-
-
 封面介绍Zhao, Hewei et al. on page 1208-1222: When Al2O3 materials are subjected to external forces, the ionic bonds or covalent bonds within the material will inhibit the generation and movement of dislocations, resulting in a significant brittle fracture, thereby significantly restricting the large-scale application of Al2O3 materials in main load-bearing components. This review systematically summarizes the strengthening and toughening strategies of Al2O3 and Al2O3-based composites, including: phase regulation, compositional optimization, and bioinspired micro-nano structural design. It provides a theoretical basis and technical reference for the efficient construction of high-strength and high-toughness ceramic-based composites in the future.
封面介绍Zhao, Hewei et al. on page 1208-1222: When Al2O3 materials are subjected to external forces, the ionic bonds or covalent bonds within the material will inhibit the generation and movement of dislocations, resulting in a significant brittle fracture, thereby significantly restricting the large-scale application of Al2O3 materials in main load-bearing components. This review systematically summarizes the strengthening and toughening strategies of Al2O3 and Al2O3-based composites, including: phase regulation, compositional optimization, and bioinspired micro-nano structural design. It provides a theoretical basis and technical reference for the efficient construction of high-strength and high-toughness ceramic-based composites in the future. -
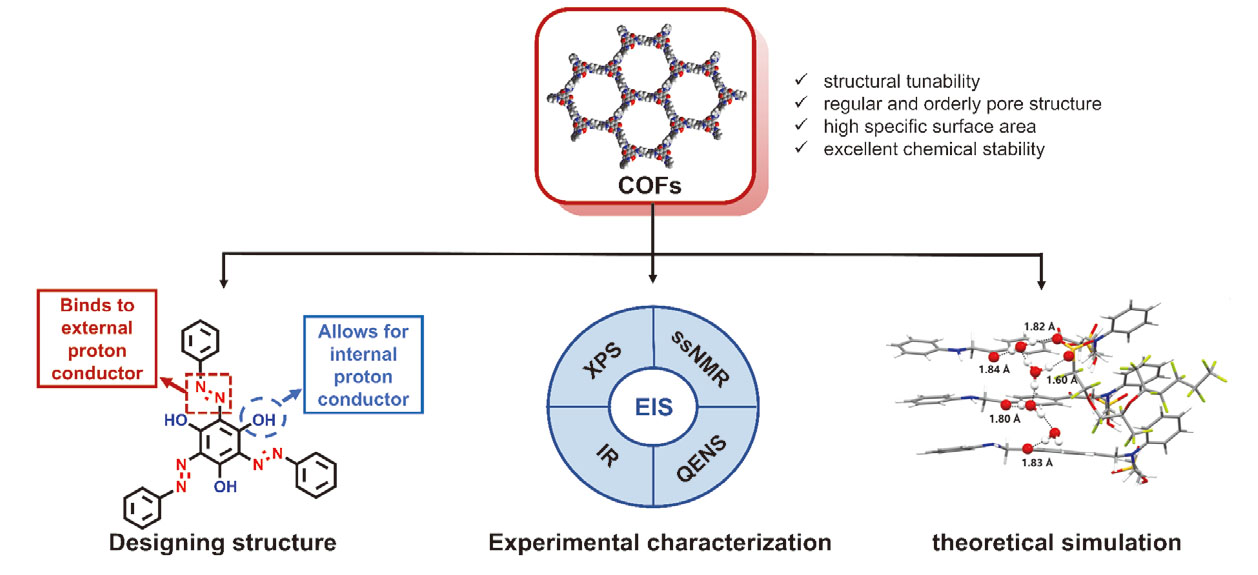
 封面介绍Feng, Xiao et al. on page 1223-1236: In covalent organic frameworks (COFs), the synergistic effect between highly ordered nanochannel architectures and precisely engineered functional groups constructs efficient proton transport pathways. These pathways highly facilitate the Grotthuss mechanism, which leads to a proton conductivity significantly superior to that of bulk water. This review introduces the proton conduction capacity of COFs from three perspectives: structural design, experimental characterization, and theoretical simulation, aiming to characterize the proton conduction performance and reveal the microscopic conduction mechanism of protons.
封面介绍Feng, Xiao et al. on page 1223-1236: In covalent organic frameworks (COFs), the synergistic effect between highly ordered nanochannel architectures and precisely engineered functional groups constructs efficient proton transport pathways. These pathways highly facilitate the Grotthuss mechanism, which leads to a proton conductivity significantly superior to that of bulk water. This review introduces the proton conduction capacity of COFs from three perspectives: structural design, experimental characterization, and theoretical simulation, aiming to characterize the proton conduction performance and reveal the microscopic conduction mechanism of protons. -
 封面介绍Wu, Yuchen & Gao, Hanfei & Wen, Wen et al. on page 1267-1284: This review systematically summarizes recent progress on the liquid-bridge-confined long-range-ordered assembly and their emerging applications in photoelectronic devices. By analyzing key mechanisms, interfacial phenomena, and design strategies, it provides comprehensive insights for understanding controllable nanoscale assembly and guiding next-generation optoelectronic device development.
封面介绍Wu, Yuchen & Gao, Hanfei & Wen, Wen et al. on page 1267-1284: This review systematically summarizes recent progress on the liquid-bridge-confined long-range-ordered assembly and their emerging applications in photoelectronic devices. By analyzing key mechanisms, interfacial phenomena, and design strategies, it provides comprehensive insights for understanding controllable nanoscale assembly and guiding next-generation optoelectronic device development.
-
-
本期栏目
目录
研究通讯
研究论文
研究展望
综述