化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (10): 1208-1222.DOI: 10.6023/A25050161 上一篇 下一篇
综述
李彤†, 李博†, 张晗†, 高名蕊†, 钟铱涵, 郭恒阳, 汪少雄*( ), 刘少佳*(
), 刘少佳*( ), 赵赫威*(
), 赵赫威*( )
)
投稿日期:2025-05-11
发布日期:2025-07-21
通讯作者:
汪少雄, 刘少佳, 赵赫威
作者简介:

|
|
李彤, 现为北京航空航天大学2023级硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为类牙釉质结构Al2O3基复合材料. |

|
|
李博, 2022年获得北京科技大学硕士学位. 现为北京航空航天大学2022级博士, 主要研究方向为纳米材料在生物应用领域的可控制备与组装. |

|
|
张晗, 现为北京航空航天大学2023级硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为构型碳化硅复合材料的可控制备及其力学性能. |

|
|
高名蕊, 2022年毕业于北京航空航天大学, 获化学硕士学位. 现为北京航空航天大学2022级博士, 主要研究方向为透明材料的可控制备及力学性能研究. |

|
|
钟铱涵, 现为北京航空航天大学2024级硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为纳米材料的合成和组装. |

|
|
郭恒阳, 现为北京航空航天大学2024级硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为轻质高强氧化铝陶瓷气凝胶. |

|
|
汪少雄, 现为北京航空航天大学2020级博士生, 专业为纳米材料与技术, 主要研究微纳米陶瓷及其复合材料的可控制备、组装及其力学性能. |

|
|
刘少佳, 2022年毕业于北京航空航天大学纳米材料与技术专业, 获博士学位. 现任北京航空航天大学博士后, 主要研究方向为纳米材料的可控制备与组装及应用探究. |

|
|
赵赫威, 现任北京航空航天大学化学学院教授. 2011年和2017年分别获得北京航空航天大学学士和博士学位. 主要研究方向为轻质高强微纳米陶瓷基复合材料的可控制备及性能研究. |
★ “中国青年化学家”专辑.
基金资助:
Tong Li, Bo Li, Han Zhang, Mingrui Gao, Yihan Zhong, Hengyang Guo, Shaoxiong Wang*( ), Shaojia Liu*(
), Shaojia Liu*( ), Hewei Zhao*(
), Hewei Zhao*( )
)
Received:2025-05-11
Published:2025-07-21
Contact:
Shaoxiong Wang, Shaojia Liu, Hewei Zhao
About author:★ For the VSI “Rising Stars in Chemistry”.
Supported by:文章分享

氧化铝(Al2O3)材料因其高强度、高硬度、低导热性以及化学稳定性, 被广泛应用于航空航天、军事装备、牙齿修复、汽车制造、电子器件等领域. 然而, 其本征脆性导致的低断裂韧性显著限制了其在主承重部件中的规模化应用. 因此, 同步提升Al2O3材料的强度和韧性, 已成为材料领域亟需突破的技术瓶颈. 本综述首先简要概述了Al2O3材料的基本属性, 随后从物相、组分及仿生微纳结构三个方面系统总结了Al2O3材料的强韧化研究进展, 为后续高强高韧陶瓷基复合材料的高效构筑提供理论基础与技术参考.
李彤, 李博, 张晗, 高名蕊, 钟铱涵, 郭恒阳, 汪少雄, 刘少佳, 赵赫威. 氧化铝材料的强韧化研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(10): 1208-1222.
Tong Li, Bo Li, Han Zhang, Mingrui Gao, Yihan Zhong, Hengyang Guo, Shaoxiong Wang, Shaojia Liu, Hewei Zhao. Research Progress on Strengthening and Toughening of Alumina Materials★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(10): 1208-1222.
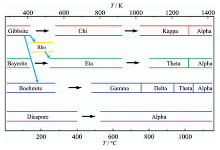

| 氧化铝多晶型物 | 晶体结构 | 晶格常数 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | α(º) | β(º) | Г(º) | ||
| α-Al2O3 | 三方 | 0.475 | 0.475 | 1.290 | 90 | 90 | 120 |
| γ-Al2O3 | 立方 | 0.792 | 0.792 | 0.792 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| δ-Al2O3 | 四方 | 0.502 | 0.502 | 0.986 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| θ-Al2O3 | 单斜 | 1.180 | 0.475 | 0.562 | 90 | 103 | 90 |
| ι-Al2O3 | 正交 | 0.773 | 0.761 | 0.292 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| κ-Al2O3 | 正交 | 0.370 | 1.220 | 0.286 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| σ-Al2O3 | 立方 | 0.794 | 0.794 | 0.794 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| 氧化铝多晶型物 | 晶体结构 | 晶格常数 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | α(º) | β(º) | Г(º) | ||
| α-Al2O3 | 三方 | 0.475 | 0.475 | 1.290 | 90 | 90 | 120 |
| γ-Al2O3 | 立方 | 0.792 | 0.792 | 0.792 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| δ-Al2O3 | 四方 | 0.502 | 0.502 | 0.986 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| θ-Al2O3 | 单斜 | 1.180 | 0.475 | 0.562 | 90 | 103 | 90 |
| ι-Al2O3 | 正交 | 0.773 | 0.761 | 0.292 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| κ-Al2O3 | 正交 | 0.370 | 1.220 | 0.286 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| σ-Al2O3 | 立方 | 0.794 | 0.794 | 0.794 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| α-Al2O3性质 | 密度/(g•cm-3) | 抗弯强度/MPa | 抗压强度/MPa | 弹性模量/GPa | 维氏硬度/GPa | 断裂韧性/(MPa•m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数值 | 3.99 | 300~480 | 280~350 | 366~410 | 19~25 | 2.7~4.5 |
| α-Al2O3性质 | 密度/(g•cm-3) | 抗弯强度/MPa | 抗压强度/MPa | 弹性模量/GPa | 维氏硬度/GPa | 断裂韧性/(MPa•m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数值 | 3.99 | 300~480 | 280~350 | 366~410 | 19~25 | 2.7~4.5 |
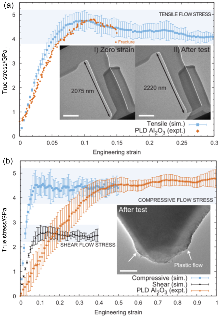



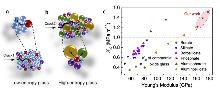


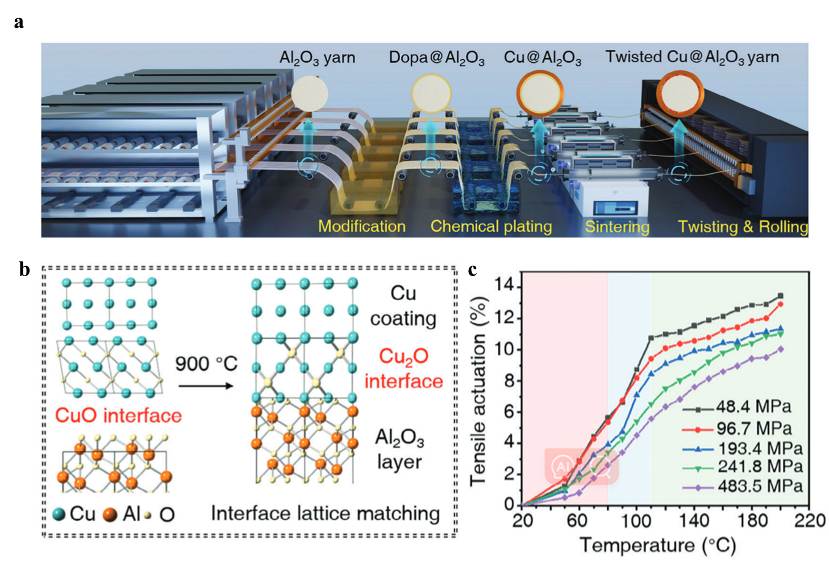

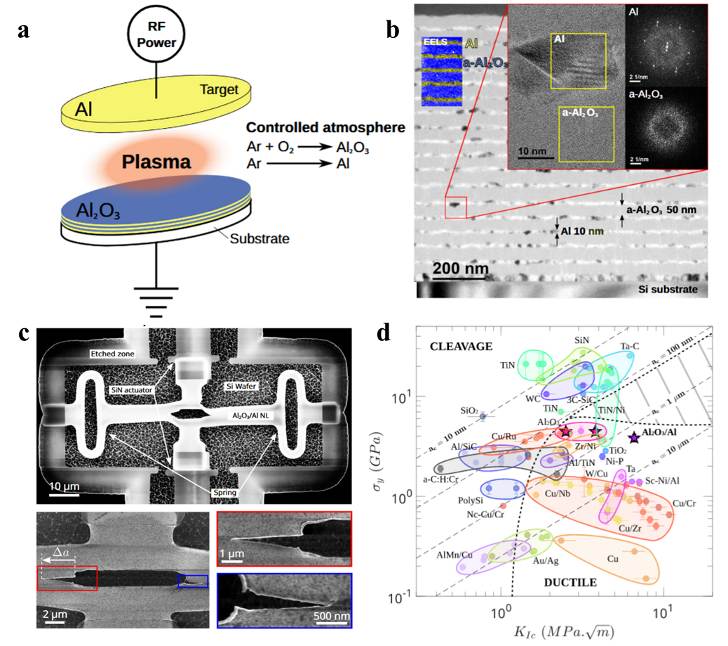












| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.1038/nmat3915 pmid: 24658117 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1557/jmr.2019.178 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.150 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
|
(王华高, 程群峰, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1231.)
doi: 10.6023/A23050207 |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
doi: 10.1039/d0nj05578f |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
doi: 10.1039/c8cs00321a pmid: 30444247 |
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
|
(李江, 潘裕柏, 刘珏, 曾燕萍, 郭景坤, 硅酸盐学报, 2009, 37, 270.)
|
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aav1254 pmid: 31727833 |
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
|
(高莹, 高名蕊, 赵赫威, 化学通报, 2024, 87, 1020.)
|
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1164865 pmid: 19056979 |
| [91] |
|
|
(白明敏, 李伟信, 洪毓鸿, 饶平根, 陶瓷学报, 2019, 40, 72.)
|
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [1] | 彭亚晶, 赵雨新, 杨金辉, 仉昕昕, 程佳玲. CsPbBrxI3-x全无机钙钛矿量子点的组分及浓度对电子结构及荧光性质影响研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(8): 879-886. |
| [2] | 邓沈娜, 彭常春, 牛云宏, 许云, 张云霄, 陈祥, 王红敏, 刘珊珊, 沈晓. 自由基Brook重排调控的α-氟烷基-α-硅基甲醇参与的烯烃双官能团化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 119-125. |
| [3] | 李晖, 殷亮. 一价铜催化的酮或酮亚胺的不对称烯丙基化反应研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(12): 1274-1288. |
| [4] | 贾凌轩, 詹泽庞, 贺紫晗, 狄重安, 朱道本. 面向神经电子接口器件的有机材料进展与展望★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1175-1186. |
| [5] | 高至亮, 李梦琦, 郝京诚, 崔基炜. 胶体粒子的机械性能调控及其在药物递送中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 1010-1020. |
| [6] | 贺续发, 贾康乐, 余龙飞, 刘明杰, 郑小珊, 李欢玲, 辛锦兰, 黄淋佳. 马来松香酸和纳米氧化铝颗粒协同稳定具有pH响应性的Pickering乳液[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 765-771. |
| [7] | 谢君瑶, 曾小明, 罗美明. 镍催化α,β-不饱和醛的选择性α,β-双芳基化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(9): 1118-1122. |
| [8] | 杜英喆, 张恒, 苑世领. Al2O3/PDMS复合材料热传导的分子动力学模拟[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 787-793. |
| [9] | 郭镇域, 周欢萍. 钙钛矿组分和结构设计及其发光二极管器件性能研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(3): 223-237. |
| [10] | 马国佳, 郑海坤, 常士楠, 王硕硕. 微纳结构超疏水表面的浸润性分析及设计[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(3): 269-277. |
| [11] | 姚坤, 刘浩, 袁乾家, 刘燕刚, 刘德龙, 张万斌. 钯催化三组分烯丙基串联反应: 化学专一性合成N-酰亚甲基-2-吡啶酮[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(10): 993-998. |
| [12] | 陈薪羽, 解俊杰, 王炜, 袁慧慧, 许頔, 张焘, 何云龙, 沈沪江. 钙钛矿材料组分调控策略及其光电器件性能研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(1): 9-23. |
| [13] | 赵克丽, 郝莹, 朱墨, 程国胜. 石墨烯材料生物降解的策略研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(3): 168-176. |
| [14] | 余思凡, 傅祥, 刘耿鑫, 邱晃, 胡文浩. 通过不对称多组分反应高效构建手性磺酰胺类化合物[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(11): 895-900. |
| [15] | 贾涛, 郑楠楠, 蔡万清, 应磊, 黄飞. 基于萘并二酰亚胺的胺基功能化聚合物的三组分一锅法合成及其在聚合物太阳电池中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(8): 808-818. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||