Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (12): 1425-1437.DOI: 10.6023/A21070341 Previous Articles Next Articles
Review
刘毅川a,b, 刘雅兰b, 姜仕林b, 李梅a,*( ), 石伟群b,*(
), 石伟群b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2021-07-23
发布日期:2021-09-13
通讯作者:
李梅, 石伟群
作者简介: |
刘毅川,哈尔滨工程大学博士研究生,主要从事熔盐中锕系镧系化学研究. |
 |
刘雅兰, 中国科学院高能物理研究所副研究员, 研究方向为锕系镧系熔盐化学, 多年来致力于氧化物乏燃料干法后处理领域, 聚焦于锕-镧分离研究. 首先开展了锕、镧系氧化物在熔盐中的溶解及其电化学行为研究, 随后在固态活性铝阴极上进行了锕-镧的电化学分离, 并采用原位光谱技术监测了分离过程中锕、镧元素的化学种态变化, 发现了铀的循环电解并将其消除, 提高了电流效率. 最终成功实现了锕-镧元素的有效分离, 与传统的液态Cd阴极相比将分离因子提高了两个数量级. 在此基础上, 进一步总结了锕、镧氧化物在氯化物熔盐中的溶解规律, 提出了利用其溶解性差异实现一步分离的新方法. 基于相关工作,在电化学领域与核能领域著名期刊Electrochim. Acta, J. Electrochem. Soc., Electrochem. Commun.和J. Nucl. Mater.等上共发表论文40余篇, 其中第一作者及通讯作者论文20篇. |
 |
姜仕林, 中国科学院高能物理研究所博士研究生, 主要从事锕系镧系熔盐电化学研究. |
 |
李梅, 哈尔滨工程大学教授, 国家自然科学基金通讯评审专家, 教育部学位与研究生教育评估专家. Electrochimica Acta, Journal of The Electrochemical Society, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, Journal of Nuclear Materials, ACS inoganic Chemistry, ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering等国际期刊审稿人. 近来年发表SCI检索论文60余篇, 其中以第一/通讯作者在Electrochimica Acta, Journal of The Electrochemical Society, Journal of Nuclear Materials, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, RSC Advances等期刊上发表SCI收录论文40余篇. 申请专利12项, 获授权发明专利6项, 获省部级二等奖1项. |
 |
石伟群, 中国科学院高能物理研究所研究员, 国家杰出青年科学基金获得者, 长期致力于核燃料循环化学与锕系元素化学相关基础研究, 在JACS, Angew. Chem., Chem, CCS Chem., Nat. Commun, Adv. Mater., Environ. Sci. Technol.等国际知名期刊发表SCI论文200余篇, 成果被国内外同行广泛关注和引用, 文章总引8000余次, H因子46 (Google Scholar). 分别担任英文期刊Journal of Nuclear Fuel Cycle and Waste Technology和Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology的编委与国际顾问编委, 中文期刊《核化学与放射化学》编委. 现为中国化学会核化学与放射化学专业委员会委员、中国核学会锕系物理与化学分会副理事长、中国有色金属学会熔盐化学与技术专业委员会副主任委员、中国核学会核化工分会理事兼副秘书长. |
基金资助:
Yichuan Liua,b, Yalan Liub, Shilin Jiangb, Mei Lia( ), Weiqun Shib(
), Weiqun Shib( )
)
Received:2021-07-23
Published:2021-09-13
Contact:
Mei Li, Weiqun Shi
Supported by:Share
Yichuan Liu, Yalan Liu, Shilin Jiang, Mei Li, Weiqun Shi. Recent Progress on Chemical Species of Uranium in Molten Chlorides[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(12): 1425-1437.
| 铀离子价态 | 吸收波长/nm | 摩尔消光系数/ (L•mol-1•cm-1) |
|---|---|---|
| U3+ | 480 | 1260 |
| 570 | 963 | |
| U4+ | 455 | 8.87 |
| 605 | 4.88 | |
| 670 | 6.47 | |
| UO2+ | 395 | 832 |
| 775 | 15.9 | |
| 620 | 12.5 | |
| UO22+ | 450 | 57.2 |
| 铀离子价态 | 吸收波长/nm | 摩尔消光系数/ (L•mol-1•cm-1) |
|---|---|---|
| U3+ | 480 | 1260 |
| 570 | 963 | |
| U4+ | 455 | 8.87 |
| 605 | 4.88 | |
| 670 | 6.47 | |
| UO2+ | 395 | 832 |
| 775 | 15.9 | |
| 620 | 12.5 | |
| UO22+ | 450 | 57.2 |
| 熔盐组成(物质的量比) | E(U4+/U3+)/mV | E(U3+/U0)/mV |
|---|---|---|
| LiCl | –131 | –1477 |
| LiCl-SrCl2([Li]∶[Sr]=88.9∶11.1) | –131 | –1478 |
| CsCl | –97.5 | –1137 |
| CsCl-SrCl2([Cs]∶[Sr]=78.6∶21.4) | –107 | –1077 |
| 熔盐组成(物质的量比) | E(U4+/U3+)/mV | E(U3+/U0)/mV |
|---|---|---|
| LiCl | –131 | –1477 |
| LiCl-SrCl2([Li]∶[Sr]=88.9∶11.1) | –131 | –1478 |
| CsCl | –97.5 | –1137 |
| CsCl-SrCl2([Cs]∶[Sr]=78.6∶21.4) | –107 | –1077 |
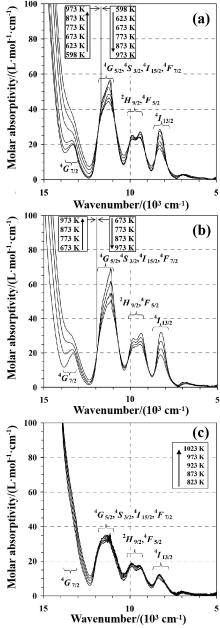

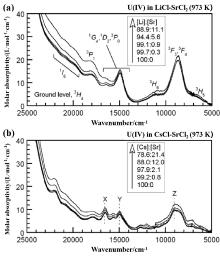
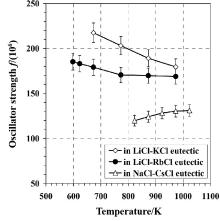
| 离子类型 | 跃迁轨道 | 吸收带/cm-1 | 跃迁类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| U4+ | 5f2-5f16d1 | >25000 | — |
| 5f2-5f2 | 22000~20000 | 1I6 ← 3H4 | |
| 18000 | 3P1 ← 3H4 | ||
| 16500~14900 | 1G4, 1D2, 3P0 ←3H4 | ||
| 13000~10500 | 3H6 ← 3H4 | ||
| 8600 | 3F3, 3F4 ← 3H4 | ||
| 7500~5500 | 3H5 ← 3H4 | ||
| U3+ | 5f3-5f26d1 | 25000~14000 | — |
| 5f3-5f3 | 13300 | 4G7/2 ←4I9/2 | |
| 11500~11200 | 4G5/2, 4S3/2, 4I15/2, 4F7/2 ←4I9/2 | ||
| 9800~9400 | 2H9/2, 4F5/2 ←4I9/2 | ||
| 8250 | 4I13/2 ←4I9/2 |
| 离子类型 | 跃迁轨道 | 吸收带/cm-1 | 跃迁类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| U4+ | 5f2-5f16d1 | >25000 | — |
| 5f2-5f2 | 22000~20000 | 1I6 ← 3H4 | |
| 18000 | 3P1 ← 3H4 | ||
| 16500~14900 | 1G4, 1D2, 3P0 ←3H4 | ||
| 13000~10500 | 3H6 ← 3H4 | ||
| 8600 | 3F3, 3F4 ← 3H4 | ||
| 7500~5500 | 3H5 ← 3H4 | ||
| U3+ | 5f3-5f26d1 | 25000~14000 | — |
| 5f3-5f3 | 13300 | 4G7/2 ←4I9/2 | |
| 11500~11200 | 4G5/2, 4S3/2, 4I15/2, 4F7/2 ←4I9/2 | ||
| 9800~9400 | 2H9/2, 4F5/2 ←4I9/2 | ||
| 8250 | 4I13/2 ←4I9/2 |
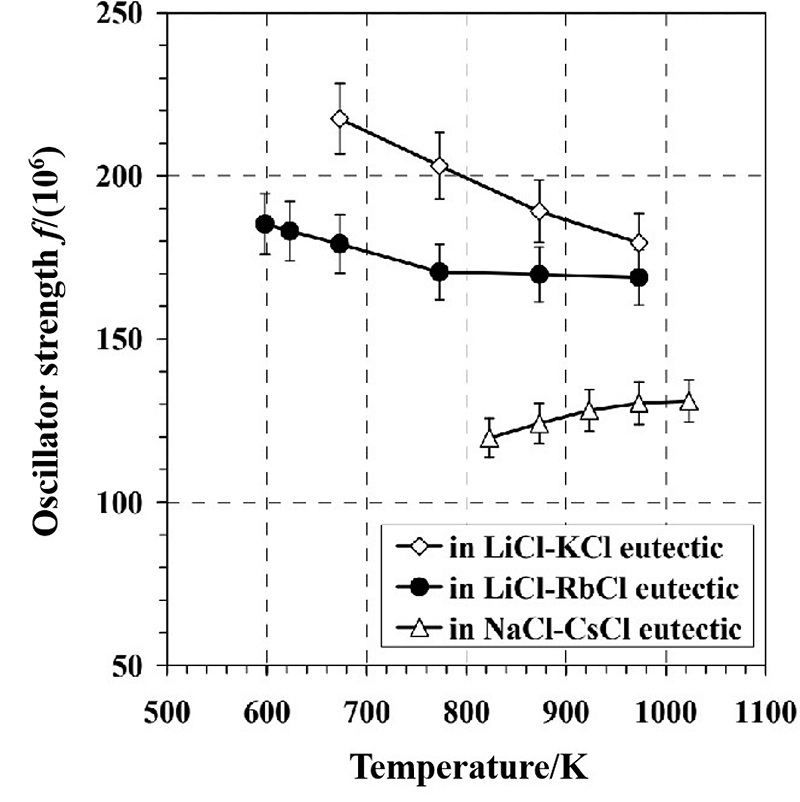
| 熔盐 | 还原剂 | 还原产物 |
|---|---|---|
| 3LiCl-2KCl | 真空(0.665 Pa) | UO2Cl43-、UO2 |
| NaCl-KCl | ||
| NaCl-2CsCl | ||
| 3LiCl-2KCl | 真空(0.665 Pa) Zr吸气剂 | |
| NaCl-KCl | ||
| NaCl-2CsCl | ||
| NaCl-2CsCl | Pd | |
| Te | ||
| Ag | ||
| LiCl | Mo | |
| 3LiCl-2KCl | ||
| NaCl-KCl | ||
| NaCl-2CsCl | ||
| 3LiCl-2KCl | H2 | |
| NaCl-KCl | ||
| NaCl-2CsCl | ||
| 3LiCl-2KCl | Nb | UO2Cl43-、UCl62-、UO2、UCl63- |
| NaCl-KCl | ||
| NaCl-2CsCl | UO2Cl43-、UCl62-、UO2 | |
| 3LiCl-2KCl | Zr | UO2Cl43-、UCl62-、UO2 |
| NaCl-KCl | ||
| NaCl-2CsCl | ||
| LiCl-BeCl2 | BeCl2 (HCl or Cl2气氛) | UCl62- |
| 熔盐 | 还原剂 | 还原产物 |
|---|---|---|
| 3LiCl-2KCl | 真空(0.665 Pa) | UO2Cl43-、UO2 |
| NaCl-KCl | ||
| NaCl-2CsCl | ||
| 3LiCl-2KCl | 真空(0.665 Pa) Zr吸气剂 | |
| NaCl-KCl | ||
| NaCl-2CsCl | ||
| NaCl-2CsCl | Pd | |
| Te | ||
| Ag | ||
| LiCl | Mo | |
| 3LiCl-2KCl | ||
| NaCl-KCl | ||
| NaCl-2CsCl | ||
| 3LiCl-2KCl | H2 | |
| NaCl-KCl | ||
| NaCl-2CsCl | ||
| 3LiCl-2KCl | Nb | UO2Cl43-、UCl62-、UO2、UCl63- |
| NaCl-KCl | ||
| NaCl-2CsCl | UO2Cl43-、UCl62-、UO2 | |
| 3LiCl-2KCl | Zr | UO2Cl43-、UCl62-、UO2 |
| NaCl-KCl | ||
| NaCl-2CsCl | ||
| LiCl-BeCl2 | BeCl2 (HCl or Cl2气氛) | UCl62- |


| [1] |
Glatz, J. P.; Malmbeck, R.; Souček, P.; Claux, B.; Meier, R.; Ougier, M.; Murakami, T. Molten Salts Chemistry, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2013, pp. 541-560.
|
| [2] |
Inoue, T.; Koch, L. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2008, 40, 183.
doi: 10.5516/NET.2008.40.3.183 |
| [3] |
Hoover, R. O.; Shaltry, M. R.; Martin, S.; Sridharan, K.; Phongikaroon, S. J. Nucl. Mater. 2014, 452, 389.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2014.05.057 |
| [4] |
Salanne, M.; Simon, C.; Turq, P.; Madden, P. A. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 1177.
doi: 10.1021/jp075299n |
| [5] |
Masset, P.; Bottomley, D.; Konings, R.; Malmbeck, R.; Rodrigues, A.; Serp, J.; Glatz, J.-P. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A1109.
doi: 10.1149/1.1901083 |
| [6] |
Shirai, O.; Iwai, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Sakamura, Y.; Tanaka, H. J. Alloys Compd. 1998, 271, 685.
|
| [7] |
Yin, T.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wang, G.; Chai, Z.; Shi, W. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, D722.
doi: 10.1149/2.0571814jes |
| [8] |
Yang, D. W.; Liu, Y. L.; Yin, T. Q.; Jiang, S. L.; Zhong, Y. K.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Chai, Z. F.; Shi, W. Q. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 353, 136449.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136449 |
| [9] |
Salanne, M.; Simon, C.; Turq, P.; Ohtori, N.; Madden, P. A. Molten Salts Chemistry, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2013, pp. 1-16.
|
| [10] |
Li, X.; Song, J.; Shi, S.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, T.; Peng, S. J. Phys. Chem. A 2017, 121, 571.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.6b10193 |
| [11] |
Kwon, C.; Kang, J.; Han, B. Int. J. Energ. Res. 2016, 40, 1381.
doi: 10.1002/er.v40.10 |
| [12] |
Dai, S.; Toth, L. M.; Del Cul, G. D.; Metcalf, D. H. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 220.
doi: 10.1021/jp952100a |
| [13] |
Polovov, I. B.; Volkovich, V. A.; Charnock, J. M.; Kralj, B.; Lewin, R. G.; Kinoshita, H.; May, I.; Sharrad, C. A. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 7474.
doi: 10.1021/ic701415z pmid: 18665589 |
| [14] |
Volkovich, V. A.; Bhatt, A. I.; May, I.; Griffiths, T. R.; Thied, R. C. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2014, 39, 595.
|
| [15] |
Nagai, T.; Uehara, A.; Fujii, T.; Shirai, O.; Sato, N.; Yamana, H. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2005, 42, 1025.
doi: 10.1080/18811248.2005.9711055 |
| [16] |
May, I. ECS Proceedings Volumes, 2004, 2004-24, 814.
|
| [17] |
Volkovich, V. A.; May, I.; Griffiths, T. R.; Charnock, J. M.; Bhatt, A. I.; Lewin, B. J. Nucl. Mater. 2005, 344, 100.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2005.04.024 |
| [18] |
Volkovich, V. A.; Aleksandrov, D. E.; Vasin, B. D.; Khabibullin, T. K.; Polovov, I. B.; Griffiths, T. R. ECS Trans. 2009, 16, 325.
|
| [19] |
Nagai, T.; Fujii, T.; Shirai, O.; Yamana, H. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2004, 41, 690.
doi: 10.1080/18811248.2004.9715534 |
| [20] |
Fujii, T.; Moriyama, H.; Yamana, H. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 351, L6.
doi: 10.1016/S0925-8388(02)01081-2 |
| [21] |
Fujii, T.; Nagai, T.; Sato, N.; Shirai, O.; Yamana, H. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 393, L1.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2004.10.013 |
| [22] |
Fujii, T.; Nagai, T.; Uehara, A.; Yamana, H. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 441, L10.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.09.113 |
| [23] |
Kim, T. J.; Jeong, Y. K.; Kang, J. G.; Jung, Y.; Ahn, D. H.; Lee, H. S. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2010, 286, 283.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-010-0651-0 |
| [24] |
Volkovich, V. A.; Polovov, I. B.; Vasin, B. D.; Griffiths, T. R.; Sharrad, C. A.; May, I.; Charnock, J. M. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A 2007, 62, 671.
doi: 10.1515/zna-2007-10-1116 |
| [25] |
Fujii, T.; Uda, T.; Iwadate, Y.; Nagai, T.; Uehara, A.; Yamana, H. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 440, 575.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2013.04.010 |
| [26] |
Preetz, W.; Ruf, D.; Tensfeldt, D. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B 1984, 39, 1100.
doi: 10.1515/znb-1984-0820 |
| [27] |
Kwon, C.; Kang, J.; Kang, W.; Kwak, D.; Han, B. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 195, 216.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.02.123 |
| [28] |
Till, C.; Chang, Y.; Hannum, W. Prog. Nucl. Energ. 1997, 31, 3.
doi: 10.1016/0149-1970(96)00001-7 |
| [29] |
Karell, E. J.; Gourishankar, K. V.; Smith, J. L.; Chow, L. S.; Redey, L. Nucl. Technol. 2001, 136, 342.
doi: 10.13182/NT136-342 |
| [30] |
Simpson, M. F. Developments of spent nuclear fuel pyroprocessing technology at Idaho National Laboratory, Idaho National Laboratory (INL), 2012.
|
| [31] |
Gruen, D.; McBeth, R. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1959, 9, 290.
doi: 10.1016/0022-1902(59)80233-5 |
| [32] |
Wenz, D. A.; Adams, M. D.; Steunenberg, R. K. Inorg. Chem. 1964, 3, 989.
doi: 10.1021/ic50017a014 |
| [33] |
Adams, M.; Wenz, D.; Steunenberg, R. J. Phys. Chem. 1963, 67, 1939.
doi: 10.1021/j100803a518 |
| [34] |
Li, B.; Dai, S.; Jiang, D. E. ACS Appl. Energ. Mater. 2019, 2, 2122.
|
| [35] |
Li, B.; Dai, S.; Jiang, D. E. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 299, 112184.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.112184 |
| [36] |
Wu, F.; Roy, S.; Ivanov, A. S.; Gill, S. K.; Topsakal, M.; Dooryhee, E.; Abeykoon, M.; Kwon, G.; Gallington, L. C.; Halstenberg, P.; Layne, B.; Ishii, Y.; Mahurin, S. M.; Dai, S.; Bryantsev, V. S.; Margulis, C. J. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 7603.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b02845 |
| [37] |
Okamoto, Y.; Kobayashi, F.; Ogawa, T. J. Alloys Compd. 1998, 271, 355.
|
| [38] |
Okamoto, Y.; Madden, P. A.; Minato, K. J. Nucl. Mater. 2005, 344, 109.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2005.04.026 |
| [39] |
Okamoto, Y.; Akabori, M.; Itoh, A.; Ogawa, T. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2014, 39, 638.
|
| [40] |
In ACTINIDES 2009, IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Vol. 9, Eds.: Rao, L.; Tobin, J. G.; Shuh, D. K., IOP publishing, Bristol, 2010, p. 012050.
|
| [41] |
Fujii, T.; Uehara, A.; Nagai, T.; Kim, T.-J.; Sato, N.; Sakamura, Y.; Yamana, H. Electrochemistry 2009, 77, 667.
doi: 10.5796/electrochemistry.77.667 |
| [42] |
Nagai, T.; Uehara, A.; Fujii, T.; Sato, N.; Yamana, H. J. Nucl. Mater. 2011, 414, 226.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2011.03.048 |
| [43] |
Nagai, T.; Uehara, A.; Fujii, T.; Yamana, H. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 439, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2013.03.078 |
| [44] |
Fujii, T. KURRI Progress Report 2016, 2015(APRIL 2015-MARCH 2016), 24.
|
| [45] |
Choi, E. Y.; Jeon, M. K.; Hur, J.-M. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2017, 314, 207.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-017-5404-x |
| [46] |
Choi, E. Y.; Lee, J. J. Nucl. Mater. 2017, 494, 439.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2017.07.036 |
| [47] |
Choi, E. Y.; Lee, J.; Heo, D. H.; Lee, S. K.; Jeon, M. K.; Hong, S. S.; Kim, S. W.; Kang, H. W.; Jeon, S. C.; Hur, J. M. J. Nucl. Mater. 2017, 489, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2017.03.035 |
| [48] |
Cho, Y. H.; Bae, S. E.; Kim, D. H.; Park, T. H.; Kim, J. Y.; Song, K.; Yeon, J. W. Microchem. J. 2015, 122, 33.
doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2015.04.001 |
| [49] |
Park, Y. J.; Bae, S. E.; Cho, Y. H.; Kim, J. Y.; Song, K. Microchem. J. 2011, 99, 170.
doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2011.04.013 |
| [50] |
Cho, Y. H.; Bae, S. E.; Park, Y. J.; Oh, S. Y.; Kim, J. Y.; Song, K. Microchem. J. 2012, 102, 18.
doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2011.05.006 |
| [51] |
Volkovich, V. A.; Griffiths, T. R.; Fray, D. J.; Thied, R. C. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 3871.
doi: 10.1039/b004464o |
| [52] |
Bhatt, A. I.; du Fou de Kerdaniel, E.; Kinoshita, H.; Livens, F. R.; May, I.; Polovov, I. B.; Sharrad, C. A.; Volkovich, V. A.; Charnock, J. M.; Lewin, R. G. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 2.
doi: 10.1021/ic048617v |
| [53] |
Volkovich, V.; Aleksandrov, D.; Maltsev, D.; Vasin, B.; Polovov, I.; Griffiths, T. Molten Salts Chemistry and Technology, John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey, 2014, pp. 507-520.
|
| [54] |
Volkovich, V. A.; Aleksandrov, D. E.; Griffiths, T. R.; Vasin, B. D.; Khabibullin, T. K.; Maltsev, D. S. Pure Appl. Chem. 2010, 82, 1701.
doi: 10.1351/PAC-CON-09-09-30 |
| [55] |
Volkovich, V. A.; Aleksandrov, D. E.; Vasin, B. D.; Maltsev, D. S.; Griffiths, T. R. ECS Trans. 2010, 33, 371.
|
| [56] |
Polovov, I. B.; Sharrad, C. A.; May, I.; Vasin, B. D.; Volkovich, V. A.; Griffiths, T. R. ECS Trans. 2007, 3, 503.
doi: 10.1149/1.2798693 |
| [57] |
Jiang, T.; Wang, N.; Peng, S.; Yan, L. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2015, 31, 281.
doi: 10.1007/s40242-015-4331-z |
| [58] |
Liu, Y. L.; Yuan, L. Y.; Zheng, L. R.; Wang, L.; Yao, B. L.; Chai, Z. F.; Shi, W. Q. Electrochem. Commun. 2019, 103, 55.
doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2019.05.009 |
| [59] |
Song, J.; Shi, S.; Li, X.; Yan, L. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 234, 279.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2017.03.099 |
| [60] |
Liu, Y. L.; Luo, L. X.; Liu, N.; Yao, B. L.; Liu, K.; Yuan, L. Y.; Chai, Z. F.; Shi, W. Q. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 508, 63.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2018.05.034 |
| [61] |
Liu, Y. C.; Liu, Y. L.; Wang L.; Zhong Y. K.; Li M.; Han W.; Zhao Y.; Zhou T.; Zou Q.; Zeng X.; Shi W. Q. J. Nucl. Mater. 2020, 542, 152475.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2020.152475 |
| [62] |
Liu Y. C.; Liu Y. L.; Zhao Y.; Liu Z.; Zhou T.; Zou Q.; Zeng X.; Zhong Y. K.; Li M.; Sun Z. X.; Shi W. Q. J. Nucl. Mater. 2020, 532, 152049.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2020.152049 |
| [1] | Yizhi Han, Jianhui Lan, Xue Liu, Weiqun Shi. Advances in Molecular Dynamics Studies of Molten Salts Based on Machine Learning [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(11): 1663-1672. |
| [2] | Yilong Hua, Donghan Li, Tianhang Gu, Wei Wang, Ruofan Li, Jianping Yang, Wei-xian Zhang. Enrichment of Uranium from Aqueous Solutions with Nanoscale Zero-valent Iron: Surface Chemistry and Application Prospect [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(8): 1008-1022. |
| [3] | Li Zhangnan, Sha Haoyan, Yang Nan, Yuan Ye, Zhu Guangshan. Phosphoric Acid Based Porous Aromatic Framework for Uranium Extraction [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2019, 77(5): 469-474. |
| [4] | Chen Haijun, Huang Shuyi, Zhang Zhibin, Liu Yunhai, Wang Xiangke. Synthesis of Functional Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Composites for the Application of Radioactive Uranium Enrichment from Environment: A Review [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2017, 75(6): 560-574. |
| [5] | Chen Fangyuan, Qu Ning, Wu Qunyan, Zhang Hongxing, Shi Weiqun, Pan Qingjiang. Structures and Uranium-Uranium Multiple Bond of Binuclear Divalent Uranium Complex of Pyrrolic Schiff-base Macrocycle: a Relativistic DFT Probe [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2017, 75(5): 457-463. |
| [6] | Yue Guozong, Gao Rui, Zhao Pengxiang, Chu Mingfu, Shuai Maobing. Trivalent Uranium Complex in Small Molecules Activation [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2016, 74(8): 657-663. |
| [7] | Zhao Siwei, Zhong Yuxi, Guo Yuanru, Zhang Hongxing, Pan Qingjiang. A Relativistic DFT Study of Mixed Oxo-Imido Uranium Complexes of Polypyrrolic Macrocycle: Structure, Vibrational Spectrum and Oxo/Imido Exchange Reaction [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2016, 74(8): 683-688. |
| [8] | Zuo Xiaoxi, Li Qi, Liu Jiansheng, Xiao Xin, Fan Chengjie, Nan Junmin. Preparation and Performances of Room Molten Salt as Electrolyte in Carbon-carbon Capacitor Based on LiPF6 and Trifluoroacetamide [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2012, 70(04): 367-371. |
| [9] | Zhu Fayan, Fang Chunhui, Fang Yan, Zhou Yongquan, Xu Sha, Tao Song, Cao Lingdi. Structure of Aqueous Potassium Tetraborate Solutions [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2012, 0(04): 445-452. |
| [10] | WAN Qin-Fang, REN Ya-Min, WANG Liang, JIANG Hai-Zhou, DENG Da-Chao, BAI Yun, XIA Chuan-Qin. Phytoremediation for Soil Contaminated by Uranium [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2011, 69(15): 1780-1788. |
| [11] | JI Mei-Zhen, LIN Gao-Jiang, XU Zuo-Long. Purification of Single-walled Carbon Nanotubes by Oxygen Oxidation in LiCl-KCl Molten Salt [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2010, 68(05): 413-417. |
| [12] | LIU Wen-Ke*; LONG Xing-Gui; PENG Shu-Ming; WANG Wei-Du; YANG Ben-Fu; CAO Xiao-Hua; CHENG Gui-Jun. Measurement of Tritium Residual in Uranium Bed [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2007, 65(8): 699-704. |
| [13] | XU Jin-Qiang, YANG Jun*, NULI Yan-Na, ZHANG Wan-Bin. Study of Ionic Liquid Electrolytes for Secondary Lithium Batteries [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2005, 63(18): 1733-1738. |
| [14] | LIU Han-Xing, SUN Xiao-Qin, XIAO Jing, CHENG Zhi-Zheng, ZHOU Jian, OUYANG Shi-Xi. Study on Tabular SrTiO3 Processed by Molten Salt Synthesis Method [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2004, 62(3): 324-327. |
| [15] | WANG Gui-Hua, WEI Yong-Ge, SHU Gui-Ming, ZHANG Li-Dan, GUO Hong-You, WANG Ping. Solid State Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Reflectance Spectra of K2Ge4Se8 [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2004, 62(2): 165-169. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||