有机化学 ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (8): 3015-3033.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202012036 上一篇 下一篇
综述与进展
陈超a,b, 胡晓东b, 王春喜b, 蓝文贤b, 吴小余a,*( ), 曹春阳b,*(
), 曹春阳b,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-12-22
修回日期:2021-03-12
发布日期:2021-04-29
通讯作者:
吴小余, 曹春阳
基金资助:
Chao Chena,b, Xiaodong Hub, Chunxi Wangb, Wenxian Lanb, Xiaoyu Wua( ), Chunyang Caob(
), Chunyang Caob( )
)
Received:2020-12-22
Revised:2021-03-12
Published:2021-04-29
Contact:
Xiaoyu Wu, Chunyang Cao
Supported by:文章分享

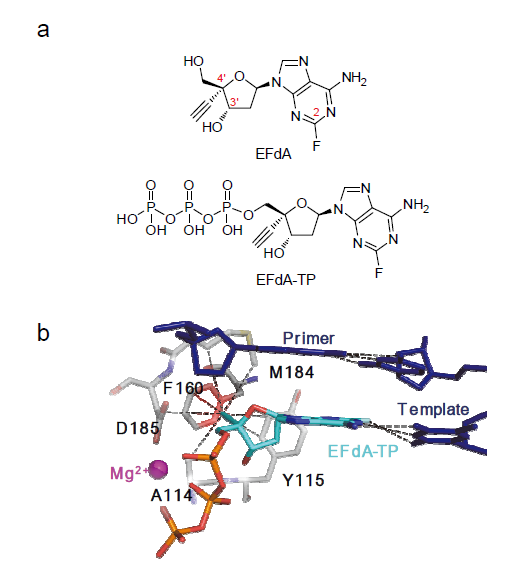
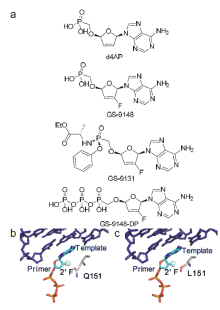
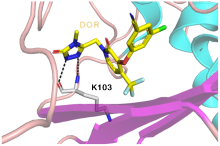
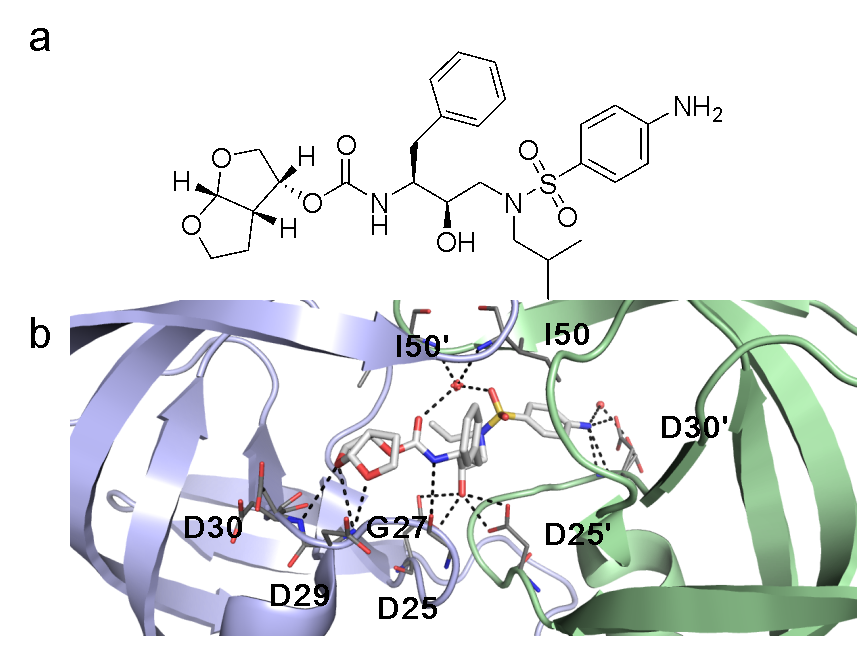
人体免疫缺陷病毒(Human immunodeficiency virus, HIV)是一种主要以CD4+T淋巴细胞和巨噬细胞等免疫细胞为靶点的感染性逆转录病毒, HIV感染的最终阶段为出现获得性免疫缺陷综合征(Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, AIDS). HIV迄今为止已经夺去近3300万人生命, 是全球最大的公共卫生挑战之一. 自从抗逆转录病毒治疗(Antiretrovial therapy, ART)出现以后, 抗逆转录药物的联合使用使艾滋病从致死性疾病变成慢性可控性疾病. 为了开发新的抗艾滋病药物, 基于病毒复制周期中的不同靶标将近年发展的抗艾滋病药物进行分类简述, 重点关注于药物的作用机制研究、临床应用现状及未来发展方向.
陈超, 胡晓东, 王春喜, 蓝文贤, 吴小余, 曹春阳. 基于靶标结构及作用机制的抗艾滋病药物研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(8): 3015-3033.
Chao Chen, Xiaodong Hu, Chunxi Wang, Wenxian Lan, Xiaoyu Wu, Chunyang Cao. Structure- and Mechanism-Based Research Progress of Anti-acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome Drugs[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 41(8): 3015-3033.
| 药物类型 | 药物名称 | 研发状况 | 公司 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 核苷类反转录酶抑制剂 | EFdA (MK-8591, Islatravir ) | Ⅲ期临床 | Merck & Co | |
| GS-9131 (Rovafovir Etalafenamide) | 临床前期 | Gilead Sciences | ||
| 非核苷类反转录酶抑制剂 | Doravirine (MK-1439) | 已上市 | Merck & Co | |
| Elsulfavirine (VM1500) | Ⅱ/Ⅲ期临床 | Viriom | ||
| 蛋白酶抑制剂 | Darunavir | 已上市 | Tibotec | |
| 整合酶抑制剂 | Cabotegravir (GSK1265744) | 已上市 | ViiV Healthcare | |
| 侵入抑制剂 | 附着抑制剂 | Fostemsavir (GSK-3684394, BMS-663068) | 已上市 | ViiV Healthcare |
| 附着后抑制剂 | Trogarzo (ibalizumab-uiyk) | 已上市 | TaiMed Biologics | |
| 趋化因子受体抑制剂 | Thioraviroc | Ⅰ期临床 | 上海药物研究所 昆明动物研究所 | |
| 融合抑制剂 | Albuvirtide | 已上市 | 前沿生物 | |
| 衣壳抑制剂 | Lenacapavir (GS-6207) | Ⅱ/Ⅲ期临床 | Gilead Sciences | |
| 成熟抑制剂 | GSK2838232 | Ⅱ期临床 | GlaxoSmithKline |
| 药物类型 | 药物名称 | 研发状况 | 公司 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 核苷类反转录酶抑制剂 | EFdA (MK-8591, Islatravir ) | Ⅲ期临床 | Merck & Co | |
| GS-9131 (Rovafovir Etalafenamide) | 临床前期 | Gilead Sciences | ||
| 非核苷类反转录酶抑制剂 | Doravirine (MK-1439) | 已上市 | Merck & Co | |
| Elsulfavirine (VM1500) | Ⅱ/Ⅲ期临床 | Viriom | ||
| 蛋白酶抑制剂 | Darunavir | 已上市 | Tibotec | |
| 整合酶抑制剂 | Cabotegravir (GSK1265744) | 已上市 | ViiV Healthcare | |
| 侵入抑制剂 | 附着抑制剂 | Fostemsavir (GSK-3684394, BMS-663068) | 已上市 | ViiV Healthcare |
| 附着后抑制剂 | Trogarzo (ibalizumab-uiyk) | 已上市 | TaiMed Biologics | |
| 趋化因子受体抑制剂 | Thioraviroc | Ⅰ期临床 | 上海药物研究所 昆明动物研究所 | |
| 融合抑制剂 | Albuvirtide | 已上市 | 前沿生物 | |
| 衣壳抑制剂 | Lenacapavir (GS-6207) | Ⅱ/Ⅲ期临床 | Gilead Sciences | |
| 成熟抑制剂 | GSK2838232 | Ⅱ期临床 | GlaxoSmithKline |








| [1] |
World Health Organization. HIV/AIDS[EB/OL] (2020-07-06). https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hiv-aids
|
| [2] |
Klatzmann, D.; Barre-Sinoussi, F.; Nugeyre, M. T.; Danquet, C.; Vilmer, E.; Griscelli, C.; Brun-Veziret, F.; Rouzioux, C.; Gluckman, J. C.; Chermann, J. C.; Montagnier, L. Science 1984, 225, 59.
pmid: 6328660 |
| [3] |
Esbjornsson, J.; Mansson, F.; Kvist, A.; da Silva, Z. J.; Andersson, S.; Fenyo, E. M.; Isberg, P. E.; Biague, A. J.; Lindman, J.; Palm, A. A.; Rowland-Jones, S. L.; Jansson, M.; Medstrand, P.; Norrgren, H.; Sweden and Guinea-Bissau Cohort Research Group. Lancet HIV 2019, 6, 25.
|
| [4] |
Fanales-Belasio, E.; Raimondo, M.; Suligoi, B.; Butto, S. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2010, 46, 5.
doi: 10.4415/ANN_10_01_02 pmid: 20348614 |
| [5] |
Richter, S. N.; Frasson, I.; Palu, G. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 267.
pmid: 19149577 |
| [6] |
Shum, K. T.; Zhou, J.; Rossi, J. J. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 1507.
doi: 10.3390/ph6121507 |
| [7] |
Gelderblom, H. R.; Ozel, M.; Pauli, G. Arch. Virol. 1989, 106, 1.
pmid: 2669684 |
| [8] |
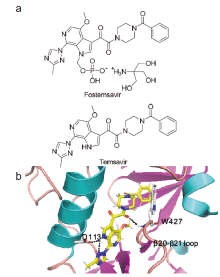
Palmisano, L.; Vella, S. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2011, 47, 44.
doi: 10.4415/ANN_11_01_10 pmid: 21430338 |
| [9] |
Castro, S. D.; Camarasa, M. J. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 150, 206.
doi: S0223-5234(18)30242-3 pmid: 29529501 |
| [10] |
Kleinpeter, A. B.; Freed, E. O. Viruses 2020, 12, 940.
doi: 10.3390/v12090940 |
| [11] |
Kakuda, T. N. Clin. Ther. 2000, 22, 685.
pmid: 10929917 |
| [12] |
Ruane, P. J.; DeJesus, E.; Berger, D.; Markowitz, M.; Bredeek, U. F.; Callebaut, C.; Zhong, L.; Ramanathan, S.; Rhee, M. S.; Fordyce, M. W.; Yale, K. J. Acquired Immune Defic. Syndr. 2013, 63, 449.
|
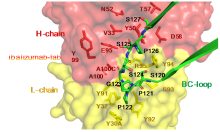
| [13] |
Ohrui, H. Chem. Rec. 2006, 6, 133.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1528-0691 |
| [14] |
Ohrui, H.; Kohgo, S.; Hayakawa, H.; Kodama, E.; Matsuoka, M.; Nakata, T.; Mitsuya, H. Nucleosides, Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2007, 26, 1543.
doi: 10.1080/15257770701545218 |
| [15] |
Kawamoto, A.; Kodama, E.; Sarafianos, S. G.; Sakagami, Y.; Kohgo, S.; Kitano, K.; Ashida, N.; Iwai, Y.; Hayakawa, H.; Nakata, H.; Mitsuya, H.; Arnold, E.; Matsuoka, M. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 2410.
doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.04.007 |
| [16] |
Kirby, K. A.; Michailidis, E.; Fetterly, T. L.; Steinbach, M. A.; Singh, K.; Marchand, B.; Leslie, M. D.; Hagedorn, A. N.; Kodama, E. N.; Marquez, V. E.; Hughes, S. H.; Mitsuya, H.; Parniak, M. A.; Sarafianos, S. G. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 6254.
doi: 10.1128/AAC.01703-13 |
| [17] |
Muftuoglu, Y.; Sohl, C. D.; Mislak, A. C.; Mitsuya, H.; Sarafianos, S. G.; Anderson, K. S. Antiviral Res. 2014, 106, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.03.001 |
| [18] |
Michailidis, E.; Marchand, B.; Kodama, E. N.; Singh, K.; Matsuoka, M.; Kirby, K. A.; Ryan, E. M.; Sawani, A. M.; Nagy, E.; Ashida, N.; Mitsuya, H.; Parniak, M. A.; Sarafianos, S. G. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35681.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.036616 |
| [19] |
Salie, Z. L.; Kirby, K. A.; Michailidis, E.; Marchand, B.; Singh, K.; Rohan, L. C.; Kodama, E. N.; Mitsuya, H.; Parniak, M. A.; Sarafianos, S. G. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2016, 113, 9274.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1605223113 pmid: 27489345 |
| [20] |
McLaughlin, M.; Kong, J.; Belyk, K. M.; Chen, B.; Gibson, A. W.; Keen, S. P.; Lieberman, D. R.; Milczek, E. M.; Moore, J. C.; Murray, D.; Peng, F.; Qi, J.; Reamer, R. A.; Song, Z. J.; Tan, L.; Wang, L.; Williams, M. J. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 926.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b00091 pmid: 28165251 |
| [21] |
Nawrat, C. C.; Whittaker, A. M.; Huffman, M. A.; McLaughlin, M.; Cohen, R. D.; Andreani, T.; Ding, B.; Li, H.; Weisel, M.; Tschaen, D. M. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 2167.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c00239 |
| [22] |
Michailidis, E.; Ryan, E. M.; Hachiya, A.; Kirby, K. A.; Marchand, B.; Leslie, M. D.; Huber, A. D.; Ong, Y. T.; Jackson, J. C.; Singh, K.; Kodama, E. N.; Mitsuya, H.; Parniak, M. A.; Sarafianos, S. G. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 65.
doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-65 |
| [23] |
Stoddart, C. A.; Galkina, S. A.; Joshi, P.; Kosikova, G.; Moreno, M. E.; Rivera, J. M.; Sloan, B.; Reeve, A. B.; Sarafianos, S. G.; Murphey-Corb, M.; Parniak, M. A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 4190.
doi: 10.1128/AAC.05036-14 pmid: 25941222 |
| [24] |
Schurmann, D.; Rudd, D. J.; Zhang, S.; De Lepeleire, I.; Robberechts, M.; Friedman, E.; Keicher, C.; Huser, A.; Hofmann, J.; Grobler, J. A.; Stoch, S. A.; Iwamoto, M.; Matthews, R. P. Lancet HIV 2020, 7, 164.
|
| [25] |
Markowitz, M.; Gettie, A.; St Bernard, L.; Andrews, C. D.; Mohri, H.; Horowitz, A.; Grasperge, B. F.; Blanchard, J. L.; Niu, T.; Sun, L.; Fillgrove, K.; Hazuda, D. J.; Grobler, J. A. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 211, 1398.
|
| [26] |
Markowitz, M.; Sarafianos, S. G. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2018, 13, 294.
doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000467 pmid: 29697468 |
| [27] |
Mackman, R. L.; Ray, A. S.; Hui, H. C.; Zhang, L.; Birkus, G.; Boojamra, C. G.; Desai, M. C.; Douglas, J. L.; Gao, Y.; Grant, D.; Laflamme, G.; Lin, K. Y.; Markevitch, D. Y.; Mishra, R.; McDermott, M.; Pakdaman, R.; Petrakovsky, O. V.; Vela, J. E.; Cihlar, T. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 3606.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.03.041 |
| [28] |
Nie, B.; Jin, C.-F.; Zhong, W.-H.; Ren, Q.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Zhang, J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 37, 2818. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201705022 |
|
(聂飚, 金传飞, 钟文和, 任青云, 张英俊, 张霁, 有机化学, 2017, 37, 2818.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201705022 |
|
| [29] |
Liu, Y.-C.; Cheng, J.-F.; Hong, R. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 3237. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202005030 |
|
(刘祎辰, 程杰飞, 洪然, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 3237.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202005030 |
|
| [30] |
Cihlar, T.; Ray, A. S.; Boojamra, C. G.; Zhang, L.; Hui, H.; Laflamme, G.; Vela, J. E.; Grant, D.; Chen, J.; Myrick, F.; White, K. L.; Gao, Y.; Lin, K. Y.; Douglas, J. L.; Parkin, N. T.; Carey, A.; Pakdaman, R.; Mackman, R. L. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 655.
pmid: 18056282 |
| [31] |
Boojamra, C. G.; Mackman, R. L.; Markevitch, D. Y.; Prasad, V.; Ray, A. S.; Douglas, J.; Grant, D.; Kim, C. U.; Cihlar, T. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 1120.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.11.125 |
| [32] |
Scarth, B. J.; White, K. L.; Chen, J. M.; Lansdon, E. B.; Swaminathan, S.; Miller, M. D.; Gotte, M. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2662.
doi: 10.1128/AAC.01738-10 pmid: 21402840 |
| [33] |
Lansdon, E. B.; Samuel, D.; Lagpacan, L.; Brendza, K. M.; White, K. L.; Hung, M.; Liu, X.; Boojamra, C. G.; Mackman, R. L.; Cihlar, T.; Ray, A. S.; McGrath, M. E.; Swaminathan, S. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 397, 967.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.02.019 pmid: 20156454 |
| [34] |
Zdanowicz, M. M. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2006, 70, 100.
pmid: 17149429 |
| [35] |
(a) Bastos, M. M.; Costa, C.; Bezerra, T. C.; da Silva, F. C.; Boechat, N. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 108, 455.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.11.025 pmid: 8592986 |
|
(b) Young, S. D.; Britcher, S. F.; Tran, L. O.; Payne, L. S.; Lumma, W. C.; Lyle, T. A.; Huff, J. R.; Anderson, P. S.; Olsen, D. B.; Carroll, S. S. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 2602.
doi: 10.1128/AAC.39.12.2602 pmid: 8592986 |
|
|
(c) Kawai, H.; Kitayama, T.; Tokunaga, E.; Shibata, N. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 30, 5959.
pmid: 8592986 |
|
| [36] |
Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Meggers, E. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2018, 22, 103.
doi: 10.1021/acs.oprd.7b00376 |
| [37] |
Cote, B.; Burch, J. D.; Asante-Appiah, E.; Bayly, C.; Bedard, L.; Blouin, M.; Campeau, L. C.; Cauchon, E.; Chan, M.; Chefson, A.; Coulombe, N.; Cromlish, W.; Debnath, S.; Deschenes, D.; Dupont-Gaudet, K.; Falgueyret, J. P.; Forget, R.; Gagne, S.; Gauvreau, D.; Girardin, M.; Guiral, S.; Langlois, E.; Li, C. S.; Nguyen, N.; Papp, R.; Plamondon, S.; Roy, A.; Roy, S.; Seliniotakis, R.; St-Onge, M.; Ouellet, S.; Tawa, P.; Truchon, J. F.; Vacca, J.; Wrona, M.; Yan, Y.; Ducharme, Y. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 917.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.12.070 |
| [38] |
Gauthier, D. R. Jr.; Sherry, B. D.; Cao, Y.; Journet, M.; Humphrey, G.; Itoh, T.; Mangion, I.; Tschaen, D. M. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 1353.
doi: 10.1021/ol503625z pmid: 25751537 |
| [39] |
Lai, M. T.; Feng, M.; Falgueyret, J. P.; Tawa, P.; Witmer, M.; DiStefano, D.; Li, Y.; Burch, J.; Sachs, N.; Lu, M.; Cauchon, E.; Campeau, L. C.; Grobler, J.; Yan, Y.; Ducharme, Y.; Cote, B.; Asante-Appiah, E.; Hazuda, D. J.; Miller, M. D. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1652.
doi: 10.1128/AAC.02403-13 |
| [40] |
Ren, J.; Bird, L. E.; Chamberlain, P. P.; Stewart-Jones, G. B.; Stuart, D. I.; Stammers, D. K. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2002, 99, 14410.
pmid: 12386343 |
| [41] |
Sanchez, R. I.; Fillgrove, K. L.; Yee, K. L.; Liang, Y.; Lu, B.; Tatavarti, A.; Liu, R.; Anderson, M. S.; Behm, M. O.; Fan, L.; Li, Y.; Butterton, J. R.; Iwamoto, M.; Khalilieh, S. G. Xenobiotia 2019, 49, 422.
|
| [42] |
Rock, A. E.; Lerner, J.; Badowski, M. E. HIV/AIDS 2020, 12, 201.
doi: 10.2147/HIV.S184018 |
| [43] |
Orkin, C.; Squires, K. E.; Molina, J. M.; Sax, P. E.; Wong, W. W.; Sussmann, O.; Kaplan, R.; Lupinacci, L.; Rodgers, A.; Xu, X.; Lin, G.; Kumar, S.; Sklar, P.; Nguyen, B. Y.; Hanna, G. J.; Hwang, C.; Martin, E. A. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 535.
doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy540 |
| [44] |
Al-Salama, Z. T. Drugs 2017, 77, 1811.
doi: 10.1007/s40265-017-0820-3 pmid: 28940154 |
| [45] |
Namasivayam, V.; Vanangamudi, M.; Kramer, V. G.; Kurup, S.; Zhan, P.; Liu, X.; Kongsted, J.; Byrareddy, S. N. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 62, 4851.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00843 |
| [46] |
Rai, M. A.; Pannek, S.; Fichtenbaum, C. J. Expert Opin. Emerging Drugs 2018, 23, 149.
doi: 10.1080/14728214.2018.1474202 |
| [47] |
Brik, A.; Wong, C. H. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, 5.
doi: 10.1039/b208248a |
| [48] |
McKeage, K.; Perry, C. M.; Keam, S. J. Drugs 2009, 69, 477.
doi: 10.2165/00003495-200969040-00007 pmid: 19323590 |
| [49] |
Tashima, K.; Crofoot, G.; Tomaka, F. L.; Kakuda, T. N.; Brochot, A.; Van de Casteele, T.; Opsomer, M.; Garner, W.; Margot, N.; Custodio, J. M.; Fordyce, M. W.; Szwarcberg, J. AIDS Res. Ther. 2014, 11, 39.
doi: 10.1186/1742-6405-11-39 pmid: 25926858 |
| [50] |
Kozisek, M.; Lepsik, M.; Grantz saskova, K.; Brynda, J.; Konvalinka, J.; Rezacova, P. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 1834.
doi: 10.1111/febs.12743 |
| [51] |
Huang, D.; Caflisch, A. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 1786.
doi: 10.1021/ct300032r |
| [52] |
Hohlfeld, K.; Wegner, J. K.; Kesteleyn, B.; Linclau, B.; Unge, J. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4029.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00358 pmid: 25897791 |
| [53] |
Agniswamy, J.; Louis, J. M.; Shen, C. H.; Yashchuk, S.; Ghosh, A. K.; Weber, I. T. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 5088.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00474 pmid: 26010498 |
| [54] |
Ghosh, A. K.; Williams, J. N.; Ho, R. Y.; Simpson, H. M.; Hattori, S. I.; Hayashi, H.; Agniswamy, J.; Wang, Y. F.; Weber, I. T.; Mitsuya, H. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 9722.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01227 pmid: 30354121 |
| [55] |
Ghosh, A. K.; Martyr, C. D.; Kassekert, L. A.; Nyalapatla, P. R.; Steffey, M.; Agniswamy, J.; Wang, Y. F.; Weber, I. T.; Amano, M.; Mitsuya, H. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 11607.
doi: 10.1039/c5ob01930c pmid: 26462551 |
| [56] |
Amano, M.; Miguel Salcedo-Gomez, P.; Yedidi, R. S.; Delino, N. S.; Nakata, H.; Venkateswara Rao, K.; Ghosh, A. K.; Mitsuya, H. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12235.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12052-9 |
| [57] |
Strom, T. A.; Durdagi, S.; Ersoz, S. S.; Salmas, R. E.; Supuran, C. T.; Barron, A. R. J. Pept. Sci. 2015, 21, 862.
doi: 10.1002/psc.2828 |
| [58] |
Barzegar, A.; Jafari Mousavi, S.; Hamidi, H.; Sadeghi, M. Phys. E (Amsterdam, Neth.) 2017, 93, 324.
doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2017.06.016 |
| [59] |
Yasuno, T.; Ohe, T.; Kataoka, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Ishikawa, Y.; Furukawa, K.; Tateishi, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Takahashi, K.; Nakamura, S.; Mashino, T. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 31, 127675.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127675 |
| [60] |
Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zeng, Y.; Han, Y.; Ng, T. B. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 339.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.030 |
| [61] |
Chen, M. H.; Chang, S. S.; Dong, B.; Yu, L. Y.; Wu, Y. X.; Wang, R. Z.; Jiang, W.; Gao, Z. P.; Si, S. Y. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 5138.
doi: 10.1039/C7RA13241G |
| [62] |
Gao, K.; Butler, S. L.; Bushman, F. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 3565.
pmid: 11432843 |
| [63] |
Wang, H.; Kowalski, M. D.; Lakdawala, A. S.; Vogt, F. G.; Wu, L. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 564.
doi: 10.1021/ol503580t |
| [64] |
Margolis, D. A.; Boffito, M. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2015, 10, 246.
doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000169 pmid: 26049949 |
| [65] |
Trezza, C.; Ford, S. L.; Spreen, W.; Pan, R.; Piscitelli, S. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2015, 10, 239.
doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000168 |
| [66] |
Spreen, W. R.; Margolis, D. A.; Pottage, J. C. Jr. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2013, 8, 565.
doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000002 |
| [67] |
Murray, M.; Antela, A.; Mills, A.; Huang, J.; Jager, H.; Bernal, E.; Lombaard, J.; Katner, H.; Walmsley, S.; Khuong-Josses, M. A.; Hudson, K.; Dorey, D.; Griffith, S.; Spreen, W.; Vanveggel, S.; Shaefer, M.; Margolis, D.; Chounta, V. AIDS Behav. 2020, 24, 3533.
doi: 10.1007/s10461-020-02929-8 |
| [68] |
Andrews, C. D.; Yueh, Y. L.; Spreen, W. R.; St Bernard, L.; Boente- Carrera, M.; Rodriguez, K.; Gettie, A.; Russell-Lodrigue, K.; Blanchard, J.; Ford, S.; Mohri, H.; Cheng-Mayer, C.; Hong, Z.; Ho, D. D.; Markowitz, M. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 270ra4.
doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3010298 |
| [69] |
Mostashari, Rad, T.; Saghaie,, L.; Fassihi,, A. Chem. Biodiversity 2018, 15, e1800159.
doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201800159 |
| [70] |
Melikyan, G. B. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 16511.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.H117.791731 pmid: 28986430 |
| [71] |
Markham, A. Drugs 2020, 80, 1615.
doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01403-y |
| [72] |
Pancera, M.; Lai, Y. T.; Bylund, T.; Druz, A.; Narpala, S.; O'Dell, S.; Schon, A.; Bailer, R. T.; Chuang, G. Y.; Geng, H.; Louder, M. K.; Rawi, R.; Soumana, D. I.; Finzi, A.; Herschhorn, A.; Madani, N.; Sodroski, J.; Freire, E.; Langley, D. R.; Mascola, J. R.; McDermott, A. B.; Kwong, P. D. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 1115.
doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2460 pmid: 28825711 |
| [73] |
Meanwell, N. A.; Krystal, M. R.; Nowicka-Sans, B.; Langley, D. R.; Conlon, D. A.; Eastgate, M. D.; Grasela, D. M.; Timmins, P.; Wang, T.; Kadow, J. F. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 62.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01337 |
| [74] |
Nowicka-Sans, B.; Gong, Y. F.; McAuliffe, B.; Dicker, I.; Ho, H. T.; Zhou, N.; Eggers, B.; Lin, P. F.; Ray, N.; Wind-Rotolo, M.; Zhu, L.; Majumdar, A.; Stock, D.; Lataillade, M.; Hanna, G. J.; Matiskella, J. D.; Ueda, Y.; Wang, T.; Kadow, J. F.; Meanwell, N. A.; Krystal, M. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 3498.
doi: 10.1128/AAC.00426-12 pmid: 22547625 |
| [75] |
Hiryak, K.; Koren, D. E. Ann. Pharmacother. 2021, 55, 792.
doi: 10.1177/1060028020962424 |
| [76] |
Blair, H. A. Drugs 2020, 80, 189.
doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01258-3 |
| [77] |
Nakane, S.; Iwamoto, A.; Matsuda, Z. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 15279.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.628610 |
| [78] |
Beccari, M. V.; Mogle, B. T.; Sidman, E. F.; Mastro, K. A.; Asiago-Reddy, E.; Kufel, W. D. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00110.
|
| [79] |
Freeman, M. M.; Seaman, M. S.; Rits-Volloch, S.; Hong, X.; Kao, C. Y.; Ho, D. D.; Chen, B. Structure 2010, 18, 1632.
doi: 10.1016/j.str.2010.09.017 |
| [80] |
Pace, C. S.; Fordyce, M. W.; Franco, D.; Kao, C. Y.; Seaman, M. S.; Ho, D. D. J. Acquired Immune Defic. Syndr. 2013, 62, 1.
|
| [81] |
Emu, B.; Fessel, J.; Schrader, S.; Kumar, P.; Richmond, G.; Win, S.; Weinheimer, S.; Marsolais, C.; Lewis, S. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 645.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1711460 |
| [82] |
Bettiker, R. L.; Koren, D. E.; Jacobson, J. M. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2018, 13, 354.
doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000473 pmid: 29746266 |
| [83] |
Thompson, D. A.; Cormier, E. G.; Dragic, T. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 3059.
pmid: 11861874 |
| [84] |
Woollard, S. M.; Kanmogne, G. D. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 5447.
doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S90580 pmid: 26491256 |
| [85] |
Tan, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Han, G. W.; Kufareva, I.; Li, T.; Ma, L.; Fenalti, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Xie, X.; Yang, H.; Jiang, H.; Cherezov, V.; Liu, H.; Stevens, R. C.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, B. Science 2013, 341, 1387.
doi: 10.1126/science.1241475 |
| [86] |
Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Lin, K.; Wang, B.; Zhou, W. Synth. Commun. 2019, 49, 1721.
doi: 10.1080/00397911.2019.1607875 |
| [87] |
Peng, P.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Luo, R. H.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Yang, L. M.; Jiang, H.; Xie, X.; Wu, B.; Zheng, Y. T.; Liu, H. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 9621.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01077 |
| [88] |
Luo, W.; Srinivasulu, C.; Hao, X.; Liu, X.; Zhan, P. Expert Opin. Drug Discovery 2020, 15, 1115.
doi: 10.1080/17460441.2020.1775577 |
| [89] |
Chan, D. C.; Fass, D.; Berger, J. M.; Kim, P. S. Cell 1997, 89, 263.
pmid: 9108481 |
| [90] |
Ding, X.; Zhang, X.; Chong, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, H.; Wu, X.; He, J.; Wang, X.; He, Y. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00831.
|
| [91] |
Patel, I. H.; Zhang, X.; Nieforth, K.; Salgo, M.; Buss, N. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2005, 44, 175.
doi: 10.2165/00003088-200544020-00003 |
| [92] |
Chong, H.; Yao, X.; Zhang, C.; Cai, L.; Cui, S.; Wang, Y.; He, Y. PLoS One 2012, 7, e32599.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032599 |
| [93] |
Zhang, H.; Jin, R.; Yao, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, M.; Xia, W.; Peng, H.; Wang, X.; Lu, R.; Wang, C.; Xie, D.; Wu, H. AIDS Res. Ther. 2016, 13, 8.
doi: 10.1186/s12981-016-0091-1 |
| [94] |
Cambou, M. C.; Landovitz, R. J. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2020, 17, 118.
|
| [95] |
Ganser, B. K.; Li, S.; Klishko, V. Y.; Finch, J. T.; Sundquist, W. I. Science 1999, 283, 80.
pmid: 9872746 |
| [96] |
Link, J. O.; Rhee, M. S.; Tse, W. C.; Zheng, J.; Somoza, J. R.; Rowe, W.; Begley, R.; Chiu, A.; Mulato, A.; Hansen, D.; Singer, E.; Tsai, L. K.; Bam, R. A.; Chou, C. H.; Canales, E.; Brizgys, G.; Zhang, J. R.; Li, J.; Graupe, M.; Morganelli, P.; Liu, Q.; Wu, Q.; Halcomb, R. L.; Saito, R. D.; Schroeder, S. D.; Lazerwith, S. E.; Bondy, S.; Jin, D.; Hung, M.; Novikov, N.; Liu, X.; Villasenor, A. G.; Cannizzaro, C. E.; Hu, E. Y.; Anderson, R. L.; Appleby, T. C.; Lu, B.; Mwangi, J.; Liclican, A.; Niedziela-Majka, A.; Papalia, G. A.; Wong, M. H.; Leavitt, S. A.; Xu, Y.; Koditek, D.; Stepan, G. J.; Yu, H.; Pagratis, N.; Clancy, S.; Ahmadyar, S.; Cai, T. Z.; Sellers, S.; Wolckenhauer, S. A.; Ling, J.; Callebaut, C.; Margot, N.; Ram, R. R.; Liu, Y. P.; Hyland, R.; Sinclair, G. I.; Ruane, P. J.; Crofoot, G. E.; McDonald, C. K.; Brainard, D. M.; Lad, L.; Swaminathan, S.; Sundquist, W. I.; Sakowicz, R.; Chester, A. E.; Lee, W. E.; Daar, E. S.; Yant, S. R.; Cihlar T. Nature 2020, 584, 614.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2443-1 |
| [97] |
Kleinpeter, A. B.; Freed, E. O. Viruses 2020, 12, 940.
doi: 10.3390/v12090940 |
| [98] |
Johnson, M.; Jewell, R. C.; Peppercorn, A.; Gould, E.; Xu, J.; Lou, Y.; Davies, M.; Baldwin, S.; Tenorio, A. R.; Burke, M.; Jeffrey, J.; Johns, B. A. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2018, 6, e00408.
doi: 10.1002/prp2.408 |
| [99] |
DeJesus, E.; Harward, S.; Jewell, R. C.; Johnson, M.; Dumont, E.; Wilches, V.; Halliday, F.; Talarico, C. L.; Jeffrey, J.; Gan, J.; Xu, J.; Felizarta, F.; Scribner, A.; Ramgopal, M.; Benson, P.; Johns, B. A. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1255.
doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz938 pmid: 31769793 |
| [100] |
Wen, Z.; Sun, C. Vaccines 2020, 8, 511.
doi: 10.3390/vaccines8030511 |
| [101] |
Hashmat, R.; Yousaf, M. Z.; Rahman, Z.; Anjum, K. M.; Yaqoob, A.; Imran, M. Crit. Rev. Eukaryotic Gene Expression 2020, 30, 77.
doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.v30.i1 |
| [102] |
Xiao, Q.; Guo, D.; Chen, S. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 69.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00069 |
| [103] |
Deeks, S. G. Nature 2012, 487, 439.
doi: 10.1038/487439a |
| [104] |
Abner, E.; Jordan, A. Antiviral Res. 2019, 166, 19.
doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.03.008 |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||