化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (6): 751-754.DOI: 10.6023/A21050200 上一篇 下一篇
研究通讯
卢小彪a, 肖茜a, 万常峰a,*( ), 汪志勇b, 刘晋彪c
), 汪志勇b, 刘晋彪c
投稿日期:2021-05-10
发布日期:2021-05-28
通讯作者:
万常峰
基金资助:
Xiaobiao Lua, Xi Xiaoa, Changfeng Wana( ), Zhiyong Wangb, Jinbiao Liuc
), Zhiyong Wangb, Jinbiao Liuc
Received:2021-05-10
Published:2021-05-28
Contact:
Changfeng Wan
Supported by:文章分享
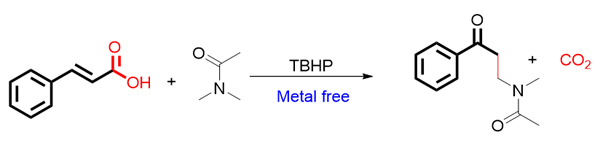
碳-碳键的构建是有机反应中最常见的一类反应, 也是构建有机化合物骨架最常用的手段. 近些年, 通过脱羧反应来构建碳-碳键, 碳-杂原子键得到了广泛而深入的研究. 肉桂酸类化合物的脱羧偶联反应也得到了较多的关注. 这类反应一般包括两个过程, 自由基加成和羧基的脱去, 从而得到新的有机化合物. 这类反应的特点是用氧化剂产生自由基, 在反应过程产生二氧化碳和水为副产物, 相比使用卤代试剂或者有机金属试剂来说, 更为绿色. 作者在之前的研究过程基础上发现, 在无需任何金属催化剂的条件下, 只用过氧叔丁醇(有机溶剂)作为氧化剂, 肉桂酸类衍生物和酰胺类能够发生脱羧氧化偶联反应, 实现C(sp3)―C(sp3)键的生成. 该反应特点是没有用过渡金属盐作为催化剂, 符合绿色化学的发展要求.
卢小彪, 肖茜, 万常峰, 汪志勇, 刘晋彪. 无金属条件下的肉桂酸类和酰胺的脱羧氧化偶联反应构建碳-碳键[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 751-754.
Xiaobiao Lu, Xi Xiao, Changfeng Wan, Zhiyong Wang, Jinbiao Liu. Direct C—C Bond Formation through Decarboxylative Oxidative Cross-Coupling of Cinnamic Acids with Amides under Metal-Free Condition[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(6): 751-754.
| [1] |
(a) Crabtree, R. H. The Organometallic Chemistry of Transition Metals, 4th ed., Wiley Interscience, New York, 2005, pp. 1~560.
|
|
(b) McQuillin, F. J.; Parker, D. G.; Stephenson, G. R. Transition Metal Organometallics for Organic Synthesis, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K., 1991, pp.1~614.
|
|
| [2] |
(a) Saito, B.; Fu, G. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9602.
doi: 10.1021/ja074008l |
|
(b) Li, S. H.; Lin, Y. J.; Cao, J. G.; Zhang, S. B. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 4067.
doi: 10.1021/jo0626257 |
|
|
(c) Gurung, S. K.; Thapa, S.; Kafle, A.; Dickie, D. A.; Giri, R. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 1264.
doi: 10.1021/ol500310u |
|
| [3] |
(a) Heck, R. F.; Nolley, J. P. J. Org. Chem. 1972, 37, 2320.
doi: 10.1021/jo00979a024 pmid: 21677934 |
|
(b) Beletskaya, I. P.; Cheprakov, A. V. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 3009.
doi: 10.1021/cr9903048 pmid: 21677934 |
|
|
(c) Cartney, D. M.; Guiry, P. J. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5122.
doi: 10.1039/c1cs15101k pmid: 21677934 |
|
| [4] |
(a) Li, C. J. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 335.
doi: 10.1021/ar800164n |
|
(b) Xie, Y. X.; Song, R. J.; Xiang, J. N.; Li, J. H. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 32, 1555. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc1204017 |
|
|
(谢叶香, 宋仁杰, 向建南, 李金恒, 有机化学, 2012, 32, 1555.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc1204017 |
|
|
(c) Liao, G.; Wu, Y. J.; Shi, B. F. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 289. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20020027 |
|
|
(廖港, 吴勇杰, 史炳锋, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 289.)
doi: 10.6023/A20020027 |
|
|
(d) Zhang, H. H.; Yu, S. Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 832. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19050177 |
|
|
(张洪浩, 俞寿云, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 832.)
doi: 10.6023/A19050177 |
|
|
(e) Xiao, L.; Li, J. H.; Wang, T. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 841. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
(肖丽, 李嘉恒, 王挺, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 841.)
doi: 10.6023/A19050183 |
|
|
(f) Cheng, Z. M.; Chen, P. H.; Liu, G. S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77,856. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
(成忠明, 陈品红, 刘国生, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 856.)
doi: 10.6023/A19070252 |
|
|
(g) Yang, Q. L.; Wang, X. Y.; Weng, X. J.; Yang, X.; Xu, X. T.; Tong, X. F.; Fang, P.; Wu, X. Y.; Mei, T. S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 866. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
(杨启亮, 王向阳, 翁信军, 杨祥, 徐学涛, 童晓峰, 方萍, 伍新燕, 梅天胜, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 866.)
doi: 10.6023/A19040135 |
|
|
(h) Xiao, Y. X.; Liu, Z. Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 874. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19050189 |
|
|
(肖莹霞, 柳忠全, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 874.)
doi: 10.6023/A19050189 |
|
|
(i) Zhao, Y.; Li, S. H.; Zhang, M. M.; Liu, F. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 916. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
(赵勇, 李施宏, 张苗苗, 刘峰, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 916.)
doi: 10.6023/A19040121 |
|
|
(j) Wu, Y. J.; Shi, B. F. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40,3517. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
(吴勇杰, 史炳锋, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 3517.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202003057 |
|
|
(k) Yuan, X. Y.; Yang, G. P.; Yu, B. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40,3620. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
(袁晓亚, 杨国平, 於兵, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 3620.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202006068 |
|
|
(l) Jiang, X. L.; Hao, J. Q.; Zhou, G. Q.; Hou, C. C.; Hu, F. D. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 39,1811. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
(姜晓蕾, 郝佳奇, 周国庆, 侯程程, 胡芳东, 有机化学, 2019, 39, 1811.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201902019 |
|
|
(m) Li, X. F.; Xiong, W. K.; Ding, Q. P. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 39, 1867. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
(李小芳, 熊伟康, 丁秋平, 有机化学, 2019, 39, 1867.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201901029 |
|
|
(n) Wang, R. H.; Luan, Y. X.; Ye, M. C. Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 720.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v37.7 |
|
|
(o) Shi, Z. J.; Wang, L. H.; Cui, X. L. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 39, 1596. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201902001 |
|
|
(施兆江, 王连会, 崔秀灵, 有机化学, 2019, 39, 1596.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201902001 |
|
|
(p) Shi, B. F.; Zhang, Y. H.; Lam, J. K.; Wang, D. H.; Yu, J. Q. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 460.
doi: 10.1021/ja909571z |
|
| [5] |
(a) Nieman, J. A.; Coleman, J. E.; Wallace, D. J.; Piers, E.; Lim, L. Y.; Roberge, M.; Andersen, R. J. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 183.
pmid: 12702571 |
|
(b) Loganzo, F.; Discafani, C. M.; Annable, T.; Beyer, C.; Musto, S.; Hari, M.; Tan, X. Z.; Hardy, C.; Hernandez, R.; Baxter, M.; Singanallore, T.; Khafizova, G.; Poruchynsky, M. S.; Fojo, T.; Nieman, J. A.; Ayral-Kaloustian, S.; Zask, A.; Andersen, R. J.; Greenberger, L. M. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1838.
pmid: 12702571 |
|
| [6] |
(a) Heitz, D. R.; Tellis, J. C.; Molander, G. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 12715.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b04789 |
|
(b) Kawasaki, T.; Ishida, N.; Murakami, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 3366.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b13920 |
|
|
(c) Si, X. J.; Zhang, L. M.; Hashmi, A. S. K. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 6329.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b02226 |
|
|
(d) Fan, X. Z.; Rong, J. W.; Wu, H. L.; Zhou, Q.; Deng, H. P.; Tan, J. D.; Xue, C. W.; Wu, L. Z.; Tao, H. R.; Wu, J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 8514.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.28 |
|
|
(e) Wang, J.; Li, J.; Huang, J. B.; Zhu, Q. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 3017.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.6b00096 |
|
|
(f) Zhong, R.; Xu, Y.; Sun, M. M.; Wang, Y. R. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 5255.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c00150 |
|
| [7] |
(a) Tang, R. Y.; Xie, Y. X.; Xie, Y. L.; Xiang, J. N.; Li, J. H. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12867.
doi: 10.1039/c1cc15397h |
|
(b) Shepherd, N. E.; Tanabe, H.; Xu, Y. J.; Matsunaga, S.; Shibasaki, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 3666.
doi: 10.1021/ja1002636 |
|
|
(c) Mitchell, E. A.; Peschiulli, A.; Lefevre, N.; Meerpoel, L.; Maes, B. U. W. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 10092.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201201539 |
|
|
(d) Dai, C. H.; Meschini, F.; Narayanam, J. M. R.; Stephenson, C. R. J. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 4425.
doi: 10.1021/jo300162c |
|
|
(e) Li, G. C.; Qian, S. Y.; Wang, C. X.; You, J. S. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7837.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v52.30 |
|
| [8] |
(a) Zhang, J. X.; Wang, Y. J.; Wang, N. X.; Zhang, W.; Bai, C. B.; Li, Y. H.; Wen, J. L. Synlett 2014,249.
|
|
(b) Yan, H.; Lu, L. H.; Rong, G. W.; Liu, D. F.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Mao, J. C. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 7103.
doi: 10.1021/jo501274f |
|
| [9] |
Ye, W. B.; Yan, Z. C.; Wan, C. F.; Hou, H. Q.; Wang, Z. Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 99. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A17110519 |
|
(叶文波, 晏子聪, 万常峰, 侯豪情, 汪志勇, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 99.)
doi: 10.6023/A17110519 |
|
| [10] |
Yang, X. H.; Wei, W. T.; Li, H. B.; Song, R. J.; Li, J. H. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12867.
doi: 10.1039/C4CC05051G |
| [1] | 翟彤仪, 葛畅, 钱鹏程, 周波, 叶龙武. Brønsted酸催化炔酰胺分子内氢烷氧化/Claisen重排反应★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1101-1107. |
| [2] | 王瑞祥, 赵庆如, 顾庆, 游书力. 金/铱接力催化炔基酰胺环化/不对称烯丙基苄基化串联反应★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 431-434. |
| [3] | 何倩, 李杰, 喻思佳, 吴东坪, 叶剑良, 黄培强. 铱催化叔酰胺与呋喃硅醚间的类插烯Aldol缩合反应: γ-亚苄基-丁烯酸内酯的合成★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1265-1270. |
| [4] | 李善武, 朱陈宇杰, 罗尹豪, 张亚茹, 滕汉明, 王宗瑞, 甄永刚. 酰胺与酰亚胺类n型有机半导体材料的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(12): 1600-1617. |
| [5] | 方婧, 赵文娟, 张明浩, 方千荣. 一种新型酰胺功能化的共价有机框架用于选择性染料吸附[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 186-191. |
| [6] | 杜重阳, 陈耀峰. 二乙基锌促进CO2的硅氢化反应以及CO2为C1合成子的有机胺甲酰化或脲化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(9): 938-944. |
| [7] | 梁欢, 苟阿龙, 高珠鹏, 雷林生, 王博文, 余兰, 徐学涛, 王少华. 铜催化的α-氨基丙二腈的脱氰氧代反应:一种合成叔酰胺的新方法[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(10): 1064-1068. |
| [8] | 刘文强, 杨修龙, 佟振合, 吴骊珠. S—H键和N—H键交叉偶联放氢制备亚磺酰胺[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(9): 861-865. |
| [9] | 靳继康, 张凤莲, 汪义丰. 路易斯碱-硼自由基促进的邻苯二甲酰亚胺类羧酸酯的Giese反应和Barton脱羧反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(9): 889-894. |
| [10] | 李忠原, 景昆, 李祁利, 王官武. 钯催化的2-苯氧基吡啶导向的脱羧酯基化反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(8): 729-734. |
| [11] | 王昱赟, 刘云云. 无金属催化的吡啶C2位碳-氢键胺甲酰化反应合成吡啶甲酰胺[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(5): 418-421. |
| [12] | 张硕, 侯梓桐, 宋子贺, 苏晓峰, 王峰, 于一涛, 彭丹, 崔仕麒, 刘一帆, 王佳睿, 宋建军. Zn/Ni双金属接力催化:一锅法分子内环异构化/分子间酰胺化反应构建噁唑衍生物[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(11): 1168-1172. |
| [13] | 尹欣驰, 江游, 楚士颖, 翁国锋, 方向, 潘远江. 气相中铜催化的脱羧碘化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(6): 436-439. |
| [14] | 黄培强. 酰胺直接转化:策略与近期进展[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(5): 357-365. |
| [15] | 叶文波, 晏子聪, 万常峰, 侯豪情, 汪志勇. 一种新的肉桂酸类化合物的脱羧/甲基化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(2): 99-102. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||