Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 4257-4270.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202504015 Previous Articles Next Articles
REVIEWS
收稿日期:2025-04-13
修回日期:2025-05-26
发布日期:2025-06-06
通讯作者:
陈洁, 王斌
基金资助:
Xin Liu, Shixin Zheng, Huajie Zhao, Jie Chen*( ), Bin Wang*(
), Bin Wang*( )
)
Received:2025-04-13
Revised:2025-05-26
Published:2025-06-06
Contact:
Jie Chen, Bin Wang
Supported by:Share
Xin Liu, Shixin Zheng, Huajie Zhao, Jie Chen, Bin Wang. Recent Advances in Biomimetic Asymmetric Catalysis for Olefin cis-Dihydroxylation[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(12): 4257-4270.
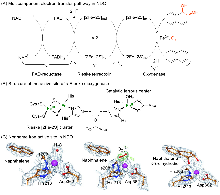

| Entry | Substrate | TONa | RCb/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cis-Diol | Epoxide | cis-Diol/Epoxide | |||
| 1 | Styrene | 8.0 | 0.1 | 80 | — |
| 2 | 1-Octene | 7.6 | 0.1 | 76 | — |
| 3 | Cyclohexene | 6.2 | 0.7 | 9 | — |
| 4 | cis-2-Heptene | 4.9 | 0.7 | 7 | 99 |
| 5 | trans-2-Heptene | 4.9 | 0.5 | 10 | ˃ 99 |
| 6 | Ethyl trans-crotonate | 7.4 | — | ˃ 100 | — |
| 7 | tert-Butyl acrylate | 5.5 | — | ˃ 100 | — |
| 8 | Dimethyl fumarate | 5.3 | — | ˃ 100 | — |
| Entry | Substrate | TONa | RCb/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cis-Diol | Epoxide | cis-Diol/Epoxide | |||
| 1 | Styrene | 8.0 | 0.1 | 80 | — |
| 2 | 1-Octene | 7.6 | 0.1 | 76 | — |
| 3 | Cyclohexene | 6.2 | 0.7 | 9 | — |
| 4 | cis-2-Heptene | 4.9 | 0.7 | 7 | 99 |
| 5 | trans-2-Heptene | 4.9 | 0.5 | 10 | ˃ 99 |
| 6 | Ethyl trans-crotonate | 7.4 | — | ˃ 100 | — |
| 7 | tert-Butyl acrylate | 5.5 | — | ˃ 100 | — |
| 8 | Dimethyl fumarate | 5.3 | — | ˃ 100 | — |
| Entry | Substrate | Yielda/% | RCb/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cis-Diol | Epoxide | cis-Diol/Epoxide | |||
| 1 | 1-Octene | 67 | 20 | 3.4 | — |
| 2 | 1-Decene | 62 | 18 | 3.4 | — |
| 3 | Vinylcyclohexane | 57 | 16 | 3.6 | — |
| 4 | Cyclohexene | 45 | 30 | 1.5 | — |
| 5 | cis-2-Heptene | 60 | 20 | 3.0 | 97 |
| 6 | trans-2-Heptene | 61 | 14 | 4.4 | 99 |
| Entry | Substrate | Yielda/% | RCb/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cis-Diol | Epoxide | cis-Diol/Epoxide | |||
| 1 | 1-Octene | 67 | 20 | 3.4 | — |
| 2 | 1-Decene | 62 | 18 | 3.4 | — |
| 3 | Vinylcyclohexane | 57 | 16 | 3.6 | — |
| 4 | Cyclohexene | 45 | 30 | 1.5 | — |
| 5 | cis-2-Heptene | 60 | 20 | 3.0 | 97 |
| 6 | trans-2-Heptene | 61 | 14 | 4.4 | 99 |
| Entry | Complex | Labile site | Substrate | TONa | ee/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cis-Diol | Epoxide | cis-Diol/Epoxide | |||||
| 1 | 4b | Two cis-α | trans-2-Heptene | 0.3 | 5.4 | 0.055 | 29 |
| 2 | 5c | Two cis-β | trans-2-Heptene | 7.5 | 2.4 | 3.1 | 79 |
| 3 | cis-2-Heptene | 7.8 | 4.5 | 1.7 | 9 | ||
| 4 | 1-Octene | 8.1 | 1.3 | 6.2 | 60 | ||
| 5 | tert-Butyl acrylate | 10 | 0.5 | 20 | 23 | ||
| 6 | 6d | Two cis-α | trans-2-Heptene | 1.1 | 5.1 | 0.22 | 38 |
| 7 | 1-Octene | 1.7 | 2.6 | 0.67 | 11 | ||
| 8 | tert-Butyl acrylate | 0.1 | 3.0 | 0.033 | — | ||
| 9 | 7d | Two cis-α | trans-2-Heptene | 5.2 | 0.2 | 26 | 97 |
| 10 | cis-2-Heptene | 3.4 | 0.6 | 5.7 | 11 | ||
| 11 | 1-Octene | 6.4 | 0.1 | 64 | 76 | ||
| 12 | Styrene | 6.5 | <0.1 | >65 | 15 | ||
| 13 | tert-Butyl acrylate | 4.0 | <0.1 | >40 | 68 | ||
| 14 | Ethyl trans-crotonate | 7.5 | 0.1 | >75 | 78 | ||
| 15 | 8d | Two cis-α | trans-2-Heptene | 3.6 | 0.9 | 4 | 78 |
| 16 | 1-Octene | 4.6 | 0.5 | 9 | 29 | ||
| 17 | tert-Butyl acrylate | 2.7 | <0.1 | >27 | 23 | ||
| Entry | Complex | Labile site | Substrate | TONa | ee/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cis-Diol | Epoxide | cis-Diol/Epoxide | |||||
| 1 | 4b | Two cis-α | trans-2-Heptene | 0.3 | 5.4 | 0.055 | 29 |
| 2 | 5c | Two cis-β | trans-2-Heptene | 7.5 | 2.4 | 3.1 | 79 |
| 3 | cis-2-Heptene | 7.8 | 4.5 | 1.7 | 9 | ||
| 4 | 1-Octene | 8.1 | 1.3 | 6.2 | 60 | ||
| 5 | tert-Butyl acrylate | 10 | 0.5 | 20 | 23 | ||
| 6 | 6d | Two cis-α | trans-2-Heptene | 1.1 | 5.1 | 0.22 | 38 |
| 7 | 1-Octene | 1.7 | 2.6 | 0.67 | 11 | ||
| 8 | tert-Butyl acrylate | 0.1 | 3.0 | 0.033 | — | ||
| 9 | 7d | Two cis-α | trans-2-Heptene | 5.2 | 0.2 | 26 | 97 |
| 10 | cis-2-Heptene | 3.4 | 0.6 | 5.7 | 11 | ||
| 11 | 1-Octene | 6.4 | 0.1 | 64 | 76 | ||
| 12 | Styrene | 6.5 | <0.1 | >65 | 15 | ||
| 13 | tert-Butyl acrylate | 4.0 | <0.1 | >40 | 68 | ||
| 14 | Ethyl trans-crotonate | 7.5 | 0.1 | >75 | 78 | ||
| 15 | 8d | Two cis-α | trans-2-Heptene | 3.6 | 0.9 | 4 | 78 |
| 16 | 1-Octene | 4.6 | 0.5 | 9 | 29 | ||
| 17 | tert-Butyl acrylate | 2.7 | <0.1 | >27 | 23 | ||
| [22] |
pmid: 11439071 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.200705061 pmid: 18236485 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v55.35 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1038/nature10535 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1021/ja201873d pmid: 21553923 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.38 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.31635/ccschem.022.202201780 |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1039/c1cc11999k |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1021/ic7003613 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c09508 pmid: 38064642 |
| [33] |
(a)
pmid: 19229926 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/cs200292h pmid: 19229926 |
|
| [1] |
doi: 10.1021/cr00032a009 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1016/0040-4020(72)80158-3 |
| [3] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/ja00230a045 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)80274-4 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1021/jo00008a051 |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.1021/jo00125a003 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.1021/jo015967f |
|
| [4] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
|
(c)
|
|
| [5] |
(a)
pmid: 21049111 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1039/b923880h pmid: 21049111 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1070/RCR4904 pmid: 21049111 |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.1002/ejoc.v2021.6 pmid: 21049111 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.1055/a-1325-4092 pmid: 21049111 |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1021/jo800145x |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b12113 pmid: 27976875 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1038/s41929-021-00574-5 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20020916)41:18<3479::AID-ANIE3479>3.0.CO;2-O |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b05792 |
| [11] |
pmid: 12586937 |
| [12] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
| [13] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/cs400087p pmid: 18277980 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1038/nchembio.71 pmid: 18277980 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.12.007 pmid: 18277980 |
|
| [14] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b01822 pmid: 26154836 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00573 pmid: 26154836 |
|
| [15] |
(a)
pmid: 12403773 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209604200 pmid: 12403773 |
|
| [16] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c13551 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c08559 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c09354 |
|
| [17] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/ja1021014 pmid: 21105649 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1002/anie.v46:42 pmid: 21105649 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1021/ic061129y pmid: 21105649 |
|
| [18] |
(a)
doi: 10.1038/nature07371 |
|
(b)
|
|
|
(c)
|
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.04.005 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00285 |
|
|
(f)
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c02073 |
|
|
(g)
doi: 10.1007/s11426-023-1578-y |
|
|
(h)
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214945 |
|
| [19] |
pmid: 10425491 |
| [20] |
pmid: 16277487 |
| [33] |
(c)
doi: 10.1002/chem.200802597 pmid: 19229926 |
| [34] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/ar990028j |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1002/ijch.v60.10-11 |
|
| [35] |
(a)
doi: 10.1002/chem.201905119 pmid: 31804749 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.1c01993 pmid: 31804749 |
|
| [36] |
(a)
pmid: 38123164 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c08565 pmid: 38123164 |
|
| [21] |
|
| [1] | Ye Wu, Chunxia Chen, Jinsong Peng. Research Progress of C—H Bond Asymmetric Hydroxylation [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(8): 2726-2745. |
| [2] | Yadan Chen, Songgang Huang, Jie Chen, Bin Wang. Nonheme Iron(III)-Monoamidate Complexes as Catalysts for Methylene-Selective Oxidation of Simple Alkanes [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(12): 4453-4462. |
| [3] | Bo Cao, Xiang Wen, Jie Chen, Bin Wang. “Click” Tetradentate Nitrogen Donor Ligands for Nonheme Iron-Catalyzed Asymmetric Epoxidation Reactions [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(12): 4490-4496. |
| [4] | Honghua Zuo, Fangrui Zhong. Reactivity Modulation of Labile Quinones and Biomimetic Catalytic Transformations [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(3): 665-678. |
| [5] | Liu Di, Zhang Chenghui, Han Nan, Du Mengmeng, Zhang Xiaolu, Zhao Pengshan, Yang Ping. Progress in Oxidative Coupling of Amines to Imines [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2018, 38(6): 1350-1363. |
| [6] | REN Qing-Gang, ZHOU Xian-Tai, JI Hong-Bing. Progress of Water-Soluble Metalloporphyrins in Catalytic Reactions [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2010, 30(11): 1605-1614. |
| [7] |
ZHOU Xian-Taia,JI Hong-Bing*,a,PEI Li-Xiaa,SHE Yuan-Binb XU Jian-Changa,WANG Le-Fua. Advance of Homogeneous Oxidation with Metalloporphyrins as Catalysts [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2007, 27(9): 1039-1059. |
| [8] | HU An-Jun,LÜ Chun-Xu*,LI Bin-Dong,HUO Ting. Study on a Novel Catalysis System for the Selective Oxidation of p-Chlorotoluene [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2006, 26(08): 1083-1086. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||