(c)
pmid: 30088504 |
|
|
(d)
pmid: 30088504 |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aal2490 pmid: 28126814 |
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [1] | Junjie Liu, Hongping Zhao, Yuanyuan Hu, Hengxin Wang, Weiming Yuan. Photoinduced Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive Heck Reaction [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(5): 1691-1697. |
| [2] | Tong Tian, Pu Chen, Huawen Huang. Visible Light-Induced Synthesis of Polysubstituted Dihydrofurans via Cyclization of Aromatic Aldehydes with Acrylonitriles [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(5): 1763-1769. |
| [3] | Yan Tan, Jiale Ying, Bing Yu, Zhan Lu. Visible Light-Promoted Aerobic Oxo-azidation of Alkenyl Silanes [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(5): 1684-1690. |
| [4] | Hui Li, Ablimit Abdukader, Lei Zhou. Radical Denitrogenative Ring Opening of N-Benzyl-benzotriazoles for the Synthesis of 6-Substituted Phenanthridines under Visible Light Conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(5): 1770-1777. |
| [5] | Jieqing Ou, Peizhen Qu, Liang Zhao. Visible Light Mediated Palladium-Catalyzed Hydrodebromination of Aliphatic α-Bromotrifluoromethyl Compounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(4): 1334-1341. |
| [6] | Lingwei Wu, Hao Cui, Xiao Zhang. Recent Advances in Water-Soluble Photocatalysts-Mediated Aqueous Reactions [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(4): 1097-1118. |
| [7] | Jia Zhao, Qiuyun Gan, Yaofeng Yuan. Research Progress in Free Radical Fluorosulfonylation [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(4): 1206-1222. |
| [8] | Dongsen Duan, Yuan Ma, Yubo Liu, Fu Cheng, Daoyong Zhu, Shaohua Wang. Visible Light-Induced Decarbon-Carboxylation of Activated Alkenes by Carbon Dioxide [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(5): 1675-1685. |
| [9] | Wenwen Chen, Qin Zhang, Songyue Zhang, Fangfang Huang, Xinyin Zhang, Jianfeng Jia. Visible Light Promoted Coupling Reaction of Alkynyl Iodide and Sodium Sulphinate without Photocatalyst [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(2): 584-592. |
| [10] | Yanshuo Zhu, Hongyan Wang, Penghua Shu, Ke'na Zhang, Qilin Wang. Recent Advances on Alkoxy Radicals-Mediated C(sp3)—H Bond Functionalization via 1,5-Hydrogen Atom Transfer [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(1): 1-17. |
| [11] | Sijie Fan, Wuheng Dong, Caiyun Liang, Guichao Wang, Yao Yuan, Zuodong Yin, Zhaoguo Zhang. Visible Light-Induced Radical Cyclization for the Construction of 4-Aryl-1,2-dihydronaphthalenes [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(9): 3277-3286. |
| [12] | Wei Xu, Hongbin Zhai, Bin Cheng, Taimin Wang. Visible Light-Induced Pd-Catalyzed Heck Reactions [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(9): 3035-3054. |
| [13] | Xiaona Yang, Hongyu Guo, Rong Zhou. Progress in Visible-Light Promoted Transformations of Organosilicon Compounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(8): 2720-2742. |
| [14] | Yanhua Gao, Yinpan Zhang, Yan Zhang, Tao Song, Yong Yang. Visible-Light-Induced Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols over Surface Oxygen Vacancies-Enriched Nb2O5 [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(7): 2572-2579. |
| [15] | Jing Liu, Jian Hao, Qilong Shen. Visible-Light-Promoted Direct Trifluoromethylation of Tryptophan-Containing Oligapeptides with YlideFluor [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(4): 1517-1524. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
