Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 2509-2519.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202411024 Previous Articles Next Articles
ARTICLES
张威光a,†, 张国锋a,†, 李梦a, 李雪莲c, 包书红a, 葛李宵a, 施志平a, 申强强a, 姚李a,*( ), 朱三娥a,b,*(
), 朱三娥a,b,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-29
修回日期:2025-01-06
发布日期:2025-02-07
作者简介:基金资助:
Weiguang Zhanga, Guofeng Zhanga, Meng Lia, Xuelian Lic, Shuhong Baoa, Lixiao Gea, Zhiping Shia, Qiangqiang Shena, Li Yaoa,*( ), San E Zhua,b,*(
), San E Zhua,b,*( )
)
Received:2024-11-29
Revised:2025-01-06
Published:2025-02-07
Contact:
*E-mail: yaoli@hfuu.edu.cn; zhuse@hfuu.edu.cn
About author:Supported by:Share
Weiguang Zhang, Guofeng Zhang, Meng Li, Xuelian Li, Shuhong Bao, Lixiao Ge, Zhiping Shi, Qiangqiang Shen, Li Yao, San E Zhu. Synthesis, Photophysical Properties, and Reactive Oxygen Species Generation Mechanism of Type I and Type II D-π-A Hemicyanine Photosensitizers[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(7): 2509-2519.
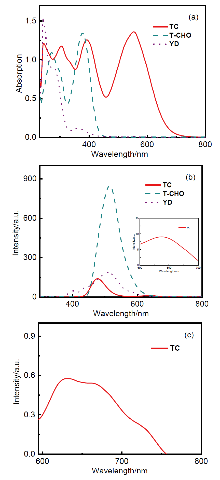

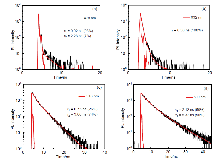

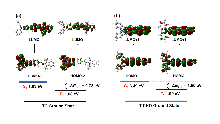





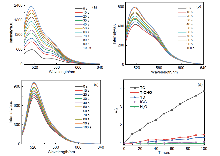



| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
( 张碧玮, 袁展翔, 徐建兴, 籍少敏, 霍延平, 梁亮, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 2929.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202002027 |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4085-0 pmid: 35126878 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [1] | Maocai Xu, Jiazhuang Tian, Yanhua Yang, Gaozhang Gou, Fumin Li, Lin Shao, Kexin Chi. Reversible Mechanofluorochromic and Data Security Protection of a Triphenylamine-Based Difluoroboron Luminescent Compound [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(5): 1824-1831. |
| [2] | Ni Wang, Zijun Zheng, Xiaoping Jia, Mengyuan Zhao, Yalei Wang, Chen Zhou, Zhijia Wang, Zelin Xiao, Hongmin Liu, Yu Ke. Study on Synthesis and Pharmacological Research of Jiyuan Oridonin A Derivatives as Potential Anti-tumor Drugs [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(2): 646-659. |
| [3] | Sihong Chen, Qi Chen, Shihe Luo, Xiying Cao, Guoxian Yang, Xiaoqing Zeng, Zhaoyang Wang. Progress in Design, Synthesis and Application of Triphenylamine-Based Fluorescent Probes [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 41(3): 919-933. |
| [4] | Wang Wenyuan, Chen Hongjin, Zhang Gang, Zhang Rui, Liu Jian. Synthesis and Properties of Donor-Acceptor Type Electrochromic Materials Based on Triphenylamine and Quinoxaline [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2020, 40(8): 2513-2519. |
| [5] | Zhang Yan, Wang Yunyun, Zhao Yuxun, Zhang Chenglong, Gu Wen, Wang Zhonglong, Zhu Yongqiang, Wang Shifa. Camphor-Based Thiosemicarbazone Analogues Induced G2 Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis via Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Mediated Mitochondrial Pathway in Human Breast Cancer Cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2020, 40(8): 2374-2386. |
| [6] | Zhou Xinyun, Xie Lingchao, Wu Kaile, Tan Songting. Synthesis and Photovoltaic Properties of Organic Dyes Containing Dendritic and 3D Triphenylamine Derivatives [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2019, 39(9): 2589-2598. |
| [7] | Yan Jianfeng, Zhang Ruiqi, Yuan Ye, Yuan Yaofeng. 4,4'-Dimethoxy-triphenylamine Conjugated Azobenzene Photochromic Switches:Synthesis, Electrochemical and Photoisomerization Studies [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2019, 39(7): 2009-2017. |
| [8] | Hou Jiting, Li Kun, Qin Caiqin, Yu Xiaoqi. Review of the Small Molecular Fluorescent Sensors for Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2018, 38(3): 612-628. |
| [9] | Mao Lijun, Tan Qinglong, Xin Guanqiong, Han Mingliang, Zhang Xuejun. Synthesis and Study of Properties for Asymmetric Triphenylamine-Zinc Phthalocyanine [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2012, 32(12): 2315-2321. |
| [10] | MENG Xiang-Li*, HUANG Yu-Dong, NIU Hai-Jun, LEI Zuo-Tao. Synthesis and Purification of 4,4'-Diaminotriphenylamine [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2007, 27(05): 682-684. |
| [11] |
FAN Fang-Lia,QIAO Ze-Banga,CHEN Qin-Wena,WANG Lan-Ying*,a WEN Zhen-Yib,ZHANG Zu-Xuna. Microwave-Assisted Solvent-Free Synthesis of 2-Substituted Pyridinium Hemicyanine Dyes with Theoretical Study of Spectrum Property [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2006, 26(10): 1389-1393. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||