Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (3): 253-263.DOI: 10.6023/A22120483 Previous Articles Next Articles
Review
朱子煜, 梁阿新, 浩天瑞霖, 唐珊珊, 刘淼, 解炳腾, 罗爱芹*( )
)
投稿日期:2022-12-03
发布日期:2023-02-15
作者简介: |
朱子煜, 北京理工大学生命学院2021级生物学专业硕士研究生. 2021年进入北京理工大学生命学院罗爱芹教授课题组进行研究生阶段学习. 目前主要从事面向新冠病毒快速检测的生物传感技术研究. |
 |
梁阿新, 博士, 北京理工大学生命学院助理研究员, 2021年于北京理工大学获得理学博士学位. 主要从事电化学生物传感器构建、纳米多孔材料制备与微纳加工的研究. 先后在国际高水平期刊发表SCI论文14篇, 以第一发明人申请国家发明专利4项(已授权2项). |
 |
浩天瑞霖, 北京理工大学生命学院2021级生物学专业硕士研究生. 2021年进入北京理工大学生命学院罗爱芹教授课题组进行研究生阶段学习. 目前主要从事基于COFs的电化学生物传感器的研究. |
 |
唐珊珊,北京理工大学生命学院2019级生物医学工程专业博士研究生. 2019年进入北京理工大学生命学院罗爱芹教授课题组进行博士研究生阶段学习. 目前主要从事基于电化学生物传感器应用与疾病标志物同时检测的研究. |
 |
刘淼, 北京理工大学生命学院2020级生物学专业博士研究生. 2020年进入北京理工大学生命学院罗爱芹教授课题组进行博士研究生阶段学习. 目前主要从事分子印迹电化学传感器的制备及其在心脑血管疾病生物标志物中的应用研究. |
 |
解炳腾, 博士, 生命学院助理教授. 目前的研究方向为解析肿瘤发生机制, 筛选新的抗癌靶点, 构建新型疾病标志物传感器. 获得国家自然科学基金、国家重点研发计划、中国博士后基金资助. 现已在Cell Research, Science Advances, Cancer Research等杂志发表SCI论文30余篇, 申请国家发明专利2项. |
 |
罗爱芹, 北京理工大学生命学院院长, 教授, 博士生导师, 工业和信息化部分子医学与生物诊疗重点实验室主任. 主要研究方向为分子识别与生物传感、生物医学分析与检测研究. 主持或承担项目20余项, 包括国家自然科学基金面上和重点项目、部委重点基础研究项目、部委重大专项、国际合作基金等. |
基金资助:
Ziyu Zhu, Axin Liang, Ruilin Haotian, Shanshan Tang, Miao Liu, Bingteng Xie, Aiqin Luo( )
)
Received:2022-12-03
Published:2023-02-15
Contact:
E-mail: About author:Supported by:Share
Ziyu Zhu, Axin Liang, Ruilin Haotian, Shanshan Tang, Miao Liu, Bingteng Xie, Aiqin Luo. Application of Biosensors in the Detection of SARS-CoV-2[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(3): 253-263.
| Techique | Apparatus | Time required | Sensitivity | Detection limit | Detection range | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest CT scan | CT machine | — | 97%, 25% | — | [ | |
| RT-PCR | PCR apparatus | 4 h | 71% | — | [ | |
| MNPs with RT-PCR | PCR apparatus | Around 30 min | — | 10 copies | [ | |
| Colorimetric assay | Water bath | 30 min | 97.6% | 60 copies per μL | 60~1000 copies per μL | [ |
| ELISA reder | ELISA machine | 2 h | 87.3% | — | [ | |
| Plasmonic biosensor | Dual-functional LSPR System | — | 3.7 RNA copies | 0.1 fmol/L | 0.1~10 fmol/L | [ |
| Electrochemical biosensor | Electrochemical work station | Few min | 0.21 fmol/L | 0.63 fmol/L | 0.63 fmol/L~ 1 μmol/L | [ |
| Field-effect transistor- based biosensor | Semiconductor analyzer | — | — | 2.42×102 copies/mL | [ |
| Techique | Apparatus | Time required | Sensitivity | Detection limit | Detection range | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest CT scan | CT machine | — | 97%, 25% | — | [ | |
| RT-PCR | PCR apparatus | 4 h | 71% | — | [ | |
| MNPs with RT-PCR | PCR apparatus | Around 30 min | — | 10 copies | [ | |
| Colorimetric assay | Water bath | 30 min | 97.6% | 60 copies per μL | 60~1000 copies per μL | [ |
| ELISA reder | ELISA machine | 2 h | 87.3% | — | [ | |
| Plasmonic biosensor | Dual-functional LSPR System | — | 3.7 RNA copies | 0.1 fmol/L | 0.1~10 fmol/L | [ |
| Electrochemical biosensor | Electrochemical work station | Few min | 0.21 fmol/L | 0.63 fmol/L | 0.63 fmol/L~ 1 μmol/L | [ |
| Field-effect transistor- based biosensor | Semiconductor analyzer | — | — | 2.42×102 copies/mL | [ |


| Biomarker | Property | Recognition element (probe) | Detecting mechanism | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RNA | N gene gRNA | CRISPR-Cas12 | Complementary interaction of genes | [ |
| E gene | Aptamer | — | [ | |
| RdRp/Helicase (Hel) | Complementary DNA/RNA | [ | ||
| Whole virus and Proteins | Receptor binding domain (RBD) | Antibody | Conformational recognition | [ |
| Spike protein 1 (S1) | Aptamer | Protein-protein interaction | [ | |
| Spike protein 2 (S2) | — | Protein-aptamer interaction | [ | |
| N proteins | — | — | [ | |
| Antibody | IgM antibody | S proteins | Protein-antibody interaction | [ |
| IgG antibody | N proteins | Antigen-specific antibody response | [ | |
| Neutralizing antibodies:SNAb, REGN-COV2, S309 | The receptor-binding domain (RBD) | — | [ |
| Biomarker | Property | Recognition element (probe) | Detecting mechanism | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RNA | N gene gRNA | CRISPR-Cas12 | Complementary interaction of genes | [ |
| E gene | Aptamer | — | [ | |
| RdRp/Helicase (Hel) | Complementary DNA/RNA | [ | ||
| Whole virus and Proteins | Receptor binding domain (RBD) | Antibody | Conformational recognition | [ |
| Spike protein 1 (S1) | Aptamer | Protein-protein interaction | [ | |
| Spike protein 2 (S2) | — | Protein-aptamer interaction | [ | |
| N proteins | — | — | [ | |
| Antibody | IgM antibody | S proteins | Protein-antibody interaction | [ |
| IgG antibody | N proteins | Antigen-specific antibody response | [ | |
| Neutralizing antibodies:SNAb, REGN-COV2, S309 | The receptor-binding domain (RBD) | — | [ |
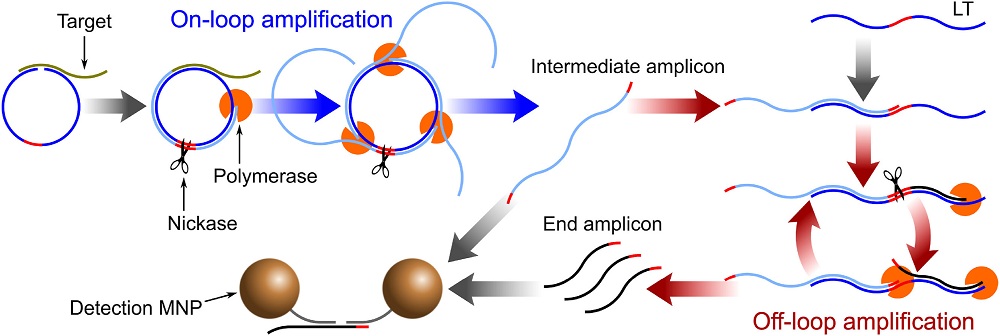
| Material | Detecting technology | Object | Sample | Required time | Lower detection limit | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au nanoparticles | Electrochemical biosensors | RNA | Nasal/throat solution | 5 min | 6.9 copies/μL | [ |
| Electrochemical biosensors | Antibodies | Serum | 30 min | [ | ||
| Colorimetric biosensors | RNA | N/A | >45 min | 160 fmol/L | [ | |
| Macro/ nanostructure Au substrate, Au nanoparticles | SERS-based biosensors | Virus particles | Nasal/throat solution | 15 min | 0.06 copies/μL | [ |
| SPR-based biosensors | Pseudovirus particles | N/A | 15 min | 0.37 vp/μL | [ | |
| Graphene & Copper | Electrochemical biosensors | Cholinesterase | Blood | ca. 7 s | 0.079 μmol/L | [ |
| Graphene | Electrochemical biosensors | RNA | Nasal/throat solution | 1 min | 0.01~0.02 copies/μL | [ |
| Fluorescence biosensors | RNA | Lysis solution | 15 samples/45 min | 0.6 copies/μL | [ |
| Material | Detecting technology | Object | Sample | Required time | Lower detection limit | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au nanoparticles | Electrochemical biosensors | RNA | Nasal/throat solution | 5 min | 6.9 copies/μL | [ |
| Electrochemical biosensors | Antibodies | Serum | 30 min | [ | ||
| Colorimetric biosensors | RNA | N/A | >45 min | 160 fmol/L | [ | |
| Macro/ nanostructure Au substrate, Au nanoparticles | SERS-based biosensors | Virus particles | Nasal/throat solution | 15 min | 0.06 copies/μL | [ |
| SPR-based biosensors | Pseudovirus particles | N/A | 15 min | 0.37 vp/μL | [ | |
| Graphene & Copper | Electrochemical biosensors | Cholinesterase | Blood | ca. 7 s | 0.079 μmol/L | [ |
| Graphene | Electrochemical biosensors | RNA | Nasal/throat solution | 1 min | 0.01~0.02 copies/μL | [ |
| Fluorescence biosensors | RNA | Lysis solution | 15 samples/45 min | 0.6 copies/μL | [ |
| [1] |
Huang C. L.; Wang Y. M.; Li X. W.; Ren L. L.; Zhao J. P.; Hu Y.; Zhang Y.; Fan G. H.; Xu J. Y.; Gu X. Y.; Cheng Z. S.; Yu T.; Xia J. A.; Wei Y.; Wu W. J.; Xie X. L.; Yin W.; Li H.; Liu M.; Xiao Y.; Gao H.; Guo L.; Xie J. G.; Wang G. F.; Jiang R. M.; Gao Z. C.; Jin Q.; Wang J. W.; Cao B. Lancet 2020, 395, 497.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5 |
| [2] |
Lee C. Y.; Degani I.; Cheong J.; Lee J.-H.; Choi H.-J.; Cheon J.; Lee H. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178, 113049.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113049 |
| [3] |
Li Q.; Guan X. H.; Wu P.; Wang X. Y.; Zhou L.; Tong Y. Q.; Ren R. Q.; Leung K.; Lau E. H. Y.; Wong J. Y.; Xing X. S.; Xiang N. J. New Eng. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1199.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001316 |
| [4] |
Wang Y. X.; Zhang Y.; Chen J. B.; Wang M. J.; Zhang T.; Luo W. X.; Li Y. L.; Wu Y. P.; Zeng B.; Zhang K. X.; Deng R. J.; Li W. M. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3393.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04303 |
| [5] |
Oran D. P.; Topol E. J. Ann. Int. Med. 2020, 173, 362.
doi: 10.7326/M20-3012 |
| [6] |
Wang C.; Gao Z. D.; Shen K.; Cao J.; Shen Z. L.; Jiang K. W.; Wang S.; Ye Y. J. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 46, 667.
|
| [7] |
Yadav P. D.; Sapkal G. N.; Ella R.; Sahay R. R.; Nyayanit D. A.; Patil D. Y.; Deshpande G.; Shete A. M.; Gupta N.; Mohan V. K. J. Travel Med. 2021, 28, taab104.
|
| [8] |
Connor B. A.; Couto-Rodriguez M.; Barrows J. E.; Gardner M.; Rogova M.; O'Hara N. B.; Nagy-Szakal D. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 110, 232.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.07.029 |
| [9] |
Pal M.; Berhanu G.; Desalegn C.; Kandi V. Cureus 2020, 12, e7423.
|
| [10] |
Docea A. O.; Tsatsakis A.; Albulescu D.; Cristea O.; Zlatian O.; Vinceti M.; Moschos S. A.; Tsoukalas D.; Goumenou M.; Drakoulis N. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 1631.
doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4555 pmid: 32236624 |
| [11] |
Azzi L.; Carcano G.; Gianfagna F.; Grossi P.; Dalla Gasperina D.; Genoni A.; Fasano M.; Sessa F.; Tettamanti L.; Carinci F. J. Infect. 2020, 81, e45.
|
| [12] |
Sea-Liang N.; Sereemaspun A.; Patarakul K.; Gaywee J.; Rodkvamtook W.; Srisawat N.; Wacharaplusadee S.; Hemachudha T. PLoS Negl.Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007440.
|
| [13] |
Lucas E. J.; Leber A.; Ardura M. I. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2019, 38, 786.
doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002308 |
| [14] |
Kim H.; Park M.; Hwang J.; Kim J. H.; Chung D.-R.; Lee K.-s.; Kang M. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1306.
doi: 10.1021/acssensors.9b00175 |
| [15] |
Xu Y.; Xiao M.; Liu X.; Xu S.; Du T.; Xu J.; Yang Q.; Xu Y.; Han Y.; Li T. Emerg. Microb. Infect. 2020, 9, 924.
doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1752610 |
| [16] |
Sun F.; Ganguli A.; Nguyen J.; Brisbin R.; Shanmugam K.; Hirschberg D. L.; Wheeler M. B.; Bashir R.; Nash D. M.; Cunningham B. T. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 1621.
doi: 10.1039/d0lc00304b pmid: 32334422 |
| [17] |
Palmieri V.; Papi M. Nano Today 2020, 33, 100883.
doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2020.100883 |
| [18] |
Maghdid H. S.; Ghafoor K. Z.; Sadiq A. S.; Curran K.; Rabie K. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.07434. 2003.
|
| [19] |
Mahmoudi M. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 18, 476.
doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00371 |
| [20] |
Xu L.; Li D.; Ramadan S.; Li Y.; Klein N. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 170, 112673.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112673 |
| [21] |
Fathi-Hafshejani P.; Azam N.; Wang L.; Kuroda M. A.; Hamilton M. C.; Hasim S.; Mahjouri-Samani M. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 11461.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c01188 pmid: 34181385 |
| [22] |
Kaur H.; Shorie M. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 2123.
doi: 10.1039/C9NA00153K |
| [23] |
Dincer C.; Bruch R.; Costa‐Rama E.; Fernández‐Abedul M. T.; Merkoçi A.; Manz A.; Urban G. A.; Güder F. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1806739.
|
| [24] |
Rezaei Z.; Mahmoudifard M. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 4602.
doi: 10.1039/c9tb00682f pmid: 31364667 |
| [25] |
Zhang X.; Yang S.; Jiang R.; Sun L.; Pang S.; Luo A. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2018, 254, 1078.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2017.07.205 |
| [26] |
Feng D.; Huang P.; Miao Y.; Liang A.; Wang X.; Tang B.; Hou H.; Ren M.; Gao S.; Geng L.; Luo A. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2022, 368, 132121.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2022.132121 |
| [27] |
Liang A.; Tang S.; Liu M.; Yi Y.; Xie B.; Hou H.; Luo A. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 146, 108154.
doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2022.108154 |
| [28] |
Luo A.; Cai Y.; Liu M.; Tang S.; Zhu Z.; Haotian R.; Xie B.; Yi Y.; Hao Z.; Liang A. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 117504.
doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/ac9ee7 |
| [29] |
Liu M.; Pan B.; Tang S.; Wang W.; Hou H.; Xie B.; Liang A.; Luo A. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 087503.
doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/ac837b |
| [30] |
Ai T.; Yang Z.; Hou H.; Zhan C.; Chen C.; Lv W.; Tao Q.; Sun Z.; Xia L. Radiology 2020, 26, 200642.
|
| [31] |
Fang Y.; Zhang H.; Xie J.; Lin M.; Ying L.; Pang P.; Ji W. Radiology 2020, 19, 200432.
|
| [32] |
Pan Y.; Li X.; Yang G.; Fan J.; Tang Y.; Zhao J.; Long X.; Guo S.; Zhao Z.; Liu Y. J. Infect. 2020, 81, e28.
|
| [33] |
Yu L.; Wu S.; Hao X.; Dong X.; Mao L.; Pelechano V.; Chen W. H.; Yin X. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 975.
doi: 10.1093/clinchem/hvaa102 |
| [34] |
Xiang J.; Yan M.; Li H.; Liu T.; Lin C.; Huang S.; Shen C. MedRxiv 2020, 1.
|
| [35] |
Liu J.; Chen X.; Wang Q.; Xiao M.; Zhong D.; Sun W.; Zhang G.; Zhang Z. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 1437.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b03818 |
| [36] |
Kumar N.; Shetti N. P.; Jagannath S.; Aminabhavi T. M. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132966.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.132966 |
| [37] |
Asif M.; Aziz A.; Wang H.; Wang Z.; Wang W.; Ajmal M.; Xiao F.; Chen X.; Liu H. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 61.
doi: 10.1007/s00604-018-3158-y |
| [38] |
Giannetti A.; Bocková M. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 33.
doi: 10.3390/chemosensors8020033 |
| [39] |
Ji T.; Liu Z.; Wang G.; Guo X.; Lai C.; Chen H.; Huang S.; Xia S.; Chen B.; Jia H. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 166, 112455.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112455 |
| [40] |
Mahapatra S.; Chandra P. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112361.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112361 |
| [41] |
Palestino G.; García-Silva I.; González-Ortega O.; Rosales-Mendoza S. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 849.
doi: 10.1080/14787210.2020.1776115 pmid: 32574081 |
| [42] |
Wen T.; Huang C.; Shi F. J.; Zeng X. Y.; Lu T.; Ding S. N.; Jiao Y. J. Analyst 2020, 145, 5345.
doi: 10.1039/D0AN00629G |
| [43] |
Thapa D.; Samadi N.; Tabatabaei N. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 18504.
doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3089016 |
| [44] |
Li Z.; Yi Y.; Luo X.; Xiong N.; Liu Y.; Li S.; Sun R.; Wang Y.; Hu B.; Chen W. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1518.
doi: 10.1002/jmv.v92.9 |
| [45] |
Łoczechin A.; Séron K.; Barras A.; Giovanelli E.; Belouzard S.; Chen Y.-T.; Metzler-Nolte N.; Boukherroub R.; Dubuisson J.; Szunerits S. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 42964.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b15032 |
| [46] |
Manivannan S.; Ponnuchamy K. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5887.
|
| [47] |
Huang J. C.; Chang Y. F.; Chen K. H.; Su L. C.; Lee C. W.; Chen C. C.; Chen Y. M. A.; Chou C. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 320.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2009.07.012 |
| [48] |
Lin Q.; Wen D.; Wu J.; Liu L.; Wu W.; Fang X.; Kong J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9454.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01635 |
| [49] |
Wu K.; Saha R.; Su D.; Krishna V. D.; Liu J.; Cheeran M. C. J.; Wang J. P. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007. 04809 2020.
|
| [50] |
Asad M.; Zulfiqar A.; Raza R.; Yang M.; Hayat A.; Akhtar N. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 11.
doi: 10.1002/elan.v32.1 |
| [51] |
Gowri A.; Kumar N. A.; Anand B. S. S. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 137, 116205.
doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2021.116205 |
| [52] |
Krejcova L.; Hynek D.; Adam V.; Hubalek J.; Kizek R. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 10779.
|
| [53] |
Dziąbowska K.; Czaczyk E.; Nidzworski D. Biosensors 2018, 8, 94.
doi: 10.3390/bios8040094 |
| [54] |
Xie M.; Zhao F.; Zhang Y.; Xiong Y.; Han S. Food Control 2022, 131, 108399.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108399 |
| [55] |
Sedki M.; Shen Y.; Mulchandani A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 176, 112941.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112941 |
| [56] |
Zhang Y.; Feng D.; Xu Y.; Yin Z.; Dou W.; Habiba U. E.; Pan C.; Zhang Z.; Mou H.; Deng H. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 548, 149169.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149169 |
| [57] |
Novodchuk I.; Bajcsy M.; Yavuz M. Carbon 2021, 172, 431.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.10.048 |
| [58] |
Song P.; Fu H.; Wang Y.; Chen C.; Ou P.; Rashid R. T.; Duan S.; Song J.; Mi Z.; Liu X. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 190, 113264.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113264 |
| [59] |
Seo G.; Lee G.; Kim M. J.; Baek S. H.; Choi M.; Ku K. B.; Lee C. S.; Jun S.; Park D.; Kim H. G. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5135.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c02823 |
| [60] |
Kim H. E.; Schuck A.; Lee S. H.; Lee Y.; Kang M.; Kim Y.-S. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 182, 113168.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113168 |
| [61] |
Tripathy S.; Singh S. G. Trans. Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 2020, 5, 205.
doi: 10.1007/s41403-020-00103-z |
| [62] |
Mahari S.; Roberts A.; Shahdeo D.; Gandhi S. BioRxiv 2020, 4, 059204.
|
| [63] |
Chu D. K. W.; Pan Y.; Cheng S. M. S.; Hui K. P. Y.; Krishnan P.; Liu Y.; Ng D. Y. M.; Wan C. K. C.; Yang P.; Wang Q. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 549.
doi: 10.1093/clinchem/hvaa029 |
| [64] |
Corman V. M.; Landt O.; Kaiser M.; Molenkamp R.; Meijer A.; Chu D. K. W.; Bleicker T.; Brünink S.; Schneider J.; Schmidt M. L. Euro. Surveill. 2020, 25, 2000045.
|
| [65] |
Won J.; Lee S.; Park M.; Kim T. Y.; Park M. G.; Choi B. Y.; Kim D.; Chang H.; Kim V. N.; Lee C. J. Exp. Neurobiol. 2020, 29, 107.
doi: 10.5607/en20009 |
| [66] |
Wu A.; Peng Y.; Huang B.; Ding X.; Wang X.; Niu P.; Meng J.; Zhu Z.; Zhang Z.; Wang J. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 325.
doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.02.001 |
| [67] |
Nieto-Torres J. L.; DeDiego M. L.; Verdiá-Báguena C.; Jimenez-Guardeño J. M.; Regla-Nava J. A.; Fernandez-Delgado R.; Castaño-Rodriguez C.; Alcaraz A.; Torres J.; Aguilella V. M. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004077.
|
| [68] |
Zhou P.; Yang X. L.; Wang X. G.; Hu B.; Zhang L.; Zhang W.; Si H. R.; Zhu Y.; Li B.; Huang C. L. Nature 2020, 579, 270.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7 |
| [69] |
Jiang H.; Li Y.; Zhang H.; Wang W.; Men D.; Yang X.; Qi H.; Zhou J.; Tao S. MedRxiv 2020, doi: 10.1101/2020.03.20.20039495.
doi: 10.1101/2020.03.20.20039495 |
| [70] |
To K. K. W.; Yip C. C. Y.; Lai C. Y. W.; Wong C. K. H.; Ho D. T. Y.; Pang P. K. P.; Ng A. C. K.; Leung K. H.; Poon R. W. S.; Chan K. H. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 372.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2018.06.009 |
| [71] |
Zhang W.; Du R. H.; Li B.; Zheng X. S.; Yang X. L.; Hu B.; Wang Y. Y.; Xiao G. F.; Yan B.; Shi Z. L. EMI 2020, 9, 386.
|
| [72] |
Peng M.; Yang J.; Shi Q.; Ying L.; Zhu H.; Zhu G.; Ding X.; He Z.; Qin J.; Wang J. SSRN 2020, doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3541119.
doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3541119 |
| [73] |
Crean C.; Mcgeouge C.; O’kennedy R.In Biosensors for Medical Applications, Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials, Woodhead Publishing, Sawston, Cambridge, 2012, pp. 301-330.
|
| [74] |
Zeng X.; Peng R.; Fan Z.; Lin Y. Mater. Today Energy 2022, 23, 100900.
|
| [75] |
Yang M.; Wang H.; Liu P.; Cheng J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 179, 113082.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113082 |
| [76] |
Tu J.; Torrente‐Rodríguez R. M.; Wang M.; Gao W. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1906713.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v30.29 |
| [77] |
Mujawar M. A.; Gohel H.; Bhardwaj S. K.; Srinivasan S.; Hickman N.; Kaushik A. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 17, 100306.
|
| [78] |
Sharma A.; Badea M.; Tiwari S.; Marty J. L. Molecules 2021, 26, 748.
doi: 10.3390/molecules26030748 |
| [79] |
Stojanović R.; Škraba A.; Djurković J.; Lutovac B.In 2022 11th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), IEEE, New York, 2022, pp. 1-5.
|
| [80] |
Tavakoli M.; Carriere J.; Torabi A. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 2000071.
doi: 10.1002/aisy.v2.7 |
| [81] |
Karpova E. V.; Karyakin A. A. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2020, 23, 16.
|
| [82] |
Seshadri D. R.; Davies E. V.; Harlow E. R.; Hsu J. J.; Knighton S. C.; Walker T. A.; Voos J. E.; Drummond C. K. Front. Digit. Health 2020, 2, 8.
doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2020.00008 pmid: 34713021 |
| [83] |
Atangana E.; Atangana A. Results Phys. 2020, 19, 103425.
doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2020.103425 |
| [84] |
Xie J.; Zhu Y. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138201.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138201 |
| [85] |
Schünemann H. J.; Akl E. A.; Chou R.; Chu D. K.; Loeb M.; Lotfi T.; Mustafa R. A.; Neumann I.; Saxinger L.; Sultan S. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 954.
doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30352-0 pmid: 32758441 |
| [86] |
Jeong H.; Rogers J. A.; Xu S. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabd4794.
|
| [87] |
Deng W.; Sun Y.; Yao X.; Subramanian K.; Ling C.; Wang H.; Chopra S. S.; Xu B. B.; Wang J. X.; Chen J. F. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2102189.
doi: 10.1002/advs.v9.3 |
| [88] |
Liu X.; Zhang S. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2020, 14, 472.
doi: 10.1111/irv.v14.4 |
| [89] |
Rabiee N.; Bagherzadeh M.; Ghasemi A.; Zare H.; Ahmadi S.; Fatahi Y.; Dinarvand R.; Rabiee M.; Ramakrishna S.; Shokouhimehr M. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5126.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21145126 |
| [90] |
Wang Y.; Hu Y.; He Q.; Yan J.; Xiong H.; Wen N.; Cai S.; Peng D.; Liu Y.; Liu Z. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112604.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112604 |
| [91] |
Islam M. A.; Ahsan M. Z. Am. J. Nanosci 2020, 6, 6.
doi: 10.11648/j.ajn.20200602.11 |
| [92] |
Tian B.; Fock J.; Minero G. A. S.; Hansen M. F. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 160, 112219.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112219 |
| [93] |
Tian B.; Gao F.; Fock J.; Dufva M.; Hansen M. F. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112356.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112356 |
| [94] |
Zhao Z.; Cui H.; Song W.; Ru X.; Zhou W.; Yu X. BioRxiv 2020, doi: 10.1101/2020.02.22.961268.
doi: 10.1101/2020.02.22.961268 |
| [95] |
Wang J.; Drelich A. J.; Hopkins C. M.; Mecozzi S.; Li L.; Kwon G.; Hong S. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 14, e1754.
|
| [96] |
Qiu G.; Gai Z.; Tao Y.; Schmitt J.; Kullak-Ublick G. A.; Wang J. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5268.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c02439 |
| [97] |
Moitra P.; Alafeef M.; Dighe K.; Frieman M. B.; Pan D. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 7617.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c03822 |
| [98] |
Zhao Y.; Chen J.; Hu Z.; Chen Y.; Tao Y.; Wang L.; Li L.; Wang P.; Li H. Y.; Zhang J.; Tang J.; Liu H. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 202, 113974.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.113974 |
| [99] |
Zhao J.; Fu Z.; Li H.; Xiong Y.; Cai S.; Wang C.; Chen Y.; Han N.; Yang R. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 404, 139766.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.139766 |
| [100] |
Vadlamani B. S.; Uppal T.; Verma S. C.; Misra M. Sensors 2020, 20, 5871.
doi: 10.3390/s20205871 |
| [101] |
Chinnappan R.; Rahamn A. A.; AlZabn R.; Kamath S.; Lopata A. L.; Abu-Salah K. M.; Zourob M. Food Chem. 2020, 314, 126133.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.126133 |
| [102] |
Song Y.; Song J.; Wei X.; Huang M.; Sun M.; Zhu L.; Lin B.; Shen H.; Zhu Z.; Yang C. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9895.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01394 |
| [103] |
Tian J.; Liang Z.; Hu O.; He Q.; Sun D.; Chen Z. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 387, 138553.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138553 |
| [104] |
Abrego-Martinez J. C.; Jafari M.; Chergui S.; Pavel C.; Che D.; Siaj M. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 195, 113595.
|
| [105] |
Alafeef M.; Dighe K.; Moitra P.; Pan D. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 17028.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c06392 pmid: 33079516 |
| [106] |
Lorenzen A. L.; Dos Santos A. M.; Dos Santos L. P.; da Silva Pinto L.; Conceição F. R.; Wolfart F. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 404, 139757.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.139757 |
| [107] |
Godakhindi V. S.; Kang P.; Serre M.; Revuru N. A.; Zou J. M.; Roner M. R.; Levitz R.; Kahn J. S.; Randrianalisoa J.; Qin Z. ACS Sensors 2017, 2, 1627.
doi: 10.1021/acssensors.7b00482 pmid: 28994578 |
| [108] |
Li Y.; Lin C.; Peng Y.; He J.; Yang Y. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2022, 365, 131974.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2022.131974 |
| [109] |
Huang L.; Ding L.; Zhou J.; Chen S.; Chen F.; Zhao C.; Xu J.; Hu W.; Ji J.; Xu H.; Liu G. L. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112685.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112685 |
| [110] |
ElDin N. B.; Abd El-Rahman M. K.; Zaazaa H. E.; Moustafa A. A.; Hassan S. A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 190, 113439.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113439 |
| [111] |
Wang L.; Wang X.; Wu Y.; Guo M.; Gu C.; Dai C.; Kong D.; Wang Y.; Zhang C.; Qu D.; Fan C.; Xie Y.; Zhu Z.; Liu Y.; Wei D. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 276.
doi: 10.1038/s41551-021-00833-7 |
| [112] |
Chu Y.; Qiu J.; Wang Y.; Wang M.; Zhang Y.; Han L. Chem.- Eur. J. 2022, 28, e202104054.
|
| [1] | Chaofan Ma, Wei Xu, Wei Liu, Changhui Xu, Jingjie Sha. Proactive Manipulation Techniques for Protein Transport at Confined Nanoscale [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(7): 857-868. |
| [2] | Lanying Li, Qing Tao, Yanli Wen, Lele Wang, Ruiyan Guo, Gang Liu, Xiaolei Zuo. Poly-adenine-based DNA Probes and Their Applications in Biosensors★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 681-690. |
| [3] | Huarun Liang, Haoxuan Ma, Xinrong Duan, Jie Yu, Haomin Wang, Shuo Li, Mengjia Zhu, Aibing Chen, Hui Zheng, Yingying Zhang. Flexible Electrochemical Sensors and Their Applications in Noninvasive Medical Detection★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(10): 1402-1419. |
| [4] | Xu Yan, Hemi Qu, Ye Chang, Xuexin Duan. Application of Metal-Organic Frameworks in Gas Pre-concentration, Pre-separation and Detection [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(8): 1183-1202. |
| [5] | Lixuan Liu, Yang Yang, Zhixiang Wei. Chiral Organic Optoelectronic Materials and Circularly Polarized Light Luminescence and Detection [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 970-992. |
| [6] | Fen Zhang, Xiaoqi Li, Shiguo Han, Fafa Wu, Xitao Liu, Zhihua Sun, Junhua Luo. Bulk Single Crystal Growth of a Two-Dimensional Halide Perovskite Ferroelectric for Highly Polarized-Sensitive Photodetection※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 237-243. |
| [7] | Ruilin Haotian, Ziyu Zhu, Yanhui Cai, Wei Wang, Zhen Wang, Axin Liang, Aiqin Luo. Application of Covalent Organic Framework-Based Electrochemical Biosensors in Biological Sample Detection [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(11): 1524-1535. |
| [8] | Xu Yang, Zeying Zhang, Meng Su, Yanlin Song. Research Progress on Nano Photonics Technology-based SARS-CoV-2 Detection※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(1): 80-88. |
| [9] | Yao Shi, Qianfeng Xia, Zhengqing He, Huangxian Ju. Biosensing Technology for Dengue Virus Detection [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(1): 69-79. |
| [10] | Chen-chen Li, Hui-yan Chen, Yue-hong Dong, Xiliang Luo, Juan Hu, Chun-yang Zhang. Advances in Detection of Epigenetic Modification—5-Hydroxymethylcytosine [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(5): 614-627. |
| [11] | Ni Liao, Xia Zhong, Wen-Bin Liang, Ruo Yuan, Ying Zhuo. Metal-organic Frameworks (MOF)-based Novel Electrochemiluminescence Biosensing Platform for Quantification of H2O2 Releasing from Tumor Cells [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(10): 1257-1264. |
| [12] | Hui He, Lingli Zhou, Zhen Liu. Advances in Protein Biomarker Assay via the Combination of Molecular Imprinting and Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(1): 45-57. |
| [13] | Fan Lei, Jiang Qunying, Pan Min, Wang Wenxiao, Zhang Li, Liu Xiaoqing. Dual-Mode Sensing of Biomarkers by Mimic Enzyme-Natural Enzyme Cascade Signal Amplification [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(5): 419-426. |
| [14] | Wang Mingyuan, Cui Xiaoyu, Cai Wensheng, Shao Xueguang. Temperature-Dependent Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Sensitive Detection of Glucose [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(2): 125-129. |
| [15] | Sun Yanhui, Qi Youxiao, Shen You, Jing Cuijie, Chen Xiaoxiao, Wang Xinxing. Preparation of Electrochemical Sensor Based on RGO-Au-ZIF-8 Composite and Its Application in Simultaneous Detection of Lead Ions and Copper Ions [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(2): 147-154. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||