Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (8): 1008-1022.DOI: 10.6023/A21040160 Previous Articles Next Articles
Review
滑熠龙a,b, 李冬涵b, 顾天航c, 王伟c, 李若繁c, 杨建平a,*( ), 张伟贤c,d,*(
), 张伟贤c,d,*( )
)
投稿日期:2021-04-18
发布日期:2021-06-30
通讯作者:
杨建平, 张伟贤
作者简介: |
滑熠龙, 南华大学环境科学与工程系教师. 同济大学环境科学与工程专业博士, 东华大学材料科学与工程专业博士后. 主要从事铁基纳米材料的研发及应用, 放射性废水污染控制及资源化的研究及实践工作. 已成功应用nZVI连续流工艺治理铀尾矿库含铀废水. |
 |
李冬涵, 南华大学资源环境与安全工程学院2020级硕士生, 研究方向为资源与环境. |
 |
顾天航, 同济大学环境科学与工程学院2018级博士生, 研究方向为纳米零价铁富集水中稀有元素. |
 |
王伟, 博士, 同济大学化学专业博士后, 主要从事铁基纳米材料用于重金属污染控制及资源化方面的研究及实践工作, 作为主要完成人之一将铁基纳米技术成功应用于复杂多金属废水处理工程, 已发表SCI论文10余篇. |
 |
杨建平, 东华大学研究员、博士生导师. 2013年获复旦大学无机化学博士学位, 在同济大学、澳大利亚伍伦贡大学、澳大利亚莫纳什大学进行博士后和访学研究. 2016年加入东华大学从事无机材料界面调控及环境资源应用研究, 发表SCI论文130多篇, 总引用10000余次, H指数46. 担任Environmental Protection Research副主编; 荣获上海市东方学者特聘教授(2017年)、上海千人(2018年)、霍英东青年基金(2020年); 入选英国皇家化学会JMCA和ChemComm新锐科学家(Emerging Investigators, 2020和2021年). |
 |
张伟贤, 教授, 博士生导师, “千人计划”国家特聘专家, 2011年5月起任污染控制与资源化研究国家重点实验室主任. 1984年毕业于同济大学, 1996年获美国约翰·霍普金斯大学(The Johns Hopkins University)环境工程博士学位, 曾任美国里海大学(Lehigh University)教授. 2000年获美国国家科学基金会(NSF)青年教授奖(CAREER AWARD). 主持过国家自然科学基金海外及港澳学者合作研究基金及多项国家自然科学基金. 长期致力于环境中重金属及持久性有机污染物的基础与应用研究, 是环境纳米技术的先驱之一, 纳米零价铁技术的创始研究者. 在纳米零价铁合成、表征、污染物反应机理、应用于地下水修复及废水处理方面发表了系列经典论文. |
基金资助:
Yilong Huaa,b, Donghan Lib, Tianhang Guc, Wei Wangc, Ruofan Lic, Jianping Yanga( ), Wei-xian Zhangc,d(
), Wei-xian Zhangc,d( )
)
Received:2021-04-18
Published:2021-06-30
Contact:
Jianping Yang, Wei-xian Zhang
Supported by:Share
Yilong Hua, Donghan Li, Tianhang Gu, Wei Wang, Ruofan Li, Jianping Yang, Wei-xian Zhang. Enrichment of Uranium from Aqueous Solutions with Nanoscale Zero-valent Iron: Surface Chemistry and Application Prospect[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(8): 1008-1022.


| 材料 | 铀溶液 | 研究内容 | 主要结论 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nZVI | 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, nZVI富集水溶液中低浓度铀的溶液化学反应特性, 并从原子尺度分析了固相反应机理. | (1) 铀富集在nZVI颗粒核心; (2) 还原作用是主要反应机理; (3) 铀去除负荷达到1410 mg/g. | [ |
| 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, pH、碳酸氢根、钙离子对nZVI分离、还原溶液中铀的影响. | (1) 碳酸氢根、钙离子抑制nZVI分离、还原铀; (2) 铀被还原为UO2; (3) nZVI被氧化为FeOOH或Fe2O3. | [ | |
| 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, U/Fe物质的量比对nZVI颗粒中铀、铁化合物结构演变规律的影响. | (1) 反应后nZVI颗粒中铀的价态包括IV、V和IV; (2) nZVI转变为Fe2(OH)2CO3. | [ | |
| 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, 新制备的nZVI、厌氧老化的nZVI、腐蚀后的nZVI对铀的分离性能和反应机理. | (1) nZVI与铀反应的步骤是先吸附再还原; (2) 厌氧老化的nZVI对铀的分离速率最快; (3) 铀被还原并形成UO2. | [ | |
| 自配水 | 好氧条件下, 溶液pH对nZVI分离溶液中高浓度铀的性能和反应机理. | (1) nZVI与铀的主要反应机理是还原作用; (2) 铀被分离的速率随着pH升高而加快; (3) 溶液pH≥5时, 铀水解形成沉淀UO3•2H2O. | [ | |
| 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, Fe(II)或Fe(III)对nZVI还原铀的影响. | (1) 1,10-邻菲罗啉或三乙醇胺不利于铀被还原; (2) nZVI表面的Fe(II)促进铀被还原的过程. | [ | |
| 自配水/含铀废水 | 好氧条件下, 钙离子、钠离子、碳酸氢根对nZVI分离自配水、实际废水中低浓度铀的影响. | (1) 0.5 h内, 钙离子、钠离子、碳酸氢根对nZVI去除铀的反应速率无明显影响; (2) 钙离子、碳酸氢根共存时, 颗粒中的铀易脱附. | [ | |
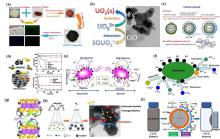
| nZVI/C | 自配水 | 以Fe2O3和松木屑合成nZVI/C, 研究其分离铀的性能和机理. | (1) 主要反应机理包括还原、吸附; (2) nZVI/C富集铀的负荷为186.92 mg/g. | [ |
| nZVI/AC | 自配水 | 以nZVI和AC制备nZVI/AC, 并研究其分离铀的溶液化学及固液界面机理. | (1) nZVI/AC主要通过吸附作用去除铀; (2) nZVI/AC富集铀的负荷为138.88 mg/g; (3) 反应时间延长, 反应后nZVI/AC中铁氧化物由Fe3O4转变为g-FeOOH. | [ |
| nZVI/MC | 自配水 | 高温条件下以nZVI和磁性生物炭(MC)制备nZVI/MC, 并研究其分离铀的性能和机理. | (1) 800 ℃条件提高复合材料中nZVI的分散、抗氧化性能; (2) nZVI/MC通过吸附、还原作用去除铀; (3) nZVI/MC富集铀的负荷为203.94 mg/g; (4) nZVI/MC重复性能强, 最适pH为5~6. | [ |
| nZVI/ 红土 | 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, 钙离子、碳酸根对nZVI及红土分离溶液中铀的影响. | (1) nZVI去除铀的机理包括吸附、还原作用; (2) nZVI对铀的去除能力比红土强; (3) nZVI和红土对铀的分离性能随着pH升高、碳酸根和钙离子浓度的增加而降低. | [ |
| nZVI/硅藻土 | 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, nZVI/硅藻土复合材料对铀的分离性能及反应机理. | (1) nZVI/硅藻土将铀还原为UO2; (2) nZVI/硅藻土去除铀的性能明显提高; (3) 硅藻土捕获铀、缓冲pH、分散nZVI颗粒. | [ |
| nZVI/膨润土 | 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, nZVI/膨润土复合材料对铀的分离性能及反应机理. | (1) nZVI/膨润土将铀还原为UO2; (2) 膨润土可捕获铀、提供活性位点、缓冲pH、分散nZVI颗粒、吸附Fe(II)而促进还原铀. | [ |
| nZVI/石墨烯 | 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, nZVI/石墨烯复合材料对铀的分离性能及反应机理. | (1) 石墨烯提高了去除铀的速率和负荷; (2) 石墨烯抑制Fe3O4/γ-Fe2O3向γ-FeOOH转变; (3) 铀在复合材料表面形成“内层”配合物. | [ |
| nZVI/ LDH | 自配水 | (1) nZVI/LDH比表面积大334.0 m2/g, 富含M-O、C-O和O-H官能团和吸附态Fe(II); (2) nZVI/LDH主要通过吸附、还原作用去除铀; (3) nZVI/LDH富集铀的负荷为176 mg/g. | [ | |
| SnZVI | 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, 以Na2S为硫化剂制备FeS@nZVI并研究其富集铀的机理. | (1) FeS@nZVI通过吸附、还原作用固定铀; (2) FeS和nZVI的最佳质量比为1∶1; (3) 溶液pH(5.5~9.0)增加, FeS@nZVI分离铀的性能升高; (4) 腐殖酸、碳酸氢根和钙离子的抑制作用较弱. | [ |
| SnZVI/BC | 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, 以Na2S2O4和生物炭(Dictyophora indusiate)制备SnZVI/BC并研究其富集铀的机理. | (1) SnZVI/BC提高nZVI颗粒的分散性和抗氧化性; (2) SnZVI/BC表面的官能团(如O-H、C-O、C-H、C-C、C=C)和FeSx壳层通过吸附作用、还原作用去除铀; (3) SnZVI/BC循环性能强, 且富集铀的负荷为427.9 mg/g. | [ |
| 材料 | 铀溶液 | 研究内容 | 主要结论 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nZVI | 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, nZVI富集水溶液中低浓度铀的溶液化学反应特性, 并从原子尺度分析了固相反应机理. | (1) 铀富集在nZVI颗粒核心; (2) 还原作用是主要反应机理; (3) 铀去除负荷达到1410 mg/g. | [ |
| 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, pH、碳酸氢根、钙离子对nZVI分离、还原溶液中铀的影响. | (1) 碳酸氢根、钙离子抑制nZVI分离、还原铀; (2) 铀被还原为UO2; (3) nZVI被氧化为FeOOH或Fe2O3. | [ | |
| 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, U/Fe物质的量比对nZVI颗粒中铀、铁化合物结构演变规律的影响. | (1) 反应后nZVI颗粒中铀的价态包括IV、V和IV; (2) nZVI转变为Fe2(OH)2CO3. | [ | |
| 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, 新制备的nZVI、厌氧老化的nZVI、腐蚀后的nZVI对铀的分离性能和反应机理. | (1) nZVI与铀反应的步骤是先吸附再还原; (2) 厌氧老化的nZVI对铀的分离速率最快; (3) 铀被还原并形成UO2. | [ | |
| 自配水 | 好氧条件下, 溶液pH对nZVI分离溶液中高浓度铀的性能和反应机理. | (1) nZVI与铀的主要反应机理是还原作用; (2) 铀被分离的速率随着pH升高而加快; (3) 溶液pH≥5时, 铀水解形成沉淀UO3•2H2O. | [ | |
| 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, Fe(II)或Fe(III)对nZVI还原铀的影响. | (1) 1,10-邻菲罗啉或三乙醇胺不利于铀被还原; (2) nZVI表面的Fe(II)促进铀被还原的过程. | [ | |
| 自配水/含铀废水 | 好氧条件下, 钙离子、钠离子、碳酸氢根对nZVI分离自配水、实际废水中低浓度铀的影响. | (1) 0.5 h内, 钙离子、钠离子、碳酸氢根对nZVI去除铀的反应速率无明显影响; (2) 钙离子、碳酸氢根共存时, 颗粒中的铀易脱附. | [ | |
| nZVI/C | 自配水 | 以Fe2O3和松木屑合成nZVI/C, 研究其分离铀的性能和机理. | (1) 主要反应机理包括还原、吸附; (2) nZVI/C富集铀的负荷为186.92 mg/g. | [ |
| nZVI/AC | 自配水 | 以nZVI和AC制备nZVI/AC, 并研究其分离铀的溶液化学及固液界面机理. | (1) nZVI/AC主要通过吸附作用去除铀; (2) nZVI/AC富集铀的负荷为138.88 mg/g; (3) 反应时间延长, 反应后nZVI/AC中铁氧化物由Fe3O4转变为g-FeOOH. | [ |
| nZVI/MC | 自配水 | 高温条件下以nZVI和磁性生物炭(MC)制备nZVI/MC, 并研究其分离铀的性能和机理. | (1) 800 ℃条件提高复合材料中nZVI的分散、抗氧化性能; (2) nZVI/MC通过吸附、还原作用去除铀; (3) nZVI/MC富集铀的负荷为203.94 mg/g; (4) nZVI/MC重复性能强, 最适pH为5~6. | [ |
| nZVI/ 红土 | 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, 钙离子、碳酸根对nZVI及红土分离溶液中铀的影响. | (1) nZVI去除铀的机理包括吸附、还原作用; (2) nZVI对铀的去除能力比红土强; (3) nZVI和红土对铀的分离性能随着pH升高、碳酸根和钙离子浓度的增加而降低. | [ |
| nZVI/硅藻土 | 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, nZVI/硅藻土复合材料对铀的分离性能及反应机理. | (1) nZVI/硅藻土将铀还原为UO2; (2) nZVI/硅藻土去除铀的性能明显提高; (3) 硅藻土捕获铀、缓冲pH、分散nZVI颗粒. | [ |
| nZVI/膨润土 | 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, nZVI/膨润土复合材料对铀的分离性能及反应机理. | (1) nZVI/膨润土将铀还原为UO2; (2) 膨润土可捕获铀、提供活性位点、缓冲pH、分散nZVI颗粒、吸附Fe(II)而促进还原铀. | [ |
| nZVI/石墨烯 | 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, nZVI/石墨烯复合材料对铀的分离性能及反应机理. | (1) 石墨烯提高了去除铀的速率和负荷; (2) 石墨烯抑制Fe3O4/γ-Fe2O3向γ-FeOOH转变; (3) 铀在复合材料表面形成“内层”配合物. | [ |
| nZVI/ LDH | 自配水 | (1) nZVI/LDH比表面积大334.0 m2/g, 富含M-O、C-O和O-H官能团和吸附态Fe(II); (2) nZVI/LDH主要通过吸附、还原作用去除铀; (3) nZVI/LDH富集铀的负荷为176 mg/g. | [ | |
| SnZVI | 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, 以Na2S为硫化剂制备FeS@nZVI并研究其富集铀的机理. | (1) FeS@nZVI通过吸附、还原作用固定铀; (2) FeS和nZVI的最佳质量比为1∶1; (3) 溶液pH(5.5~9.0)增加, FeS@nZVI分离铀的性能升高; (4) 腐殖酸、碳酸氢根和钙离子的抑制作用较弱. | [ |
| SnZVI/BC | 自配水 | 厌氧条件下, 以Na2S2O4和生物炭(Dictyophora indusiate)制备SnZVI/BC并研究其富集铀的机理. | (1) SnZVI/BC提高nZVI颗粒的分散性和抗氧化性; (2) SnZVI/BC表面的官能团(如O-H、C-O、C-H、C-C、C=C)和FeSx壳层通过吸附作用、还原作用去除铀; (3) SnZVI/BC循环性能强, 且富集铀的负荷为427.9 mg/g. | [ |
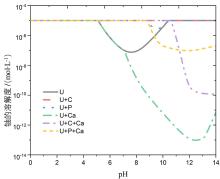



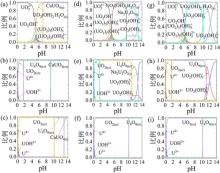
| No. | U/(mmol•L–1) | nZVI/(mmol•L–1) | U/nZVI | pH | 去除 | 还原 | Kd/(mL•g–1) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.04 | 17.86 | 2.24×10-3 | 4.0 | 87% | — | 6.7×103 | [ |
| 2 | 0.08 | 17.86 | 4.48×10-3 | 4.0 | 93% | — | 1.3×104 | [ |
| 3 | 0.25 | 35.71 | 7.00×10-3 | 6.5 | 91% | 92% | 5.1×103 | [ |
| 4 | 0.21 | 0.84 4.41 | 2.50×10-1 4.76×10-2 | 7.0 | 100% | — | 2.1×106 4.0×105 | [ |
| 5 | 0.04 | 8.93 | 4.48×10-3 | 6~11 | >95% | ≈58% | 3.8×104 | [ |
| 6 | 0.22 | 8.93 | 2.46×10-2 | 6.0 | 99% | 82.7% | 1.0×106 | [ |
| 7 | 9.75×10-6 3.71×10-3 | 17.86 17.86 | 5.46×10-7 2.08×10-4 | 3~11 | 99% | — | 1.0×106 2.5×104 | [ |
| 8 | 0.10 1.40 | 1.43 1.43 | 6.99×10-2 9.79×10-1 | 5.0 | 98% | 99.3% 66% | 1.2×106 1.2×106 | [ |
| 9 | 0.15 | 35.71 | 4.20×10-3 | 7.0 | 98% | 97% | 2.5×104 | [ |
| 10 | 0.20 | 0.49 | 4.08×10-1 | 6.9 | 99% | 99.8% | 3.6×106 | [ |
| 11 | 4.2×10-4 | 1.79 | 2.35×10-4 | 3.0 | 97% | 99% | 3.2×105 | [ |
| 12 | 0.50 | 44.64 | 1.12×10-2 | 10.0 | 92% | — | 4.6×103 | [ |
| 13 | 0.21 0.42 0.63 0.84 | 1.79 | 1.17×10-1 2.35×10-1 3.52×10-1 4.69×10-1 | — | 99% 49% 29% 19% | — | 9.9×105 9.6×103 4.1×103 2.4×103 | [ |
| 14 | 3.57 | 2.90 | 1.23 | 6.5 | 98.88 | — | 6.1×105 | [ |
| No. | U/(mmol•L–1) | nZVI/(mmol•L–1) | U/nZVI | pH | 去除 | 还原 | Kd/(mL•g–1) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.04 | 17.86 | 2.24×10-3 | 4.0 | 87% | — | 6.7×103 | [ |
| 2 | 0.08 | 17.86 | 4.48×10-3 | 4.0 | 93% | — | 1.3×104 | [ |
| 3 | 0.25 | 35.71 | 7.00×10-3 | 6.5 | 91% | 92% | 5.1×103 | [ |
| 4 | 0.21 | 0.84 4.41 | 2.50×10-1 4.76×10-2 | 7.0 | 100% | — | 2.1×106 4.0×105 | [ |
| 5 | 0.04 | 8.93 | 4.48×10-3 | 6~11 | >95% | ≈58% | 3.8×104 | [ |
| 6 | 0.22 | 8.93 | 2.46×10-2 | 6.0 | 99% | 82.7% | 1.0×106 | [ |
| 7 | 9.75×10-6 3.71×10-3 | 17.86 17.86 | 5.46×10-7 2.08×10-4 | 3~11 | 99% | — | 1.0×106 2.5×104 | [ |
| 8 | 0.10 1.40 | 1.43 1.43 | 6.99×10-2 9.79×10-1 | 5.0 | 98% | 99.3% 66% | 1.2×106 1.2×106 | [ |
| 9 | 0.15 | 35.71 | 4.20×10-3 | 7.0 | 98% | 97% | 2.5×104 | [ |
| 10 | 0.20 | 0.49 | 4.08×10-1 | 6.9 | 99% | 99.8% | 3.6×106 | [ |
| 11 | 4.2×10-4 | 1.79 | 2.35×10-4 | 3.0 | 97% | 99% | 3.2×105 | [ |
| 12 | 0.50 | 44.64 | 1.12×10-2 | 10.0 | 92% | — | 4.6×103 | [ |
| 13 | 0.21 0.42 0.63 0.84 | 1.79 | 1.17×10-1 2.35×10-1 3.52×10-1 4.69×10-1 | — | 99% 49% 29% 19% | — | 9.9×105 9.6×103 4.1×103 2.4×103 | [ |
| 14 | 3.57 | 2.90 | 1.23 | 6.5 | 98.88 | — | 6.1×105 | [ |
| [1] |
Canu, I. G.; Jacob, S.; Cardis, E.; Wild, P.; Cae, S. r; Acker, A.; Tirmarche, M.; Laurier, D. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 68, Suppl 1.
|
| [2] |
Träber, S. C.; Höllriegl, V.; Li, W. -B.; Czeslik, U.; Rühm, W.; Oeh, U.; Michalke, B. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 24.
|
| [3] |
Wu, Y.; Wang, Y. -X.; Xie, X. -J. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 809.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.109 |
| [4] |
Winde, F.; Erasmus, E.; Geipel, G. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 400.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.035 |
| [5] |
Bister, S.; Birkhan, J.; Lüllau, T.; Bunka, M.; Solle, A.; Stieghorst, C.; Riebe, B.; Michel, R.; Walther, C. J. Environ. Radioactiv. 2015, 144, 21.
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2015.02.024 pmid: 25791900 |
| [6] |
Cinelli, G.; Tondeur, F.; Dehandschutter, B.; Bossew, P.; Tollefsen, T.; De Cort, M. J. Environ. Radioactiv. 2017, 166, 220.
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2016.04.026 |
| [7] |
Haribala,
|
| [8] |
Shelley, R.; Kim, N. -S.; Parsons, P. J.; Lee, B. -K.; Agnew, J.; Jaar, B. G.; Steuerwald, A. J.; Matanoski, G.; Fadrowski, J.; Schwartz, B. S.; Todd, A. C.; Simon, D.; Weaver, V. M. J. Expo. Sci. Env. Epid. 2013, 24, 58.
doi: 10.1038/jes.2013.18 |
| [9] |
Kreuzer, M.; Fenske, N.; Schnelzer, M.; Walsh, L. Brit. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1367.
doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.324 pmid: 26393888 |
| [10] |
Ohba, T.; Tanigawa, K.; Liutsko, L. Environ. Int. 2021, 148, 106379.
doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.106379 |
| [11] |
Murugan, R.; Kavasi, N.; Sahoo, S. K.; Omori, Y.; Sorimachi, A.; Takahashi, H.; Aono, T. J. Environ. Radioactiv. 2021, 232, 106568-106568.
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2021.106568 pmid: 33740532 |
| [12] |
Hirouchi, J.; Takahara, S.; Yoshimura, K. J. Environ. Radioactiv. 2021, 232, 106572-106572.
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2021.106572 pmid: 33706142 |
| [13] |
Zuykov, M.; Fowler, S. W.; Archambault, P.; Spiers, G.; Schindler, M. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110860.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110860 |
| [14] |
Miki, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Shigenobu, Y.; Ambe, D.; Kaeriyama, H.; Takagi, K.; Ono, T.; Watanabe, T.; Sugisaki, H.; Morita, T. Fish. Oceanogr. 2017, 26, 221.
doi: 10.1111/fog.2017.26.issue-2 |
| [15] |
Wang, Y. -N. China Econ. Wkly. 2020, (20), 92-95. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 王亦楠, 中国经济周刊, 2020, (20), 92-95.)
|
|
| [16] |
Jin, YGlob. Times 2021, 15. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 金嬴, 环球时报, 2021, 15.)
|
|
| [17] |
Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 852, 156993.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156993 |
| [18] |
Zheng, H.; Ren, X.; Zhang, X.; Song, G.; Chen, D.; Chen, C. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, C.
|
| [19] |
Zhao, X.; Liu, W.; Cai, Z.; Fu, J.; Duan, J.; Zhao, D.; M, Bozack.; Feng, Y.. Colloid Surface A. 2020, 604, 125315.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125315 |
| [20] |
Zhang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Huang, Z.; Nie, X.; Chi, F.; Pan, N.; Ding, C. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Ch. 2020, 326, 845.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-020-07371-7 |
| [21] |
Yang, F.; Xie, S.; Wang, G.; Yu, C. W.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2020, 27, 20246.
doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08381-4 |
| [22] |
Xiao, M.; Hu, R.; Cui, X.; W, Gwenzi.; C, Noubactep. Processes, 2020, 8, 409.
doi: 10.3390/pr8040409 |
| [23] |
Xiao, M.; Cui, X.; Hu, R.; W, Gwenzi.; C, Noubactep. Processes, 2020, 8, 1162.
doi: 10.3390/pr8091162 |
| [24] |
Xiao, J.; Pang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Chu, L.; Rong, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Tian, L. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 244, 116667.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116667 |
| [25] |
Xiang, S.; Cheng, W.; Chi, F.; Nie, X.; T, Hayat.; N.S, Alharbi. Acs Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 1131.
doi: 10.1021/acsanm.9b01581 |
| [26] |
Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, P.; Du, K.; Yuan, L.; Ning, S.; Wei, Y.; Shi, W. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 408, 124949.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124949 |
| [27] |
Wang, J.; Pang, H.; Tang, H.; Yu, S.; Zhu, H.; Wang, X. J. Inorg. Mater. 2020, 35, 373.
|
| [28] |
Sharma, N.; Ghosh, A.; Fortner, J. D.; Giammar, D. E. Environ. Sci.-Nano 2020, 7, 2010.
doi: 10.1039/D0EN00416B |
| [29] |
Liao, H.; Yu, J.; Zhu, W.; Kuang, M.; Duan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Luo, X.; Zhou, J. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 507, 145075.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.145075 |
| [30] |
Duan, J.; Ji, H.; Zhao, X.; Tian, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Zhao, D. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124692.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124692 |
| [31] |
Zhang, Q.; Zhao, D.; Feng, S.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Chen, C. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2019, 552, 735.
doi: S0021-9797(19)30673-3 pmid: 31176920 |
| [32] |
Zhang, H. -M.; Ruan, Y.; Liang, A. -P.; Shih, K. M.; Diao, Z. H.; Su, M. H.; Hou, L. A.; Chen, D. Y.; Lu, H.; Kong, L. J. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 117873.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117873 |
| [33] |
Yu, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pang, H.; Song, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 365, 51.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.024 |
| [34] |
Wang, M.; Cheng, W.; Wan, T.; Hu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Song, X.; Sun, Y. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 99.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.138 |
| [35] |
Sihn, Y.; Bae, S.; Lee, W. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 626.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.073 |
| [36] |
Pang, H.; Diao, Z.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Z.; Hu, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 368.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.098 |
| [37] |
Lv, Z.; Yang, S.; Chen, L.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Chen, C. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 76, 377.
doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.06.001 |
| [38] |
Li, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Guo, X.; Li, X.; Ma, L.; Li, S. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 365, 70.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.002 |
| [39] |
Duan, J.; Ji, H.; Liu, W.; Zhao, X.; Han, B.; Tian, S.; Zhao, D. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 1617.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.008 |
| [40] |
Kong, L. -J.; Zhang, H. -M.; Shih, K. M.; Su, M. -H.; Diao, Z. -H.; Long, J. -Y.; Hou, L. -A.; Song, G.; Chen, D. -Y. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 357, 168.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.05.067 |
| [41] |
Hua, Y.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Gu, T.; Ding, D.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W. -X. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 603.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.041 |
| [42] |
Ding, C. -C.; Cheng, W. -C.; Nie, X. -Q.; Yi, F. -C.; Xiang, S. -H.; Asiri, A. M.; Marwani, H. M. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 61, 236.
doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2017.12.021 |
| [43] |
Liu, H.; Li, M.; Chen, T.; Chen, C.; N.S., Alharbi.; Hayat, T.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Environ. Sci.Technol. 2017, 51, 9227.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b02431 |
| [44] |
Hu, S. -H.; Lin, X. -Y.; Zhang, Y. -H.; Shi, M. -L.; Luo, X. -G. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Ch. 2017, 314, 2405.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-017-5529-y |
| [45] |
Shao, D. -D.; Wang, X. -X.; Wang, X. -L.; Hu, S.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Li, J. -X.; Wang, S. -H.; Hu, J.; Wang, X. -K. Rsc Adv. 2016, 6, 52076.
doi: 10.1039/C6RA10817B |
| [46] |
Kong, L. -J.; Zhu, Y. -T.; Wang, M.; Li, Z. -X.; Tan, Z. -C.; Xu, R. -B.; Tang, H. -M.; Chang, X. -Y.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, D. -Y. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 320, 435.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.08.060 |
| [47] |
Hu, B. -W.; Ye, F.; Ren, X. -M.; Zhao, D. -L.; Sheng, G. -D.; Li, H.; Ma, J. -Y.; Wang, X. -K.; Huang, Y. -Y. Environ. Sci.-Nano, 2016, 3, 1460.
doi: 10.1039/C6EN00421K |
| [48] |
Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Cao, X.; Luo, X.; Hua, R.; Liu, Y.; Yu, X.; He, L.; Liu, Y. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 633.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.07.058 |
| [49] |
Ling, L.; Zhang, W. -X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2788.
doi: 10.1021/ja510488r pmid: 25689272 |
| [50] |
Li, Z. -J.; Wang, L.; Yuan, L. -Y.; Xiao, C. -L.; Mei, L.; Zheng, L. -R.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J. -H.; Zhao, Y. -L.; Zhu, Z. -T.; Chai, Z. -F.; Shi, W. -Q. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 290, 26.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.02.028 |
| [51] |
Hua, Y. -L.; Wang, W.; Hu, N.; Gu, T.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W. -X. Environ. Sci.-Nano 2021, 8, 666.
doi: 10.1039/D0EN01029D |
| [52] |
Sun, Y. -P.; Li, X. -Q.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W. -X.; Wang, H. -P. Adv. Colloid Interfac. 2006, 120, 47.
doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2006.03.001 |
| [53] |
Kumar, M. A.; Bae, S.; Han, S.; Chang, Y.; Lee, W. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 340, 399.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.07.030 |
| [54] |
Bhattacharjee, S.; Ghoshal, S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8631.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b01646 pmid: 27377979 |
| [55] |
Nunez, Garcia, A.; Boparai,, H. K.; O'Carroll,, D. M. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5243.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b00734 pmid: 27128632 |
| [56] |
Bae, S.; Hanna, K. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10536.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b01298 |
| [57] |
Xu, C. -H.; Zhang, B. -L.; Wang, Y. -H.; Shao, Q. -Q.; Zhou, W. -Z.; Fan, D. -M.; Bandstra, J. Z.; Shi, Z. -Q.; Tratnyek, P. G. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11879.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b03184 |
| [58] |
He, Y.; Gao, J. -F.; Feng, F. -Q.; Liu, C.; Peng, Y. -Z.; Wang, S. -Y. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 179, 8.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.107 |
| [59] |
Gu, Y.; Wang, B.; He, F.; Bradley, M. J.; Tratnyek, P. G. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12653.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b03604 |
| [60] |
Hua, Y. -L.; Xia, X. -F.; Huang, X. -Y.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W. -X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 594. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A17030099 |
|
( 滑熠龙, 夏雪芬, 黄潇月, 凌岚, 张伟贤, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 594.)
doi: 10.6023/A17030099 |
|
| [61] |
Xie, Y.; Dong, H.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Hou, K.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Deng, J. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 338, 306.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.05.053 |
| [62] |
Su, Y. -M.; Adeleye, A. S., Keller, A. A., Huang, Y. -X.; Dai, C. -M.; Zhou, X. -F.; Zhang, Y. -L. Water Res. 2015, 74, 47.
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.02.004 |
| [63] |
Dong, H.; Deng, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Hou, K.; Zeng, G. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 332, 79.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.03.002 |
| [64] |
Ling, L.; Huang, X. -Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, W. -X. Environ. Sci.Technol. 2017, 51, 14293.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b02233 |
| [65] |
Gu, T. -H.; Shi, J. -M.; Hua, Y. -L.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W. -X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 991. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A17070345 |
|
( 顾天航, 石君明, 滑熠龙, 刘静, 王伟, 张伟贤, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 991.)
doi: 10.6023/A17070345 |
|
| [66] |
Ling, L.; Huang, X. -Y.; Zhang, W. -X. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705703.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v30.17 |
| [67] |
Huang, X. -Y.; Wang, W.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W. -X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 529. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A17020051 |
|
( 黄潇月, 王伟, 凌岚, 张伟贤, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 529.)
doi: 10.6023/A17020051 |
|
| [68] |
Wang, W.; Li, S. -L.; Lei, H.; Pan, B. -C.; Zhang, W. -X. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 616.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.09.042 |
| [69] |
Li, S. -L.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y. -Y.; Zhang, W. -X. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 115.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.111 |
| [70] |
Elliott, D. W.; Zhang, W. -X. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4922.
pmid: 11775172 |
| [71] |
Yan, S.; Hua, B.; Bao, Z. -Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, C. -X.; Deng, B. -L. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7783.
doi: 10.1021/es9036308 |
| [72] |
Tsarev, S.; Collins, R. N.; Ilton, E. S.; Fahy, A.; Waite, T. D. Environ. Sci.-Nano 2017, 4, 1304.
doi: 10.1039/C7EN00024C |
| [73] |
Riba, O.; Scott, T. B.; Ragnarsdottir, K. V.; Allen, G. C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2008, 72, 4047.
doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.04.041 |
| [74] |
Burghardt, D.; Kassahun, A. Environ. Geol. 2005, 49, 314.
doi: 10.1007/s00254-005-0093-0 |
| [75] |
Dickinson, M.; Scott, T. B. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 171.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.01.060 pmid: 20129731 |
| [76] |
Li, X. -Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y. -B.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Hua, R.; Liu, Y. -H. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2015, 25, 3505. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63992-9 |
|
( 李小燕, 张明, 刘义保, 李寻, 杨波, 花榕, 刘云海, 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25, 3505.)
|
|
| [77] |
Crane, R. A.; Pullin, H.; Scott, T. B. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 277, 252.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.03.085 |
| [78] |
Ding, C.; Cheng, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2015, 165, 86.
doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.05.036 |
| [79] |
Chen, H. -J.; Huang, H. -S.; Zhang, Z. -B.; Liu, Y. -H; Wang, X. -K. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 560. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A17010039 |
|
( 陈海军, 黄舒怡, 张志宾, 刘云海, 王祥科, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 560.)
doi: 10.6023/A17010039 |
|
| [80] |
Hu, B.; Mei, X.; Li, X.; Hu, J.; Xu, D.; Ma, J.; Huang, Y. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 237, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2017.04.084 |
| [81] |
Crane, R. A.; Scott, T. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2813.
doi: 10.1007/s11051-014-2813-4 |
| [82] |
Xu, J. -L.; Li, Y. -L.; Jing, C.; Zhang, H. -C.; Ning, Y. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Ch. 2014, 299, 329.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-013-2779-1 |
| [83] |
Crane, R.; Pullin, H.; Macfarlane, J.; Silion, M.; Popescu, I.; Andersen, M.; Calen, V.; Scott, T. J. Environ. Eng. 2015, 141, 04015011.
doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0000936 |
| [84] |
Jing, C.; Li, Y.; Cui, R.; Xu, J. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Ch. 2015, 304, 859.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-014-3850-2 |
| [85] |
Sheng, G. -D.; Yang, P. -J.; Tang, Y. -N.; Hu, Q. -Y.; Li, H.; Ren, X. -M.; Hu, B. -W.; Wang, X. -K.; Huang, Y. -Y. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2016, 193, 189.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.04.035 |
| [86] |
Cantrell, K. J.; Kaplan, D. I.; Wietsma, T. W. J. Hazard. Mater. 1995, 42, 201.
doi: 10.1016/0304-3894(95)00016-N |
| [87] |
Tsarev, S.; Collins, R. N.; Fahy, A.; Waite, T. D. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2595.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b06160 |
| [88] |
Crane, R. A.; Dickinson, M.; Scott, T. B. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 319.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.09.084 |
| [89] |
Crane, R. A.; Scott, T. B. J. Nanomater. 2014, 956360, 1.
|
| [90] |
Crane, R. A.; Scott, T. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2813.
doi: 10.1007/s11051-014-2813-4 |
| [91] |
Popescu, I. C.; Filip, P.; Humelnicu, D.; Humelnicu, I.; Scott, T. B.; Crane, R. A. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 443, 250.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2013.07.018 |
| [92] |
Crane, R. A.; Scott, T. B. J. Nanotech. 2013, 173625, 1.
|
| [93] |
Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Hua, R.; He, C. Water Qual. Expos. Hea. 2013, 5, 31.
|
| [94] |
Sheng, G. -D.; Shao, X. -Y.; Li, Y. -M.; Li, J. -F.; Dong, H. -P.; Cheng, W.; Gao, X.; Huang, Y. -Y. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2014, 118, 2952.
doi: 10.1021/jp412404w |
| [95] |
Sun, Y.; Ding, C.; Cheng, W.; Wang, X. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 399.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.08.023 |
| [96] |
Yan, S.; Chen, Y. -H.; Xiang, W.; Bao, Z. -Y.; Liu, C. -X.; Deng, B. -L. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 625.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.09.087 |
| [97] |
Li, J. -H.; Yang, L. -X.; Li, J. Q.; Yin, W. -H.; Tao, Y.; Wu, H. -Q.; Luo, F. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 269, 16.
doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2018.09.013 |
| [98] |
Xu, J.; Avellan, A.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Noel, V.; Lou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Kaegi, R.; Henkelman, G.; Lowry, G. V. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906910.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v32.17 |
| [99] |
Xu, J.; Avellan, A.; Li, H.; Clark, E. A.; Kaegi, R.; Lowry, G. V. Environ. Sci.Technol. 2020, 54, 13294.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c03879 |
| [100] |
Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Liang, L.; Pan, B. -C.; Zhang, W.; Guan, X. Environ. Sci.Technol. 2017, 91, 13533.
|
| [101] |
Qin, H.; Guan, X.; Bandstra, J. Z.; Johnson, R. L.; Tratnyek, P. G. Environ. Sci.Technol. 2018, 52, 13887.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b04436 |
| [102] |
Kim, E. J.; Kim, J. H.; Azad, A. M.; Chang, Y. -S. Acs Appl. Mater. Inter. 2011, 3, 1457.
doi: 10.1021/am200016v |
| [103] |
Rajajayavel, S. R.C.; Ghoshal, S. Water Res. 2015, 78, 144.
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.04.009 pmid: 25935369 |
| [104] |
Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.; Guan, X. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2988.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b06502 |
| [105] |
Huang, S.; Xu, C.; Shao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Gao, B.; Zhou, W.; Tratnyek, P. G. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 539.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.033 |
| [106] |
He, F.; Li, Z.; Shi, S.; Xu, W.; Sheng, H.; Gu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xi, B. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8627.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b01735 |
| [107] |
Rossberg, A.; Ulrich, K. -U.; Weiss, S.; Tsushima, S.; Hiemstra, T.; Scheinost, A. C. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1400.
pmid: 19350910 |
| [108] |
Kerisit, S.; Felmy, A. R.; Ilton, E. S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2770.
doi: 10.1021/es1037639 |
| [109] |
Li, W. -L.; Troyer, L. D.; Lee, S. S.; Wu, J. -W.; Kim, C.; Lafferty, B. J.; Catalano, J. G.; Fortner, J. D. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 13163.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b01042 |
| [110] |
Skomurski, F. N.; Ilton, E. S.; Engelhard, M. H.; Arey, B. W.; Rosso, K. M. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2011, 75, 7277.
doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2011.08.006 |
| [111] |
Zhu, S.; Leng, Y.; Yan, M.; Tuo, X.; Yang, J.; Almásy, L.; Tian, Q.; Sun, G.; Zou, L.; Li, Q.; Courtois, J.; Zhang, H. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 447, 381.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.04.016 |
| [112] |
Qiu, M. -Q.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Q. -Z.; Hu, B. -W.; Zhu, Y. -L. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 764.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.057 |
| [113] |
Collins, R. N.; Rosso, K. M. J. Phys. Chem. A 2017, 121, 6603.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.7b05965 |
| [114] |
Ma, B.; Fernandez-Martinez, A.; Kang, M.; Wang, K.; Lewis, A. R.; Maffeis, T. G.G.; Findling, N.; Salas-Colera, E.; Tisserand, D.; Bureau, S.; Charlet, L. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8104.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c01854 |
| [115] |
Dewey, C.; Sokaras, D.; Kroll, T.; Bargar, J. R.; Fendorf, S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6021.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b05870 |
| [116] |
Jang, J. -H.; Dempsey, B. A.; Burgos, W. D. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2269.
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2007.12.007 |
| [117] |
Yuan, K.; Renock, D.; Ewing, R. C.; Becker, U. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2015, 156, 194.
doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.02.014 |
| [118] |
Ilton, E. S.; Boily, J. F.; Buck, E. C.; Skomurski, F. N.; Rosso, K. M.; Cahill, C. L.; Bargar, J. R.; Felmy, A. R. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 170.
doi: 10.1021/es9014597 |
| [119] |
Wander, M. C.F.; Kerisit, S.; Rosso, K. M.; Schoonen, M. A.A. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 9691.
doi: 10.1021/jp062325t |
| [120] |
Latta, D. E.; Gorski, C. A.; Boyanov, M. I.; O'Loughlin, E. J.; Kemner, K. M.; Scherer, M. M. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 778.
doi: 10.1021/es2024912 pmid: 22148359 |
| [121] |
Meinrath, G.; Kato, Y.; Kimura, T.; Yoshida, Z. Radiochim. Acta 1996, 75, 159.
doi: 10.1524/ract.1996.75.3.159 |
| [122] |
Langmuir, D. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 1978, 42, 547.
doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(78)90001-7 |
| [123] |
Grenthe, I.; Fuger, J.; Konings, R. J.M.; Lemire, R. J.; Muller, A. B.; Cregu, C. N.-T.; Wanner, H. J. Nucl. Mater. 1993, 200, 154.
doi: 10.1016/0022-3115(93)90021-P |
| [124] |
Jang, J. -H.; Dempsey, B. A.; Burgos, W. D. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2738.
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2006.04.014 |
| [125] |
Cheng, T.; Barnett, M. O.; Roden, E. E.; Zhuang, J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6059.
pmid: 15573607 |
| [126] |
Mehta, V. S.; Maillot, F.; Wang, Z.; Catalano, J. G.; Giammar, D. E. Chem. Geol. 2014, 364, 66.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.12.002 |
| [127] |
Nico, P. S.; Stewart, B. D.; Fendorf, S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7391.
doi: 10.1021/es900515q |
| [128] |
McBriarty, M. E.; Kerisit, S.; Bylaska, E. J.; Shaw, S.; Morris, K.; Ilton, E. S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6282.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b00297 pmid: 29757622 |
| [129] |
Marshall, T. A.; Morris, K.; Law, G. T.W.; Livens, F. R.; Mosselmans, J. F.W.; Bots, P.; Shaw, S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3724.
doi: 10.1021/es500212a pmid: 24580024 |
| [130] |
McBriarty, M. E.; Soltis, J. A.; Kerisit, S.; Qafoku, O.; Bowden, M. E.; Bylaska, E. J.; De Yoreo, J. J.; Ilton, E. S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4970.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b00432 pmid: 28407467 |
| [131] |
Pullin, H.; Springell, R.; Parry, S.; Scott, T. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 568.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.088 |
| [132] |
Xu, H.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Guan, X. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8214.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b01763 |
| [133] |
Roh, Y.; Lee, S. Y.; Elless, M. P.; Foss, J. E. Clay Clay Miner. 2000, 48, 266.
doi: 10.1346/CCMN |
| [134] |
Stewart, B. D.; Nico, P. S.; Fendorf, S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4922.
pmid: 19673286 |
| [135] |
Roberts, H. E.; Morris, K.; Law, G. T.W.; Mosselmans, J. F.W.; Bots, P.; Kvashnina, K.; Shaw, S. Environ. Sci. Tech. Let. 2017, 4, 421.
|
| [136] |
Klimkova, S.; Cernik, M.; Lacinova, L.; Filip, J.; Jancik, D.; Zboril, R. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1178.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.11.075 |
| [137] |
Liesch, T.; Hinrichsen, S.; Goldscheider, N. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 981.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.05.133 |
| [138] |
Stumm, W. Chemistry of the Solid-Water Interface: Processes at the Mineral-Water and Particle-Water Interface in Natural Systems, Wiley, New York, 1992, pp.309-325.
|
| [139] |
Markich, S. J. Sci. World. J. 2002, 2, 707.
pmid: 12805996 |
| [140] |
Dong, W.; Brooks, S. C. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4689.
doi: 10.1021/es0606327 |
| [141] |
Lu, X. -C.; Wang, H. -M. Elements 2012, 8, 119.
doi: 10.2113/gselements.8.2.119 |
| [142] |
Cheng, Y.; Holman, H. -Y.; Lin, Z. Elements 2012, 8, 107.
doi: 10.2113/gselements.8.2.107 |
| [143] |
Abdelouas, A. Elements 2006, 2, 335.
doi: 10.2113/gselements.2.6.335 |
| [144] |
Liger, E.; Charlet, L.; Van Cappellen, P. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 1999, 63, 2939.
doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00265-3 |
| [145] |
Wazne, M.; Korfiatis, G. P.; Meng, X. -G. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 3619.
doi: 10.1021/es034166m |
| [146] |
Villalobos, M.; Trotz, M. A.; Leckie, J. O. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3849.
pmid: 11642443 |
| [147] |
Crane, R. A.; Dickinson, M.; Popescu, I. C.; Scott, T. B. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2931.
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.03.012 pmid: 21470652 |
| [148] |
Seder-Colomina, M.; Morin, G.; Brest, J.; Ona-Nguema, G.; Gordien, N.; Pernelle, J. -J.; Banerjee, D.; Mathon, O.; Esposito, G; van Hullebusch, E. D Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14065.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b03148 pmid: 26544528 |
| [149] |
Du, X.; Boonchayaanant, B.; Wu, W. -M.; Fendorf, S.; Bargar, J.; Criddle, C. S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4718.
doi: 10.1021/es2006012 |
| [150] |
Taylor, S. D.; Marcano, M. C.; Rosso, K. M.; Becker, U. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2015, 156, 154.
doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.01.021 |
| [151] |
Hu, S. -H.; Lin, X. -Y.; Zhao, W. -H.; Luo, X. -G. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Ch. 2018, 315, 223.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-017-5662-7 |
| [152] |
Mehta, V. S.; Maillot, F.; Wang, Z.; Catalano, J. G.; Giammar, D. E. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3128.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b06212 |
| [153] |
Tang, G.; Luo, W.; Watson, D. B.; Brooks, S. C.; Gu, B. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5787.
doi: 10.1021/es400169y |
| [154] |
Li, D.; Kaplan, D. I. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 243, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.09.011 |
| [155] |
Missana, T.; García-Gutiérrez, M.; Fernńdez, V. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2003, 67, 2543.
doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(02)01350-9 |
| [156] |
Waite, T. D.; Davis, J. A.; Payne, T. E.; Waychunas, G. A.; Xu, N. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 1994, 58, 5465.
doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90243-7 |
| [157] |
Millero, F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 34, 447.
|
| [158] |
Millero, F. J.; Izaguirre, M. J. Solution Chem. 1989, 18, 585.
doi: 10.1007/BF00664239 |
| [159] |
Missana, T.; Maffiotte, C.; Garcı́a-Gutiérrez, M. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2003, 261, 154.
doi: 10.1016/S0021-9797(02)00227-8 |
| [160] |
Lenhart, J. J.; Honeyman, B. D. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 1999, 63, 2891.
doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00269-0 |
| [161] |
Sherman, D. M.; Peacock, C. L.; Hubbard, C. G. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2008, 72, 298.
doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.10.023 |
| [162] |
Moon, H. S.; Komlos, J.; Jaffé, P. R. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4587.
pmid: 17695901 |
| [163] |
Liu, J.; Gu, T. -H.; Wang, W.; Liu, A. -R.; Zhang, W. -X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 121. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A18100412 |
|
( 刘静, 顾天航, 王伟, 刘爱荣, 张伟贤, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 121.)
doi: 10.6023/A18100412 |
|
| [164] |
Scott, T. B.; Popescu, I. C.; Crane, R. A.; Noubactep, C. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 280.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.10.113 pmid: 21115222 |
| [165] |
Altmaier, M.; Gaona, X.; Fanghänel, T. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 901.
doi: 10.1021/cr300379w pmid: 23369090 |
| [166] |
Zanonato, P.; Di Bernardo, P.; Bismondo, A.; Liu, G.; Chen, X.; Rao, L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5515.
doi: 10.1021/ja0398666 |
| [167] |
Ji, Y. Colloid. Surface. A 2014, 444, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.12.031 |
| [168] |
Tewari, P. H.; McLean, A. W. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 1972, 40, 267.
doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(72)90016-1 |
| [169] |
Environmental Protection Agency, National Primary Drinking Water Regulations, 2009, p. 6.
|
| [170] |
World Health Organization, Guidelines for drinking-water quality: fourth edition incorporating first addendum, 4th ed.+1st add ed., Geneva, 2017, p. 178.
|
| [171] |
Health, Canada, Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality: Guideline Technical Document-Uranium, 1999, pp.7-8.
|
| [172] |
Umwelt Bundesamt, Uranium (U) in drinking water: Brief justification of the health limit value of the drinking water supply (10 μg/L U) and the limit value for "baby-appropriate" packaged water (2 μg/L U), 2013, pp.1-3.
|
| [1] | Guanglong Huang, Xiao-Song Xue. Computational Study on the Mechanism of Chen’s Reagent as Trifluoromethyl Source [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 132-137. |
| [2] | Guoqing Cui, Yiyang Hu, Yingjie Lou, Mingxia Zhou, Yuming Li, Yajun Wang, Guiyuan Jiang, Chunming Xu. Research Progress on the Design, Preparation and Properties of Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Alcohols [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(8): 1081-1100. |
| [3] | Xinpu Fu, Xiuling Wang, Weiwei Wang, Rui Si, Chunjiang Jia. Fabrication and Mechanism Study of Clustered Au/CeO2 Catalyst for the CO Oxidation Reaction★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(8): 874-883. |
| [4] | Luocong Wang, Zhewei Li, Caiwei Yue, Peihuan Zhang, Ming Lei, Min Pu. Theoretical Study on the Isomerization Mechanism of Azobenzene Derivatives under Electric Field [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(6): 781-787. |
| [5] | Siming Yang, Airong Liu, Jing Liu, Zhaoli Liu, Weixian Zhang. Advance of Sulfidated Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron: Synthesis, Properties and Environmental Application [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(11): 1536-1554. |
| [6] | Yichuan Liu, Yalan Liu, Shilin Jiang, Mei Li, Weiqun Shi. Recent Progress on Chemical Species of Uranium in Molten Chlorides [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(12): 1425-1437. |
| [7] | Ziang Bai, Ruixing Chen, Hongwei Pang, Xiangxue Wang, Gang Song, Shujun Yu. Investigation on the Efficient Removal of U(VI) from Water by Sulfide Nanoscale Zero-valent Iron [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(10): 1265-1272. |
| [8] | Huang Rongyi, Shen Qiong, Zhang Chao, Zhang Shaoyong, Xu Heng. Studies on the Mechanism of the Transition Metal-Catalyzed Reaction of Organonitrile with Sodium Azide [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(6): 565-571. |
| [9] | Li Zhangnan, Sha Haoyan, Yang Nan, Yuan Ye, Zhu Guangshan. Phosphoric Acid Based Porous Aromatic Framework for Uranium Extraction [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2019, 77(5): 469-474. |
| [10] | Liu Jing, Gu Tianhang, Wang Wei, Liu Ai-rong, Zhang Wei-xian. Surface Chemistry and Phase Transformation of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) in Aquatic Media [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2019, 77(2): 121-129. |
| [11] | Wu Weirong, Yuan Xiaomin, Hou Hua, Wang Baoshan. Theoretical Investigations on the Mechanisms for the Reactions of Sevoflurane Radicals[(CF3)2C(·)OCH2F, (CF3)2CHOC(·)HF] with O2and the OH· Radicals Regeneration [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2018, 76(10): 793-801. |
| [12] | Mu Weihua, Ma Yao, Fang Decai, Wang Rong, Zhang Haina. Computational Insights into the Diels-Alder-alike Reactions of 1-Iodo-2-Lithio-o-Carborane with Fulvenes [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2018, 76(1): 55-61. |
| [13] | Tang Jing, Tang Lin, Feng Haopeng, Dong Haoran, Zhang Yi, Liu Sishi, Zeng Guangming. Research Progress of Aqueous Pollutants Removal by Sulfidated Nanoscale Zero-valent Iron [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2017, 75(6): 575-582. |
| [14] | Chen Haijun, Huang Shuyi, Zhang Zhibin, Liu Yunhai, Wang Xiangke. Synthesis of Functional Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Composites for the Application of Radioactive Uranium Enrichment from Environment: A Review [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2017, 75(6): 560-574. |
| [15] | Huang Xiao-yue, Wang Wei, Ling Lan, Zhang Wei-xian. Heavy Metal-nZVI Reactions: the Core-shell Structure and Applications for Heavy Metal Treatment [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2017, 75(6): 529-537. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||