化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (10): 1174-1183.DOI: 10.6023/A25060209 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2025-06-09
发布日期:2025-08-21
通讯作者:
高希珂
基金资助:
Diefeng Rena,b, Junjun Xiangb, Xike Gaob,*( )
)
Received:2025-06-09
Published:2025-08-21
Contact:
Xike Gao
Supported by:文章分享

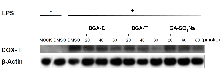
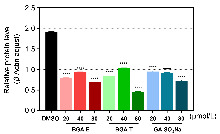
炎症介质释放失衡可诱发多种慢性疾病, 开发高效抗炎药物具有重要临床意义. 天然产物的桥联二聚体化可显著增强单体生物活性、选择性和稳定性. 本工作设计以天然双环倍半萜化合物愈创木薁(GA)为母体单元, 以三甘醇为连接片段, 合成了酯基和醚键连接的二聚体化合物(BGA-E和BGA-T), 并研究了新化合物与对比化合物(GA和愈创木薁磺酸钠)的抗炎和抗氧化活性. 通过1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)自由基清除法和铁离子还原抗氧化能力(FRAP)法检测了化合物的抗氧化能力; 采用Griess法、常规酶联免疫分析(ELISA)法和Western blot实验检测化合物对炎症因子的抑制效果; 使用Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)法检测了化合物的细胞毒性. 结果显示, 化合物BGA-T能高效抑制脂多糖(LPS)诱导的炎症因子白细胞介素6 (IL-6)的释放, IL-6的分泌量降至空白对照组的34.89%, 抑制效果为GA的8倍. BGA-T还通过下调环氧合酶(COX-Ⅱ)的表达发挥抗炎效果. 以上化合物均无明显细胞毒性. 该研究为基于天然产物的桥联二聚体设计及抗炎药物的研发提供了新思路.
任蝶沨, 向焌钧, 高希珂. 三甘醇桥联的愈创木薁二聚体的设计合成及抗炎、抗氧化活性研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(10): 1174-1183.
Diefeng Ren, Junjun Xiang, Xike Gao. Design, Synthesis, and Anti-inflammatory/Antioxidant Activities of Guaiazulene Dimers Bridged by Triethylene Glycol[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(10): 1174-1183.
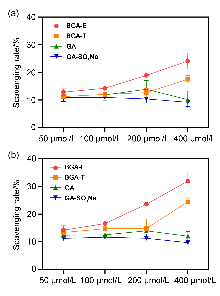

| 化合物 | 时间/h | 自由基清除率a/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 μmol•L−1 | 100 μmol•L−1 | 200 μmol•L−1 | 400 μmol•L−1 | ||
| BGA-E | 0.5 | 12.86 | 14.25 | 18.90 | 24.13 |
| 4 | 14.19 | 16.58 | 23.58 | 31.91 | |
| BGA-T | 0.5 | 11.25 | 12.06 | 12.70 | 17.52 |
| 4 | 13.35 | 14.72 | 14.83 | 24.44 | |
| GA | 0.5 | 11.84 | 11.86 | 13.88 | 10.15 |
| 4 | 12.35 | 12.51 | 13.91 | 12.03 | |
| GA-SO3Na | 0.5 | 10.86 | 10.95 | 10.40 | 9.20 |
| 4 | 11.23 | 11.64 | 11.24 | 9.69 | |
| 化合物 | 时间/h | 自由基清除率a/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 μmol•L−1 | 100 μmol•L−1 | 200 μmol•L−1 | 400 μmol•L−1 | ||
| BGA-E | 0.5 | 12.86 | 14.25 | 18.90 | 24.13 |
| 4 | 14.19 | 16.58 | 23.58 | 31.91 | |
| BGA-T | 0.5 | 11.25 | 12.06 | 12.70 | 17.52 |
| 4 | 13.35 | 14.72 | 14.83 | 24.44 | |
| GA | 0.5 | 11.84 | 11.86 | 13.88 | 10.15 |
| 4 | 12.35 | 12.51 | 13.91 | 12.03 | |
| GA-SO3Na | 0.5 | 10.86 | 10.95 | 10.40 | 9.20 |
| 4 | 11.23 | 11.64 | 11.24 | 9.69 | |
| 化合物 | OD值 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 μmol•L−1 | 100 μmol•L−1 | 200 μmol•L−1 | 400 μmol•L−1 | |
| BGA-E | 0.0685 | 0.0827 | 0.1011 | 0.1389 |
| BGA-T | 0.1005 | 0.1503 | 0.2267 | 0.3357 |
| GA | 0.1084 | 0.1772 | 0.3135 | 0.5741 |
| GA-SO3Na | 0.0955 | 0.1370 | 0.2090 | 0.3346 |
| 化合物 | OD值 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 μmol•L−1 | 100 μmol•L−1 | 200 μmol•L−1 | 400 μmol•L−1 | |
| BGA-E | 0.0685 | 0.0827 | 0.1011 | 0.1389 |
| BGA-T | 0.1005 | 0.1503 | 0.2267 | 0.3357 |
| GA | 0.1084 | 0.1772 | 0.3135 | 0.5741 |
| GA-SO3Na | 0.0955 | 0.1370 | 0.2090 | 0.3346 |
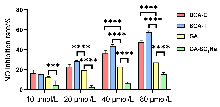

| 化合物 | 浓度/(μmol•L−1) | 抑制率a/% |
|---|---|---|
| BGA-E | 10 | 16.60 |
| 20 | 23.01 | |
| 40 | 36.23 | |
| 80 | 47.75 | |
| BGA-T | 10 | 15.61 |
| 20 | 28.57 | |
| 40 | 43.99 | |
| 80 | 57.92 | |
| GA | 10 | 12.88 |
| 20 | 19.52 | |
| 40 | 23.05 | |
| 80 | 27.19 | |
| GA-SO3Na | 10 | 4.49 |
| 20 | 2.85 | |
| 40 | 6.18 | |
| 80 | 15.32 | |
| 模型组 | — | 0 |
| 化合物 | 浓度/(μmol•L−1) | 抑制率a/% |
|---|---|---|
| BGA-E | 10 | 16.60 |
| 20 | 23.01 | |
| 40 | 36.23 | |
| 80 | 47.75 | |
| BGA-T | 10 | 15.61 |
| 20 | 28.57 | |
| 40 | 43.99 | |
| 80 | 57.92 | |
| GA | 10 | 12.88 |
| 20 | 19.52 | |
| 40 | 23.05 | |
| 80 | 27.19 | |
| GA-SO3Na | 10 | 4.49 |
| 20 | 2.85 | |
| 40 | 6.18 | |
| 80 | 15.32 | |
| 模型组 | — | 0 |
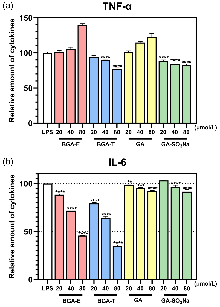

| 化合物 | 浓度/ (μmol•L−1) | 相对含量a/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | IL-6 | ||
| BGA-E | 20 | 101.71 | 88.40 |
| 40 | 105.33 | 71.76 | |
| 80 | 139.79 | 45.83 | |
| BGA-T | 20 | 94.47 | 79.25 |
| 40 | 89.67 | 63.89 | |
| 80 | 77.14 | 34.89 | |
| GA | 20 | 101.29 | 98.72 |
| 40 | 114.84 | 95.28 | |
| 80 | 122.68 | 92.17 | |
| GA-SO3Na | 20 | 88.96 | 103.13 |
| 40 | 84.68 | 96.59 | |
| 80 | 82.98 | 91.48 | |
| 模型组 | — | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 化合物 | 浓度/ (μmol•L−1) | 相对含量a/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | IL-6 | ||
| BGA-E | 20 | 101.71 | 88.40 |
| 40 | 105.33 | 71.76 | |
| 80 | 139.79 | 45.83 | |
| BGA-T | 20 | 94.47 | 79.25 |
| 40 | 89.67 | 63.89 | |
| 80 | 77.14 | 34.89 | |
| GA | 20 | 101.29 | 98.72 |
| 40 | 114.84 | 95.28 | |
| 80 | 122.68 | 92.17 | |
| GA-SO3Na | 20 | 88.96 | 103.13 |
| 40 | 84.68 | 96.59 | |
| 80 | 82.98 | 91.48 | |
| 模型组 | — | 100.00 | 100.00 |


| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01380 pmid: 27010926 |
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
pmid: 9306266 |
| [11] |
pmid: 12049221 |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
((a)
|
|
(李蕾, 朱聪聪, 朱权刚, 陈中建, 高希珂, 有机化学, 2022, 42, 2906.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202204025 |
|
|
((b)
|
|
|
肖梦佳, 高希珂, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 3246.).
|
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
|
(张晓雨, 李欣燕, 崔冰, 邵志晖, 赵铭钦, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 2885.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202301007 |
|
| [21] |
(a)
|
|
((b)
|
|
|
(李瑶, 陈丙年, 罗丹, 雷珊, 王力, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1318.)
doi: 10.6023/A23060276 |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1006/abio.1996.0292 pmid: 8660627 |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90101-0 pmid: 212198 |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2012.02096.x pmid: 22788664 |
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [1] | 王英辉, 王雨辉, 熊佳瑶, 苏思琪, 郝梦珂, 魏思敏. 葛根素纳米银合成及光热杀菌和促糖尿病感染伤口愈合作用研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(11): 1150-1161. |
| [2] | 陈其文, 张先正. 纳米酶介导的炎性肠道疾病治疗研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 1043-1051. |
| [3] | 殷雪旸, 顾恺, 邵正中. 载药蛋白质/聚苯硼酸复合纳米微球制备及其释药性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 116-123. |
| [4] | 李瑶, 陈丙年, 罗丹, 雷珊, 王力. 多酸型α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂的抗氧化性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1318-1326. |
| [5] | 赵晋源, 张乾, 王坚, 张琦, 李恒, 杜亚平. 活性氧捕获材料的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 570-580. |
| [6] | 尚阳, 肖检, 王雅雯, 彭羽. 不对称构筑二芳基次甲基立体中心的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(11): 1303-1319. |
| [7] | 周怡青, 肖友利. 活性天然产物靶标蛋白的鉴定[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(3): 177-189. |
| [8] | 杨鲍潮, 高栓虎. 光促进的山道年重排反应在复杂萜类天然产物全合成中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(3): 161-167. |
| [9] | 谭芬, 肖文精. 可见光促进的氧化还原催化反应在天然产物全合成中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(2): 85-89. |
| [10] | 于海昕, 万春云, 韩静, 李昂. 一种β-取代烯酮的α-溴代方法[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(11): 1488-1491. |
| [11] | 彭金宝, 后小军, 张书宇, 涂永强. 8-epi-Liphagal的合成研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(21): 2232-2235. |
| [12] | 潘成学, 关一富, 张洪彬. Brazilin类似物的合成[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(02): 183-189. |
| [13] | 赵芳, 梁慧, 程惠, 王军. 大黄酸金属配合物的合成、表征及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(08): 925-930. |
| [14] | 陈炜, 陈艳雪, 安平, 李阳, 闫喜龙, 陈立功. 新型树枝状受阻胺光稳定剂的设计、合成及性能评价[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(23): 2487-2492. |
| [15] | 陈战国, 王传宁, 赵朋飞, 王芸, 周利燕. 2-甲基苯并咪唑基异黄酮衍生物的合成及抗氧化活性[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(22): 2347-2355. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||