化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (2): 132-137.DOI: 10.6023/A23090434 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 有机氟化学合集
研究论文
投稿日期:2023-09-30
发布日期:2023-11-29
作者简介:基金资助:
Guanglong Huang, Xiao-Song Xue( )
)
Received:2023-09-30
Published:2023-11-29
Contact:
E-mail: About author:Supported by:文章分享
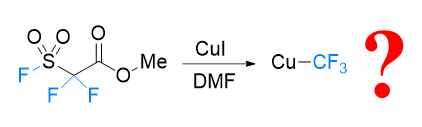
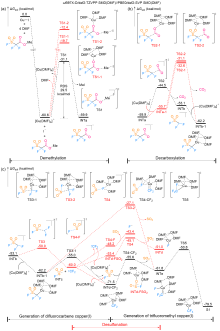
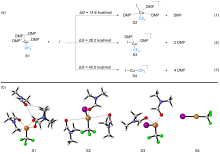
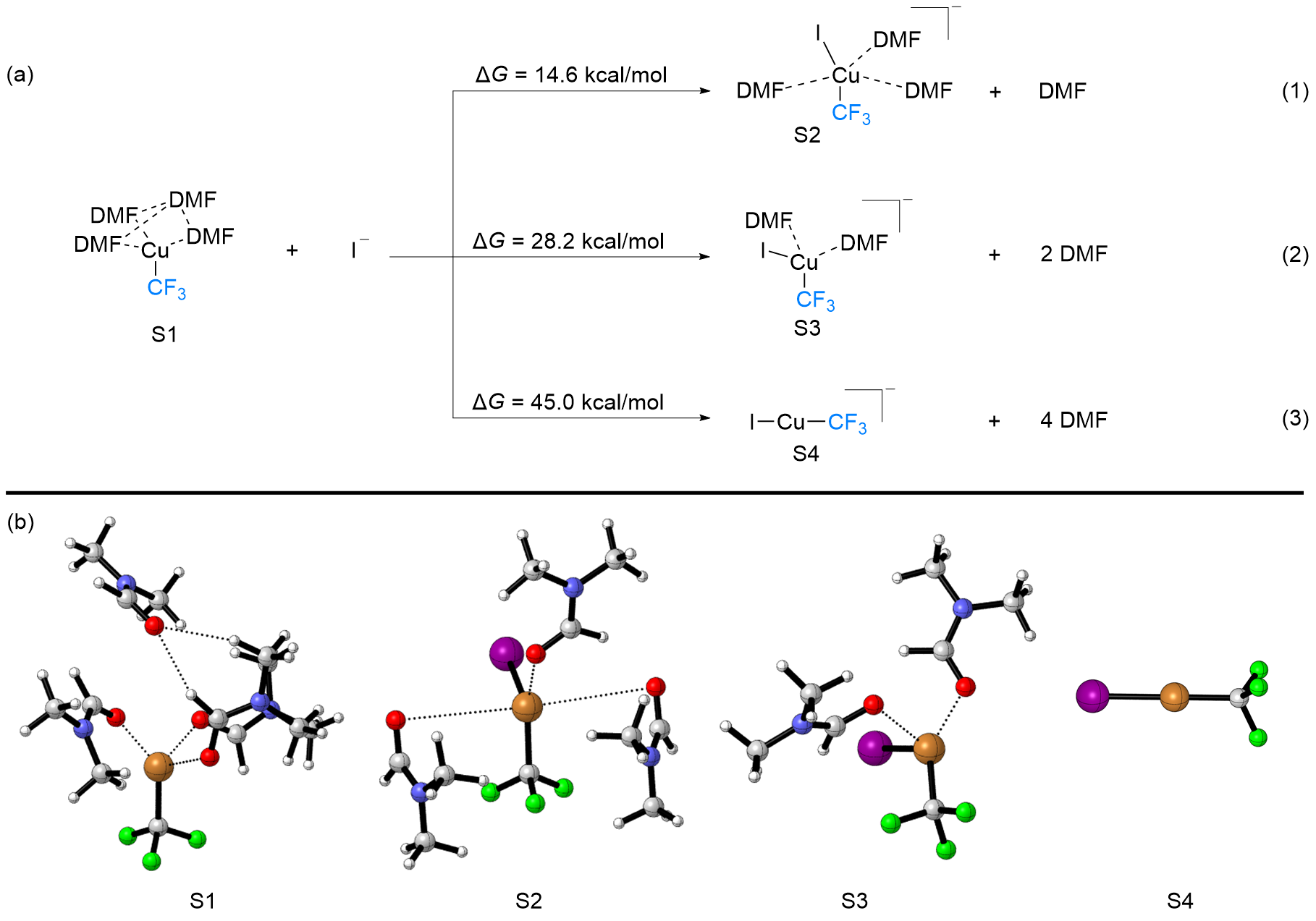
FSO2CF2CO2Me (MFSDA)是陈庆云院士课题组于1989年开发的一种十分有效的三氟甲基化试剂, 在学术界和工业界有着广泛地应用, 是我国有机氟化学领域早期最重要的研究成果之一, 该试剂也被命名为“陈试剂”. 此研究采用密度泛函理论(DFT)方法研究了碘化亚铜介导“陈试剂”形成三氟甲基亚铜的反应机理. 计算结果揭示了反应中碘化亚铜催化剂的双重作用: 一方面碘负离子通过进攻“陈试剂”中具有亲电性的甲基启动反应; 另一方面一价铜阳离子络合物捕获原位生成二氟卡宾形成二氟卡宾亚铜中间体. 发现与过去普遍假设的机理不同, (1)关键的脱羧过程并不需要一价铜阳离子参与, (2)三氟甲基是通过二氟卡宾亚铜中间体与氟离子络合后形成, 而非二氟卡宾直接捕获氟离子. 研究结果丰富了对“陈试剂”形成三氟甲基源的认识, 为进一步开发基于“陈试剂”的新反应提供了理论依据.
黄广龙, 薛小松. “陈试剂”作为三氟甲基源机理的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 132-137.
Guanglong Huang, Xiao-Song Xue. Computational Study on the Mechanism of Chen’s Reagent as Trifluoromethyl Source[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 132-137.



| [1] |
(a) Chen, Q.-Y.; Zhu, S. Z. Sci. China Chem. B 1986, 6, 561. (in Chinese)
|
|
(陈庆云, 朱仕正, 中国科学(B辑), 1986, 6, 561.)
|
|
|
(b) Chen, Q.-Y.; Wu, S.-W. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1989, 705.
|
|
| [2] |
(a) Jiang, X. K. Acta Chim. Sinica 1957, 5, 330. (in Chinese)
|
|
(蔣錫夔, 化学学报, 1957, 5, 330.)
|
|
|
(b) Olah, G. A.; Iyer, P. S.; Prakash, G. K. S. Synthesis 1986, 513.
|
|
|
(c) England, D. C. US 2852554, 1958.
|
|
|
(d) England, D. C.; Dietrich, M. A.; Lindsey, R. V. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1960, 82, 6181.
doi: 10.1021/ja01508a051 |
|
|
(e) Dmitriev, M. A.; Sokol'skii, G. A.; Knunyants, I. L. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR, Div. Chem. Sci. 1960, 9, 792.
doi: 10.1007/BF01179175 |
|
|
(f) Dmitriev, M. A.; Sokol'skii, G. A.; Knunyants, I. L. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR, Div. Chem. Sci. 1960, 9, 966.
doi: 10.1007/BF00903970 |
|
|
(g) Zhao, G.; Wu, H.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Liu, C. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 50250.
doi: 10.1039/C6RA09011G |
|
|
(h) Zhang, C.-P.; Chen, Q.-Y; Guo, Y.; Xiao, J.-C.; Gu, Y.-C. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2014, 261, 28.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.11.010 |
|
| [3] |
Chen, Q.-Y.; Yang, G.-Y.; Wu, S.-W. J. Fluorine Chem. 1991, 55, 291.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-1139(00)82357-X |
| [4] |
Zhao, S.; Guo, Y.; Han, E.-J.; Luo, J.; Liu, H.-M.; Liu, C.; Xie, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M. Org. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 1143.
doi: 10.1039/C8QO00025E |
| [5] |
Chen, Q.-Y. J. Fluorine Chem. 1995, 72, 241.
doi: 10.1016/0022-1139(94)00414-B |
| [6] |
(a) Eusterwiemann, S.; Martinez, H.; Dolbier, W. R. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 5461.
doi: 10.1021/jo300876z pmid: 22612642 |
|
(b) Thomoson, C. S.; Martinez, H.; Dolbier, W. R. J. Fluorine Chem. 2013, 150, 53.
doi: 10.1016/j.jfluchem.2013.02.026 pmid: 22612642 |
|
|
(c) Yu, W.; Xu, X.-H.; Qing, F.-L. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 5130.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b02580 pmid: 22612642 |
|
|
(d) Zhao, G.; Wu, H.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Liu, C. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 50250.
doi: 10.1039/C6RA09011G pmid: 22612642 |
|
|
(e) Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Guo, Y.; Xiao, J.-C.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Liu, C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15432.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.48 pmid: 22612642 |
|
| [7] |
(a) Tomashenko, O. A.; Grushin, V. V. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 4475.
doi: 10.1021/cr1004293 pmid: 21456523 |
|
(b) Clarke, S. L.; McGlacken, G. P. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 1.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v22.1 pmid: 21456523 |
|
|
(c) Xie, Q.; Hu, J. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 202.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v38.2 pmid: 21456523 |
|
|
(d) Chen, Q. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 21, 805. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v21:7 pmid: 21456523 |
|
|
(陈庆云, 有机化学, 2001, 21, 805.)
pmid: 21456523 |
|
| [8] |
(a) Wiemers, D. M.; Burton, D. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 832.
doi: 10.1021/ja00264a043 pmid: 25222650 |
|
(b) Dubinina, G. G.; Furutachi, H.; Vicic, D. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8600.
doi: 10.1021/ja802946s pmid: 25222650 |
|
|
(c) Morimoto, H.; Tsubogo, T.; Litvinas, N. D.; Hartwig, J. F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3793.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v50.16 pmid: 25222650 |
|
|
(d) Litvinas, N. D.; Fier, P. S.; Hartwig, J. F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 536.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v51.2 pmid: 25222650 |
|
|
(e) Ni, C.; Hu, J. Synthesis 2014, 46, 842.
doi: 10.1055/s-00000084 pmid: 25222650 |
|
|
(f) Konovalov, A. I.; Lishchynskyi, A.; Grushin, V. V. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13410.
doi: 10.1021/ja507564p pmid: 25222650 |
|
|
(g) de Salinas, S. M.; Mudarra, Á. L.; Odena, C.; Belmonte, M. M.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; Maseras, F.; Pérez-Temprano, M. H. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 9390.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v25.40 pmid: 25222650 |
|
|
(h) Yu, W.; Ouyang, Y.; Xu, X.-H.; Qing, F.-L. Chin. J. Chem. 2018, 36, 1024.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v36.11 pmid: 25222650 |
|
|
(i) Zhang, W.; Lin, J.-H.; Wu, W.; Cao, Y.-C.; Xiao, J.-C. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 169.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v38.2 pmid: 25222650 |
|
| [9] |
Frisch, M. J.; Trucks, G. W.; Schlegel, H. B.; Scuseria, G. E.; Robb, M. A.; Cheeseman, J. R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G. A.; Nakatsuji, H.; Li, X.; Caricato, M.; Marenich, A. V.; Bloino, J.; Janesko, B. G.; Gomperts, R.; Mennucci, B.; Hratchian, H. P.; Ortiz, J. V.; Izmaylov, A. F.; Sonnenberg, J. L.; Williams-Young, D.; Ding, F.; Lipparini, F.; Egidi, F.; Goings, J.; Peng, B.; Petrone, A.; Henderson, T.; Ranasinghe, D.; Zakrzewski, V. G.; Gao, J.; Rega, N.; Zheng, G.; Liang, W.; Hada, M.; Ehara, M.; Toyota, K.; Fukuda, R.; Hasegawa, J.; Ishida, M.; Nakajima, T.; Honda, Y.; Kitao, O.; Nakai, H.; Vreven, T.; Throssell, K.; Montgomery Jr., J. A.; Peralta, J. E.; Ogliaro, F.; Bearpark, M. J.; Heyd, J. J.; Brothers, E. N.; Kudin, K. N.; Staroverov, V. N.; Keith, T. A.; Kobayashi, R.; Normand, J.; Raghavachari, K.; Rendell, A. P.; Burant, J. C.; Iyengar, S. S.; Tomasi, J.; Cossi, M.; Millam, J. M.; Klene, M.; Adamo, C.; Cammi, R.; Ochterski, J. W.; Martin, R. L.; Morokuma, K.; Farkas, O.; Foresman, J. B.; Fox, D. J. Gaussian 16, Revision A.03, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, 2016.
|
| [10] |
Marenich, A. V.; Cramer, C. J.; Truhlar, D. G. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378.
doi: 10.1021/jp810292n |
| [11] |
(a) Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D. G. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 194101.
doi: 10.1063/1.2370993 pmid: 16405344 |
|
(b) Quintal, M. M.; Karton, A.; Iron, M. A.; Boese, A. D.; Martin, J. M. L. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 709.
pmid: 16405344 |
|
| [12] |
Weigend, F.; Ahlrichs, R. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297.
doi: 10.1039/b508541a |
| [13] |
Chai, J.-D.; Head-Gordon, M. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 6615.
doi: 10.1039/b810189b |
| [14] |
Weigend, F. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 1057.
doi: 10.1039/b515623h |
| [15] |
Funes-Ardoiz, I.; Paton, R. S., GoodVibes v2. 0.2, 2016, (http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.595246).
|
| [16] |
Legault, C. Y., CYLview, 1.0b, Université de Sherbrooke, 2009. (http://www.cylview.org).
|
| [1] | 付信朴, 王秀玲, 王伟伟, 司锐, 贾春江. 团簇Au/CeO2的制备及其催化CO氧化反应构效关系的研究★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 874-883. |
| [2] | 崔国庆, 胡溢玚, 娄颖洁, 周明霞, 李宇明, 王雅君, 姜桂元, 徐春明. CO2加氢制醇类催化剂的设计制备及性能研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 1081-1100. |
| [3] | 王珞聪, 李哲伟, 岳彩巍, 张培焕, 雷鸣, 蒲敏. 电场下偶氮苯衍生物分子顺反异构化反应机理的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 781-787. |
| [4] | 杨思明, 刘爱荣, 刘静, 刘钊丽, 张伟贤. 硫化纳米零价铁研究进展: 合成、性质及环境应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(11): 1536-1554. |
| [5] | 滑熠龙, 李冬涵, 顾天航, 王伟, 李若繁, 杨建平, 张伟贤. 纳米零价铁富集水溶液中铀的表面化学及应用展望[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(8): 1008-1022. |
| [6] | 黄荣谊, 沈琼, 张超, 张少勇, 徐衡. 过渡金属催化有机腈和叠氮酸钠反应机理的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(6): 565-571. |
| [7] | 李曼, 康会英, 薛小松, 程津培. 常见三氟甲基源释放三氟甲基自由基能力的理论计算研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(12): 988-996. |
| [8] | 武卫荣, 员晓敏, 侯华, 王宝山. 两种七氟醚自由基[(CF3)2C(·)OCH2F,(CF3)2CHOC(·)HF]与氧气反应及OH·再生机理的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(10): 793-801. |
| [9] | 母伟花, 马瑶, 方德彩, 王蓉, 张海娜. 1-碘-2-锂-邻碳硼烷与环戊二烯衍生物的类Diels-Alder反应的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(1): 55-61. |
| [10] | 黄潇月, 王伟, 凌岚, 张伟贤. 纳米零价铁与重金属的反应:“核-壳”结构在重金属去除中的作用[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(6): 529-537. |
| [11] | 丁爽, 葛庆峰, 祝新利. 金属氧化物催化生物质衍生羧酸酮基化研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(5): 439-447. |
| [12] | 杨镇, 薛一江, 何远航. CL20/DNB共晶的热感度分子动力学研究[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(7): 612-619. |
| [13] | 杨一诺, 张琪, 石景, 傅尧. Mn(I)催化亚胺和炔烃脱氢偶联反应的机理研究[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(5): 422-428. |
| [14] | 马军, 李榕, 任馗玮, 马禧龙, 朱开礼, 耿志远. 两态反应Ni2+与c-C6H12的机理及自旋-轨道耦合研究[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(5): 431-440. |
| [15] | 王瀛, 张丽敏, 胡天军. 金属空气电池阴极氧还原催化剂研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(4): 316-325. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||