有机化学 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (10): 3221-3239.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202207045 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 不对称催化专辑
综述与进展
收稿日期:2022-07-30
修回日期:2022-08-20
发布日期:2022-11-02
通讯作者:
卢岩, 张兆国
基金资助:
Yuxuan Zhang, Limin Xu, Yan Lu( ), Zhaoguo Zhang(
), Zhaoguo Zhang( )
)
Received:2022-07-30
Revised:2022-08-20
Published:2022-11-02
Contact:
Yan Lu, Zhaoguo Zhang
Supported by:文章分享
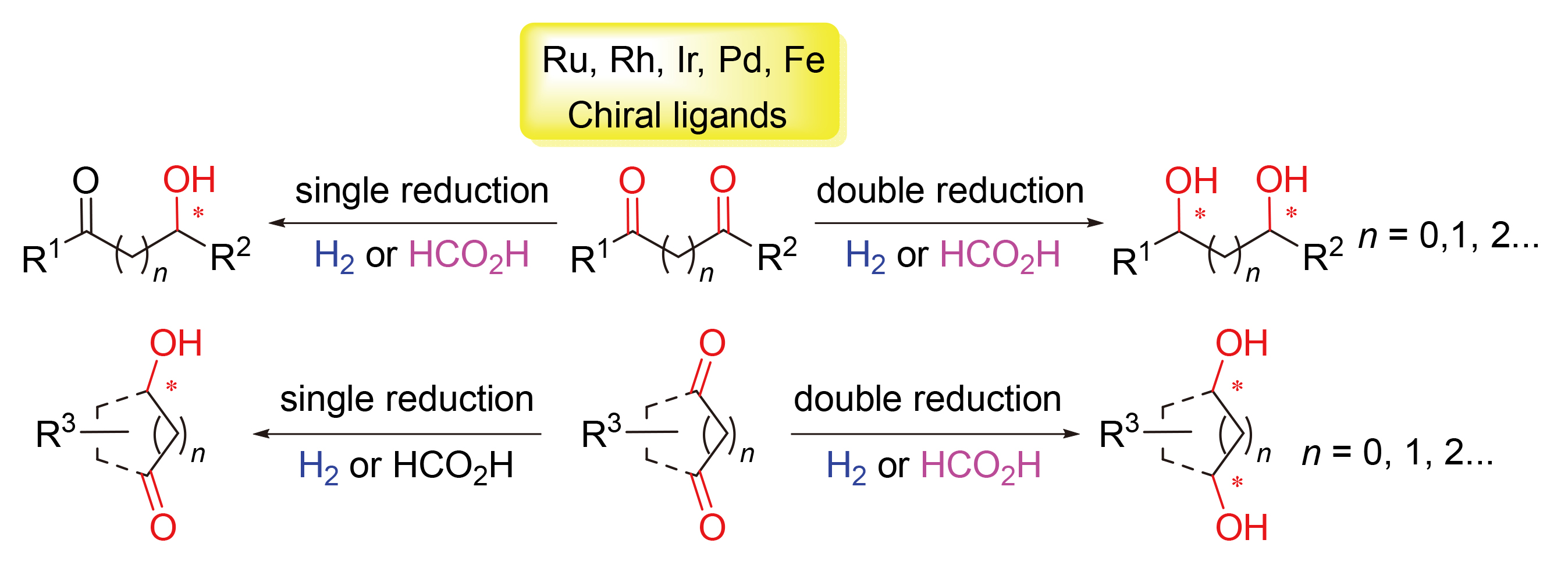
手性二醇类化合物是一类重要的手性结构单元和手性中间体, 过渡金属催化的二酮类化合物的不对称氢化和氢转移反应是获得手性二醇最为直接高效的方法之一. 同时, 手性羟基酮作为二酮的不对称单还原产物, 也广泛应用于手性片段的构建, 其中环状二酮的去对称化甚至可一步构建多个手性中心. 从不同底物类型(1,2-/1,3-/1,4-)的二酮角度出发, 综述了近几十年来二酮类化合物的不对称氢化和氢转移反应研究进展, 着重讨论底物与催化剂配位模式对反应选择性的影响, 并对该领域未来的挑战和发展方向进行了展望.
张宇轩, 许立民, 卢岩, 张兆国. 二酮的不对称催化还原反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(10): 3221-3239.
Yuxuan Zhang, Limin Xu, Yan Lu, Zhaoguo Zhang. Progress in Asymmetric Catalytic Reduction of Diketones[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(10): 3221-3239.
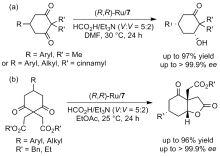
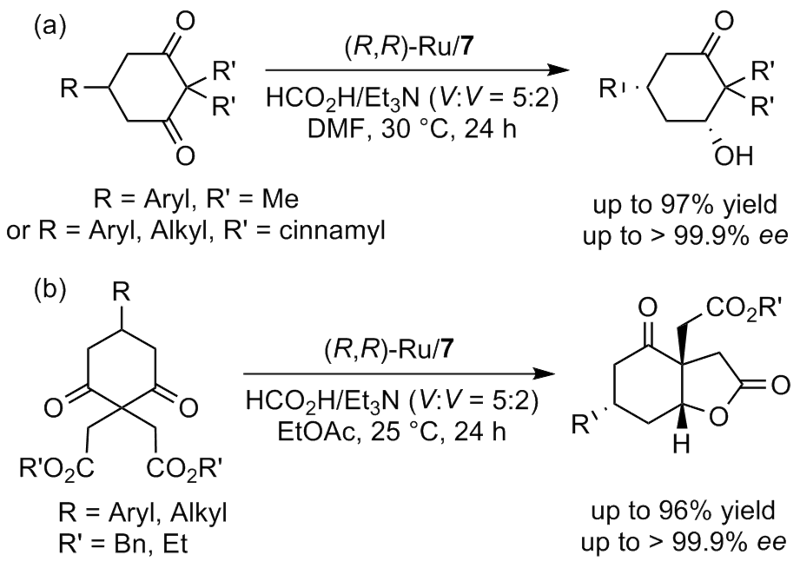
| [1] |
Noyori, R.; Ohkuma, T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 40.
|
| [2] |
(a) de Vries, J. G.; Elsevier, C. J. Handbook of Homogeneous Hydrogenation, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany, 2007.
|
|
(b) Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y. J.; Zhang, W. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 27, 289. (in Chinese).
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.200990046 |
|
|
(马元辉, 张勇健, 张万斌, 有机化学, 2007, 27, 289.)
|
|
|
(c) Blaser, H.-U.; Federsel, H.-J. Asymmetric Catalysis on Industrial Scale, 2nd ed., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany, 2010.
|
|
|
(d) Xie, J.-H.; Zhou, Q.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 1427. (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A12060268 |
|
|
(谢建华, 周其林, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 1427.)
doi: 10.6023/A12060268 |
|
|
(e) Etayo, P.; Vidal-Ferran, A. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 728.
doi: 10.1039/C2CS35410A |
|
|
(f) Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 35, 528. (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201502017 |
|
|
(王英杰, 张振锋, 张万斌, 有机化学, 2015, 35, 528.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201502017 |
|
|
(g) Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 447. (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201512009 |
|
|
(王志惠, 张振锋, 刘燕刚, 张万斌, 有机化学, 2016, 36, 447.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201512009 |
|
| [3] |
Noyori, R.; Ohkuma, T.; Kitamura, M.; Takaya, H.; Sayo, N.; Kumobayashi, H.; Akutagawa, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 5856.
doi: 10.1021/ja00253a051 |
| [4] |
(a) Sheldon, R. A. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas 1996, 115, 155.
|
|
(b) Noyori, R.; Takaya, H. Acc. Chem. Res. 1990, 23, 345.
doi: 10.1021/ar00178a005 |
|
| [5] |
Rossen, K. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 4611.
|
| [6] |
(a) Noyori, R.; Koizumi, M.; Ishii, D.; Ohkuma, T. Pure Appl. Chem. 2001, 73, 227.
doi: 10.1351/pac200173020227 |
|
(b) Dub, P. A.; Gordon, J. C. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 6756.
doi: 10.1039/C6DT00476H |
|
|
(c) Haack, K.-J.; Hashiguchi, S.; Fujii, A.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 1997, 36, 285.
doi: 10.1002/anie.199702851 |
|
| [7] |
(a) Wu, X.; Xiao, J. Chem. Commun. 2007, 2449.
|
|
(b) Ohkuma, T. Proc. Jpn. Acad., Ser. B. 2010, 86, 202.
|
|
|
(c) Štefane, B.; Požgan, F. Catal. Rev. 2014, 56, 82.
doi: 10.1080/01614940.2013.869461 |
|
|
(d) Yoshimura, M.; Tanaka, S.; Kitamura, M. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 3635.
doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2014.04.129 |
|
|
(e) Li, Y.-Y.; Yu, S.-L.; Shen, W.-Y.; Gao, J.-X. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 2587.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00043 |
|
|
(f) Xie, J.-H.; Bao, D.-H.; Zhou, Q.-L. Synthesis 2015, 47, 460.
doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1378939 |
|
|
(g) Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Duan, K.; Wang, J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 32, 19. (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/cjoc1104231 |
|
|
(李小娜, 张鹏亮, 段凯, 王家喜, 有机化学, 2012, 32, 19.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc1104231 |
|
| [8] |
Kitamura, M.; Ohkuma, T.; Inoue, S.; Sayo, N.; Kumobayashi, H.; Akutagawa, S.; Ohta, T.; Takaya, H.; Noyori, R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 629.
doi: 10.1021/ja00210a070 |
| [9] |
Fan, Q.; Yeung, C.; Chan, A. S. C. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 1997, 8, 4041.
|
| [10] |
Casey, C. P.; Guan, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 5816.
doi: 10.1021/ja071159f |
| [11] |
Huang, X.; Li, N.; Geng, Z.; Pan, F.; Wang, X. Chin. J. Chem. 2012, 30, 2657.
|
| [12] |
Swamy, P. C. A.; Varenikov, A.; de Ruiter, G. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 2333.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201904911 |
| [13] |
Murata, K.; Okano, K.; Miyagi, M.; Iwane, H.; Noyori, R.; Ikariya, T. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 1119.
doi: 10.1021/ol990226a |
| [14] |
Koike, T.; Murata, K.; Ikariya, T. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 3833.
pmid: 11101431 |
| [15] |
Wu, X.; Li, X.; Zanotti-Gerosa, A.; Pettman, A.; Liu, J.; Mills, A. J.; Xiao, J. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 2209.
doi: 10.1002/chem.200701258 |
| [16] |
Touge, T.; Hakamata, T.; Nara, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Sayo, N.; Saito, T.; Kayaki, Y.; Ikariya, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 14960.
doi: 10.1021/ja207283t |
| [17] |
Gladiali, S.; Alberico, E. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 226.
doi: 10.1039/B513396C |
| [18] |
Zhang, H.; Feng, D.; Sheng, H.; Ma, X.; Wan, J.; Tang, Q. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 6417.
doi: 10.1039/c3ra47129b |
| [19] |
Kišić, A.; Stephan, M.; Mohar, B. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 3193.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.201400265 |
| [20] |
Kišić, A.; Stephan, M.; Mohar, B. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2015, 357, 2540.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.201500288 |
| [21] |
De Luca, L.; Mezzetti, A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 11949.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201706261 |
| [22] |
Luca, L. D.; Mezzetti, A. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 5807.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.9b03408 |
| [23] |
Murayama, H.; Heike, Y.; Higashida, K.; Shimizu, Y.; Yodsin, N.; Wongnongwa, Y.; Jungsuttiwong, S.; Mori, S.; Sawamura, M. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2020, 362, 4655.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.202000615 |
| [24] |
Kawano, H.; Ishii, Y.; Saburi, M.; Uchida, Y. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1988, 87.
|
| [25] |
Shao, L.; Seki, T.; Kawano, H.; Saburi, M. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 7699.
doi: 10.1016/0040-4039(91)80569-R |
| [26] |
Kiegiel, J.; Jóźwik, J.; Woźniak, K.; Jurczak, J. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 4959.
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)00747-4 |
| [27] |
Hu, A.; Lin, W. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 455.
doi: 10.1021/ol0474812 |
| [28] |
(a) Rychnovsky, S. D.; Griesgraber, G.; Zeller, S.; Skalitzky, D. J. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 5161.
doi: 10.1021/jo00017a032 |
|
(b) Rychnovsky, S. D. Org. Synth. 2000, 77, 1.
doi: 10.15227/orgsyn.077.0001 |
|
| [29] |
(a) Zhou, S.-Z.; Anné, S.; Vandewalle, M. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 7637.
doi: 10.1016/0040-4039(96)01700-5 pmid: 23451721 |
|
(b) Jung, M. E.; Kretschik, O. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 2975.
doi: 10.1021/jo9721655 pmid: 23451721 |
|
|
(c) Werness, J. B.; Tang, W. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 3664.
doi: 10.1021/ol201477u pmid: 23451721 |
|
|
(d) Walleser, P.; Bruckner, R. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 1294.
doi: 10.1021/ol400232m pmid: 23451721 |
|
|
(e) Singh, G.; Meyer, A.; Aube, J. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 452.
doi: 10.1021/jo402539p pmid: 23451721 |
|
| [30] |
(a) Bianchini, C.; Barbaro, P.; Scapacci, G.; Zanobini, F. Organometallics 2000, 19, 2450.
doi: 10.1021/om000137y |
|
(b) Dubrovina, N. V.; Tararov, V. I.; Monsees, A.; Kadyrov, R.; Fischer, C.; Borner, A. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2003, 14, 2739.
|
|
|
(c) Brunner, H.; Terfort, A. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 1995, 6, 919.
|
|
| [31] |
(a) Poss, C. S.; Rychnovsky, S. D.; Schreiber, S. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 3360.
doi: 10.1021/ja00061a057 pmid: 12556171 |
|
(b) Wovkulich, P. M.; Shankaran, K.; Kiegiel, J.; Uskokovic, M. R. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 832.
doi: 10.1021/jo00056a013 pmid: 12556171 |
|
|
(c) Schulz, S. Chem. Commun. 1999, 1239.
pmid: 12556171 |
|
|
(d) Juszkiewicz, G.; Jurczak, J. Org. Prep. Proced. Int. 2002, 34, 187.
doi: 10.1080/00304940209355756 pmid: 12556171 |
|
|
(e) Arsene, C.; Schulz, S. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 2869.
doi: 10.1021/ol026265v pmid: 12556171 |
|
|
(f) Stritzke, K.; Schulz, S.; Nishida, R. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 2002, 3884.
pmid: 12556171 |
|
|
(g) Wender, P. A.; Mayweg, A. V.; VanDeusen, C. L. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 277.
pmid: 12556171 |
|
|
(h) Polkowska, J.; Lukaszewicz, E.; Kiegiel, J.; Jurczak, J. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 3873.
pmid: 12556171 |
|
| [32] |
(a) Balog, A.; Harris, C.; Savin, K.; Zhang, X.-G.; Chou, T.-C.; Danishefsky, S. J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2675.
pmid: 11052097 |
|
(b) Harris, C. R.; Kuduk, S. D.; Balog, A.; Savin, K.; Glunz, P. W.; Danishefsky, S. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 7050.
doi: 10.1021/ja991189l pmid: 11052097 |
|
|
(c) Glunz, P. W.; He, L.; Horwitz, S. B.; Chakravarty, S.; Ojima, I.; Chou, T.-C.; Danishefsky, S. J. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 6895.
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(99)01433-1 pmid: 11052097 |
|
|
(d) Stachel, S. J.; Chappell, M. D.; Lee, C. B.; Danishefsky, S. J.; Chou, T.-C.; He, L.; Horwitz, S. B. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 1637.
pmid: 11052097 |
|
|
(e) Lee, C. B.; Chou, T.-C.; Zhang, X.-G.; Wang, Z.-G.; Kuduk, S. D.; Chappell, M. D.; Stachel, S. J.; Danishefsky, S. J. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 6525.
pmid: 11052097 |
|
|
(f) Haydl, A. M.; Breit, B. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 541.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201605011 pmid: 11052097 |
|
| [33] |
Mezzetti, A.; Consiglio, G. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1991, 1675.
|
| [34] |
Mezzetti, A.; Tschumper, A.; Consiglio, G. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1995, 49.
|
| [35] |
Pini, D.; Mandoli, A.; Iuliano, A.; Salvadori, P. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 1995, 6, 1031.
|
| [36] |
Blanc, D.; Ratovelomanana-Vidal, V.; Marinetti, A.; Genêt, J.-P. Synlett 1999, 1999, 480.
doi: 10.1055/s-1999-2631 |
| [37] |
Michaud, G.; Bulliard, M.; Ricard, L.; Genêt, J. P.; Marinetti, A. Chem. Eur. J. 2002, 8, 3327.
|
| [38] |
(a) Duprat de Paule, S.; Jeulin, S.; Ratovelomanana-Vidal, V.; Genêt, J.-P.; Champion, N.; Deschaux, G.; Dellis, P. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2003, 7, 399.
doi: 10.1021/op034016w |
|
(b) Duprat de Paule, S.; Jeulin, S.; Ratovelomanana-Vidal, V.; Genêt, J.-P.; Champion, N.; Dellis, P. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 1931.
|
|
| [39] |
Genêt, J.-P.; Ratovelomanana-Vidal, V.; Jeulin, S.; Champion, N.; Dellis, P. Synthesis 2005, 3666.
|
| [40] |
Clarke, M. L.; France, M. B.; Knight, F. R.; Frew, J. J. R.; Roff, G. J. Synlett 2007, 1739.
|
| [41] |
Jeulin, S.; Duprat de Paule, S.; Ratovelomanana-Vidal, V.; Genêt, J. P.; Champion, N.; Dellis, P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 320.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200352453 |
| [42] |
Kesselgruber, M.; Lotz, M.; Martin, P.; Melone, G.; Muller, M.; Pugin, B.; Naud, F.; Spindler, F.; Thommen, M.; Zbinden, P.; et al. Chem Asian J 2008, 3, 1384.
doi: 10.1002/asia.200800186 |
| [43] |
Li, W.; Fan, W.; Ma, X.; Tao, X.; Li, X.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Z. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8976.
doi: 10.1039/c2cc33695b |
| [44] |
Li, W.; Lu, B.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Z. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 5509.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b01829 |
| [45] |
Yamamura, T.; Nakatsuka, H.; Tanaka, S.; Kitamura, M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9313.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201304408 |
| [46] |
Yu, C.-B.; Wang, H.-D.; Song, B.; Shen, H.-Q.; Fan, H.-J.; Zhou, Y.-G. Sci. China Chem. 2020, 63, 215.
doi: 10.1007/s11426-019-9601-7 |
| [47] |
(a) Ireland, T.; Grossheimann, G.; Wieser-Jeunesse, C.; Knochel, P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 3212.
|
|
(b) Ireland, T.; Tappe, K.; Grossheimann, G.; Knochel, P. Chem. Eur. J. 2002, 8, 843.
|
|
|
(c) Lotz, M.; Polborn, K.; Knochel, P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 4708.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200290024 |
|
|
(d) Tappe, K.; Knochel, P. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2004, 15, 91.
|
|
| [48] |
Spindler, F.; Malan, C.; Lotz, M.; Kesselgruber, M.; Pittelkow, U.; Rivas-Nass, A.; Briel, O.; Blaser, H. U. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2004, 15, 2299.
|
| [49] |
(a) Sturm, T.; Weissensteiner, W.; Spindler, F. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2003, 345, 160.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.200390003 |
|
(b) Wang, Y.; Sturm, T.; Steurer, M.; Arion, V. B.; Mereiter, K.; Spindler, F.; Weissensteiner, W. Organometallics 2008, 27, 1119.
doi: 10.1021/om701103d |
|
| [50] |
(a) Zirakzadeh, A.; Gross, M. A.; Wang, Y.; Mereiter, K.; Spindler, F.; Weissensteiner, W. Organometallics 2013, 32, 1075.
pmid: 24795493 |
|
(b) Zirakzadeh, A.; Gross, M. A.; Wang, Y.; Mereiter, K.; Weissensteiner, W. Organometallics 2014, 33, 1945.
pmid: 24795493 |
|
| [51] |
(a) Fukuzawa, S.; Oki, H.; Hosaka, M.; Sugasawa, J.; Kikuchi, S. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 5557.
doi: 10.1021/ol702519f |
|
(b) Oki, H.; Oura, I.; Nakamura, T.; Ogata, K.; Fukuzawa, S. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2009, 20, 2185.
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)97603-3 |
|
| [52] |
Espino, G.; Xiao, L.; Puchberger, M.; Mereiter, K.; Spindler, F.; Manzano, B. R.; Jalon, F. A.; Weissensteiner, W. Dalton Trans. 2009, 2751.
|
| [53] |
Gong, Q.; Wen, J.; Zhang, X. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 6350.
doi: 10.1039/C9SC01769K |
| [54] |
Morken, J. P.; Russell, A. E; Taylor, S. J. In Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, Eds.: John, W.; Sons, L., John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., New York, 2018, p. 1.
|
| [55] |
Blandin, V.; Carpentier, J.-F.; Mortreux, A. New J. Chem. 2000, 24, 309.
doi: 10.1039/b000962h |
| [56] |
Marinetti, A.; Jus, S.; Genêt, J. P.; Ricard, L. J. Organomet. Chem. 2001, 624, 162.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-328X(00)00910-4 |
| [57] |
Imamoto, T.; Nishimura, M.; Koide, A.; Yoshida, K. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 7413.
pmid: 17691743 |
| [58] |
(a) Xie, J. H.; Liu, X. Y.; Yang, X. H.; Xie, J. B.; Wang, L. X.; Zhou, Q. L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 201.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201105780 |
|
(b) Yang, X. H.; Xie, J. H.; Zhou, Q. L. Org. Chem. Front. 2014, 1, 190.
doi: 10.1039/c3qo00056g |
|
| [59] |
Chen, Y.-C.; Deng, J.-G.; Wu, T.-F.; Cui, X.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Choi, M. C. K.; Chan, A. S. C. Chin. J. Chem. 2001, 19, 807.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.20010190817 |
| [60] |
Cossy, J.; Eustache, F.; Dalko, P. I. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 5005.
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)00906-6 |
| [61] |
Eustache, F.; Dalko, P. I.; Cossy, J. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 1263.
doi: 10.1021/ol025527q |
| [62] |
Eustache, F.; Dalko, P. I.; Cossy, J. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 9994.
doi: 10.1021/jo035068m |
| [63] |
Watanabe, M.; Murata, K.; Ikariya, T. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 1712.
doi: 10.1021/jo011076w |
| [64] |
Chen, Y. C.; Wu, T. F.; Deng, J. G.; Liu, H.; Cui, X.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, Y. Z.; Choi, M. C.; Chan, A. S. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 5301.
doi: 10.1021/jo0257795 |
| [65] |
Soni, R.; Collinson, J. M.; Clarkson, G. C.; Wills, M. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 4304.
doi: 10.1021/ol201643v |
| [66] |
Kuang, L.; Liu, L. L.; Chiu, P. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 14287.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201502890 |
| [67] |
Cotman, A. E.; Cahard, D.; Mohar, B. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5294.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201600812 |
| [68] |
Yu, C.-B.; Song, B.; Chen, M.-W.; Shen, H.-Q.; Zhou, Y.-G. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 9401.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b03622 |
| [69] |
Ding, Y.-X.; Zhu, Z.-H.; Wang, H.; Yu, C.-B.; Zhou, Y.-G. Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 232.
doi: 10.1007/s11426-020-9873-6 |
| [70] |
Wang, J.; Shao, P.-L.; Lin, X.; Ma, B.; Wen, J.; Zhang, X. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 18166.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202006661 |
| [71] |
Clay, D. R.; Rosenberg, A. G.; McIntosh, M. C. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2011, 22, 713.
|
| [72] |
Fang, Z.; Wills, M. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 8594.
doi: 10.1021/jo401284c |
| [73] |
Echeverria, P.-G.; Férard, C.; Phansavath, P.; Ratovelomanana-Vidal, V. Catal. Commun. 2015, 62, 95.
doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2015.01.012 |
| [74] |
Zheng, L.-S.; Llopis, Q.; Echeverria, P.-G.; Férard, C.; Guillamot, G.; Phansavath, P.; Ratovelomanana-Vidal, V. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 5607.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.7b00436 |
| [75] |
Hong, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 2640.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b01073 |
| [76] |
Zhang, F.-H.; Zhang, F.-J.; Li, M.-L.; Xie, J.-H.; Zhou, Q.-L. Nat. Catal. 2020, 3, 621.
doi: 10.1038/s41929-020-0474-5 |
| [1] | 褚杨杨, 韩召斌, 丁奎岭. 动力学拆分在过渡金属催化的不对称(转移)氢化中的应用研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(6): 1934-1951. |
| [2] | 张同利, 晏君, 何敬立, 寇学振, 申杰峰, 刘德龙, 张万斌. Ir-BiphPHOX催化的不对称氢化反应合成手性5-芳基噁唑烷-2-酮[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(6): 1747-1758. |
| [3] | 刘晨光, 刘强. 丰产金属催化的碳氮不饱和键不对称氢化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(10): 3213-3220. |
| [4] | 赵芳, 叶文静, 王凯. 手性单齿亚磷酸酯配体在不对称氢化反应中的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(7): 2650-2665. |
| [5] | 盛力, 高浩凌, 吴旭锋, 范钢, 刘鹏程. 铑/(2S,2'S,3S,3'S)-3,3'-二叔丁基-4,4'-二甲氧基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-2,2'-联苯并[d][1,3]草酰膦(MeO-BIBOP)催化的不对称还原烯胺合成(R)-3-叔丁氧羰基氨基-4-(2,4,5-三氟苯基)丁酸[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(5): 2105-2111. |
| [6] | 许容华, 杨贺, 汤文军. P-手性膦配体促进的手性药物高效合成[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(6): 1409-1422. |
| [7] | 刘元华, 董秀琴, 张绪穆. 镍催化均相不对称氢化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(5): 1096-1104. |
| [8] | 古国贤, 胡杨, 刘绍东, 董秀琴, 张绪穆. Indan-f-amphox:可用于铱催化β-芳基β-酮酸酯不对称加氢反应的PNN配体[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(4): 997-1002. |
| [9] | 张齐英, 张一铭, 郝二军, 白娟, 渠桂荣, 郭海明. 通过不对称氢转移/动态动力学拆分合成碳环N3-嘌呤核苷[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(2): 376-383. |
| [10] | 杨小会, 顾雪松, 宾怀玉, 谢建华, 周其林. (-)-吲哚里西啶167B和(+)-毒芹碱的不对称合成[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(11): 3963-3968. |
| [11] | 孔胜男, Abaid Ullah Malik, 钱雪峰, 舒谋海, 肖文德. 多孔有机聚合物负载钌催化的β-酮酸酯的不对称氢化[J]. 有机化学, 2018, 38(3): 656-664. |
| [12] | 陈姝琪, 杨文, 姚永祺, 杨新, 邓颖颍, 杨定乔. 钌催化β-酮酸酯不对称氢化反应的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2018, 38(10): 2534-2552. |
| [13] | 王群, 江黎黎, 卢斌, 胡北, 谢小敏, 李泽标, 张兆国. 手性辅基诱导β-脱氢氨基酸酯的非均相不对称氢化(英文)[J]. 有机化学, 2017, 37(6): 1398-1406. |
| [14] | 王志惠, 张振锋, 刘燕刚, 张万斌. 烯醇酯的不对称催化氢化研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2016, 36(3): 447-459. |
| [15] | 杨文, 潘雪静, 杨定乔. 铂催化α-酮酸酯不对称氢化反应的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2015, 35(6): 1216-1228. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||