化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (10): 1438-1446.DOI: 10.6023/A23050246 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 庆祝《化学学报》创刊90周年合辑
综述
投稿日期:2023-05-24
发布日期:2023-07-03
通讯作者:
朱云卿, 杜建忠
作者简介: |
溥旭, 同济大学材料科学与工程学院高分子材料系2021级硕士研究生, 研究方向为基于可降解阳离子聚合物的淋巴结靶向核酸递送载体. |
 |
李泽娟, 同济大学材料科学与工程学院高分子材料系2022级硕士研究生, 研究方向为基于可降解阳离子聚合物的骨靶向核酸递送载体. |
 |
石隽秋, 同济大学材料科学与工程学院高分子材料系2020级博士研究生, 研究方向为非侵入性可降解核酸递送系统的构建与研究. |
 |
朱云卿, 2016 年在英国帝国理工大学获得博士学位. 2017~2019年分别在英国牛津大学和帝国理工大学从事博士后研究工作, 2019年6月入职同济大学. 同济大学青年百人计划研究员, 博士生导师. 主要从事环境友好高分子材料研究, 主持了国家自然科学基金青年科学基金、面上项目等. 以第一/通讯作者在Nature, J. Am. Chem. Soc., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.等期刊发表SCI论文30多篇, 包括2篇ESI热点论文. |
 |
杜建忠, 中国科学院化学研究所博士(2004年), 谢菲尔德大学、剑桥大学博士后(2004~2010年), 洪堡学者(2006年), 东方学者(2009年). 同济大学长聘特聘教授、学术委员会委员、高分子材料系主任、博士生导师. 英国皇家化学会会士、中国化学会高分子学科委员会委员、中国生物材料学会生物医用高分子材料分会委员、Biomacromolecules等期刊顾问编委. 主要研究领域为高分子化学与物理、生物医用材料, 已在J. Am. Chem. Soc.等期刊发 |
基金资助:
Xu Pu, Zejuan Li, Junqiu Shi, Yunqing Zhu( ), Jianzhong Du(
), Jianzhong Du( )
)
Received:2023-05-24
Published:2023-07-03
Contact:
Yunqing Zhu, Jianzhong Du
About author:Supported by:文章分享
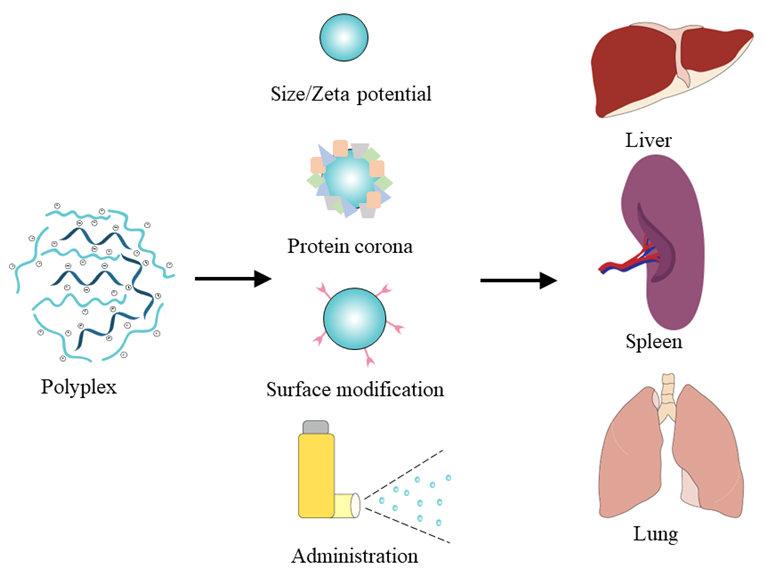
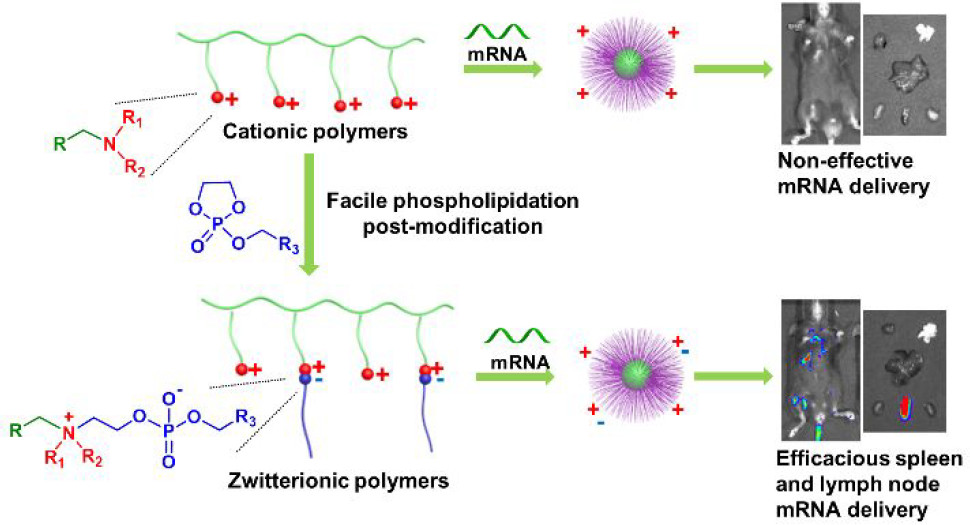
核酸药物治疗在近年来得到了蓬勃发展, 其有效治疗与核酸的安全、高效递送息息相关. 一方面, 核酸自身难以进入细胞表达, 另一方面, 与其他药物不同, 一些核酸药物需要在特定器官/细胞上表达才能发挥疗效. 因此其递送载体就显得尤为重要: 它们既要保护核酸并实现高效转染, 又要能够靶向特定部位以增加核酸在靶细胞的表达几率. 鉴于聚合物载体是一类重要的核酸递送载体, 因此在该综述中, 主要总结聚合物核酸载体的研究进展, 主要包括如何实现从给药部位到靶向部位的聚集、器官靶向核酸载体的研究现状, 最后对聚合物核酸载体的器官靶向进行了展望.
溥旭, 李泽娟, 石隽秋, 朱云卿, 杜建忠. 器官靶向的聚合物核酸载体研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1438-1446.
Xu Pu, Zejuan Li, Junqiu Shi, Yunqing Zhu, Jianzhong Du. Recent Advances in Organ-Targeting Polymeric Delivery Vectors for Nucleic Acids★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(10): 1438-1446.
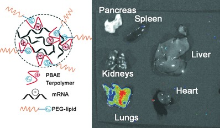
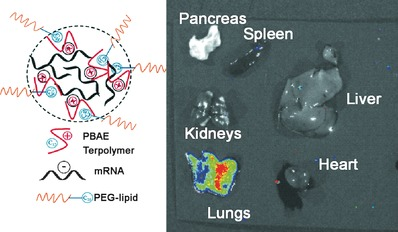
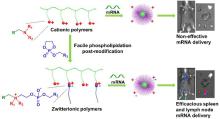
| [1] |
van den Berg, A. I. S.; Yun, C. O.; Schiffelers, R. M.; Hennink, W. E. J. Controlled Release 2021, 331, 121.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.01.014 |
| [2] |
Kulkarni, J. A.; Witzigmann, D.; Thomson, S. B.; Chen, S.; Leavitt, B. R.; Cullis, P. R.; van der Meel, R. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 630.
doi: 10.1038/s41565-021-00898-0 |
| [3] |
Guo, Z. P.; Lin, L.; Chen, J.; Tian, H. Y.; Chen, X. S. Chem. J. Chinese U. 2020, 41, 235 (in Chinese).
|
|
(郭兆培, 林琳, 陈杰, 田华雨, 陈学思, 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41, 235.)
|
|
| [4] |
Kis, Z.; Kontoravdi, C.; Dey, A. K.; Shattock, R.; Shah, N. J. Adv. Manuf. Process. 2020, 2, e10060.
|
| [5] |
Weng, Y. H.; Li, C. H.; Yang, T. R.; Hu, B.; Zhang, M. J.; Guo, S.; Xiao, H. H.; Liang, X. J.; Huang, Y. Y. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 40, 107534.
doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2020.107534 |
| [6] |
Hajj, K. A.; Whitehead, K. A. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17056.
doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2017.56 |
| [7] |
Kowalski, P. S.; Rudra, A.; Miao, L.; Anderson, D. G. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 710.
doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.02.012 |
| [8] |
Meyer, R. A.; Neshat, S. Y.; Green, J. J.; Santos, J. L.; Tuesca, A. D. Mater. Today Adv. 2022, 14, 100240.
|
| [9] |
Servick, K. Science 2020, 370, 1388.
doi: 10.1126/science.370.6523.1388 |
| [10] |
Blakney, A. K.; Zhu, Y.; McKay, P. F.; Bouton, C. R.; Yeow, J.; Tang, J.; Hu, K.; Samnuan, K.; Grigsby, C. L.; Shattock, R. J.; Stevens, M. M. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5711.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c00326 |
| [11] |
Han, X.; Zhang, L. W.; Zhang, Q.; Sui, X. H.; Qian, M.; Chen, Q. X.; Wang, J. Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 794 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A21030090 |
|
(韩旭, 张留伟, 张强, 睢晞航, 钱明, 陈麒先, 王静云, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 794.)
|
|
| [12] |
Wang, H.; Chang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Y. Top. Curr. Chem. 2017, 375, 62.
|
| [13] |
Kumar, R.; Santa Chalarca, C. F.; Bockman, M. R.; Van Bruggen, C.; Grimme, C. J.; Dalal, R. J.; Hanson, M. G.; Hexum, J. K.; Reineke, T. M. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 11527.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00997 |
| [14] |
Mendes, B. B.; Conniot, J.; Avital, A.; Yao, D.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, X.; Sharf-Pauker, N.; Xiao, Y.; Adir, O.; Liang, H.; Shi, J.; Schroeder, A.; Conde, J. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 24.
doi: 10.1038/s43586-022-00104-y |
| [15] |
Bus, T.; Traeger, A.; Schubert, U. S. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 6904.
doi: 10.1039/C8TB00967H |
| [16] |
Pei, H.; Deng, H. Z.; Zhou, Y. F.; Chen, X. Y. Matter 2022, 5, 1670.
doi: 10.1016/j.matt.2022.03.006 |
| [17] |
Park, T. G.; Jeong, J. H.; Kim, S. W. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 2006, 58, 467.
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2006.03.007 |
| [18] |
Breunig, M.; Lungwitz, U.; Liebl, R.; Goepferich, A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 14454.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0703882104 |
| [19] |
Li, M.; Li, Y.; Peng, K.; Wang, Y.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z. R.; He, Q.; Sun, X. Acta Biomater. 2017, 64, 237.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.10.019 |
| [20] |
Green, J. J.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D. G. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 749.
doi: 10.1021/ar7002336 |
| [21] |
Chaudhary, N.; Weissman, D.; Whitehead, K. A. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2021, 20, 817.
doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00283-5 |
| [22] |
Kheraldine, H.; Rachid, O.; Habib, A. M.; Al Moustafa, A.-E.; Benter, I. F.; Akhtar, S. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 2021, 178, 113908.
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.113908 |
| [23] |
Laechelt, U.; Wagner, E. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11043.
doi: 10.1021/cr5006793 |
| [24] |
Cedervall, T.; Lynch, I.; Foy, M.; Berggard, T.; Donnelly, S. C.; Cagney, G.; Linse, S.; Dawson, K. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5754.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v46:30 |
| [25] |
Lima, T.; Bernfur, K.; Vilanova, M.; Cedervall, T. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1129.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-57943-6 |
| [26] |
Francia, V.; Schiffelers, R. M.; Cullis, P. R.; Witzigmann, D. Bioconjugate Chem. 2020, 31, 2046.
doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.0c00366 |
| [27] |
Mohammad-Beigi, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Zeuthen, C. M.; Eskandari, H.; Scavenius, C.; Juul-Madsen, K.; Vorup-Jensen, T.; Enghild, J. J.; Sutherland, D. S. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4535.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18237-7 |
| [28] |
Owens, D. E.,3rd; Peppas, N. A. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 307, 93.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.10.010 |
| [29] |
Akinc, A.; Querbes, W.; De, S.; Qin, J.; Frank-Kamenetsky, M.; Jayaprakash, K. N.; Jayaraman, M.; Rajeev, K. G.; Cantley, W. L.; Dorkin, J. R.; Butler, J. S.; Qin, L.; Racie, T.; Sprague, A.; Fava, E.; Zeigerer, A.; Hope, M. J.; Zerial, M.; Sah, D. W. Y.; Fitzgerald, K.; Tracy, M. A.; Manoharan, M.; Koteliansky, V.; de Fougerolles, A.; Maier, M. A. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1357.
doi: 10.1038/mt.2010.85 |
| [30] |
Dilliard, S. A.; Cheng, Q.; Siegwart, D. J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2021, 118, e2109256118.
|
| [31] |
Song, T.; Xia, Y.; Du, Y.; Chen, M. W.; Qing, H.; Ma, G. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100106.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v33.26 |
| [32] |
Cao, Y.; He, Z.; Chen, Q.; He, X.; Su, L.; Yu, W.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Huang, X.; Li, J. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 6580.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c01784 |
| [33] |
Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.3330 |
| [34] |
Fang, C.; Shi, B.; Pei, Y. Y.; Hong, M. H.; Wu, J.; Chen, H. Z. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 27, 27.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2005.08.002 |
| [35] |
Vegh, P.; Fletcher, J.; Dixon, D.; Haniffa, M., In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences, John Wiley and Sons, Hoboken, 2017, pp. 1-8.
|
| [36] |
Besin, G.; Milton, J.; Sabnis, S.; Howell, R.; Mihai, C.; Burke, K.; Benenato, K. E.; Stanton, M.; Smith, P.; Senn, J.; Hoge, S. ImmunoHorizons 2019, 3, 282.
doi: 10.4049/immunohorizons.1900029 |
| [37] |
Choi, H. S.; Liu, W.; Misra, P.; Tanaka, E.; Zimmer, J. P.; Ipe, B. I.; Bawendi, M. G.; Frangioni, J. V. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1165.
doi: 10.1038/nbt1340 |
| [38] |
Poon, W.; Zhang, Y. N.; Ouyang, B.; Kingston, B. R.; Wu, J. L. Y.; Wilhelm, S.; Chan, W. C. W. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5785.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b01383 |
| [39] |
Mitchell, M. J.; Billingsley, M. M.; Haley, R. M.; Wechsler, M. E.; Peppas, N. A.; Langer, R. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2021, 20, 101.
doi: 10.1038/s41573-020-0090-8 |
| [40] |
Dilliard, S. A.; Siegwart, D. J. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2023, 8, 282.
doi: 10.1038/s41578-022-00529-7 |
| [41] |
Poisson, J.; Lemoinne, S.; Boulanger, C.; Durand, F.; Moreau, R.; Valla, D.; Rautou, P.-E. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 212.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.07.009 |
| [42] |
Sato, Y.; Hatakeyama, H.; Hyodo, M.; Harashima, H. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 788.
doi: 10.1038/mt.2015.222 |
| [43] |
Schudel, A.; Francis, D. M.; Thomas, S. N. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 415.
doi: 10.1038/s41578-019-0110-7 |
| [44] |
Trevaskis, N. L.; Kaminskas, L. M.; Porter, C. J. H. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2015, 14, 781.
doi: 10.1038/nrd4608 |
| [45] |
Hassett, K. J.; Higgins, J.; Woods, A.; Levy, B.; Xia, Y.; Hsiao, C. J.; Acosta, E.; Almarsson, O.; Moore, M. J.; Brito, L. A. J. Controlled Release 2021, 335, 237.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.05.021 |
| [46] |
Kranz, L. M.; Diken, M.; Haas, H.; Kreiter, S.; Loquai, C.; Reuter, K. C.; Meng, M.; Fritz, D.; Vascotto, F.; Hefesha, H.; Grunwitz, C.; Vormehr, M.; Husemann, Y.; Selmi, A.; Kuhn, A. N.; Buck, J.; Derhovanessian, E.; Rae, R.; Attig, S.; Diekmann, J.; Jabulowsky, R. A.; Heesch, S.; Hassel, J.; Langguth, P.; Grabbe, S.; Huber, C.; Tureci, O.; Sahin, U. Nature 2016, 534, 396.
doi: 10.1038/nature18300 |
| [47] |
Zhao, J. Y.; Song, W. T.; Tang, Z. H.; Chen, X. S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 563 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A21120602 |
|
(赵佳雨, 宋万通, 汤朝晖, 陈学思, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 563.)
|
|
| [48] |
Li, X.; Guo, X.; Hu, M.; Cai, R.; Chen, C. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 2063.
doi: 10.1039/D2TB02455A |
| [49] |
Mi, P.; Cabral, H.; Kataoka, K. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1902604.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v32.13 |
| [50] |
Li, J. J.; Kataoka, K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 538.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c09029 |
| [51] |
Fornaguera, C.; Guerra-Rebollo, M.; Angel Lazaro, M.; Castells- Sala, C.; Meca-Cortes, O.; Ramos-Perez, V.; Cascante, A.; Rubio, N.; Blanco, J.; Borros, S. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2018, 7, 1800335.
doi: 10.1002/adhm.v7.17 |
| [52] |
Kaczmarek, J. C.; Patel, A. K.; Kauffman, K. J.; Fenton, O. S.; Webber, M. J.; Heartlein, M. W.; DeRosa, F.; Anderson, D. G. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13808.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v55.44 |
| [53] |
Ke, X.; Shelton, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chow, E.; Tang, H.; Santos, J. L.; Mao, H. Q. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35835.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c08268 |
| [54] |
Patel, A. K.; Kaczmarek, J. C.; Bose, S.; Kauffman, K. J.; Mir, F.; Heartlein, M. W.; DeRosa, F.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D. G. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1805116.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v31.8 |
| [55] |
Gilleron, J.; Querbes, W.; Zeigerer, A.; Borodovsky, A.; Marsico, G.; Schubert, U.; Manygoats, K.; Seifert, S.; Andree, C.; Stoter, M.; Epstein-Barash, H.; Zhang, L. G.; Koteliansky, V.; Fitzgerald, K.; Fava, E.; Bickle, M.; Kalaidzidis, Y.; Akinc, A.; Maier, M.; Zerial, M. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 638.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.2612 |
| [56] |
Nicoli, E.; Syga, M. I.; Bosetti, M.; Shastri, V. P. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0122581.
|
| [57] |
Kermaniyan, S. S.; Chen, M.; Zhang, C.; Smith, S. A.; Johnston, A. P. R.; Such, C.; Such, G. K. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, 2100445.
doi: 10.1002/mabi.v22.5 |
| [58] |
Trefts, E.; Gannon, M.; Wasserman, D. H. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R1147.
|
| [59] |
Rohner, E.; Yang, R.; Foo, K. S.; Goedel, A.; Chien, K. R. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1586.
doi: 10.1038/s41587-022-01491-z |
| [60] |
Kristen, A. V.; Ajroud-Driss, S.; Conceicao, I.; Gorevic, P.; Kyriakides, T.; Obici, L. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2019, 9, 5.
doi: 10.2217/nmt-2018-0033 |
| [61] |
Lam, J. K.-W.; Liang, W.; Chan, H.-K. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 2012, 64, 1.
|
| [62] |
Miao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 41.
doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01335-5 |
| [63] |
Densmore, C. L.; Orson, F. M.; Xu, B.; Kinsey, B. M.; Waldrep, J. C.; Hua, P.; Bhogal, B.; Knight, V. Mol. Ther. 2000, 1, 180.
doi: 10.1006/mthe.1999.0021 |
| [64] |
Rudolph, C.; Lausier, J.; Naundorf, S.; Muller, R. H.; Rosenecker, J. J. Gene Med. 2000, 2, 269.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-2254 |
| [65] |
Suk, J. S.; Kim, A. J.; Trehan, K.; Schneider, C. S.; Cebotaru, L.; Woodward, O. M.; Boylan, N. J.; Boyle, M. P.; Lai, S. K.; Guggino, W. B.; Hanes, J. J. Controlled Release 2014, 178, 8.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.01.007 |
| [66] |
Mastorakos, P.; da Silva, A. L.; Chisholm, J.; Song, E.; Choi, W. K.; Boyle, M. P.; Morales, M. M.; Hanes, J.; Suk, J. S. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2015, 112, 8720.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1502281112 |
| [67] |
Elfinger, M.; Maucksch, C.; Rudolph, C. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 3448.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.04.011 |
| [68] |
Rosenblum, D.; Joshi, N.; Tao, W.; Karp, J. M.; Peer, D. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1410.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03705-y |
| [69] |
Chen, Y.; De Koker, S.; De Geest, B. G. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 2055.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00260 |
| [70] |
Jiang, Y. H.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Y. H.; Xu, E.; Ho, A.; Singh, P.; Wang, Y. F.; Jiang, Z. Z.; Yang, F.; Tietjen, G. T.; Cresswell, P.; Saltzman, W. M. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 1117.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b04426 |
| [71] |
Grun, M. K.; Suberi, A.; Shin, K.; Lee, T.; Gomerdinger, V.; Moscato, Z. M.; Piotrowski-Daspit, A. S.; Saltzman, W. M. Biomaterials 2021, 272, 120780.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.120780 |
| [72] |
Huang, P.; Jiang, L. S.; Pan, H.; Ding, L. W.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, M. Y.; Zou, J. H.; Li, B. H.; Qi, M. W.; Deng, H. Z.; Zhou, Y. F.; Chen, X. Y. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207471.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v35.3 |
| [73] |
Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, X. L.; Cheng, Q.; Johnson, L. T.; Chatterjee, S.; Zhang, D.; Lee, S. M.; Sun, Y. H.; Lin, T. C.; Liu, J. L.; Siegwart, D. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 21321.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c09822 |
| [74] |
Liu, S.; Cheng, Q.; Wei, T.; Yu, X. L.; Johnson, L. T.; Farbiak, L.; Siegwart, D. J. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 701.
doi: 10.1038/s41563-020-00886-0 |
| [75] |
Yang, R.; Deng, Y.; Huang, B.; Huang, L.; Lin, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Lu, S.; Zhan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ruhan, A.; Wang, W.; Niu, P.; Zhao, L.; Li, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, W.; Liang, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.; Peng, X.; Li, H.; Tan, W. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. 2021, 6, 213.
doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00634-z |
| [76] |
Segovia, N.; Dosta, P.; Cascante, A.; Ramos, V.; Borros, S. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 2147.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.12.054 |
| [77] |
Smith, T. T.; Stephan, S. B.; Moffett, H. F.; McKnight, L. E.; Ji, W. H.; Reiman, D.; Bonagofski, E.; Wohlfahrt, M. E.; Pillai, S. P. S.; Stephan, M. T. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 813.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2017.57 |
| [78] |
Parayath, N. N.; Stephan, S. B.; Koehne, A. L.; Nelson, P. S.; Stephan, M. T. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6080.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19486-2 |
| [79] |
Kim, H. J.; Seo, S. K.; Park, H. Y. J. Controlled Release 2022, 345, 405.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.03.029 |
| [1] | 胡立伟, 刘宪虎, 刘春太, 宋延林, 李明珠. 光子晶体结构色材料的自组装制备与应用★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 809-819. |
| [2] | 李兰英, 陶晴, 闻艳丽, 王乐乐, 郭瑞妍, 刘刚, 左小磊. 多聚腺嘌呤DNA探针及其生物传感应用★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 681-690. |
| [3] | 苏东芮, 任小康, 于沄淏, 赵鲁阳, 王天宇, 闫学海. 酪氨酸衍生物调控酶催化路径可控合成功能黑色素★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1486-1492. |
| [4] | Jamshid Kadirkhanov, 钟峰, 张文建, 洪春雁. 聚合诱导自组装制备多腔室囊泡以及成核链段中亲溶剂片段的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 913-920. |
| [5] | 王志琴, 项博, 黄晓宇, 陆国林, 冯纯. 磷钨酸对对苯撑乙烯撑寡聚物-b-聚(2-乙烯基吡啶)自晶种行为的影响※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(3): 297-302. |
| [6] | 殷东, 商宏怡, 余文浩, 向仕凯, 胡平, 赵可清, 冯春, 汪必琴. 三唑环修饰的苯并菲二羧酸酯和酰亚胺: 合成、液晶及凝胶性[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(10): 1376-1384. |
| [7] | 金艳梅, 蒙叶, 李远, 史建华, 邓雷. 对称二环己基取代六元瓜环与3-吡啶甲酰肼的超分子自组装[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(1): 44-48. |
| [8] | 王旭生, 杨胥, 陈春辉, 李红芳, 黄远标, 曹荣. 石墨烯量子点/铁基金属-有机骨架复合材料高效光催化二氧化碳还原※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(1): 22-28. |
| [9] | 李卫华. 桥连对嵌段共聚物自组装的调控[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 133-138. |
| [10] | 赵晶晶, 张正中, 陈小浪, 王蓓, 邓近远, 张蝶青, 李和兴. 微波诱导组装CuS@MoS2核壳纳米管及其光催化类芬顿反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(9): 961-967. |
| [11] | 江金辉, 朱云卿, 杜建忠. 开环聚合诱导自组装的挑战与展望[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(8): 719-724. |
| [12] | 尹岑, 王子宽, 刘丹, 彭展涛, 宋环君, 祝浩, 陈其伟, 吴凯. meso-四(对甲氧基苯基)卟啉钴在货币金属单晶表面的吸附与自组装研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(7): 695-702. |
| [13] | 刘明倩, 万茜子, 王树涛. 超强纳米颗粒溶液粘合剂[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(6): 463-465. |
| [14] | 郄淑燕, 郝莹, 刘宗建, 王锦, 席家宁. 环糊精聚合物及其生物医学应用的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(3): 232-244. |
| [15] | 沈扬林, 金俊玲, 段光雄, 谢云鹏, 卢兴. [Ag14]异构引发的纺锤形Ag58团簇的形成[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(11): 1255-1259. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||