化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (8): 986-998.DOI: 10.6023/A21040140 上一篇 下一篇
综述
李斌a, 于吉攀b, 刘康b, 吴群燕b, 刘琦a,*( ), 石伟群b,*(
), 石伟群b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2021-04-09
发布日期:2021-05-25
通讯作者:
刘琦, 石伟群
作者简介: |
李斌, 2019年6月毕业于郑州大学化学学院, 获理学学士学位; 2019年9月至今为哈尔滨工程大学和中国科学院高能物理研究所联合培养研究生. |
 |
于吉攀, 博士, 助理研究员. 2008年获江苏师范大学学士学位; 2011年获南开大学硕士学位; 2014年获清华大学博士学位; 2014.07~2016.07清华大学化学系博士后; 2016年7月加入中国科学院高能物理研究所核能放射化学实验室. 目前主要研究方向: 锕系元素化学. |
 |
刘康, 2016年6月毕业于湖北大学化学化工学院, 获理学学士学位; 2016年9月至今在中国科学院高能物理研究所攻读博士学位. |
 |
吴群燕, 博士, 副研究员. 2006年获曲阜师范大学硕士学位; 2010年获北京理工大学博士学位; 2010~2013清华大学化学系博士后; 2013年6月加入中国科学院高能物理研究所核能放射化学实验室, 主要从事与核能相关的锕系化学理论方面的研究工作. |
 |
刘琦, 博士, 副教授. 2007年获哈尔滨工程大学环境工程专业学士学位; 2009年获哈尔滨工程大学应用化学专业硕士学位; 2016年获哈尔滨工程大学材料学专业博士学位; 2009年6月进入哈尔滨工程大学材料科学与化学工程学院工作, 目前主要从事海水提铀吸附剂材料的设计研究. |
 |
石伟群, 研究员, 国家杰出青年科学基金获得者, 长期致力于核燃料循环化学与锕系元素化学相关基础研究, 在JACS、Angew. Chem、Chem、CCS Chem.、Nat. Commun、Adv. Mater.、Environ. Sci. Technol.等国际知名期刊发表SCI 论文200余篇, 成果被国内外同行广泛关注和引用, 文章总引7400余次, H因子44 (Google Scholar). 分别担任英文期刊《Journal of Nuclear Fuel Cycle and Waste Technology》和《Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology》的编委与国际顾问编委, 中文期刊《核化学与放射化学》编委. 现为中国化学会核化学与放射化学专业委员会委员、中国核学会锕系物理与化学分会常务理事、中国有色金属学会熔盐化学与技术专业委员会副主任委员、中国核学会核化工分会理事兼副秘书长. |
基金资助:
Bin Lia, Jipan Yub, Kang Liub, Qunyan Wub, Qi Liua( ), Weiqun Shib(
), Weiqun Shib( )
)
Received:2021-04-09
Published:2021-05-25
Contact:
Qi Liu, Weiqun Shi
Supported by:文章分享

非水溶液体系的锕系元素化学是一个极具挑战性的前沿研究领域, 近年来在分子磁性、多重键以及小分子活化等方面获得了迅速发展. 化学键是化学科学中最重要的基本概念之一, 而金属-配体多重键是该领域重要的研究内容. 多重键的形成与锕系元素的电子结构密切相关, 相对论效应使得锕系元素的s轨道和p轨道收缩, 轨道能量降低, 收缩的s和p轨道增加了对核电荷的屏蔽效应, 从而使d和f轨道具有一定的延展性和不稳定性. 这种不稳定性降低了5f电子的结合能, 电子更容易离去, 可使锕系元素具有丰富的氧化态. 由于较高的主量子数和相对论效应, 锕系元素的5f轨道具有更大的径向延展, 在锕系元素中5f轨道的电子行为影响较大. 目前, 锕系金属-配体多重键因其独特的成键方式和电子结构特征而受到科学家的广泛关注, 在合成和分离方面存在极大的挑战, 研究锕系-配体多重键将有助于我们了解它们的电子结构和反应性. 基于口袋型拓扑结构的三脚架配体被广泛地应用于锕系-配体多重键的研究, 这为探索锕系元素的5f电子结构和锕系多重键丰富的化学行为提供了重要支撑. 本综述总结了近年来基于三脚架配体构筑的锕系-配体多重键的研究进展, 并对未来进行了展望.
李斌, 于吉攀, 刘康, 吴群燕, 刘琦, 石伟群. 基于三脚架配体构筑的锕系-配体多重键的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(8): 986-998.
Bin Li, Jipan Yu, Kang Liu, Qunyan Wu, Qi Liu, Weiqun Shi. Research Progress of Actinide-Ligand Multiple Bonding Supported by Tripodal Ligands[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(8): 986-998.
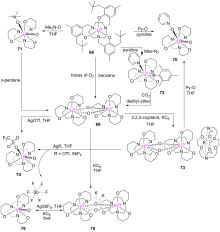
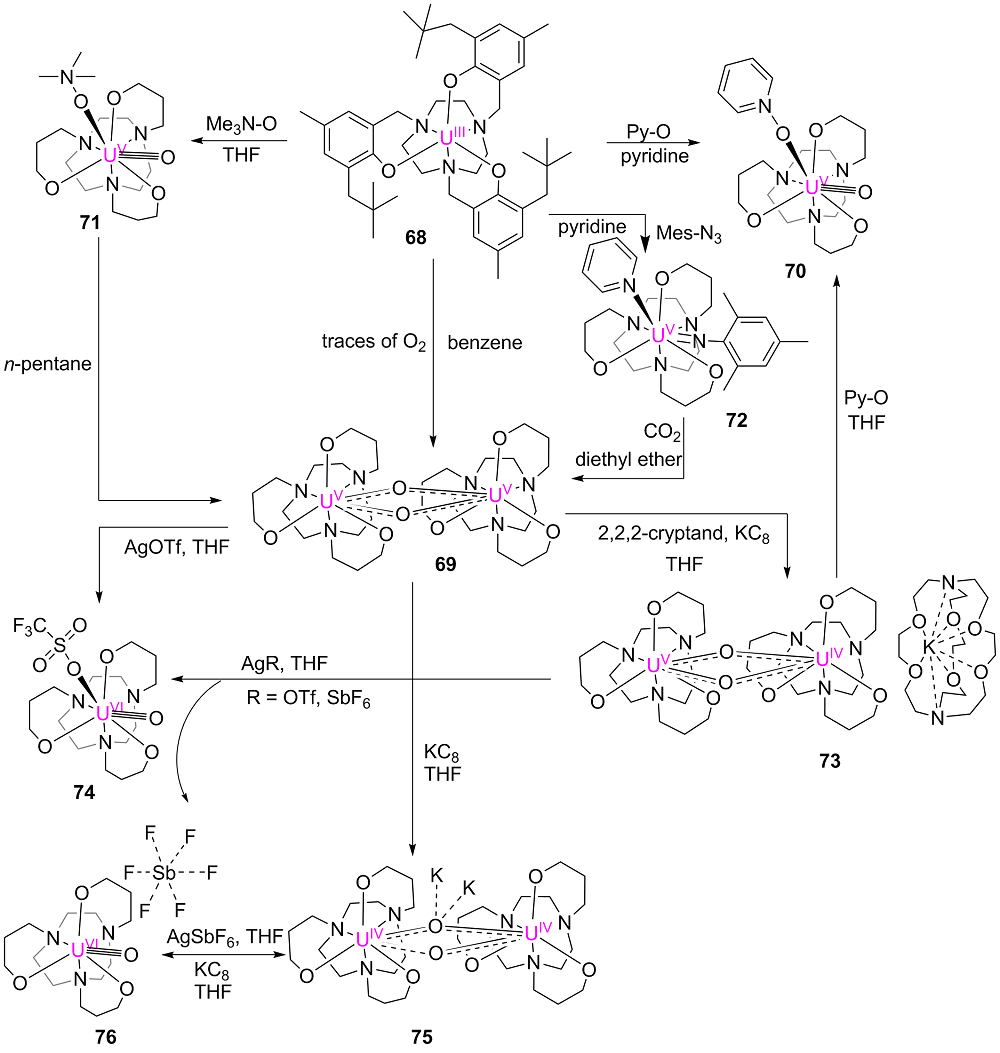

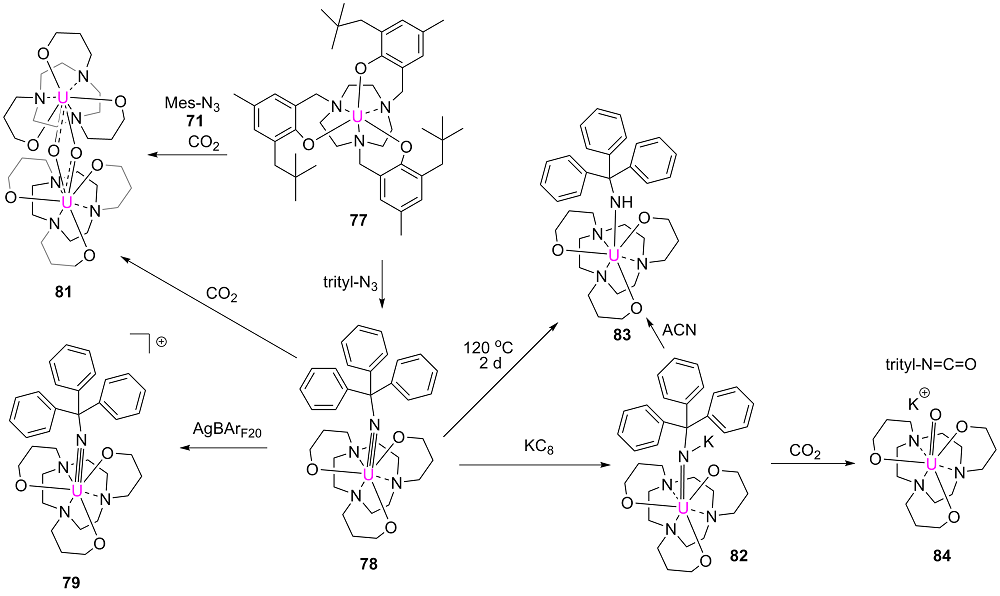
| [1] |
Fox, A. R.; Bart, S. C.; Meyer, K.; Cummins, C. C. Nature 2008, 455, 341.
doi: 10.1038/nature07372 |
| [2] |
Gardner, B. M.; Liddle, S. T. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10589.
doi: 10.1039/C5CC01360G |
| [3] |
Lu, E.; Boronski, J. T.; Gregson, M.; Wooles, A. J.; Liddle, S. T. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5506.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.19 |
| [4] |
Gregson, M.; Lu, E.; Mills, D. P.; Tuna, F.; McInnes, E. J.L.; Hennig, C.; Scheinost, A. C.; McMaster, J.; Lewis, W.; Blake, A. J.; Kerridge, A.; Liddle, S. T. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14137.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms14137 |
| [5] |
Lu, E.; Tuna, F.; Lewis, W.; Kaltsoyannis, N.; Liddle, S. T. Chem.-Eur. J. 2016, 22, 11554.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201602603 |
| [6] |
King, D. M.; Tuna, F.; McInnes, E. J.L.; McMaster, J.; Lewis, W.; Blake, A. J.; Liddle, S. T. Science 2012, 337, 717.
doi: 10.1126/science.1223488 |
| [7] |
Gardner, B. M.; Cleaves, P. A.; Kefalidis, C. E.; Fang, J.; Maron, L.; Lewis, W.; Blake, A. J.; Liddle, S. T. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 2489.
doi: 10.1039/C4SC00182F |
| [8] |
King, D. M.; Tuna, F.; McInnes, E. J.L.; McMaster, J.; Lewis, W.; Blake, A. J.; Liddle, S. T. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 482.
doi: 10.1038/nchem.1642 |
| [9] |
Thomson, R. K.; Cantat, T.; Scott, B. L.; Morris, D. E.; Batista, E. R.; Kiplinger, J. L. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 723.
doi: 10.1038/nchem.705 pmid: 20729890 |
| [10] |
King, D. M.; Tuna, F.; McMaster, J.; Lewis, W.; Blake, A. J.; McInnes, E. J.L.; Liddle, S. T. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4921.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v52.18 |
| [11] |
Cleaves, P. A.; King, D. M.; Kefalidis, C. E.; Maron, L.; Tuna, F.; McInnes, E. J.L.; McMaster, J.; Lewis, W.; Blake, A. J.; Liddle, S. T. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 10412.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201406203 |
| [12] |
King, D. M.; McMaster, J.; Tuna, F.; McInnes, E. J.L.; Lewis, W.; Blake, A. J.; Liddle, S. T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5619.
doi: 10.1021/ja502405e |
| [13] |
King, D. M.; Cleaves, P. A.; Wooles, A. J.; Gardner, B. M.; Chilton, N. F.; Tuna, F.; Lewis, W.; McInnes, E. J.L.; Liddle, S. T. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13773.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms13773 |
| [14] |
Cleaves, P. A.; Kefalidis, C. E.; Gardner, B. M.; Tuna, F.; McInnes, E. J.L.; Lewis, W.; Maron, L.; Liddle, S. T. Chem.-Eur. J. 2017, 23, 2950.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201605620 pmid: 28075505 |
| [15] |
Chatelain, L.; Louyriac, E.; Douair, I.; Lu, E.; Tuna, F.; Wooles, A. J.; Gardner, B. M.; Maron, L.; Liddle, S. T. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 337.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14221-y pmid: 31953390 |
| [16] |
Du, J.; Alvarez-Lamsfus, C.; Wildman, E. P.; Wooles, A. J.; Maron, L.; Liddle, S. T. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4203.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12206-5 |
| [17] |
Gardner, B. M.; Balázs, G.; Scheer, M.; Tuna, F.; McInnes, E. J.L.; McMaster, J.; Lewis, W.; Blake, A. J.; Liddle, S. T. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 4484.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201400798 |
| [18] |
Rookes, T. M.; Gardner, B. M.; Balázs, G.; Gregson, M.; Tuna, F.; Wooles, A. J.; Scheer, M.; Liddle, S. T. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 10495.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.35 |
| [19] |
Gardner, B. M.; Balázs, G.; Scheer, M.; Tuna, F.; McInnes, E. J.L.; McMaster, J.; Lewis, W.; Blake, A. J.; Liddle, S. T. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 582.
doi: 10.1038/nchem.2279 |
| [20] |
Du, J.; King, D. M.; Chatelain, L.; Lu, E.; Tuna, F.; McInnes, E. J.L.; Wooles, A. J.; Maron, L.; Liddle, S. T. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 3738.
doi: 10.1039/C8SC05473H |
| [21] |
Seed, J. A.; Sharpe, H. R.; Futcher, H. J.; Wooles, A. J.; Liddle, S. T. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 15870.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.37 |
| [22] |
Wildman, E. P.; Balázs, G.; Wooles, A. J.; Scheer, M.; Liddle, S. T. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12884.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms12884 |
| [23] |
Wildman, E. P.; Balázs, G.; Wooles, A. J.; Scheer, M.; Liddle, S. T. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14769.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms14769 |
| [24] |
Behrle, A. C.; Walensky, J. R. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 10042.
doi: 10.1039/C6DT00776G |
| [25] |
Scherer, O. J.; Schulze, J.; Wolmershäuser, G. J. Organomet. Chem. 1994, 484, c5.
|
| [26] |
Castro-Rodríguez, I.; Nakai, H.; Meyer, K. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2389.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3773 |
| [27] |
Castro-Rodriguez, I.; Olsen, K.; Gantzel, P.; Meyer, K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4565.
pmid: 12683828 |
| [28] |
Bart, S. C.; Anthon, C.; Heinemann, F. W.; Bill, E.; Edelstein, N. M.; Meyer, K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12536.
doi: 10.1021/ja804263w |
| [29] |
Kosog, B.; La Pierre, H. S.; Heinemann, F. W.; Liddle, S. T.; Meyer, K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5284.
doi: 10.1021/ja211618v |
| [30] |
Schmidt, A. -C.; Heinemann, F. W.; Lukens, W. W.; Meyer, K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11980.
doi: 10.1021/ja504528n |
| [31] |
Schmidt, A. -C.; Heinemann, F. W.; Maron, L.; Meyer, K. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 13142.
doi: 10.1021/ic5023517 |
| [32] |
Rosenzweig, M. W.; Scheurer, A.; Lamsfus, C. A.; Heinemann, F. W.; Maron, L.; Andrez, J.; Mazzanti, M.; Meyer, K. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 5857.
doi: 10.1039/c6sc00677a pmid: 30034726 |
| [33] |
Rosenzweig, M. W.; Hümmer, J.; Scheurer, A.; Lamsfus, C. A.; Heinemann, F. W.; Maron, L.; Mazzanti, M.; Meyer, K. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 10853.
doi: 10.1039/c9dt00530g pmid: 30950469 |
| [34] |
Halter, D. P.; Heinemann, F. W.; Maron, L.; Meyer, K. Nat. Chem. 2017, 10, 259.
doi: 10.1038/nchem.2899 |
| [35] |
Halter, D. P.; Heinemann, F. W.; Bachmann, J.; Meyer, K. Nature 2016, 530, 317.
doi: 10.1038/nature16530 |
| [36] |
Bogart, J. A.; Lippincott, C. A.; Carroll, P. J.; Schelter, E. J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8222.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201501659 |
| [37] |
Fang, H.; Cole, B. E.; Qiao, Y.; Bogart, J. A.; Cheisson, T.; Manor, B. C.; Carroll, P. J.; Schelter, E. J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 13450.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.43 |
| [38] |
Solola, L. A.; Zabula, A. V.; Dorfner, W. L.; Manor, B. C.; Carroll, P. J.; Schelter, E. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6928.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b03293 |
| [39] |
Cheisson, T.; Kersey, K. D.; Mahieu, N.; McSkimming, A.; Gau, M. R.; Carroll, P. J.; Schelter, E. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 9185.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b04061 |
| [40] |
Wu, Q. -Y.; Wang, C. -Z.; Lan, J. -H.; Chai, Z. -F.; Shi, W. -Q. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 15895.
doi: 10.1039/D0DT02909B |
| [41] |
Liu, K.; Yu, J. -P.; Wu, Q. -Y.; Tao, X. -B.; Kong, X. -H.; Mei, L.; Hu, K. -Q.; Yuan, L. -Y.; Chai, Z. -F.; Shi, W. -Q. Organometallics 2020, 39, 4069.
doi: 10.1021/acs.organomet.0c00638 |
| [42] |
Wu, Q. -Y.; Lan, J. -H.; Wang, C. -Z.; Zhao, Y. -L.; Chai, Z. -F.; Shi, W. -Q. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 119, 922.
doi: 10.1021/jp512950j |
| [43] |
Wu, Q. -Y.; Wang, C. -Z.; Lan, J. -H.; Xiao, C. -L.; Wang, X. -K.; Zhao, Y. -L.; Chai, Z. -F.; Shi, W. -Q. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 9607.
doi: 10.1021/ic501006p |
| [1] | 陶鹏, 郑小康, 王国良, 盛星浩, 姜贺, 李文桃, 靳继彪, 王瑞鸿, 苗艳勤, 王华, 黄维扬. 新型双极传输特性橙光铱(III)配合物的设计、合成及其电致发光★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 891-897. |
| [2] | 刘康, 郭燕, 于吉攀, 石伟群. 锕系单分子磁体研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(3): 264-274. |
| [3] | 汪阳, 阎敬灵. 不同配体的稀土金属配合物在烯烃聚合领域的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(3): 275-288. |
| [4] | 李志凯, 罗思琪, 陈敏, 於秀君, 李霄鹏. 双三联吡啶钌配合物的研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1447-1461. |
| [5] | 李波, 周海燕, 马海燕, 黄吉玲. 亚乙基桥联双茚锆、铪配合物的合成及催化丙烯选择性齐聚研究: 茚环3-位取代基的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1280-1294. |
| [6] | 马雪璐, 李蒙, 雷鸣. 三核过渡金属配合物在催化反应中的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(1): 84-99. |
| [7] | 张琪, 江梦云, 刘天一, 曾意迅, 石胜伟. 可蒸镀自旋交叉配合物的薄膜与器件[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1351-1363. |
| [8] | 陈霄, 许汉华, 石向辉, 魏俊年, 席振峰. 稀土和锕系配合物促进的氮气活化与转化研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1299-1308. |
| [9] | 朱诗敏, 黄鑫, 韩勰, 刘思敏. N^C^N型Pt(II)配合物与大环主体葫芦[10]脲的识别及发光性质研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1066-1070. |
| [10] | 栾雪菲, 王聪芝, 夏良树, 石伟群. 铀酰与羧酸和肟基类配体相互作用的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 708-713. |
| [11] | 金艳梅, 蒙叶, 李远, 史建华, 邓雷. 对称二环己基取代六元瓜环与3-吡啶甲酰肼的超分子自组装[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(1): 44-48. |
| [12] | 宋龙飞, 周妍妍, 高婷, 闫鹏飞, 李洪峰. 点手性调控的三股铕螺旋体的非对映选择性自组装及圆偏振发光[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(8): 1042-1048. |
| [13] | 赵添堃, 王鹏, 姬明宇, 李善家, 杨明俊, 蒲秀瑛. Salan钛双齿配合物的Sonogashira合成后修饰反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(11): 1385-1393. |
| [14] | 李金华, 卓庆德, 卓凯玥, 陈大发, 夏海平. 铱杂碳龙配合物的合成及反应性[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(1): 71-80. |
| [15] | 杨忠杰, 张小飞, 施亚男, 隆昶, 张彬灏, 闫书豪, 常琳, 唐智勇. 二维疏水铜基纳米片的合成及在硫醚类化合物催化氧化中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(9): 980-988. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||