Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (4): 377-389.DOI: 10.6023/A24120382 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
卢一林a,*( ), 董盛杰b,*(
), 董盛杰b,*( ), 崔方超c, 薄婷婷d, 毛卓e
), 崔方超c, 薄婷婷d, 毛卓e
投稿日期:2024-12-27
发布日期:2025-03-17
基金资助:
Yi-Lin Lua( ), Shengjie Dongb(
), Shengjie Dongb( ), Fangchao Cuic, Tingting Bod, Zhuo Maoe
), Fangchao Cuic, Tingting Bod, Zhuo Maoe
Received:2024-12-27
Published:2025-03-17
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:Share
Yi-Lin Lu, Shengjie Dong, Fangchao Cui, Tingting Bo, Zhuo Mao. Theoretical Construction of Hittorf’s Violet Phosphorene/SnS2 van der Waals Heterojunction as Direct Photocatalyst for Overall Water Splitting[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(4): 377-389.
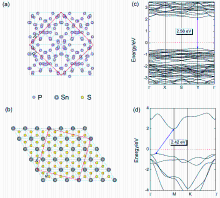


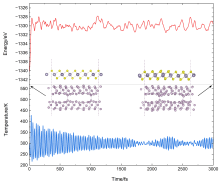

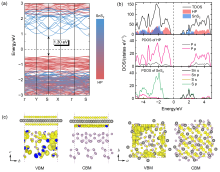

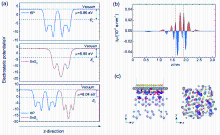

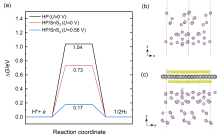

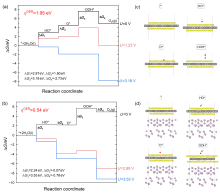

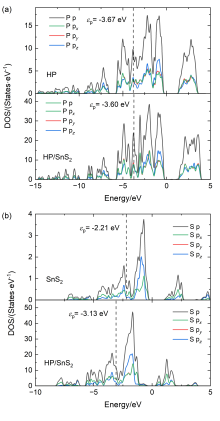

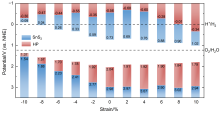

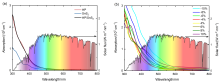

| [1] |
Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Nature 1972, 238, 37.
|
| [2] |
Zheng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Zhu, Y. H.; Li, L. H.; Han, Y.; Chen, Y.; Du, A. J.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S. Z. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3783.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms4783 pmid: 24769657 |
| [3] |
Voiry, D.; Shin, H. S.; Loh, K. P.; Chhowalla, M. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 0105.
|
| [4] |
Jin, H.; Guo, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Vasileff, A.; Jiao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Qiao, S.-Z. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 6337.
|
| [5] |
Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yin, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, W.; Chi, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 1148. (in Chinese)
|
|
(吴宇晗, 张栋栋, 尹宏宇, 陈正男, 赵文, 匙玉华, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1148.)
doi: 10.6023/A23040155 |
|
| [6] |
Huang, G.; Li, K.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, Y.; Gao, H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2024, 82, 314. (in Chinese)
|
|
(黄广峥, 李坤玮, 罗艳楠, 张强, 潘远龙, 高洪林, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 314.)
doi: 10.6023/A23110484 |
|
| [7] |
Hou, F.; Liu, F.; Wu, H.; Qasim, M.; Chen, Y.; Duan, Y.; Feng, Z.; Liu, M. Chinese J. Chem. 2022, 41, 173.
|
| [8] |
Liu, J.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 884. (in Chinese)
|
|
(刘建川, 李翠艳, 刘耀祖, 王钰杰, 方千荣, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 884.)
doi: 10.6023/A23040132 |
|
| [9] |
Wang, D.; Lan, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yin, K.; Yang, L.; Bai, L.; Wei, D.; Yang, H.; Chen, H.; Luo, M. Chinese J. Chem. 2024, 43, 308.
|
| [10] |
Fong, C. Y.; Cohen, M. L. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 5, 3095.
|
| [11] |
Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, H. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 174, 123.
|
| [12] |
Wei, R.; Hu, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Li, J. Acta Mater. 2014, 66, 163.
|
| [13] |
Guo, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 7331.
|
| [14] |
Lin, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, C.; Liu, W.; Mi, X.; Fan, D.; Fan, F.; Lu, H.; Chen, X. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 961.
|
| [15] |
Sun, L.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.; Liang, Y.; Wu, P. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 484.
|
| [16] |
Moniz, S. J. A.; Shevlin, S. A.; Martin, D. J.; Guo, Z.-X.; Tang, J. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 731.
|
| [17] |
Marschall, R. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2421.
|
| [18] |
Nasir, J. A.; Munir, A.; Ahmad, N. T. u.; Haq, Z.; Khan, Z.; Rehman, Z. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2105195.
|
| [19] |
Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, D. Solar RRL 2021, 5, 2000397.
|
| [20] |
Chen, X.; Han, W.; Yue, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, Y.; Peng, C.; Yin, H. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 17954.
|
| [21] |
Chen, C.; Shen, M.; Li, Y. Chem. Phys. 2021, 548, 111230.
|
| [22] |
Wang, J.; Luan, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.; Fan, J.; Ni, L.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Tian, Y. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2023, 155, 107225.
|
| [23] |
Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, T.; Chang, J.; Chen, H. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 2785.
|
| [24] |
Zhang, L.; Huang, H.; Zhang, B.; Gu, M.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, X.; Li, L.; Zhou, J.; Wu, K.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1074.
|
| [25] |
Schusteritsch, G.; Uhrin, M.; Pickard, C. J. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 2975.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b05068 pmid: 27110837 |
| [26] |
Ricciardulli, A. G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Samorì, P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 3660.
|
| [27] |
Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Gu, M.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, K.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 8586.
|
| [28] |
Lu, Y. L.; Dong, S.; Zhou, W.; Dai, S.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, H.; Wu, P. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 11967.
|
| [29] |
Lu, Y.-L.; Dong, S. J.; Li, J. S.; Mao, Z.; Wu, Y. Q.; Yang, L.-L. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2022, 169, 110863.
|
| [30] |
Wang, X.; Ma, M.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F. Small Structures 2023, 4, 2300123.
|
| [31] |
Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, R.; Du, W.; Wu, B.; Lei, W.; Yu, J.; Liu, G.; Tan, T.; Zheng, L.; Liu, X. Nano Today 2023, 51, 101885.
|
| [32] |
Zhao, X.; Gu, M.; Zhai, R.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, J. Small 2023, 19, 2302859.
|
| [33] |
Li, H.; Li, R.; Jing, Y.; Liu, B.; Xu, Q.; Tan, T.; Liu, G.; Zheng, L.; Wu, L. Z. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 7308.
|
| [34] |
Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F. Small 2024, 20, 2311841.
|
| [35] |
Lu, Y.-L.; Dong, S.; Cui, F.; Zhang, K.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Mao, Z. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 101, 222.
|
| [36] |
Lu, Y. L.; Dong, S.; He, H.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Wu, P. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2019, 163, 209.
|
| [37] |
Sun, Y.; Cheng, H.; Gao, S.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Lei, F.; Yao, T.; He, J.; Wei, S.; Xie, Y. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8727.
|
| [38] |
Liu, J.; Hua, E. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 25827.
|
| [39] |
Sun, Y.; Cheng, H.; Gao, S.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Lei, F.; Yao, T.; He, J.; Wei, S.; Xie, Y. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8727.
|
| [40] |
Zhang, R.; Sun, F. W.; Zhang, Z. H.; Liu, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.; Guo, T. T.; Fan, J. B.; Ni, L.; Duan, L. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 535, 147825.
|
| [41] |
Wang, Y. L.; Tian, Y.; Lang, Z. L.; Guan, W.; Yan, L. K. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 21056.
|
| [42] |
Zhang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Liu, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.; Duan, L. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 5873.
|
| [43] |
Zhang, Y.; Qiang, Z. B.; Ding, J. X.; Xie, K. X.; Duan, L.; Ni, L. CrystEngComm 2024, 26, 2621.
|
| [44] |
Wang, F.; Yang, C. L.; Wang, M. S.; Ma, X. J. Power Sources 2022, 532, 231352.
|
| [45] |
Garg, P.; Rawat, K. S.; Bhattacharyya, G.; Kumar, S.; Pathak, B. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 4238.
|
| [46] |
Peng, B.; Xu, L.; Zeng, J.; Qi, X.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, L. L.; Shuai, C. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 3059.
|
| [47] |
Bouziani, I.; Essaoudi, I.; Ahuja, R.; Ainane, A. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 35542.
|
| [48] |
He, C.; Han, F.; Zhang, W. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 404.
|
| [49] |
Zhang, W. X.; Yin, Y.; He, C. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 5064.
|
| [50] |
Dai, Z. N.; Sheng, W.; Xu, Y. J. At. Mol. Phys. 2024, 41, 061001. (in Chinese)
|
|
(戴卓旎, 盛威, 许英, 原子与分子物理学报, 2024, 41, 061001.)
|
|
| [51] |
Wang, J.; Chang, K.; Sun, Z.; Lee, J. H.; Tackett, B. M.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J. G.; Liu, C. J. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 251, 162.
|
| [52] |
Xu, K.; Huang, X.; Yang, Z. H. J. At. Mol. Phys. 2025, 42, 061002. (in Chinese)
|
|
(许康, 黄欣, 杨志红, 原子与分子物理学报, 2025, 42, 061002.)
|
|
| [53] |
Xia, F.; Yang, F. Energ. Fuel. 2022, 36, 4992.
|
| [54] |
Wirth, J.; Neumann, R.; Antonietti, M.; Saalfrank, P. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 15917.
|
| [55] |
Zhai, P.; Xia, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Gao, J.; Zhang, B.; Cao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Fan, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Miller, J. T.; Sun, L.; Hou, J. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4587.
|
| [56] |
Zhang, X.; Chen, A.; Zhang, Z.; Jiao, M.; Zhou, Z. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 11446.
|
| [57] |
Zhao, Y.; Ma, D.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Y. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 20432.
|
| [58] |
Yuan, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhou, W. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 123, 526.
|
| [59] |
Zhou, S.; Yang, X.; Pei, W.; Liu, N.; Zhao, J. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 10876.
doi: 10.1039/c8nr01090k pmid: 29616270 |
| [60] |
Pei, W.; Zhou, S.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, J. Carbon 2018, 133, 260.
|
| [61] |
Fu, C. F.; Sun, J.; Luo, Q.; Li, X.; Hu, W.; Yang, J. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 6312.
|
| [62] |
Liang, K.; Wang, J.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Duan, L. Physica E 2024, 155, 115825.
|
| [63] |
Xu, L.; Yang, Y.; Xin, C.; Jin, Z.; Chao, Y.; Wu, C.; Luo, K. W.; Wang, L. L.; Chen, T. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 109667.
|
| [64] |
Chen, X.; Han, W.; Jia, M.; Ren, F.; Peng, C.; Gu, Q.; Wang, B.; Yin, H. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2022, 55, 215502.
|
| [65] |
Chen, X.; Han, W.; Tian, Z.; Yue, Q.; Peng, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Yin, H.; Gu, Q. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 6347.
|
| [66] |
Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, R558.
|
| [67] |
Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 49, 14251.
doi: 10.1103/physrevb.49.14251 pmid: 10010505 |
| [68] |
Blochl, P. E. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 17953.
|
| [69] |
Perdew, J. P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865 pmid: 10062328 |
| [70] |
Monkhorst, H. J.; Pack, J. D. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188.
|
| [71] |
Grimme, S. J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1787.
|
| [72] |
Heyd, J.; Scuseria, G. E.; Ernzerhof, M. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 8207.
|
| [73] |
Martyna, G. J.; Klein, M. L.; Tuckerman, M. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 2635.
|
| [1] | Minghui Chen, Boxin Zhang, Tao Wei, Zhaoxue Sun, Yaqing Feng, Bao Zhang. Theoretical Calculation Studies on Interlayer Displacement Behavior and Photogenerated Carrier Dynamics of Covalent Triazine Frameworks [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(2): 93-100. |
| [2] | Ying Ma, Weixi Chen, Yuchen Liu, Ziyi Liu, Tao Wu, An-Hui Lu, Dongqi Wang. Density Functional Theory Study of Hexagonal Boron Nitride Oxidation Mode [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(1): 52-59. |
| [3] | Yuqing Zhao, Dong Liang, Jihui Jia, Rongmin Yu, Can-Zhong Lu. Synthesis and Characterization of an Emissive Ag(I) Complex with a D-A Type Ligand Containing Two Electron-withdrawing Groups [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(5): 486-492. |
| [4] | Yu-Qiang Zhao, Xia Zhang, Yunru Yang, Liping Zhu, Ying Zhou. Design and Synthesis of Aggregation-Induced Emission Photocage Molecules for In Situ Photoactivation Imaging Studies [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(3): 265-273. |
| [5] | Guanglong Huang, Xiao-Song Xue. Computational Study on the Mechanism of Chen’s Reagent as Trifluoromethyl Source [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 132-137. |
| [6] | Yichen Huang, Changming Nie, Congzhi Wang, Shusen Chen, Yan Song, Hao Li, Weiqun Shi. Theoretical Study of Hydroxyl- and Amino-substituted Amidoxime Ligands for Extraction of Uranium from Seawater [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(10): 1050-1057. |
| [7] | Xuefeng Liang, Jian Jing, Xin Feng, Yongze Zhao, Xinyuan Tang, Yan He, Lisheng Zhang, Huifang Li. Electronic Structure of Covalent Organic Frameworks COF66 and COF366: from Monomers to Two-Dimensional Framework [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(7): 717-724. |
| [8] | Lei Yang, Jiaoyang Ge, Fangli Wang, Wangyang Wu, Zongxiang Zheng, Hongtao Cao, Zhou Wang, Xueqin Ran, Linhai Xie. A Theoretical Study on the Effective Reduction of Internal Reorganization Energy Based on the Macrocyclic Structure of Fluorene [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 613-619. |
| [9] | Jie Yang, Lin Ling, Yuxue Li, Long Lu. Density Functional Theory Study on Thermal Decomposition Mechanisms of Ammonium Perchlorate [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(4): 328-337. |
| [10] | Shaoqin Zhang, Meiqing Li, Zhongjun Zhou, Zexing Qu. Theoretical Study on the Multiple Resonance Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Process [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(2): 124-130. |
| [11] | Jinjing Liu, Na Yang, Li Li, Zidong Wei. Theoretical Study on the Regulation of Oxygen Reduction Mechanism by Modulating the Spatial Structure of Active Sites on Platinum★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(11): 1478-1485. |
| [12] | Wenchao Bi, Linfeng Zhang, Jian Chen, Ruixue Tian, Hao Huang, Man Yao. Lithiation Mechanism and Performance of Monoclinic ZnP2 Anode Materials [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(6): 756-764. |
| [13] | Xuefei Luan, Congzhi Wang, Liangshu Xia, Weiqun Shi. Theoretical Studies on the Interaction of Uranyl with Carboxylic Acids and Oxime Ligands [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(6): 708-713. |
| [14] | Luocong Wang, Zhewei Li, Caiwei Yue, Peihuan Zhang, Ming Lei, Min Pu. Theoretical Study on the Isomerization Mechanism of Azobenzene Derivatives under Electric Field [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(6): 781-787. |
| [15] | Yinghui Wang, Simin Wei, Jinwei Duan, Kang Wang. Mechanism of Silyl Enol Ethers Hydrogenation Catalysed by Frustrated Lewis Pairs: A Theoretical Study [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(9): 1164-1172. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||