化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (3): 221-228.DOI: 10.6023/A24010013 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
汪子航, 钱静雯, 许佳慧, 邱浩渝, 晏梦珑, 刘芸, 罗杰, 盛毓泰, 陈易, 王贤保*( )
)
投稿日期:2024-01-14
发布日期:2024-04-14
Zihang Wang, Jingwen Qian, Jiahui Xu, Haoyu Qiu, Menglong Yan, Yun Liu, Jie Luo, Yutai Sheng, Yi Chen, Xianbao Wang( )
)
Received:2024-01-14
Published:2024-04-14
Contact:
*E-mail: wxb@hubu.edu.cn
文章分享

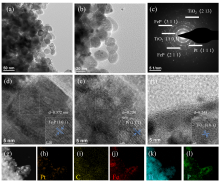
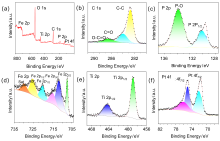
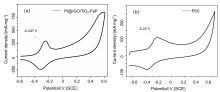
铁钛双金属由于其强烈的协同效应以及双功能机理, 在电化学领域中展现出了优秀的催化活性. 针对目前甲醇燃料电池铂基催化剂成本高、抗CO中毒能力低以及循环稳定性差等制约其商业化应用的关键瓶颈问题, 采用了一种简单的水热、低温磷化以及油浴方法, 成功合成了在石墨烯上负载的低铂/二氧化钛修饰磷化铁复合材料(Pt@rGO/TiO2-FeP)用于甲醇电池阳极催化剂. 循环伏安法(CV)、计时电流法(CA)和多电位阶跃方法(STEP)等研究表明, 使用低温磷化法可以有效提升催化剂的甲醇氧化性能, 在Pt负载量仅为4.3% (w)时, 催化剂的峰电流密度达到2319.5 mA•mg−1, 是商用Pt/C催化剂(390.5 mA•mg−1)的5.9倍. 通过扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、透射电子显微镜(TEM)、能量色散X射线光谱(EDX)、X射线电子衍射(XRD)和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)等表征方法对催化剂进行一系列分析, 发现二氧化钛、磷化铁以及铂纳米颗粒在石墨烯上均匀分布, 因为过渡双金属的负载, 促进Pt的d带中心降低, 有效提升了催化剂的甲醇氧化性能. 本工作合成的Pt@rGO/TiO2-FeP纳米复合材料, 具有优异的甲醇氧化性能和抗CO中毒能力, 为高性能甲醇燃料电池的研发提供了一个全新的思路和实践.
汪子航, 钱静雯, 许佳慧, 邱浩渝, 晏梦珑, 刘芸, 罗杰, 盛毓泰, 陈易, 王贤保. 石墨烯/二氧化钛/磷化铁复合低铂催化剂用于高效甲醇氧化[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(3): 221-228.
Zihang Wang, Jingwen Qian, Jiahui Xu, Haoyu Qiu, Menglong Yan, Yun Liu, Jie Luo, Yutai Sheng, Yi Chen, Xianbao Wang. Graphene/Titanium dioxide/Iron Phosphide Composite with Low Platinum Catalysts for Efficient Methanol Oxidation[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(3): 221-228.









| [1] |
Zhu, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, J. Micromachines (Basel) 2019, 10, 386.
|
| [2] |
Zhu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, P.; Yu, J.; Cai, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Z. Carbon 2018, 139, 477.
|
| [3] |
Zhou, M.; Weng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Xue, Y.; Zeng, X.; Bando, Y.; Golberg, D. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4335.
|
| [4] |
Zhao, W.; Ma, L.; Gan, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, X.; Wang, L. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 604, 52.
|
| [5] |
Zhao, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xu, B. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 56.
|
| [6] |
Zhang, X.; An, L.; Yin, J.; Xi, P.; Zheng, Z.; Du, Y. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43590.
|
| [7] |
Zhang, W.; Dahbi, M.; Amagasa, S.; Yamada, Y.; Komaba, S. Electrochem. Commun. 2016, 69, 11.
|
| [8] |
Zhang, P.; Cai, Z.; You, S.; Wang, F.; Dai, Y.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, N.; Zou, J. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 10461.
|
| [9] |
Zhang, D.; Li, G.; Yu, M.; Fan, J.; Li, B.; Li, L. J. Power Sources 2018, 384, 34.
|
| [10] |
Yusoff, F.; Suresh, K.; Noorashikin, M. S. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 2020, 463, 256.
|
| [11] |
Yuda, A.; Ashok, A.; Kumar, A. Catal. Rev. 2020, 64, 126.
|
| [12] |
Yuan, Z.; Chuai, W.; Guo, Z.; Tu, Z.; Kong, F. Micromachines (Basel). 2019, 10, 542.
|
| [13] |
Yu, J.; Cheng, G.; Luo, W. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 15838.
|
| [14] |
Yin, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F.; Hou, Y. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2930.
|
| [15] |
Yildiz, A.; Chouki, T.; Atli, A.; Harb, M.; Verbruggen, S. W.; Ninakanti, R.; Emin, S. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 10618.
|
| [16] |
Ye, S. H.; He, X. J.; Ding, L. X.; Pan, Z. W.; Tong, Y. X.; Wu, M.; Li, G. R. Chem. Commun. (Camb). 2014, 50, 12337.
|
| [17] |
Chen, R.-Y.; Zhen, S.-S.; Lin, Z.-L.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Wang, Z.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1286 (in Chinese).
|
|
(陈日懿, 郑淞生, 林志彬, 刘运权, 王兆林, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1286.)
doi: 10.6023/A21060280 |
|
| [18] |
Yao, F.; Bi, J.; Yu, L.; Dai, L.; Xue, W.; Deng, J.; Yao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhu, J. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2023, 13, 3001.
|
| [19] |
Yang, Y.; Fu, W.; Bell, C.; Lee, D. C.; Drexler, M.; Nuli, Y.; Ma, Z. F.; Magasinski, A.; Yushin, G.; Alamgir, F. M. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 34074.
|
| [20] |
Yang, F.; Ma, L.; Gan, M.; Zhang, J.; Yan, J.; Huang, H.; Yu, L.; Li, Y.; Ge, C.; Hu, H. Syn. Metals 2015, 205, 23.
|
| [21] |
Sun, L.; Wang, H.-L.; Yu, J.-S.; Zhou, X.-G. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 888 (in Chinese).
|
|
(孙炼, 王洪磊, 余金山, 周新贵, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 888.)
doi: 10.6023/A20060221 |
|
| [22] |
Ma, X.-L.; Li, M.; Lei, M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 84 (in Chinese).
|
|
(马雪璐, 李蒙, 雷鸣, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 84.)
doi: 10.6023/A22100425 |
|
| [23] |
Xie, D.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Hark, E.; Kochovski, Z.; Eljarrat, A.; Muller, J.; Koch, C. T.; Yuan, J.; Lu, Y. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 10554.
|
| [24] |
Wu, X.; Wu, H. B.; Xiong, W.; Le, Z.; Sun, F.; Liu, F.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, Y. Nano Energy 2016, 30, 217.
|
| [25] |
Wang, Z.; Fan, H.; Liang, H.; Ma, J.; Li, S.; Song, Y.; Wang, R. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 230, 245.
|
| [26] |
Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Dong, J.; Tian, Y. Coatings 2023, 13, 74.
|
| [27] |
Wang, Y.; Lim, Y. V.; Huang, S.; Ding, M.; Kong, D.; Pei, Y.; Xu, T.; Shi, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, H. Y. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 4341.
doi: 10.1039/c9nr09278a pmid: 31994571 |
| [28] |
Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Ma, C.; Yang, Z.; Yue, H.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Z. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 698.
|
| [29] |
Zhang, G.-Q.; Huo, J.-H.; Wang, X.; Guo, S.-W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 6 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张国强, 霍京浩, 王鑫, 郭守武, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 6.)
doi: 10.6023/A22110456 |
|
| [30] |
Su, Y.-Y.; Tang, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y, -K.; Liu, F. Precious Met. 2023, 44, 95 (in Chinese).
|
|
(栗云彦, 唐玲, 刘健, 陈慧, 赵云昆, 刘锋, 贵金属, 2023, 44, 95.)
|
|
| [31] |
Montiel, G.; Fuentes-Quezada, E.; Bruno, M. M.; Corti, H. R.; Viva, F. A. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 30631.
|
| [32] |
Mohamed, H. O.; Obaid, M.; Poo, K.-M.; Ali Abdelkareem, M.; Talas, S. A.; Fadali, O. A.; Kim, H. Y.; Chae, K.-J. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 800.
|
| [33] |
Mishra, R.; Gupta, S.; Kumar, A.; Prakash, R. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 183, 606.
|
| [34] |
Mathur, A.; Kushwaha, H. S.; Vaish, R.; Halder, A. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 94826.
|
| [35] |
Gu, Y.-Y.; Yu, Y.-C.; Long, A.-C.; Ge, X.-L.; Song, Y.-K.; Meng, M.-F.; Hu, S.-H. Nonferrous Met. Mater. Eng. 2023, 44, 35 (in Chinese).
|
|
(顾颖颖, 于永昌, 龙安椿, 葛宪龙, 宋炎锴, 蒙敏凤, 胡少华, 有色金属材料与工程, 2023, 44, 35.)
|
|
| [36] |
Zhang, M.; Han, J.-X.; Wang, Y.-X.; Chen, Y.-L.; Ren, L.-X. Zhejiang Chem. Ind. 2023, 54, 7 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张曼, 韩继续, 王盈雪, 陈俞霖, 任立新, 浙江化工, 2023, 54, 7.)
|
|
| [37] |
Du, Y.; Weng, W.; Zhang, Z.; He, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, T.; Bao, J.; Zhou, X. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 1878.
|
| [38] |
Guo, S.-Q.; Sun, Y.-X.; Li, C.-J. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 44, 625 (in Chinese).
|
|
(郭仕权, 孙亚昕, 李从举, 工程科学学报, 2022, 44, 625.)
|
|
| [39] |
Li, Q.; Yuan, J.; Tan, Q.; Wang, G.; Feng, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Q. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 5396.
|
| [40] |
Zhang, J.; Liang, P.-J.; Tang, M.-E.; Xu, X.-L.; Zhang, X.-M. J. Funct. Mater. 2023, 54, 5066 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张均, 梁平娟, 汤木娥, 许新兰, 张贤明, 动能材料, 2023, 54, 5066.)
|
|
| [41] |
Huang, Y.-F.; Xu, B.; Zeng, L.-W.; Lin, D.-H. J. Shanghai. Pol. Unive. 2023, 40, 1 (in Chinese).
|
|
(黄郁夫, 许波, 曾令文, 林东海, 上海第二工业大学学报, 2023, 40, 1.)
|
|
| [42] |
Baruah, B.; Kumar, A. Synthetic Metals 2018, 245, 74.
|
| [43] |
Zhang, Z.-F.; Tian, X.-Y.; Sun, H. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2023, 52, 2556 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张振峰, 田心瑶, 孙海, 应用化工, 2023, 52, 2556.)
|
|
| [44] |
Li, Y.; Hui, J.; Kawchuk, J.; O'Brien, A.; Jiang, Z.; Hoorfar, M. Fuel Cells 2019, 19, 43.
doi: 10.1002/fuce.201800056 |
| [45] |
Li, X.; Deng, C.; Wang, H.; Si, J.; Zhang, S.; Huang, B. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 7297.
|
| [1] | 孙伟, 辛国祥, 刘飞, 鞠藤, 程宇通, 宋金玲, 包金小, 布林朝克. 三维石墨烯/富含氧空位Fe2O3复合材料的构建实现超级电容器超高能量密度[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(3): 256-265. |
| [2] | 王南南, 陈玉贞. CoNi-MOF-74/泡沫镍衍生的CoNi@C/NF复合物用于高效有机电合成[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(6): 621-628. |
| [3] | 雷雅茹, 熊廷楷, 于湘涛, 黄秀兵, 唐晓龙, 易红宏, 周远松, 赵顺征, 孙龙, 高凤雨. 新型多孔三聚氰胺负载MnCe用于高选择性电催化CO2产甲酸[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(4): 396-408. |
| [4] | 宁聪聪, 杨倩, 毛阿敏, 唐梓嘉, 金燕, 胡宝山. 石墨烯纳米带的可控制备研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(4): 406-419. |
| [5] | 刘稳, 王昱捷, 杨慧琴, 李成杰, 吴娜, 颜洋. 离子液体非共价诱导制备碳纳米管/石墨烯集流体用于钠金属负极[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1379-1386. |
| [6] | 闫绍兵, 焦龙, 何传新, 江海龙. ZIF-67/石墨烯复合物衍生的氮掺杂碳限域Co纳米颗粒用于高效电催化氧还原[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1084-1090. |
| [7] | 蒋博龙, 崔艳艳, 史顺杰, 姜楠, 谭伟强. 双金属氮化物NiMoN析氢催化剂制备及其电解海水析氢性能的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(10): 1394-1400. |
| [8] | 王旭生, 杨胥, 陈春辉, 李红芳, 黄远标, 曹荣. 石墨烯量子点/铁基金属-有机骨架复合材料高效光催化二氧化碳还原※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(1): 22-28. |
| [9] | 翟耀, 辛国祥, 王佳琦, 张邦文, 宋金玲, 刘晓旭. 微波辅助合成具有优异电化学性能的rGO/CeO2超级电容器电极材料[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(9): 1129-1137. |
| [10] | 刘长安, 洪士博, 李蓓. 石墨烯在甘油/尿素剥离液中的稳定行为的分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 530-538. |
| [11] | 黄杰, 奚江波, 陈伟, 柏正武. 石墨烯衍生物作为无金属碳基催化剂在有机催化中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(11): 1360-1371. |
| [12] | 岳华, 马光辉. 基于石墨烯独特生物界面效应的功能化载体研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(10): 1244-1256. |
| [13] | 马明昊, 徐明, 刘思金. 氧化石墨烯的表面化学修饰及纳米-生物界面作用机理[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(9): 877-887. |
| [14] | 李海梅, 罗华健, 肖琦, 杨立云, 黄珊, 刘义. 手性石墨烯量子点与DNA相互作用及其机制研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(6): 577-586. |
| [15] | 赵雅婧, 谢亮, 马兰超, 贺军辉. 聚二甲基硅氧烷封装石墨烯基柔性红外探测器的制备及其应用[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(2): 161-169. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||