化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (2): 116-123.DOI: 10.6023/A22110464 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2022-11-16
发布日期:2022-12-13
通讯作者:
邵正中
基金资助:
Xueyang Yin, Kai Gu, Zhengzhong Shao( )
)
Received:2022-11-16
Published:2022-12-13
Contact:
Zhengzhong Shao
Supported by:文章分享
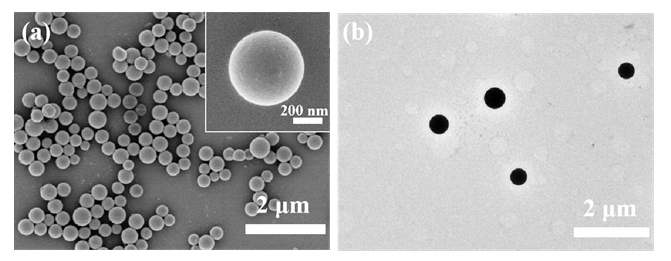
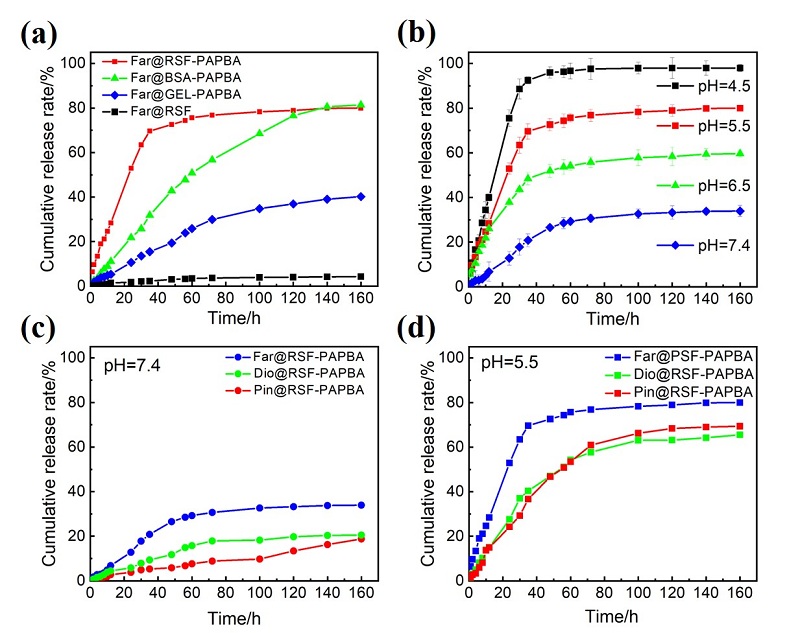
蛋白质纳米颗粒具有良好的生物相容性和生物降解性, 易于进行额外的表面修饰, 用作药物输送系统提高了生物利用度, 减少了药物分子的毒副作用. 本工作在利用苯硼酸基团与再生桑蚕丝蛋白(RSF)上相关侧基之间具有路易斯酸-碱配对反应的基础上, 通过3-丙烯酰胺苯硼酸(APBA)在RSF水溶液中原位聚合, 使RSF分子链重排形成微球并在表面负载抗炎中药, 制备了载药丝蛋白/聚苯硼酸纳米微球. 此尺寸分布均匀的微球直径约为550~600 nm, 表面光滑且在水中的分散性能良好; 对乔松素、杜鹃素和地奥司明三种药物的负载率分别为7.8%, 11.9%和13.4%, 包封率分别为75.0%, 89.1%和93.7%. 载药微球控制释放约7 d, 且缓释行为具有pH响应性. 丝蛋白/聚苯硼酸纳米微球与主体药物协同作用提高了自由基清除速度和清除效率, 优于直接给药组. 与此同时, 将RSF改换为牛血清白蛋白或明胶蛋白, 采用此方法也能制成尺寸分别为260和100 nm的白蛋白/聚苯硼酸微球或明胶蛋白/聚苯硼酸微球. 由此, 三种不同尺寸、电性和药物释放速率的蛋白质/聚苯硼酸纳米微球有望适应多种静脉注射和皮下或腹腔注射药物传输的需求.
殷雪旸, 顾恺, 邵正中. 载药蛋白质/聚苯硼酸复合纳米微球制备及其释药性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 116-123.
Xueyang Yin, Kai Gu, Zhengzhong Shao. Preparation of the Protein/Polyphenylboronic Acid Nanospheres for Drug Loading and Unloading[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(2): 116-123.
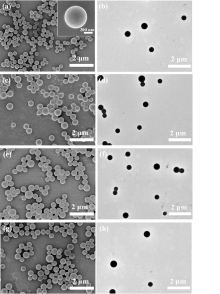

| Sample | Hydrodynamic diameter/nm | PDI | Zeta potential/mV |
|---|---|---|---|
| RSF-PAPBA | 540 | 0.04 | –23.0 |
| Pin@RSF-PAPBA | 590 | 0.06 | –31.0 |
| Far@RSF-PAPBA | 560 | 0.09 | –32.5 |
| Dio@RSF-PAPBA | 570 | 0.07 | –30.2 |
| RSF | 540 | 0.12 | –23.3 |
| Far@RSF | 290 | 0.18 | –34.4 |
| Sample | Hydrodynamic diameter/nm | PDI | Zeta potential/mV |
|---|---|---|---|
| RSF-PAPBA | 540 | 0.04 | –23.0 |
| Pin@RSF-PAPBA | 590 | 0.06 | –31.0 |
| Far@RSF-PAPBA | 560 | 0.09 | –32.5 |
| Dio@RSF-PAPBA | 570 | 0.07 | –30.2 |
| RSF | 540 | 0.12 | –23.3 |
| Far@RSF | 290 | 0.18 | –34.4 |
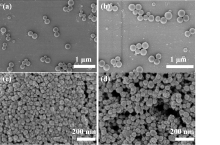

| Sample | Hydrodynamic diameter/nm | PDI | Zeta potential/mV |
|---|---|---|---|
| BSA-PAPBA | 260 | 0.05 | –24.2 |
| Far@BSA-PAPBA | 290 | 0.09 | –46.2 |
| GEL-PAPBA | 170 | 0.04 | +21.5 |
| Far@GEL-PAPBA | 180 | 0.06 | +14.3 |
| Sample | Hydrodynamic diameter/nm | PDI | Zeta potential/mV |
|---|---|---|---|
| BSA-PAPBA | 260 | 0.05 | –24.2 |
| Far@BSA-PAPBA | 290 | 0.09 | –46.2 |
| GEL-PAPBA | 170 | 0.04 | +21.5 |
| Far@GEL-PAPBA | 180 | 0.06 | +14.3 |


| [1] |
Pahwa, R.; Goyal, A.; Jialal, I. Chronic Inflammation. Vol. 1, Ed.: Bansal, P., StatPearls, Petersburg, 2020, p. 7.
|
| [2] |
Luo, W. X.; Wen, G.; Yang, L.; Tang, J.; Wang, J. G.; Wang, J. H.; Zhang, S. Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, F.; Xiao, L. L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Theranostics. 2017, 7, 452.
doi: 10.7150/thno.16677 |
| [3] |
Kamimura, M.; Furukawa, T.; Akiyama, S.; Nagasaki, Y. Biomater. Sci. 2013, 1, 361.
doi: 10.1039/c2bm00156j |
| [4] |
Davis, M. E.; Brewster, M. E. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 1023.
doi: 10.1038/nrd1576 pmid: 15573101 |
| [5] |
Lee, C. C.; MacKay, J. A.; Frechet, J. M. J.; Szoka, F. C. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1517.
doi: 10.1038/nbt1171 |
| [6] |
Serajuddin, A. T. M. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2007, 59, 603.
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2007.05.010 pmid: 17619064 |
| [7] |
Akers, M. J. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 2283.
doi: 10.1002/jps.10154 |
| [8] |
Gregoriadis, G.; Wills, E. J.; Swain, C. P.; Tavill, A. S. Lancet. 1974, 303, 1313.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(74)90682-5 |
| [9] |
Juliano, R. L. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1976, 9, 21.
pmid: 1030801 |
| [10] |
Kobayashi, H.; Turkbey, B.; Watanabe, R.; Choyke, P. L. Bioconjugate Chem. 2014, 25, 2093.
doi: 10.1021/bc500481x pmid: 25385142 |
| [11] |
Mitchell, M. J.; Jain, R. K.; Langer, R. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2017, 17, 659.
doi: 10.1038/nrc.2017.83 pmid: 29026204 |
| [12] |
Zheng, P.; Yang, L.; Chen, J. J.; Xu, W. G.; Li, G.; Ding, J. X. Chinese Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1178.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2019.12.001 |
| [13] |
Kosheli, T. M.; George, F. B.; Li, X. T.; Chen, Z. J.; He, W. Chinese Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 587.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2021.08.020 |
| [14] |
Saha, A.; Pradhan, N.; Chatterjee, S.; Singh, R. K.; Trivedi, V.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Manna, D. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 3671.
doi: 10.1021/acsanm.9b00607 |
| [15] |
Xie, M.; Fan, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; He, X.; Li, G.; Lan, P. Biomaterials. 2016, 103, 33.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.06.049 |
| [16] |
Wang, S.; Xu, T.; Yang, Y.; Shao, Z. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2015, 7, 21254.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b05335 |
| [17] |
Shao, Z. Z.; Vollrath, F. Nature. 2002, 418, 741.
doi: 10.1038/418741a |
| [18] |
Wu, M.; Yang, W.; Chen, S.; Yao, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2018, 6, 1179.
doi: 10.1039/C7TB03113K |
| [19] |
Sun, N.; Lei, R.; Xu, J. H.; Kundu, S. C.; Cai, Y. R.; Yao, J. M.; Ni, Q. Q. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 3319.
doi: 10.1007/s10853-018-3022-9 |
| [20] |
Yang, W. H.; Yu, S. Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y. Z.; Shao, Z. Z.; Chen, X. Acta Chim. Sinica. 2014, 72, 1164. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A14080596 |
|
(杨文华, 俞淑英, 陈胜, 刘也卓, 邵正中, 陈新, 化学学报, 2014, 72, 1164.)
doi: 10.6023/A14080596 |
|
| [21] |
Wang, S. H.; Sun, L. N.; Cao, H.; Zhong, Y. M.; Shao, Z. Z. Acta Chim. Sinica. 2021, 79, 1023. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21050203 |
|
(王苏杭, 孙灵娜, 曹涵, 钟一鸣, 邵正中, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1023.)
doi: 10.6023/A21050203 |
|
| [22] |
Huang, H.; Yang, D. P.; Liu, M. H.; Wang, X. S.; Zhang, Z. Y.; Zhou, G. D.; Liu, W.; Cao, Y. L.; Zhang, W. J.; Wang, X. S. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2829.
doi: 10.2147/IJN.S128270 pmid: 28435261 |
| [23] |
Lu, H. X.; Noorani, L.; Jiang, Y. Y.; Du, A. W.; Stenzel, M. H. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2017, 5, 9591.
doi: 10.1039/C7TB02902K |
| [24] |
Yu, Z.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Z. B. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 343.
doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-9-343 pmid: 25114637 |
| [25] |
Azimi, B.; Nourpanah, P.; Rabiee, M.; Arbab, S. Iran Biomed. J. 2014, 18, 34.
|
| [26] |
Sahoo, N.; Sahoo, R. K.; Biswas, N.; Guha, A.; Kuotsu, K. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 317.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.08.006 |
| [27] |
Kulkarni, S. A.; Feng, S. S. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 2512.
doi: 10.1007/s11095-012-0958-3 |
| [28] |
Lee, B. R.; Ko, H. K.; Ryu, J. H.; Ahn, K. Y.; Lee, Y. H.; Oh, S. J.; Na, J. H.; Kim, T. W.; Byun, Y.; Kwon, I. C.; Kim, K.; Lee, J. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35182.
doi: 10.1038/srep35182 |
| [29] |
Ci, X.; Chu, X.; Wei, M.; Yang, X.; Cai, Q.; Deng, X. PLoS One. 2012, 7, e34634.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034634 |
| [30] |
Fattori, V.; Rasquel-Oliveira, F. S.; Artero, N. A.; Ferraz, C. R.; Borghi, S. M.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W. A. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1018.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b00887 pmid: 32083866 |
| [31] |
Stephan, D. W. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 306.
doi: 10.1021/ar500375j |
| [32] |
Chen, H.; Shao, Z. Z. Acta Polym. Sinica. 2018, 62, 987. (in Chinese)
|
|
(陈红, 邵正中, 高分子学报, 2018, 62, 987.)
|
|
| [33] |
Chen, W.; Zhen, X.; Wu, W. Sci. China Chem. 2020, 63, 648.
doi: 10.1007/s11426-019-9699-3 |
| [34] |
Wang, L. J.; Sheng, X. L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. H. Chinese J. Org. Chem. 2021, 41, 567. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202006060 |
|
(王李娟, 盛显良, 王杰, 张玉辉, 有机化学, 2021, 41, 567.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202006060 |
|
| [35] |
Cabral, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Mizuno, K.; Chen, Q.; Murakami, M.; Kimura, M.; Kataoka, K. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 815.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.166 pmid: 22020122 |
| [36] |
Jiang, W.; Kim, B. Y.; Rutka, J. T.; Chan, W. C. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 145.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2008.30 pmid: 18654486 |
| [37] |
Reddy, S. T.; Van Der Vlies, A. J.; Simeoni, E.; Angeli, V.; Randolph, G. J.; O'Neil, C. P.; Hubbell, J. A. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1159.
doi: 10.1038/nbt1332 pmid: 17873867 |
| [38] |
Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Su, H.; Chen, K. J.; Armijo, A. L.; Lin, W. Y.; Tseng, H. R. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4344.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200900063 pmid: 19425037 |
| [39] |
Goodman, T. T.; Olive, P. L.; Pun, S. H. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 265.
|
| [40] |
Tang, L.; Yang, X.; Dobrucki, L. W.; Chaudhury, I.; Yin, Q.; Yao, C.; Cheng, J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12721.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201205271 pmid: 23136130 |
| [41] |
Tang, L.; Yang, X.; Yin, Q.; Cai, K.; Wang, H.; Chaudhury, I.; Yao, C.; Zhou, Q.; Kwon, M.; Hartman, J. A.; Dobrucki, I. T.; Dobrucki, L. W.; Borst, L. B.; Lezmi, S.; Helferich, W. G.; Ferguson, A. L.; Fan, T. M.; Cheng, J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014, 111, 15344.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411499111 |
| [42] |
Tan, H. Y.; Wang, N.; Li, S.; Hong, M.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 279, 5090.
|
| [43] |
Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Oncotarget. 2018, 9, 7204.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23208 |
| [44] |
Matsumoto, A.; Sato, N.; Kataoka, K.; Miyahara, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 12022.
doi: 10.1021/ja902964m pmid: 19663494 |
| [45] |
Wang, J.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Qian, H.; Liu, B.; Jiang, X. Biomaterials. 2014, 35, 866.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.10.028 |
| [46] |
Wang, H.; Wang, K.; Sun, J.; Fang, G. Q.; Yao, Q. Q.; Wu, Z. Y. Chinese J. Org. Chem. 2018, 38, 1035. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201709037 |
|
(王浩, 王凯, 孙捷, 方桂迁, 姚庆强, 吴忠玉, 有机化学, 2018, 38, 1035.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201709037 |
|
| [47] |
Cao, Z. B.; Chen, X.; Yao, J. R.; Huang, L.; Shao, Z. Z. Soft Matter. 2007, 3, 910.
doi: 10.1039/b703139d |
| [1] | 曾如馨, 陈鹏. RNA结合蛋白的组学解析与功能探索★[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(1): 53-61. |
| [2] | 马超凡, 徐伟, 刘巍, 徐昌晖, 沙菁㛃. 受限纳尺度下蛋白质输运的主动操纵技术[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 857-868. |
| [3] | 张娜娜, 于恺然, 李际婷, 张嘉宁, 刘宇博. 化学生物学解析疾病中O-GlcNAc糖基化功能: 研究工具与策略[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 843-856. |
| [4] | 高至亮, 李梦琦, 郝京诚, 崔基炜. 胶体粒子的机械性能调控及其在药物递送中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 1010-1020. |
| [5] | 陈玉宛, 周雯, 李欣蔚, 杨开广, 梁振, 张丽华, 张玉奎. 基于液质联用技术的蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用研究进展※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 817-826. |
| [6] | 付浩浩, 陈淏川, 张宏, 邵学广, 蔡文生. 基于几何约束的蛋白质-配体准确结合自由能计算[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 472-480. |
| [7] | 贺晖, 周玲俐, 刘震. 基于分子印迹与表面增强拉曼散射的蛋白质疾病标志物检测研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(1): 45-57. |
| [8] | 汪泽, 黄漪铃, 任娟, 陈相峰, 陈德华. 电子捕获裂解质谱研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(2): 130-142. |
| [9] | 周怡青, 肖友利. 活性天然产物靶标蛋白的鉴定[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(3): 177-189. |
| [10] | 张留伟, 钱明, 王静云. 光控释药型药物递送系统的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(8): 770-782. |
| [11] | 王杰, 陈鹏. 生物正交剪切反应及其应用[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(12): 1173-1182. |
| [12] | 王鑫, 谭丽丽, 杨英威. 金粒子包封介孔二氧化硅杂化载药控释体系[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(4): 303-311. |
| [13] | 杜方凯, 徐江生, 曾钫, 吴水珠. 基于碳点多功能纳米载药体系的制备及pH响应释药性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(3): 241-250. |
| [14] | 王建山, 夏红军, 万广平, 刘家玮, 金丽花, 白泉. 在线单柱二维液相色谱法对蛋清中三种活性蛋白的快速分离纯化[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(3): 265-270. |
| [15] | 杨麦云, 陈鹏. 生物正交标记反应研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(8): 783-792. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||