化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (6): 848-860.DOI: 10.6023/A22010053 上一篇
综述
李晓倩, 张靖, 苏芳芳, 王德超, 姚东东*( ), 郑亚萍*(
), 郑亚萍*( )
)
投稿日期:2022-01-27
发布日期:2022-07-07
通讯作者:
姚东东, 郑亚萍
作者简介: |
李晓倩, 西北工业大学化学与化工学院材料学专业在读博士研究生, 研究方向为多孔离子液体的构筑及其气体吸附分离与催化转化应用. |
 |
张靖, 西北工业大学化学与化工学院在读硕士研究生, 研究方向为先进多孔液体的合成及其催化应用. |
 |
苏芳芳, 西北工业大学化学与化工学院化学专业在读博士研究生, 研究方向为先进多孔液体及无溶剂纳米流体的合成及其在光热转化领域的应用. |
 |
王德超, 西北工业大学化学与化工学院化学专业博士研究生在读, 研究方向为新型分离复合材料(无溶剂纳米流体与多孔液体及其膜材料)、碳捕集和吸附工艺、化工过程计算机模拟. |
 |
姚东东, 西北工业大学化学与化工学院副教授, 2013年获得中国科学院化学所高分子化学与物理专业博士学位, 神奈川大学博士后, 长期从事杂化多孔液体和聚合物纳米复合材料的制备及其应用研究. |
 |
郑亚萍, 西北工业大学化学与化工学院教授, 博士生导师, 美国康奈尔大学访问学者, 研究方向为多孔液体、无溶剂纳米流体的构筑及其在CO2捕集、聚合物基复合材料纳米填料、膜分离、催化转化、光热转换等领域的应用. 现已主持完成国家自然科学基金、陕西省自然科学基金、航空科学基金等国家级、省部级纵向课题和横向课题20余项. 在AFM、ACS Nano、Angew. Chem.、Small、JMCA、CEJ、Nano-Micro Lett等权威期刊发表论文180余篇; 授权国家发明专利12件; 参编高等学校教材4部. |
基金资助:
Xiaoqian Li, Jing Zhang, Fangfang Su, Dechao Wang, Dongdong Yao( ), Yaping Zheng(
), Yaping Zheng( )
)
Received:2022-01-27
Published:2022-07-07
Contact:
Dongdong Yao, Yaping Zheng
Supported by:文章分享

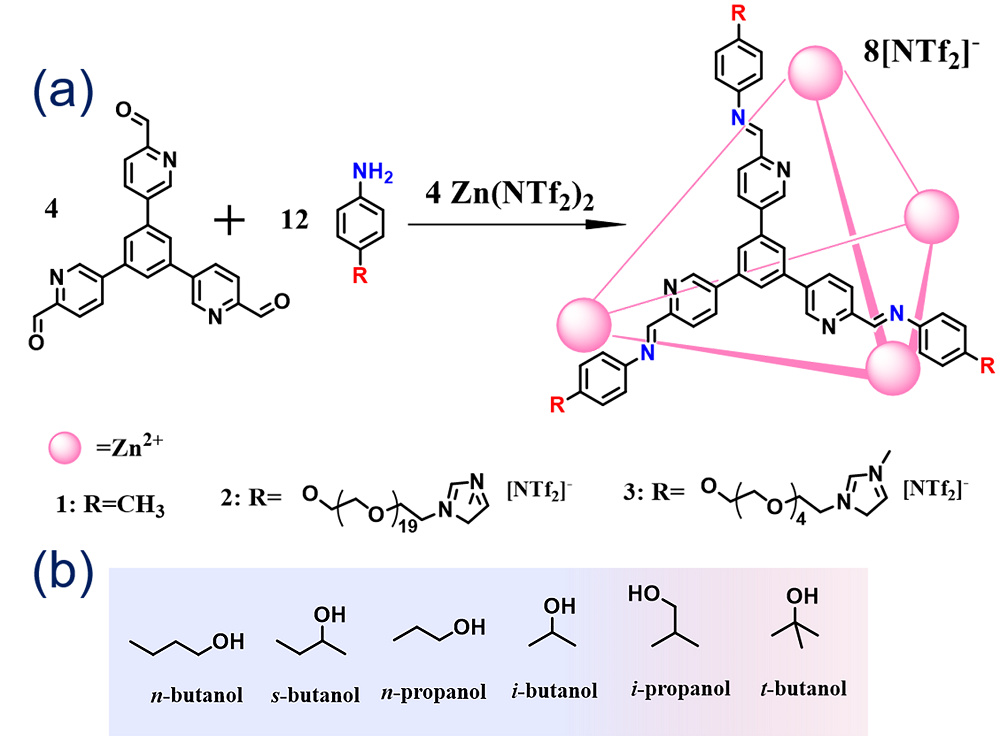
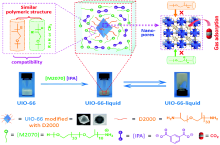
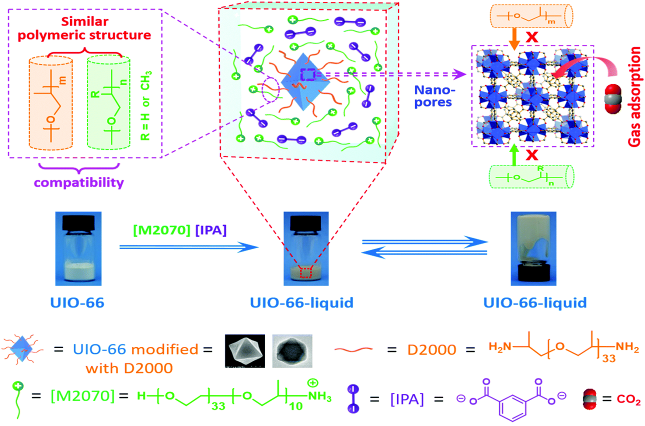
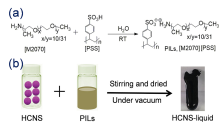
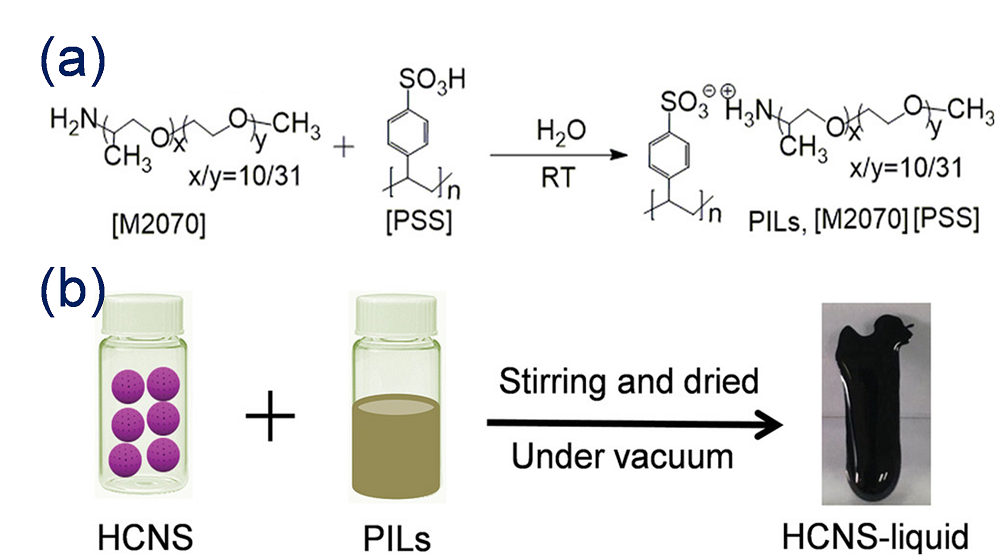
多孔液体(Porous Liquids, PLs)是一类结合了多孔固体永久性孔隙与液态流动性优势的新材料. 自2007年, PLs的概念被首次提出以来, 其在合成策略与应用领域方面均取得了较大的突破. 然而, 传统的PLs因高黏度、高密度、高熔点与高原材料成本等缺陷极大程度制约了其在流动工业系统中的大规模应用. 因此, 迫切需要寻求理想的位阻溶剂用于制备先进的多孔液体. 离子液体(Ionic Liquids, ILs)因独特的可调节物理特性、非挥发性、高稳定性、易获得、经济性高、低再生能耗等特性, 使其成为构筑PLs中最具有应用前景的理想溶剂之一. 在过去的5年间, 基于多种ILs与先进多孔固体(如有机笼、金属有机框架、中空碳、沸石、多孔聚合物等)制备的多孔离子液体(Porous Ionic Liquids, PILs)被陆续报道. PILs独特的永久性孔隙、无溶剂挥发、再生能力强、黏度可调、低熔点、高稳定性等特性加快了其在气体吸附、分离、催化、萃取、分子分离等领域的快速发展. 本综述围绕PILs的构筑策略、特性、应用领域等阐述了其研究进展. 最后, 对PILs在制备中存在的挑战与未来的研究方向进行了归纳与展望.
李晓倩, 张靖, 苏芳芳, 王德超, 姚东东, 郑亚萍. 多孔离子液体的构筑及应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 848-860.
Xiaoqian Li, Jing Zhang, Fangfang Su, Dechao Wang, Dongdong Yao, Yaping Zheng. Construction and Application of Porous Ionic Liquids[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(6): 848-860.
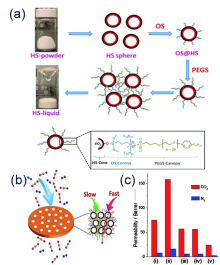

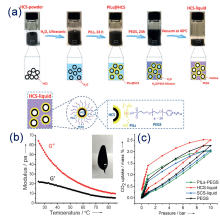

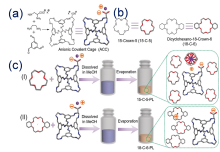

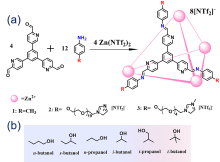
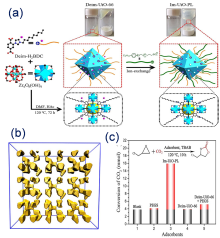

| Type | Sample name | Viscosity/ (Pa•s at 25 ℃) | Tm /℃ | CO2 adsorption | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLs | PS-OS@SiNRs | Like-gel | 15, 20 | 3.3, 4.8% (w) (0 ℃) | [ | |
| HS@OS@PEGs | 6.8 at 40 ℃ | 20 | CO2/N2 separation | [ | ||
| 4.2 at 50 ℃ | ||||||
| UiO-66-liquids | 14.000 | –4.83 | 0.25 mmol•g-1 (1 MPa 25 ℃) | [ | ||
| UiO-66-liquid-M2070 | 4.6 | –6.1 | 2.68 mmol•g-1 (1 MPa 25 ℃) | [ | ||
| PILs | HCS-liquids | High viscosity | 12 | 55.9% (w) (0.1 MPa) | [ | |
| 100-P[VHIm]-PEGS | 8.9 at 50 ℃ | 9.8 | 1.8 mmol•g-1 (0.3 MPa) | [ | ||
| 18-C-6-PL | — | 50 | 0.43 mmol•g-1 (1 MPa) | [ |
| Type | Sample name | Viscosity/ (Pa•s at 25 ℃) | Tm /℃ | CO2 adsorption | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLs | PS-OS@SiNRs | Like-gel | 15, 20 | 3.3, 4.8% (w) (0 ℃) | [ | |
| HS@OS@PEGs | 6.8 at 40 ℃ | 20 | CO2/N2 separation | [ | ||
| 4.2 at 50 ℃ | ||||||
| UiO-66-liquids | 14.000 | –4.83 | 0.25 mmol•g-1 (1 MPa 25 ℃) | [ | ||
| UiO-66-liquid-M2070 | 4.6 | –6.1 | 2.68 mmol•g-1 (1 MPa 25 ℃) | [ | ||
| PILs | HCS-liquids | High viscosity | 12 | 55.9% (w) (0.1 MPa) | [ | |
| 100-P[VHIm]-PEGS | 8.9 at 50 ℃ | 9.8 | 1.8 mmol•g-1 (0.3 MPa) | [ | ||
| 18-C-6-PL | — | 50 | 0.43 mmol•g-1 (1 MPa) | [ |
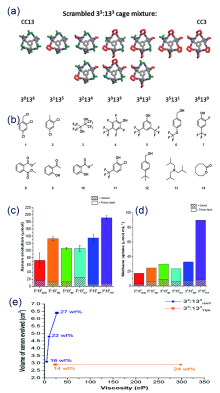

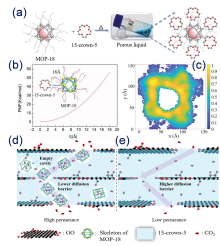

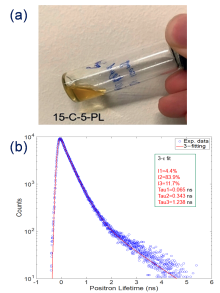

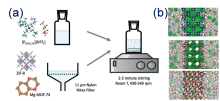

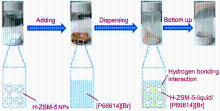
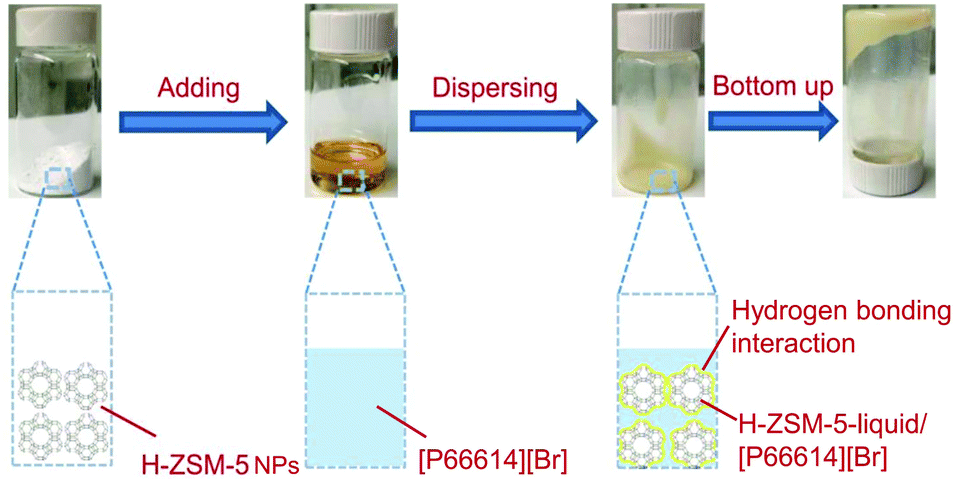
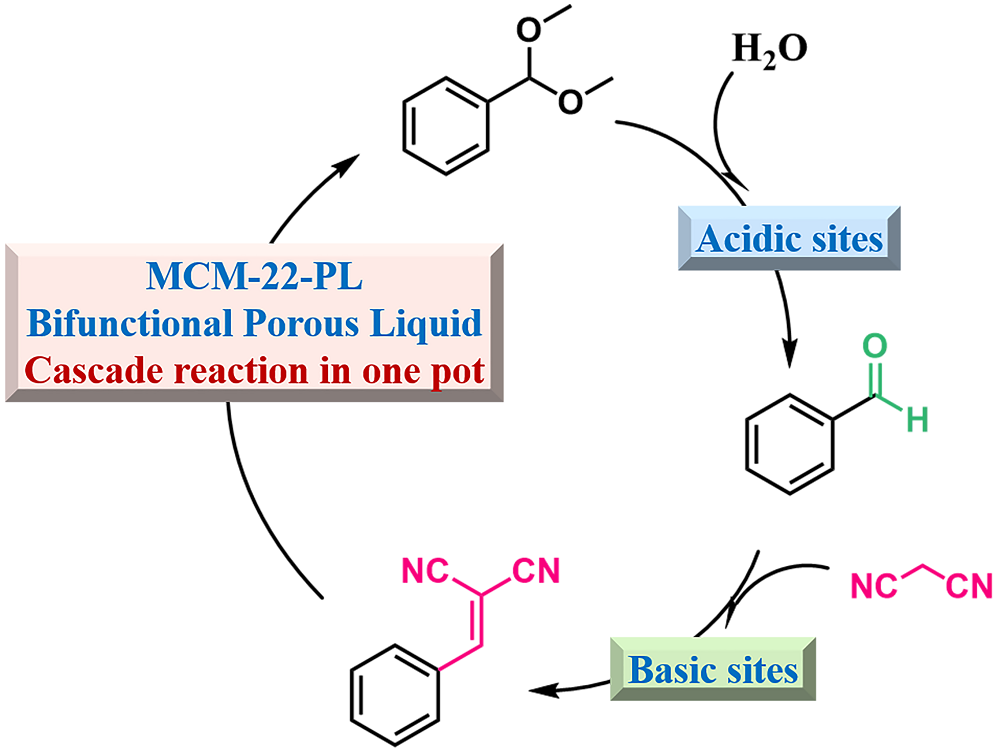
| Type | Sample name | Viscosity/ (Pa•s at 25 ℃) | Tm/℃ | CO2 adsorption (25 ℃) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLs | PL1 | 5.1 | 30.8 cm3•g-1 (1 MPa) | [ | |
| PL4 | 6.0 | –35 | 29.0 cm3•g-1 (1 MPa) | ||
| PL5 | 11.0 | 12.4 cm3•g-1 (1 MPa) | |||
| ZIF-8-g-BPEI -10 | 1.7 | –70.1 | 0.98 mL•g-1 (1 MPa) | [ | |
| ZIF-8-g-BPEI -20 | 7.1 | –60.1 | 3.49 mL•g-1 (1 MPa) | ||
| ZIF-8/[P66614][NTf2] | — | — | 2.12% (w) (0.5 MPa) | [ | |
| PILs | ZIF-8/[DBU-PEG][NTf2] | — | — | 1.56 mmol•g-1 (1 MPa) | [ |
| ZIF-8/[Bpy][NTf2] | — | — | 2.5% (w) | [ | |
| H-ZSM-5-liquid | 9.550 | –13.5 | 2% (w) (1 MPa) | [ | |
| UiO-66-liquid | — | 8 | 7.32% (w) (1 MPa) | [ | |
| ZIF-67-PLs-2 | 0.54 | 5.77 mmol•g-1 (0.1 MPa) | [ | ||
| ZIF-67-PLs-5 | 0.93 | –67 | 7.12 mmol•g-1 (0.1 MPa) | ||
| ZIF-67-PLs-10 | 1.89 | — | 9.54 mmol•g-1 (0.1 MPa) |
| Type | Sample name | Viscosity/ (Pa•s at 25 ℃) | Tm/℃ | CO2 adsorption (25 ℃) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLs | PL1 | 5.1 | 30.8 cm3•g-1 (1 MPa) | [ | |
| PL4 | 6.0 | –35 | 29.0 cm3•g-1 (1 MPa) | ||
| PL5 | 11.0 | 12.4 cm3•g-1 (1 MPa) | |||
| ZIF-8-g-BPEI -10 | 1.7 | –70.1 | 0.98 mL•g-1 (1 MPa) | [ | |
| ZIF-8-g-BPEI -20 | 7.1 | –60.1 | 3.49 mL•g-1 (1 MPa) | ||
| ZIF-8/[P66614][NTf2] | — | — | 2.12% (w) (0.5 MPa) | [ | |
| PILs | ZIF-8/[DBU-PEG][NTf2] | — | — | 1.56 mmol•g-1 (1 MPa) | [ |
| ZIF-8/[Bpy][NTf2] | — | — | 2.5% (w) | [ | |
| H-ZSM-5-liquid | 9.550 | –13.5 | 2% (w) (1 MPa) | [ | |
| UiO-66-liquid | — | 8 | 7.32% (w) (1 MPa) | [ | |
| ZIF-67-PLs-2 | 0.54 | 5.77 mmol•g-1 (0.1 MPa) | [ | ||
| ZIF-67-PLs-5 | 0.93 | –67 | 7.12 mmol•g-1 (0.1 MPa) | ||
| ZIF-67-PLs-10 | 1.89 | — | 9.54 mmol•g-1 (0.1 MPa) |
| [1] |
Singh, G.; Lee, J.; Karakoti, A.; Bahadur, R.; Yi, J. B.; Zhao, D. Y.; AlBahily, K.; Vinu, A. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 4360.
doi: 10.1039/D0CS00075B |
| [2] |
Wang, J. Y.; Huang., L.; Yang, R. Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J. W.; Gao, Y. S.; Wang, Q.; O'Hare, D.; Zhong, Z. Y. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3478.
doi: 10.1039/C4EE01647E |
| [3] |
Ning, H. L.; Yang, Z. Y.; Yin, Z. Q.; Wang, D. C.; Meng, Z. Y.; Wang, C. G.; Zhang, Y. T.; Chen, Z. P. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 17781.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c00917 |
| [4] |
Kolle, J. M.; Fayaz, M.; Sayari, A. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 7280.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00762 pmid: 33974800 |
| [5] |
Alezi, D.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Suyetin, M.; Bhatt, P. M.; Weseliński, Ł. J.; Solovyeva, V.; Adil, K.; Spanopoulos, I.; Trikalitis, P. N.; Emwas, A. H.; Eddaoudi, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13308.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b07053 |
| [6] |
Jie, K. C.; Zhou, Y. J.; Ryan, H. P.; Dai, S.; Nitschke, J. R. Adv. Mater. 2021, 202005745.
|
| [7] |
Little, M. A.; Cooper, A. I. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909842.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201909842 |
| [8] |
Zou, L. F.; Sun, Y. J.; Che, S.; Yang, X. Y.; Wang, X.; Bosch, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Smith, M.; Yuan, S.; Perry, Z.; Zhou, H. C. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700229.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201700229 |
| [9] |
Lin, Z. J.; Cao, R. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 1309. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20080359 |
|
(林祖金, 曹荣, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1309.)
doi: 10.6023/A20080359 |
|
| [10] |
Peng, Z. K.; Ding, H. M.; Chen, R. F.; Gao, C.; Wang, C. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 681. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19040118 |
|
(彭正康, 丁慧敏, 陈如凡, 高超, 汪成, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 681.)
doi: 10.6023/A19040118 |
|
| [11] |
Gao, W. L.; Liang, S. Y.; Wang, R. J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Q. W.; Xie, B. Q.; Toe, C. Y.; Zhu, X. C.; Wang, J. Y.; Huang, L.; Gao, Y. H; Wang, Z.; Jo, C. B.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L. D.; Liu, Y. F.; Louis, B.; Scott, J.; Roger, A. C.; Amal, R.; He, H.; Park, S. E. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8584.
doi: 10.1039/D0CS00025F |
| [12] |
O'Reilly, N.; Giri, N.; James, S. L. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 3020.
doi: 10.1002/chem.200700090 |
| [13] |
Ahmad, M. Z.; Alessio, F. CRGSC 2021, 4, 100070.
|
| [14] |
Egleston, B. D.; Luzyanin, K. V.; Brand, M. C.; Clowes, R.; Briggs, M. E.; Greenaway, R. L.; Cooper, A. I. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7362.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201914037 |
| [15] |
Zhang, J. H.; Wei, M. J.; Lu, Y. L.; Wei, Z. W.; Wang, H. P.; Pan, M. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 12108.
doi: 10.1021/acsaem.0c02222 |
| [16] |
Wang, D. C.; Xin, Y. Y.; Yao, D. D.; Li, X. Q.; Ning, H. L.; Zhang, H. M.; Wang, Y. D.; Ju, X. Q.; He, Z. J.; Yang, Z. Y.; Fan, W. D.; Li, P. P.; Zheng, Y. P. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 2104162.
|
| [17] |
Li, Y. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 13664.
doi: 10.1002/slct.202003957 |
| [18] |
Wang, D. C.; Xin, Y. Y.; Li, X. Q.; Yao, D. D.; Zheng, Y. P. Prog. Chem. 2021, 33, 1874. (in Chinese)
|
|
(王德超, 辛洋洋, 李晓倩, 姚东东, 郑亚萍, 化学进展, 2021, 33, 1874.)
doi: 10.7536/PC200902 |
|
| [19] |
Wang, D. C.; Xin, Y. Y.; Li, X. Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. D.; Zhang, W. R.; Zheng, Y. P.; Yao, D. D.; Yang, Z. Y.; Lei, X. F. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 127625.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127625 |
| [20] |
Liu, S.; Meng, L.; Fan, J. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 5027.
doi: 10.1002/slct.202100664 |
| [21] |
Li, X. Q.; Yao, D. D.; Wang, D. C.; He, Z. J.; Tian, X. L.; Xin, Y. Y.; Su, F. F.; Wang, H. N.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Y.; Li, M. T.; Zheng, Y. P. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132296.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.132296 |
| [22] |
Kumar, R.; Dhasaiyan, P.; Naveenkumar, P. M.; Sharma, K. P. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 4067.
doi: 10.1039/C9NA00353C |
| [23] |
Zhang, J. H.; Chai, S. H.; Qiao, Z. A.; Mahurin, S. M.; Chen, J. H.; Fang, Y. X.; Wan, S.; Nelson, K.; Zhang, P. F.; Dai, S. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 932.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201409420 |
| [24] |
Greenaway, R. L.; Holden, D.; Eden, E. G. B.; Stephenson, A.; Yong, C. W.; Bennison, M. J.; Hasell, T.; Briggs, M. E.; James, S. L.; Cooper, A. I. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 2640.
doi: 10.1039/c6sc05196k pmid: 28553499 |
| [25] |
Kai, A.; Egleston, B. D.; Tarzia, A.; Clowes, R.; Briggs, M. E.; Jelfs, K. E.; Cooper, A. I.; Greenaway, R. L. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 2106116.
|
| [26] |
Cahir, J.; Tsang, M. Y.; Lai, B. B; Hughes, D.; Alam, M. A.; Jacquemin, J.; Rooney, D.; James, S. L. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 2077.
doi: 10.1039/c9sc05770f pmid: 34123297 |
| [27] |
Li, X. Q.; Wang, D. C.; Ning, H. L; Xin, Y. Y.; He, Z. J.; Su, F. F.; Wang, Y. D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H. N.; Qian, L. W.; Zheng, Y. P.; Yao, D. D.; Li, M. T. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119305.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119305 |
| [28] |
He, S. F.; Chen, L. H.; Cui, J.; Yuan, B.; Wang, H. L.; Wang, F.; Yu, Y.; Lee, Y. J.; Li, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 19708.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b08458 |
| [29] |
Fulvio, P. F.; Dai, S. Chem 2020, 6, 3263.
doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2020.11.005 |
| [30] |
Zeeshan, M.; Nozari, V.; Yagci, M. B.; Isik, T.; Unal, U.; Ortalan, V.; Keskin, S.; Uzun, A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10113
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b05802 |
| [31] |
Armand, M.; Endres, F.; MacFarlane, D. R.; Ohno, H.; Scrosati, B. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 621.
doi: 10.1038/nmat2448 |
| [32] |
Mota-Martinez, M. T.; Brandl, P.; Hallett, J. P.; Mac Dowell, N. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2018, 3, 560.
doi: 10.1039/C8ME00009C |
| [33] |
Gomes, M. C.; Pison, L.; Cervinka, C.; Padua, A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11909.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201805495 |
| [34] |
Avila, J.; Červinka, C.; Dugas, P. Y.; Pádua, A. A. H.; Gomes, M. C. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 2001982.
|
| [35] |
McCrellis, C.; Taylor, S. F. R.; Jacquemin, J.; Hardacre, C. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2016, 61, 1092.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jced.5b00710 |
| [36] |
Bhattacharyya, S.; Filippov, A.; Shah, F. U. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 31216.
doi: 10.1039/c7cp07059d pmid: 29143022 |
| [37] |
Peplow, M. C&EN 2020, 98, 9.
|
| [38] |
Li, P. P.; Schott, J. A.; Zhang, J. S.; Mahurin, S. M.; Sheng, Y. J.; Qiao, Z. A.; Hu, X. X.; Cui, G. K.; Yao, D. D.; Brown, B.; Zheng, Y. P.; Dai, S. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14958.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201708843 |
| [39] |
Su, F. F.; Li, X. Q.; Wang, Y. D.; He, Z. J.; Fan, L.; Wang, H. N.; Xie, J. L.; Zheng, Y. P.; Yao, D. D. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119410.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119410 |
| [40] |
Hasell, T.; Copper, A. I. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16053.
doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2016.53 |
| [41] |
Jie, K. C.; Onishi, N.; Schott, J. A.; Popovs, I.; Jiang, D. E.; Mahurin, S.; Dai, S. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 2268.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201912068 |
| [42] |
Ma, L. L.; Haynes, C. J. E.; Grommet, A. B.; Walczak, A.; Parkins, C. C.; Doherty, C. M.; Longley, L.; Tron, A.; Stefankiewicz, A. R.; Bennett, T. D.; Nitschke, J. R. Nat. Chem. 2020, 12, 270.
doi: 10.1038/s41557-020-0419-2 |
| [43] |
Zou, Y. H.; Huang, Y. B.; Si, D. H.; Yin, Q.; Wu, Q. J.; Weng, Z. X.; Cao, R. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 20915.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202107156 |
| [44] |
Wang, D. C.; Xin, Y. Y.; Li, X. Q.; Ning, H. L.; Wang, Y. D.; Yao, D. D.; Zheng, Y. P.; Meng, Z. Y.; Yang, Z. Y.; Pan, Y. T.; Li, P. P.; Wang, H. N.; He, Z. J.; Fan, W. D. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 2600.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c18707 |
| [45] |
Wang, D. X.; Xin, Y. Y.; Li, X. Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. D.; Zhang, W. R.; Zheng, Y. P.; Yao, D. D.; Yang, Z. Y.; Lei, X. F. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 416, 127625.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127625 |
| [46] |
Giri, N.; Del Popolo, M. G.; Melaugh, G.; Greenaway, R. L.; Ratzke, K.; Koschine, T.; Pison, L.; Gomes, M. F.; Cooper, A. I.; James, S. L. Nature 2015, 527, 216.
doi: 10.1038/nature16072 |
| [47] |
Kearsey, R. J.; Alston, B. M.; Briggs, M. E.; Greenaway, R. L.; Cooper, A. I. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 9454.
doi: 10.1039/c9sc03316e pmid: 32110304 |
| [48] |
Deng, Z.; Ying, W.; Gong, K.; Zeng, Y. J.; Yan, Y. G.; Peng, X. S. Small 2020, 16, 1907016.
doi: 10.1002/smll.201907016 |
| [49] |
Shan, W. D.; Fulvio, P. F.; Kong, L. Y.; Schott, J. A.; Do-Thanh, C. L.; Tian, T.; Hu, X. X.; Mahurin, S. M.; Xing, H. B.; Dai, S. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 32.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b15873 |
| [50] |
Liu, S. J.; Liu, J. D.; Hou, X. D.; Xu, T. T.; Tong, J.; Zhang, J. X.; Ye, B. J.; Liu, B. Langmuir 2018, 34, 3654.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b04212 |
| [51] |
Li, P. P.; Chen, H.; Schott, J. A.; Li, B.; Zheng, Y. P.; Mahurin, S. M.; Jiang, D. E.; Cui, G. K.; Hu, X. X.; Wang, Y. Y.; Li, L. W.; Dai, S. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 1515.
doi: 10.1039/C8NR07337F |
| [52] |
Lai, B. B.; Cahir, J.; Tsang, M. Y.; Jacquemin, J.; Rooney, D.; Murrer, B.; James, S. L. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 13, 932.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c19044 |
| [53] |
Zhao, X. M.; Yuan, Y. H.; Li, P. P.; Song, Z. J.; Ma, C. X.; Pan, D.; Wu, S. D.; Ding, T.; Guo, Z. H.; Wang, N. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 13179.
doi: 10.1039/C9CC07243H |
| [54] |
Li, X. Q.; Wang, D. C.; He, Z. J.; Su, F. F.; Zhang, N.; Xin, Y. Y.; Wang, H. N.; Tian, X. L.; Zheng, Y. P.; Yao, D. D.; Li, M. T. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129239.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129239 |
| [55] |
Wang, Z. H.; Zhao, P. P.; Wu, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L. Z.; Xu, D. M. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 8557.
doi: 10.1039/D1NJ01053K |
| [56] |
Li, P. P.; Wang, D. C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y. K.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z. H.; Wu, W. W.; Liang, Y. P.; Li, Z. M.; Wang, W. D.; Zheng, Y. P. Small 2021, 2006687.
|
| [57] |
Avila, J.; Lepre, L. F.; Santini, C. C.; Tiano, S. M.; Denis-Quanquin, S.; Chung Szeto, K.; Padua, A. A. H.; Gomes, M. C. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 12876.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202100090 |
| [58] |
Wang, Y. J.; Liu, Y. Z.; Li, H.; Guan, X. Y.; Xue, M.; Yan, Y. S.; Valtchev, V.; Qiu, S. L.; Fang, Q. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 3736.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c00560 |
| [59] |
Mow, R. E.; Lipton, A. S.; Shulda, S.; Gaulding, E. A.; Gennett, T.; Braunecker, W. A. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 23455.
doi: 10.1039/D0TA06768G |
| [60] |
Yang, N.; Lu, L. J.; Zhu, L. H.; Wu, P. W.; Tao, D. J.; Gong, J. H.; Chen, L. L.; Chao, Y. H.; Zhu, W. S. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 165.
doi: 10.1039/D1QI01255J |
| [61] |
Zhou, Y.; Jocasta, A.; Berthet, N.; Legrand, S.; Santini, C. C.; Gomes, C. C.; Dufaud, V. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 7922.
doi: 10.1039/D1CC02642A |
| [62] |
Chen, H.; Yang, Z. Z.; Peng, H. G.; Jie, K. C.; Li, P. P.; Ding, S. M.; Guo, W.; Suo, X.; Liu, J. X.; Yan, R.; Liu, W. M.; Do-Thanh, C. L.; Wang, H. M.; Wang, Z. D.; Han, L.; Yang, W. M.; Dai, S. Chem 2021, 7, 3340.
doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2021.08.022 |
| [63] |
Liu, W. Q.; Li, Z.; Xia, C. G. Prog. Chem. 2018, 30, 1143. (in Chinese)
|
|
(刘文巧, 李臻, 夏春谷, 化学进展, 2018, 30, 1143.)
doi: 10.7536/PC180106 |
| [1] | 邓沈娜, 彭常春, 牛云宏, 许云, 张云霄, 陈祥, 王红敏, 刘珊珊, 沈晓. 自由基Brook重排调控的α-氟烷基-α-硅基甲醇参与的烯烃双官能团化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 119-125. |
| [2] | 陈健强, 朱钢国, 吴劼. 镍催化氮杂环丙烷的开环偶联反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 190-212. |
| [3] | 刘洋, 高丰琴, 马占营, 张引莉, 李午戊, 侯磊, 张小娟, 王尧宇. 一例钴基金属有机框架化合物活化过氧单硫酸盐高效降解水中亚甲基蓝研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 152-159. |
| [4] | 李雅宁, 王晓艳, 唐勇. 自由基聚合的立体选择性调控★[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 213-225. |
| [5] | 何文, 王波, 冯晗俊, 孔祥如, 李桃, 肖睿. CO2捕集膜分离的Pebax基材料研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 226-241. |
| [6] | 李珊, 路俊欣, 刘杰, 蒋绿齐, 易文斌. 氟烷基亚磺酸钠盐电化学合成α-氟烷基酮[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 110-114. |
| [7] | 张大伟, 赵海洋, 冯笑甜, 顾玉诚, 张新刚. 钯催化下杂芳基溴代物与偕二氟烯丙基硼试剂的交叉偶联反应[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 105-109. |
| [8] | 曾如馨, 陈鹏. RNA结合蛋白的组学解析与功能探索★[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(1): 53-61. |
| [9] | 吴宇晗, 张栋栋, 尹宏宇, 陈正男, 赵文, 匙玉华. “双碳”目标下Janus In2S2X光催化还原CO2的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1148-1156. |
| [10] | 王端达, 沈欣怡, 宋永杨, 王树涛. 新兴Janus颗粒在油水分离中的应用进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1187-1195. |
| [11] | 翟彤仪, 葛畅, 钱鹏程, 周波, 叶龙武. Brønsted酸催化炔酰胺分子内氢烷氧化/Claisen重排反应★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1101-1107. |
| [12] | 刘士琨, 邓程维, 姬峰, 闵宇霖, 李和兴. 高温质子交换膜燃料电池中阴极双催化层孔结构的设计研究★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1135-1141. |
| [13] | 徐续盼, 范凯, 赵胜泽, 李健, 高珊, 吴忠标, 孟祥举, 肖丰收. 介孔Beta沸石负载钯在甲烷催化燃烧反应中的性能研究★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1108-1112. |
| [14] | 鱼章龙, 李忠良, 杨昌江, 顾强帅, 刘心元. 铜催化的二醇类化合物对映选择性去对称化反应研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 955-966. |
| [15] | 付信朴, 王秀玲, 王伟伟, 司锐, 贾春江. 团簇Au/CeO2的制备及其催化CO氧化反应构效关系的研究★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 874-883. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||