化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (7): 749-756.DOI: 10.6023/A23040108 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 庆祝《化学学报》创刊90周年合辑
研究论文
投稿日期:2023-04-01
发布日期:2023-05-12
作者简介:基金资助:
Tianjiao Ma( ), Jin Li, Xiaodong Ma, Xuesong Jiang(
), Jin Li, Xiaodong Ma, Xuesong Jiang( )
)
Received:2023-04-01
Published:2023-05-12
Contact:
*E-mail: About author:Supported by:文章分享
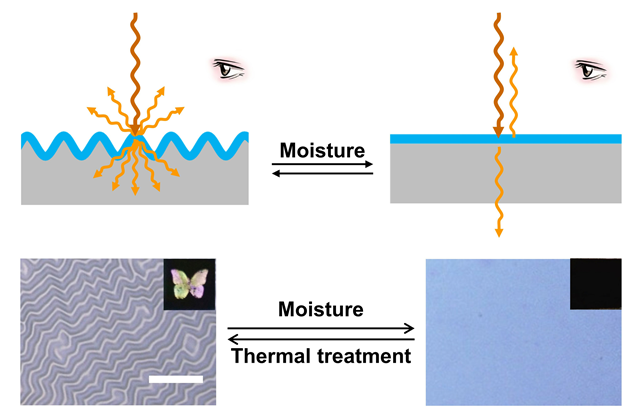
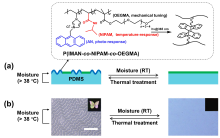
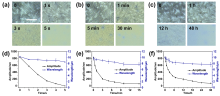
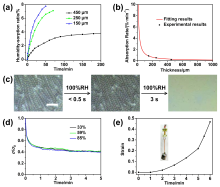
本工作利用光响应温敏聚合物构筑了温控湿度响应褶皱图案, 并探索其响应机制与应用. 将1-乙烯基-3-蒽甲基氯化咪唑鎓(IMAN)、N-异丙基丙烯酰胺(NIPAM)与聚乙二醇甲醚甲基丙烯酸酯(OEGMA)三元共聚物P(IMAN-co-NIPAM-co-OEGMA)作为表层, 与聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)基底形成双层褶皱体系. 蒽基团的光二聚交联能够使体系区域选择性起皱, 含NIPAM结构的聚合物链则赋予其温度控制的湿度响应性. 在室温、加湿条件下, 该褶皱图案消失, 其响应机制是聚合物吸湿过程中的模量降低和应力松弛; 而在较高温度下, 褶皱图案无法由湿度擦除, 这是由于顶层聚合物链疏水性增强所导致的. 这种同时具有光敏性与温度控制的湿度响应性褶皱图案, 在湿度传感、智能显示、智能窗户等领域具有潜在的应用前景.
马天骄, 李瑾, 马晓东, 姜学松. 温度调控的动态湿度响应褶皱图案★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 749-756.
Tianjiao Ma, Jin Li, Xiaodong Ma, Xuesong Jiang. Temperature-controlled Dynamic Moisture-responsive Wrinkled Patterns★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(7): 749-756.



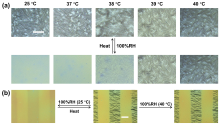



| [1] |
Bowden N.; Brittain S.; Evans A. G.; Hutchinson J. W.; Whitesides G. M. Nature 1998, 393, 146.
doi: 10.1038/30193 |
| [2] |
Chung J. Y.; Nolte A. J.; Stafford C. M. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 349.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201001759 |
| [3] |
Khang D. Y.; Jiang H.; Huang Y.; Rogers J. A. Science 2006, 311, 208.
doi: 10.1126/science.1121401 |
| [4] |
Jiang H.; Khang D. Y.; Song J.; Sun Y.; Huang Y.; Rogers J. A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 15607.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702927104 |
| [5] |
Zhou L.; Hu K.; Zhang W.; Meng G.; Yin J.; Jiang X. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1247.
doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwaa052 |
| [6] |
Hou H.; Yin J.; Jiang X. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1025.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00623 |
| [7] |
Chen S.; Yan S.; Yin J.; Jiang X. Acta Polym. Sin. 2021, 52, 1245.
|
| [8] |
Rodríguez-Hernández J. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 42, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2014.07.008 |
| [9] |
Tan Y. L.; Hu B. R.; Song J.; Chu Z. Y.; Wu W. J. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 101.
doi: 10.1007/s40820-020-00436-y |
| [10] |
Wang Q. M.; Zhao X. H. MRS Bull. 2016, 41, 115.
doi: 10.1557/mrs.2015.338 |
| [11] |
Kong X.; Wang X.; Chen J.; Yao Y.; Lin S. J. Funct. Polym. 2017, 30, 259.
|
| [12] |
Xu Z.; Xie X.; Shen H.; Guo Y.; Yang L.; Ge D. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica 2021, 38, 3151.
|
| [13] |
Lee S. G.; Lee D. Y.; Lim H. S.; Lee D. H.; Lee S.; Cho K. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 5013.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v22.44 |
| [14] |
Wang J.; Zheng Y.; Li L.; Liu E.; Zong C.; Zhao J.; Xie J.; Xu F.; Konig T. A. F.; Grenzer Saphiannikova M.; Cao Y.; Fery A.; Lu C. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25595.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b07349 |
| [15] |
Xu C.; Stiubianu G. T.; Gorodetsky A. A. Science 2018, 359, 1495.
doi: 10.1126/science.aar5191 |
| [16] |
Ma T.; Bai J.; Li T.; Chen S.; Ma X.; Yin J.; Jiang X. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2021, 118, e2114345118.
|
| [17] |
Ma T.; Zhou L.; Hua J.; Li J.; Ma X.; Qiao W.; Yin J.; Jiang X. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 16949.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c03235 |
| [18] |
Ma T.; Chen S.; Li J.; Yin J.; Jiang X. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 2233.
doi: 10.1039/D2MH00603K |
| [19] |
Efimenko K.; Rackaitis M.; Manias E.; Vaziri A.; Mahadevan L.; Genzer J. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 293.
doi: 10.1038/nmat1342 |
| [20] |
Kang J.; Wang C.; Xue Z.; Liu M.; Tan H. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 103503.
doi: 10.1063/1.4962429 |
| [21] |
Huang X.; Sun Y.; Soh S. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4062.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201501578 |
| [22] |
Chan E. P.; Smith E. J.; Hayward R. C.; Crosby A. J. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 711.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4095 |
| [23] |
Lee H.; Lee B. P.; Messersmith P. B. Nature 2007, 448, 338.
doi: 10.1038/nature05968 |
| [24] |
Hou H.; Hu K.; Lin H.; Forth J.; Zhang W.; Russell T. P.; Yin J.; Jiang X. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1803463.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v30.36 |
| [25] |
Hou H.; Li F.; Su Z.; Yin J.; Jiang X. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 8765.
doi: 10.1039/C7TC02569F |
| [26] |
Hou H.; Yin J.; Jiang X. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9126.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201602105 |
| [27] |
Kim H. S.; Crosby A. J. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4188.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201101477 |
| [28] |
Li F.; Hou H.; Yin J.; Jiang X. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar5762.
|
| [29] |
Li T.; Hu K.; Ma X.; Zhang W.; Yin J.; Jiang X. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906712.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v32.7 |
| [30] |
Ma T.; Li T.; Zhou L.; Ma X.; Yin J.; Jiang X. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1811.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15600-6 |
| [31] |
Shou H.; Ma T.; Li T.; Chen S.; Ma X.; Yin J.; Jiang X. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 5810.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v27.18 |
| [32] |
Zeng S.; Li R.; Freire S. G.; Garbellotto V. M. M.; Huang E. Y.; Smith A. T.; Hu C.; Tait W. R. T.; Bian Z.; Zheng G.; Zhang D.; Sun L. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700828.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201700828 |
| [33] |
Zhou L.; Yang L.; Liu Y.; Xu Z.; Yin J.; Ge D.; Jiang X. Adv. Optical Mater. 2020, 8, 2000234.
doi: 10.1002/adom.v8.12 |
| [34] |
Zong C.; Zhao Y.; Ji H.; Han X.; Xie J.; Wang J.; Cao Y.; Jiang S.; Lu C. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3931.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v55.12 |
| [35] |
Chen S.; Ma T.; Bai J.; Ma X.; Yin J.; Jiang X. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2002372.
doi: 10.1002/advs.v7.22 |
| [36] |
Li J.; Li T.; Ma X.; Su Z.; Yin J.; Jiang X. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 1704.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c15099 |
| [37] |
Chen S.; Hu K.; Yan S.; Ma T.; Deng X.; Zhang W.; Yin J.; Jiang X. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 2186.
doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2022.10.016 |
| [38] |
Zhang Y.; Li T.; Ma X.; Yin J.; Jiang X. Acta Polym. Sin. 2021, 52, 61.
|
| [39] |
Mai Y. J. Funct. Polym. 2018, 31, 302.
|
| [40] |
Cakmak O.; El Tinay H. O.; Chen X.; Sahin O. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800596.
doi: 10.1002/admt.v4.8 |
| [41] |
Zhang Y.; Jiang H.; Li F.; Xia Y.; Lei Y.; Jin X.; Zhang G.; Li H. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 14604.
doi: 10.1039/C7TA04208F |
| [42] |
Han D. D.; Liu Y. Q.; Ma J. N.; Mao J. W.; Chen Z. D.; Zhang Y. L.; Sun H. B. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1800258.
doi: 10.1002/admt.v3.12 |
| [43] |
Ru J.; Zhu Z.; Wang Y.; Chen H.; Bian C.; Luo B.; Li D. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 02lt01.
|
| [44] |
Sun Q.; Ayela C.; Thuau D. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 2201349.
|
| [45] |
Xue J.; Ge Y.; Liu Z.; Liu Z.; Jiang J.; Li G. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 10836.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c24018 |
| [46] |
Zain H. A.; Batumalay M.; Rahim H. R. A.; Yasin M.; Harun S. W. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2022, 6, 3500704.
|
| [47] |
Kumar P.; Sakla R.; Ghosh A.; Jose D. A. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 25600.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b05335 |
| [48] |
Lv X.; Li Y.; Li P.; Yang M. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 135, 581.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2008.10.008 |
| [49] |
Cho M. Y.; Kim I. S.; Kim M. J.; Hyun D. E.; Koo S. M.; Sohn H.; Kim N. Y.; Kim S.; Ko S.; Oh J. M. Sensors 2022, 22, 5178.
doi: 10.3390/s22145178 |
| [50] |
Choi S. J.; Yu H.; Jang J. S.; Kim M. H.; Kim S. J.; Jeong H. S.; Kim I. D. Small 2018, 14, 1703934.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v14.13 |
| [51] |
Borini S.; White R.; Wei D.; Astley M.; Haque S.; Spigone E.; Harris N.; Kivioja J.; Ryhanen T. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 11166.
doi: 10.1021/nn404889b |
| [52] |
Casalbore-Miceli G.; Yang M. J.; Li Y.; Zanelli A.; Martelli A.; Chen S.; She Y.; Camaioni N. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 114, 584.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2005.05.023 |
| [53] |
Yeo T. L.; Sun T.; Grattan K. T. V.; Parry D.; Lade R.; Powell B. D. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 110, 148.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2005.01.033 |
| [1] | 梁广玲, 叶晓亮, 王观娥, 徐刚. 原位烷基化调控无机-有机杂化类钙钛矿材料的结构及其性能※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 460-466. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||