Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (11): 1320-1330.DOI: 10.6023/A21080377 Previous Articles Next Articles
Review
投稿日期:2021-08-12
发布日期:2021-09-24
通讯作者:
王晓艳
作者简介: |
李勇, 中国科学院上海有机化学研究所2018级硕士研究生. 2018年本科毕业于中南大学. 目前研究方向为新型烯烃配位聚合催化剂的设计合成. |
 |
王晓艳, 中国科学院上海有机化学研究所副研究员. 2010年本科毕业于东北林业大学. 2015年在中国科学院长春应用化学研究所取得博士学位. 随后在中国科学院上海有机化学研究所金属有机化学实验室/南开大学化学系进行博士后的研究工作. 2017年正式加入上海有机化学研究所金属有机化学国家重点实验室, 开展新型过渡金属催化剂、“活性”自由基聚合及可控烯烃配位聚合等方面的研究. |
 |
唐勇, 中国科学院上海有机化学研究所研究员. 1986年本科毕业于四川师范学院; 1992年和1996年先后在中国科学院上海有机化学研究所获得硕士和博士学位. 1996年至1999年先后在美国科罗拉多州立大学和美国乔治城大学从事博士后研究; 1999年5月入职上海有机化学研究所, 2000年1月, 担任上海有机化学研究所“百人计划”项目研究员, 2015年当选中国科学院院士. 主要从事金属有机化学研究, 包括: 不对称催化, 烯烃聚合催化剂的设计、合成与应用, 叶立德化学以及天然产物全合成等. |
基金资助:
Yong Li, Xiao-Yan Wang( ), Yong Tang
), Yong Tang
Received:2021-08-12
Published:2021-09-24
Contact:
Xiao-Yan Wang
Supported by:Share
Yong Li, Xiao-Yan Wang, Yong Tang. Coordination Polymerization of α,ω-Diolefin: the Regulation of Polymer Microstructure by Catalyst[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(11): 1320-1330.
| Run | Cat. (μmol) | OD/ hexane/mL | Yield/ mg | Act.b | Mn/ ×104 | Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 (0.3) | 15.0/— | 160 | 1.6 | 76.3 | 1.86 |
| 2 | 1 (0.3) | 15.0/— | 160 | 1.6 | 66.4 | 1.89 |
| 3 | 1 (0.1) | 15.0/— | 120 | 3.6 | 81.1 | 1.63 |
| 4 | 1 (0.1) | 10.0/5.0 | 104 | 3.1 | 61.2 | 1.66 |
| 5 | 1 (1.0) | 7.5/7.5 | 227 | 6.8 | 37.8 | 2.00 |
| 6 | 1 (0.1) | 7.5/7.5 | 66.4 | 2.0 | 46.5 | 1.69 |
| 7 | 1 (1.0) | 5.0/10.0 | 79 | 2.4 | 17.4 | 1.89 |
| 8 | 2 (0.1) | 15.0/— | 39.0 | 1.2 | 65.1 | 1.70 |
| 9 | 2 (0.1) | 15.0/— | 39.0 | 1.2 | 65.6 | 1.76 |
| Run | Cat. (μmol) | OD/ hexane/mL | Yield/ mg | Act.b | Mn/ ×104 | Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 (0.3) | 15.0/— | 160 | 1.6 | 76.3 | 1.86 |
| 2 | 1 (0.3) | 15.0/— | 160 | 1.6 | 66.4 | 1.89 |
| 3 | 1 (0.1) | 15.0/— | 120 | 3.6 | 81.1 | 1.63 |
| 4 | 1 (0.1) | 10.0/5.0 | 104 | 3.1 | 61.2 | 1.66 |
| 5 | 1 (1.0) | 7.5/7.5 | 227 | 6.8 | 37.8 | 2.00 |
| 6 | 1 (0.1) | 7.5/7.5 | 66.4 | 2.0 | 46.5 | 1.69 |
| 7 | 1 (1.0) | 5.0/10.0 | 79 | 2.4 | 17.4 | 1.89 |
| 8 | 2 (0.1) | 15.0/— | 39.0 | 1.2 | 65.1 | 1.70 |
| 9 | 2 (0.1) | 15.0/— | 39.0 | 1.2 | 65.6 | 1.76 |

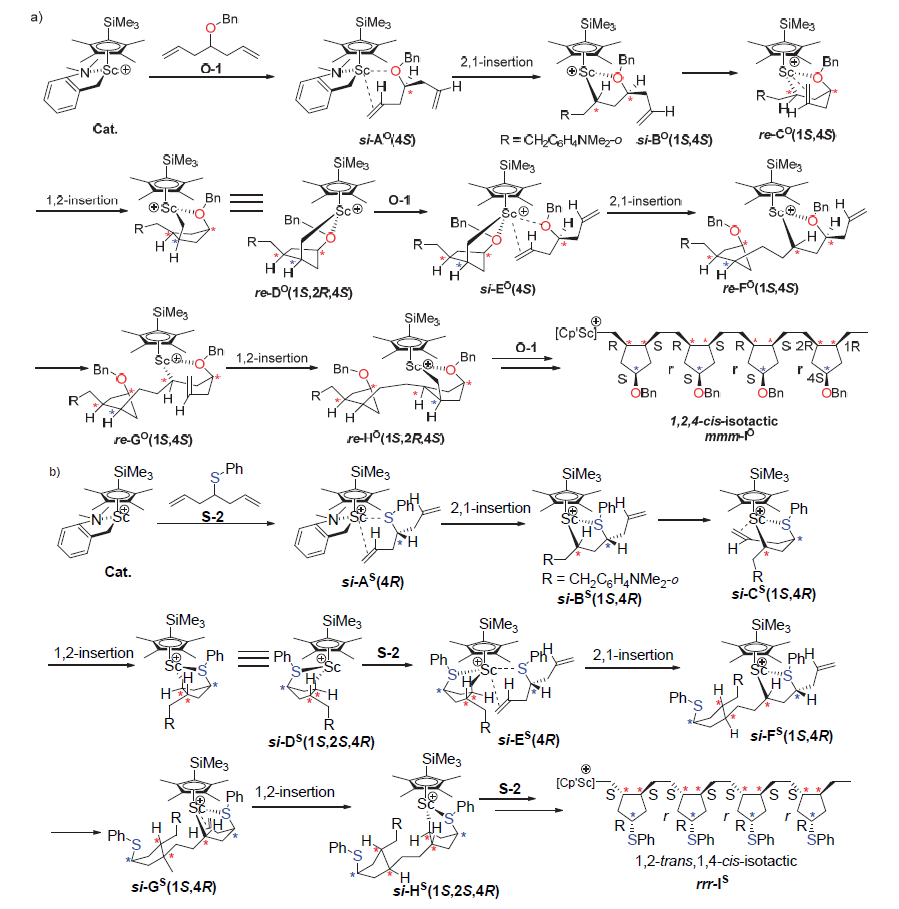
| [1] |
(a) Ziegler K.; Breil H.; Holzkamp E.; Martin H. DE 973626, 1953.
|
|
(b) Natta G.; Mitarbb U. Angew. Chem. 1955, 67, 431.
|
|
| [2] |
Marvel C. S.; Stille J. K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1740.
doi: 10.1021/ja01540a059 |
| [3] |
Pasini D.; Takeuchi D. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 8983.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00286 pmid: 30146875 |
| [4] |
Makowski H. S.; Shim K. C.; Wilshinsky Z. W. J. Polym. Sci., Part A 1964, 2, 1549.
|
| [5] |
Cheng N.; Khasat N. P. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1988, 35, 825.
doi: 10.1002/app.1988.070350321 |
| [6] |
Boor J.,Jr. Ziegler-Natta Catalysts and Polymerizations, Academic Press, New York, 1979, Chapter 13.
|
| [7] |
Marvel C. S.; Garrison Jr. W. E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1959, 81, 4737.
doi: 10.1021/ja01526a072 |
| [8] |
Resconi L.; Waymouth R. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 4953.
doi: 10.1021/ja00168a048 |
| [9] |
Cavallo L.; Guerra G.; Corradini P.; Resconi L.; Waymouth R. M. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 260.
doi: 10.1021/ma00054a003 |
| [10] |
Coates G. W.; Waymouth R. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 6270.
doi: 10.1021/ja00016a053 |
| [11] |
Coates G. W.; Waymouth R. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 91.
doi: 10.1021/ja00054a014 |
| [12] |
Jayaratne K. C.; Keaton R. J.; Henningsen D. A.; Sita L. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 10490.
doi: 10.1021/ja002558c |
| [13] |
Crawford K. E.; Sita L. R. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 506.
doi: 10.1021/mz500126r |
| [14] |
Hustad P. D.; Coates G. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 11578.
doi: 10.1021/ja0273748 |
| [15] |
Nomura K.; Liu J. Y.; Fujiki M.; Takemoto A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 14170.
doi: 10.1021/ja076633w |
| [16] |
Edson J. B.; Coates G. W. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30, 1900.
doi: 10.1002/marc.200900422 |
| [17] |
Shi X. C.; Wang Y. X.; Liu J. Y.; Cui D. M.; Men Y. F.; Li Y. S. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 1062.
doi: 10.1021/ma1023268 |
| [18] |
Shi X. C.; Tang X. Y.; Li Y. S. Polymer 2011, 52, 3053.
doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2011.04.058 |
| [19] |
Wang B.; Wang Y. X.; Cui J.; Long Y. Y.; Li Y. G.; Yuan X. Y.; Li Y. S. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 6627.
doi: 10.1021/ma501460f |
| [20] |
Park S.; Takeuchi D.; Osakada K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3510.
doi: 10.1021/ja058408p |
| [21] |
Takeuchi D.; Fukuda Y.; Park S.; Osakada K. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 5909.
doi: 10.1021/ma901069q |
| [22] |
Meinhard D.; Wegner M.; Kipiani G.; Hearly A.; Reuter P.; Fischer S.; Marti O.; Rieger B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9182.
pmid: 17602476 |
| [23] |
Takeuchi D.; Matsuura R.; Park S.; Osakada K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7002.
pmid: 17497787 |
| [24] |
Miyamura Y.; Kinbara K.; Yamamoto Y.; Praveen V. K.; Kato K.; Takata M.; Takano A.; Matsushita Y.; Lee E.; Lee M.; Aida T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 3292.
doi: 10.1021/ja910901e pmid: 20178364 |
| [25] |
Jian Z.; Baier M. C.; Mecking S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2836.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b00179 |
| [26] |
Jian Z.; Mecking S. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 15845.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v54.52 |
| [27] |
Jian Z.; Mecking S. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 4395.
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.6b00983 |
| [28] |
Schaverien C. J. Organometallics 1994, 13, 69.
doi: 10.1021/om00013a017 |
| [29] |
Guo F.; Nishiura M.; Koshino H.; Hou Z. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 2400.
doi: 10.1021/ma200441w |
| [30] |
Wang H. B.; Zhao Y. N.; Nishiura M.; Yang Y.; Luo G.; Luo Y.; Hou Z. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 12624.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b04275 |
| [1] | Yaning Li, Xiaoyan Wang, Yong Tang. The Regulation of Stereoselectivity in Radical Polymerization★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 213-225. |
| [2] | Xinpu Fu, Xiuling Wang, Weiwei Wang, Rui Si, Chunjiang Jia. Fabrication and Mechanism Study of Clustered Au/CeO2 Catalyst for the CO Oxidation Reaction★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(8): 874-883. |
| [3] | Jianchuan Liu, Cuiyan Li, Yaozu Liu, Yujie Wang, Qianrong Fang. Highly-Stable Two-Dimensional Bicarbazole-based sp2-Carbon-conjugated Covalent Organic Framework for Efficient Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(8): 884-890. |
| [4] | Guoqing Cui, Yiyang Hu, Yingjie Lou, Mingxia Zhou, Yuming Li, Yajun Wang, Guiyuan Jiang, Chunming Xu. Research Progress on the Design, Preparation and Properties of Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Alcohols [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(8): 1081-1100. |
| [5] | Tiancheng Zhao, Hongyu Jiang, Kun Zhang, Yifan Xu, Xinyue Kang, Jiancheng Xu, Xufeng Zhou, Peining Chen, Huisheng Peng. Continuous Preparation of High-performing Carbon Nanotube Fibers Based on Cycloalkane/ethanol Mixing Carbon Source [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 565-571. |
| [6] | Zihao Wang, Min Chen, Changle Chen. Catalytic Synthesis of Polyolefin Elastomer Using Unsymmetrical α-Diimine Nickel Catalyst★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 559-564. |
| [7] | Liu Lujie, Zhang Jian, Wang Liang, Xiao Fengshou. Heterogeneous Catalysts for Selective Hydrogenolysis of Biomass-derived Polyols★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(5): 533-547. |
| [8] | Bin Xu, Xiuzhi Wei, Jiangmin Sun, Jianguo Liu, Longlong Ma. In-situ Synthesis of Nitrogen-doped Graphene Layer Encapsulated Palladium Nanoparticles for Highly Selective Hydrogenation of Vanillin [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(3): 239-245. |
| [9] | Jian Liu, Jinhua Ou, Zeping Li, jingyi Jiang, Rongtao Liang, Wenjie Zhang, kaijian Liu, Yu Han. Efficient Catalytic Hydrogenation of Nitroaromatic Using Cobalt Single-atom Derived from Metal-organic Framework [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(12): 1701-1707. |
| [10] | Guan-Wen Yang, Guang-Peng Wu. Modular Bifunctional Organoboron-ammonium/phosphonium Catalysts: Design and Catalytic Performance★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(11): 1551-1565. |
| [11] | Jinjing Liu, Na Yang, Li Li, Zidong Wei. Theoretical Study on the Regulation of Oxygen Reduction Mechanism by Modulating the Spatial Structure of Active Sites on Platinum★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(11): 1478-1485. |
| [12] | Bo Li, Haiyan Zhou, Haiyan Ma, Jiling Huang. Synthesis of Ethylene-Bridged Bis(indenyl) Zirconium, Hafnium Complexes and Their Catalytic Behavior on Selective Propylene Oligomerization: the Effect of 3-Substituent on Indenyl Ring [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(10): 1280-1294. |
| [13] | Qingxin Wang, Yong Cui, Yunqi Li, Shanfu Lu, Yan Xiang. Effect of Controllable Pyrolysis of Ionomers in Fe-N-C Cathode Catalytic Layer on Cell Performance and Stability of Membrane Electrode Assembly★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(10): 1350-1356. |
| [14] | Zhiping Chen, Yongle Meng, Jing Lu, Wenwu Zhou, Zhiyuan Yang, Anning Zhou. Preparation of Fe@Si/S-34 Catalysts and Its Catalytic Performance for Syngas to Olefins [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(1): 14-19. |
| [15] | Zhaowei Tian, Weimin Da, Lei Wang, Yusen Yang, Min Wei. Structural Design and Research Progress of Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Preparation of Second Generation Biodiesel [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(9): 1322-1337. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||