化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (12): 1216-1225.DOI: 10.6023/A24080246 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
鞠嘉浩a,b, 徐吉磊b,*( ), 王康军a,*(
), 王康军a,*( ), 黄家辉b
), 黄家辉b
投稿日期:2024-08-21
发布日期:2024-11-06
基金资助:
Jiahao Jua,b, Jilei Xub( ), Kangjun Wanga(
), Kangjun Wanga( ), Jiahui Huangb
), Jiahui Huangb
Received:2024-08-21
Published:2024-11-06
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:文章分享
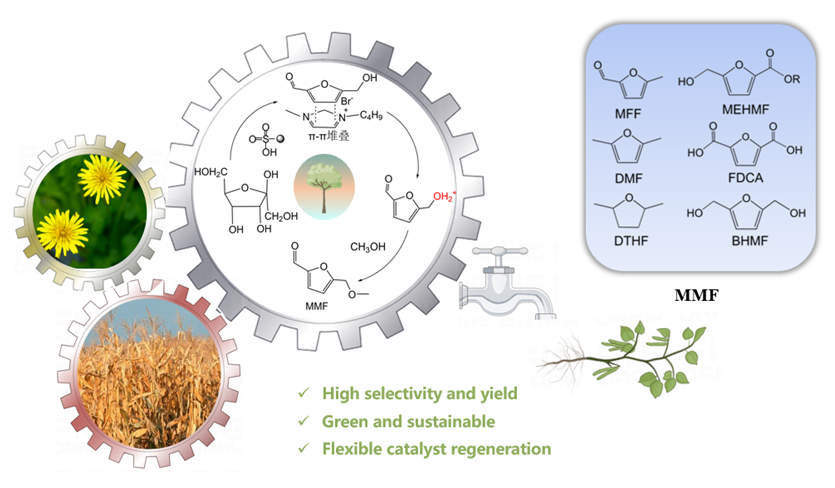
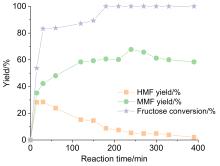
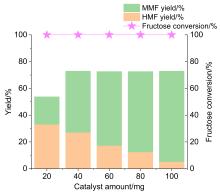
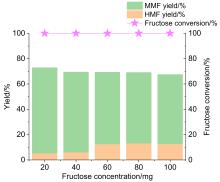
5-甲氧基甲基-2-呋喃甲醛(MMF)是一种重要的生物基平台分子, 可作为燃料添加剂和用于制备多种化合物. 本工作利用一系列商业强酸性树脂催化剂, 以离子液体和甲醇为共溶剂, 实现了从果糖一步法向MMF的转化. 离子液体与中间产物5-羟甲基糠醛(HMF)之间具有强相互作用, 可以减少HMF自身缩合等副反应的发生, 提高MMF的产率. 在最佳反应条件下, 果糖的转化近乎完全, MMF的产率达到67.7%, HMF与MMF的总产率达到接近75%. 使用BET表面分析技术、红外光谱、元素分析及酸碱滴定技术对使用前后的催化剂进行表征, 证实了催化剂失活的可能机制是胡敏覆盖催化剂活性位点、树脂催化剂与离子液体之间的离子交换及催化剂酸性位点的微量脱落. 探索出合适的催化剂再生方案, 实现了催化剂的稳定循环. 此外, 本催化体系还可以将其它碳水化合物中的果糖组分高效转化为MMF, 为生物质转化制备MMF的产业化奠定了一定的研究基础.
鞠嘉浩, 徐吉磊, 王康军, 黄家辉. 果糖一步法制备5-甲氧基甲基-2-呋喃甲醛及树脂催化剂再生方法探究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(12): 1216-1225.
Jiahao Ju, Jilei Xu, Kangjun Wang, Jiahui Huang. One-step Preparation of 5-(Methoxymethyl)-2-furaldehyde from Fructose and Regeneration of Resin Catalyst[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(12): 1216-1225.
| Entry | Catalyst | Fructose conversion/% | HMF yield/% | MMF yield/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Blank | 34.6 | 0.3 | 0 |
| 2 | DA-330 | 100 | 4.9 | 62.3 |
| 3 | DB-757 | 100 | 5.8 | 60.9 |
| 4 | DNW-Ⅱ | 100 | 11.7 | 58.5 |
| 5 | [BMIM]Cl+H2SO4 | 100 | 1.6 | 53.7 |
| 6 | [BMIM]Cl+TsOH | 100 | 4.2 | 61.7 |
| 7 | [BMIM]Cl+TfOH | 100 | 1.7 | 55.8 |
| 8 | 盐酸 | 100 | 1.6 | 46.9 |
| 9 | 硫酸 | 100 | 1.3 | 33.3 |
| 10 | 对甲苯磺酸 | 100 | 0.1 | 9.8 |
| 11 | 三氟甲基磺酸 | 100 | 0.5 | 40.1 |
| Entry | Catalyst | Fructose conversion/% | HMF yield/% | MMF yield/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Blank | 34.6 | 0.3 | 0 |
| 2 | DA-330 | 100 | 4.9 | 62.3 |
| 3 | DB-757 | 100 | 5.8 | 60.9 |
| 4 | DNW-Ⅱ | 100 | 11.7 | 58.5 |
| 5 | [BMIM]Cl+H2SO4 | 100 | 1.6 | 53.7 |
| 6 | [BMIM]Cl+TsOH | 100 | 4.2 | 61.7 |
| 7 | [BMIM]Cl+TfOH | 100 | 1.7 | 55.8 |
| 8 | 盐酸 | 100 | 1.6 | 46.9 |
| 9 | 硫酸 | 100 | 1.3 | 33.3 |
| 10 | 对甲苯磺酸 | 100 | 0.1 | 9.8 |
| 11 | 三氟甲基磺酸 | 100 | 0.5 | 40.1 |
| Entry | Resin | NaOH volume consumed/mL | Acid content/ (mmol•g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DA-330 | 5.9 | 11.8 |
| 2 | DB-757 | 5.8 | 11.6 |
| 3 | DNW-Ⅱ | 4.8 | 9.6 |
| Entry | Resin | NaOH volume consumed/mL | Acid content/ (mmol•g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DA-330 | 5.9 | 11.8 |
| 2 | DB-757 | 5.8 | 11.6 |
| 3 | DNW-Ⅱ | 4.8 | 9.6 |
| Entry | Cosolvent | Fructose conversion/% | HMF yield/% | MMF yield/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 甲醇 | 100 | 0 | 0.3 |
| 2 | 乙腈 | 100 | 2.8 | 50.5 |
| 3 | DMF | 100 | 30.7 | 8.7 |
| 4 | NMP | 100 | 0 | 59 |
| 5 | DMSO | 100 | 0.3 | 35.0 |
| 6 | THF | 100 | 0 | 7.2 |
| 7 | [BMIM]Br | 100 | 4.9 | 62.3 |
| 8 | [BMIM]Cl | 100 | 7.9 | 60.1 |
| Entry | Cosolvent | Fructose conversion/% | HMF yield/% | MMF yield/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 甲醇 | 100 | 0 | 0.3 |
| 2 | 乙腈 | 100 | 2.8 | 50.5 |
| 3 | DMF | 100 | 30.7 | 8.7 |
| 4 | NMP | 100 | 0 | 59 |
| 5 | DMSO | 100 | 0.3 | 35.0 |
| 6 | THF | 100 | 0 | 7.2 |
| 7 | [BMIM]Br | 100 | 4.9 | 62.3 |
| 8 | [BMIM]Cl | 100 | 7.9 | 60.1 |





| Entry | Sample | S% | N% | C% | H% | C/N | C/H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DA-330 | 13.3 | 0.04 | 43.1 | 5.6 | 1066.5 | 7.8 |
| 2 | Used DA-330 | 9.6 | 6.5 | 51.2 | 6.5 | 7.8 | 7.8 |
| 3 | Generated DA-330 | 12.8 | 0.7 | 45.8 | 5.1 | 61.7 | 9.0 |
| Entry | Sample | S% | N% | C% | H% | C/N | C/H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DA-330 | 13.3 | 0.04 | 43.1 | 5.6 | 1066.5 | 7.8 |
| 2 | Used DA-330 | 9.6 | 6.5 | 51.2 | 6.5 | 7.8 | 7.8 |
| 3 | Generated DA-330 | 12.8 | 0.7 | 45.8 | 5.1 | 61.7 | 9.0 |
| Entry | Sample | Surface area/(m2•g-1) | Pore volume/(cm3•g-1) | Pore size/nm | Acid content/(mmol•g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DA-330 | 7.2 | 0.007 | 68.5 | 11.8 |
| 2 | Used DA-330 | 10.5 | 0.003 | 68.4 | 6.6 |
| 3 | Generated DA-330 | 13.0 | 0.006 | 61.8 | 12.0 |
| Entry | Sample | Surface area/(m2•g-1) | Pore volume/(cm3•g-1) | Pore size/nm | Acid content/(mmol•g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DA-330 | 7.2 | 0.007 | 68.5 | 11.8 |
| 2 | Used DA-330 | 10.5 | 0.003 | 68.4 | 6.6 |
| 3 | Generated DA-330 | 13.0 | 0.006 | 61.8 | 12.0 |
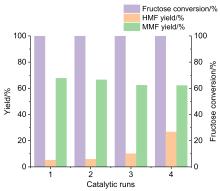

| Entry | Substrate | Conversion/% | HMF yield/% | MMF yield/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Glucose | 100 | 6.6 | 0.1 |
| 2 | Inulin | 100 | 12.3 | 49.4 |
| 3 | Starch | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | Sucrose | 100 | 7.3 | 34.1 |
| Entry | Substrate | Conversion/% | HMF yield/% | MMF yield/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Glucose | 100 | 6.6 | 0.1 |
| 2 | Inulin | 100 | 12.3 | 49.4 |
| 3 | Starch | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | Sucrose | 100 | 7.3 | 34.1 |
| [1] |
Huber, G. W.; Ibarra, S. Acc. Chem. Res. 2006, 106, 4044.
|
| [2] |
Srirangan, K.; Akawi, L.; Moo-Young, M. Appl. Energy 2012, 100, 172.
|
| [3] |
Guo, J.-R.; Zhang, S.-Y.; He, Y.-H.; Ren, S.-X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2024, 82, 242. (in Chinese)
|
|
(郭建荣, 张书玉, 贺宇辉, 任世学, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 242.)
doi: 10.6023/A23120542 |
|
| [4] |
Gao, J.-B.; Lu, Y.-Q.; Zhang, H.; Gao, L.-Z.; Xiong, X.-Q. Chinese J. Org. Chem. 2024, 44, 2732. (in Chinese)
|
|
(高晋斌, 陆颖琪, 张辉, 高立柱, 熊兴泉, 有机化学, 2024, 44, 2732.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202312011 |
|
| [5] |
Fu, J.; Lin, G.-B.; Fan, H.-A.; Chen, C.; Li, B.-L.; Zhan, Y.; Zhao, X.-Z. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 1862.
|
| [6] |
Li, N.; Zong, M.-H.; Li, Y.; Shi, S.-S. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 1437.
|
| [7] |
Pfab, E.; Filiciotto, L.; Romero, A. A.; Luque, R. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 16065.
|
| [8] |
Bicker, M.; Kaiser, D.; Ott, L.; Vogel, H. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2005, 36, 118.
|
| [9] |
Balakrishnan, M.; Sacia, E. R.; Bell, A. T. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1626.
|
| [10] |
Zhang, Z.-H.; Wang, Y.-M.; Fang, Z.-F.; Liu, B. ChemPlusChem 2014, 79, 233.
|
| [11] |
Yuan, Z.-L.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Zheng, J.-D.; Lin, J.-T. Fuel 2015, 150, 236.
|
| [12] |
Che, P.-H.; Lu, F.; Zhang, J.-Z.; Huang, Y.-Z.; Nie, X.; Gao, J. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 119, 433.
|
| [13] |
Yin, S.; Sun, J.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Z.-H. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 4992.
|
| [14] |
Liu, B.; Zhang, Z.-H. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 12313.
|
| [15] |
Lai, L.-K.; Zhang, Y.-G. ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 1745.
|
| [16] |
Kraus, G. A.; Guney, T. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1593.
|
| [17] |
Nie, Y.-F.; Hou, Q.-D.; Qian, H.-L.; Bai, X.-Y.; Xia, T.-L.; Yu, G.-J.; Ju, M.-T. Renewable Energy. 2022, 192, 279.
|
| [18] |
Dai, J.-H.; Du, Z.-T.; Cao, Q.-Y.; Yang, R.-H.; Yang, D.-L.; Li, J.-L. Mol. Catal. 2024, 599, 114112.
|
| [19] |
Guo, H.-X.; Qi, X.-H.; Shen, F. ACS Sustainable Chem. 2022, 10, 9002.
|
| [20] |
Guranix, G. J. M.; Dautzenberg, F.CN101400666A (B) 2007 [Chem. Abstr. 2007, 147, 367433].
|
| [21] |
Shibasaki-Kitakawa, N.; Honda, H.; Kuribayashi, H. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 416.
|
| [22] |
Figueira, M.; Reig, M.; de Labastida, M. F. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 314, 114984.
|
| [23] |
Li, S.-S.; Li, N.; Wang, W.; Li, G.-Y.; Chen, F. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 1218.
|
| [24] |
Zhu, H.; Cao, Q.; Li, C.-H.; Mu, X.-D. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 2016.
|
| [25] |
Fu, J.; Yang, H.; Zhou, F.; Li, J.; Ma, H.-X.; Chen, K.-Q.; Lu, X.-Y. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 4905.
|
| [26] |
Gao, F.; Bai, R.; Ferlin, F.; Vaccaro, L.; Li, M.; Gu, Y. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 6240.
|
| [27] |
Anushree, S.; Ramsingh, K.; Kanti, D. M.; Kumar, S. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 2021, 262, 120144.
|
| [28] |
Xiang, Y.-P.; Wen, S.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, K.-Y.; Guo, D.-W.; Cheng, F.; Xu, Q.; Liu, X.-X.; Yin, D.-L. RSC Adv. 2011, 11, 3585.
|
| [29] |
Kashbora, M. M.; Sutarmaa, D.; Railtona, J.; Liu, X. Appl. Catal., A 2022, 642, 118689.
|
| [30] |
Hoang, T. M. C.; Lefferts, L.; Seshan, K. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 1651.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.201300446 pmid: 23939662 |
| [31] |
Yu, Y.-M. Journal of Shengli College China University of Petroleum. 2007, 4, 21. (in Chinese)
|
|
(于颖敏, 中国石油大学胜利学院学报, 2007, 4, 21.)
|
|
| [32] |
Ren, Y.-S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Lin, J. T. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 1127.
|
| [33] |
Li, R.-P.; Wang, Y.-P.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Zhang, F.-T.; Zeng, W.; Tang, M.-H.; Xiang, J.-F.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Han, B.-X.; Liu, Z.-M. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 14216.
|
| [1] | 贺乾军, 张晨杰, 徐敏敏, 袁亚仙, 姚建林. 电化学SERS研究离子液体/金属界面水吸附行为的阳离子亲水性效应[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(12): 1202-1208. |
| [2] | 曾少娟, 孙雪琦, 白银鸽, 白璐, 郑爽, 张香平, 张锁江. CO2捕集分离的功能离子液体及材料研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 627-645. |
| [3] | 刘稳, 王昱捷, 杨慧琴, 李成杰, 吴娜, 颜洋. 离子液体非共价诱导制备碳纳米管/石墨烯集流体用于钠金属负极[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1379-1386. |
| [4] | 李晓倩, 张靖, 苏芳芳, 王德超, 姚东东, 郑亚萍. 多孔离子液体的构筑及应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 848-860. |
| [5] | 舒恒, 包义德日根, 那永. CdS基纳米管光催化氧化5-羟甲基糠醛选择性生成2,5-呋喃二甲醛[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(5): 607-613. |
| [6] | 武文俊, 李玉婷, 冯茜, 丁文星. 钙钛矿双功能钝化剂: 室温离子液体的机械化学制备[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(11): 1469-1475. |
| [7] | 王赫男, 张安歌, 张仲, 田洪瑞, 岳倩, 赵雪, 鹿颖, 刘术侠. 基于稀土阳离子和多酸阴离子的系列纯无机离子液体的合成及性质[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(7): 920-924. |
| [8] | 吕玉苗, 陈伟, 王艳磊, 霍锋, 董依慧, 魏莉, 何宏艳. 离子液体二维结构制备及其特性研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 443-458. |
| [9] | 王引航, 李伟, 罗沙, 刘守新, 马春慧, 李坚. 离子液体固载型功能材料的应用研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(2): 85-94. |
| [10] | 邱华玉, 赵井文, 周新红, 崔光磊. 离子液体-无机颗粒杂化电解质在二次电池中的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(10): 749-756. |
| [11] | 张川, 张鲁嘉, 张洋, 黄和, 胡燚. 基于分子模拟的离子液体修饰Porcine Pancreas脂肪酶催化性能和稳定性的相关研究[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(1): 74-80. |
| [12] | 何学侠, 刘富才, 曾庆圣, 刘政 . 二维材料双电层场晶体管的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(9): 924-935. |
| [13] | 冷明浩, 陈仕谋, 张军玲, 郎海燕, 康艳红, 张锁江. 含羰基有机添加剂对AlCl3-[Emim]Cl电沉积铝的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(5): 403-408. |
| [14] | 钱文静, 袁超, 郭江娜, 严锋. 聚离子液体功能材料研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(4): 310-315. |
| [15] | 刘梦莹, 车佳宁, 吴蔚闳, 卢运祥, 彭昌军, 刘洪来, 卢浩, 杨强, 汪华林. 功能性离子液体萃取水溶液中Cu2+:实验与理论[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(2): 116-125. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||