有机化学 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (8): 2790-2799.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202302012 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
刘敏a,†, 杨冬燕b,†, 肖玉梅a,*( ), 苏旺苍c, 赵峰海a, 覃兆海a,*(
), 苏旺苍c, 赵峰海a, 覃兆海a,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-02-12
修回日期:2023-04-04
发布日期:2023-06-26
作者简介:基金资助:
Min Liua,†, Dongyan Yangb,†, Yumei Xiaoa( ), Wangcang Suc, Fenghai Zhaoa, Qin Zhaohai .a(
), Wangcang Suc, Fenghai Zhaoa, Qin Zhaohai .a( )
)
Received:2023-02-12
Revised:2023-04-04
Published:2023-06-26
Contact:
*E-mail: About author:Supported by:文章分享

烯式吡虫啉是吡虫啉的高活性代谢产物. 为解决烯式吡虫啉的高蜂毒问题, 根据生物电子等排原理, 合成了一系列烯式吡虫啉的类似物1,3-二取代-5-硝基亚氨基三唑啉化合物, 研究了该系列化合物对蚜虫、褐飞虱和西花蓟马的杀虫活性和离体杀菌活性. 结果表明, 这些化合物在400 μg/mL浓度下表现出一定的杀虫活性, 其中化合物Ⅱ-7在100 μg/mL浓度对西花蓟马的致死率达100%. 用admetSAR预测了部分化合物对蜜蜂的毒性, 结果均表现为低毒. 目标化合物在50 μg/mL浓度下对9种植物病原真菌均表现出不同程度的抑菌活性, 其中化合物I-15对5种病原菌的抑菌率高于或等同于对照药恶霉灵. 构效关系分析发现, 3-位脂肪烃基取代的化合物的杀虫活性高于芳香烃取代, 提高3号位取代基的亲脂性也可明显提高化合物的抑菌活性, 1-位吡啶环和噻唑环的取代对化合物抑菌活性没有影响. 与乙酰胆碱结合蛋白(AchBP)的分子对接结果表明, 化合物Ⅱ-7与吡虫啉(IMI)的结合模式相似, 说明该类化合物也具有与AChBP结合的潜力, 为进一步分子优化提供了新的借鉴.
刘敏, 杨冬燕, 肖玉梅, 苏旺苍, 赵峰海, 覃兆海. 5-硝基亚氨基[1,4-2H]-1,2,4-三唑啉烯式吡虫啉类似物的合成及生物活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(8): 2790-2799.
Min Liu, Dongyan Yang, Yumei Xiao, Wangcang Su, Fenghai Zhao, Qin Zhaohai .. Synthesis and Bioactivities of 5-Nitroimino-[1,4-2H]-1,2,4-triazolines as Olefin-Imidacloprid Mimics[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(8): 2790-2799.
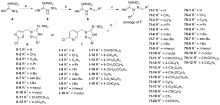

| Compd. | Honey bee toxicity | Compound | Honey bee toxicity | Compd. | Honey bee toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ-3 | Low | Ⅱ-2 | Low | 7Ⅰ-19 | Low |
| Ⅰ-7 | Low | Ⅱ-5 | Low | 7Ⅰ-20 | Low |
| Ⅰ-9 | Low | Ⅱ-7 | Low | 3 | High[ |
| Ⅰ-13 | Low | Ⅱ-10 | Low | ||
| Ⅰ-18 | Low | Ⅱ-12 | Low |
| Compd. | Honey bee toxicity | Compound | Honey bee toxicity | Compd. | Honey bee toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ-3 | Low | Ⅱ-2 | Low | 7Ⅰ-19 | Low |
| Ⅰ-7 | Low | Ⅱ-5 | Low | 7Ⅰ-20 | Low |
| Ⅰ-9 | Low | Ⅱ-7 | Low | 3 | High[ |
| Ⅰ-13 | Low | Ⅱ-10 | Low | ||
| Ⅰ-18 | Low | Ⅱ-12 | Low |
| Compd. | R2 | R1 | A.craccivora/(μg•mL-1) | N. lugens/(μg•mL-1) | F. occidentalis/(μg•mL-1) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | 100 | 400 | 100 | 400 | 100 | 50 | |||||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-1 | | H | 0 | — | 0 | — | 6.67 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-2 | CH3 | 44 | — | 4.44 | — | 0 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-3 | C2H5 | 52.87 | — | 2.13 | — | 39.33 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-4 | n-Pr | 41.77 | — | 4.35 | — | 8.33 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-5 | i-Pr | 42.35 | — | 0 | — | 3.96 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-6 | n-Bu | 26.25 | — | 0 | — | 91.09 | 0 | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-7 | sec-Bu | 22.62 | — | 0 | — | 2.27 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-8 | t-Bu | 44.71 | — | 0 | — | 43.37 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-9 | n-Hexyl | 62.9 | — | 6.25 | — | 3.88 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-10 | n-Octyl | 0 | — | 2.13 | — | 9.09 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-11 | | 2.47 | — | 4.55 | — | 22.33 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-12 | 4-ClC6H4 | 3.8 | — | 0 | — | 4.3 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-13 | 4-CH3C6H4 | 5.43 | — | 13.64 | — | 54.26 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-14 | 4-CH3OC6H4 | 0 | — | 0 | — | 64 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-15 | 4-(CH3)3CC6H4 | 0 | — | 0 | — | 4.3 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-16 | C6H5 | 2.86 | — | 0 | — | 94.51 | 0 | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-17 | 3-NO2C6H4 | 9.86 | — | 8.89 | — | 2.13 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-18 | 4-CNC6H4 | 3.03 | — | 0 | — | 4.4 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-1 | | H | 0 | — | 0 | — | 0 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-2 | CH3 | 86.25 | 0 | 0 | — | 10.42 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-3 | C2H5 | 58.02 | — | 2.17 | — | 45.26 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-4 | n-Pr | 52.78 | — | 0 | — | 3.49 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-5 | i-Pr | 4.11 | — | 0 | — | 25.53 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-6 | n-Bu | 24.29 | — | 0 | — | 3.26 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-7 | sec-Bu | 100 | 0 | 6.38 | — | 100 | 100 | 0 | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-8 | t-Bu | 28.79 | — | 0 | — | 80.23 | 0 | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-9 | n-Hexyl | 3.49 | — | 0 | — | 28.05 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-10 | n-Octyl | 42.68 | — | 2.22 | — | 2.97 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-11 | | 4.84 | — | 13.64 | — | 4.3 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-12 | 4-ClC6H4 | 2.44 | — | 2.17 | — | 0 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| 7I-19 | — | — | 48.48 | — | 0 | — | 4.44 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| 7I-20 | — | — | 2.41 | — | 46.51 | — | 0 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| 3 | — | — | 100 | 100 | 97.78 | 41.3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||||||
| Nitenpyram | — | — | 100 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Dinotefuran | — | — | — | 100 | 100 | 100 | — | — | 97.56 | ||||||||||||
| Spinosad | — | — | — | — | — | — | 100 | 100 | — | ||||||||||||
| DMF | — | — | 4.76 | 1.06 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.9 | 2.35 | ||||||||||||
| Compd. | R2 | R1 | A.craccivora/(μg•mL-1) | N. lugens/(μg•mL-1) | F. occidentalis/(μg•mL-1) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | 100 | 400 | 100 | 400 | 100 | 50 | |||||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-1 | | H | 0 | — | 0 | — | 6.67 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-2 | CH3 | 44 | — | 4.44 | — | 0 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-3 | C2H5 | 52.87 | — | 2.13 | — | 39.33 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-4 | n-Pr | 41.77 | — | 4.35 | — | 8.33 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-5 | i-Pr | 42.35 | — | 0 | — | 3.96 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-6 | n-Bu | 26.25 | — | 0 | — | 91.09 | 0 | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-7 | sec-Bu | 22.62 | — | 0 | — | 2.27 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-8 | t-Bu | 44.71 | — | 0 | — | 43.37 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-9 | n-Hexyl | 62.9 | — | 6.25 | — | 3.88 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-10 | n-Octyl | 0 | — | 2.13 | — | 9.09 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-11 | | 2.47 | — | 4.55 | — | 22.33 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-12 | 4-ClC6H4 | 3.8 | — | 0 | — | 4.3 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-13 | 4-CH3C6H4 | 5.43 | — | 13.64 | — | 54.26 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-14 | 4-CH3OC6H4 | 0 | — | 0 | — | 64 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-15 | 4-(CH3)3CC6H4 | 0 | — | 0 | — | 4.3 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-16 | C6H5 | 2.86 | — | 0 | — | 94.51 | 0 | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-17 | 3-NO2C6H4 | 9.86 | — | 8.89 | — | 2.13 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅰ-18 | 4-CNC6H4 | 3.03 | — | 0 | — | 4.4 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-1 | | H | 0 | — | 0 | — | 0 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-2 | CH3 | 86.25 | 0 | 0 | — | 10.42 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-3 | C2H5 | 58.02 | — | 2.17 | — | 45.26 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-4 | n-Pr | 52.78 | — | 0 | — | 3.49 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-5 | i-Pr | 4.11 | — | 0 | — | 25.53 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-6 | n-Bu | 24.29 | — | 0 | — | 3.26 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-7 | sec-Bu | 100 | 0 | 6.38 | — | 100 | 100 | 0 | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-8 | t-Bu | 28.79 | — | 0 | — | 80.23 | 0 | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-9 | n-Hexyl | 3.49 | — | 0 | — | 28.05 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-10 | n-Octyl | 42.68 | — | 2.22 | — | 2.97 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-11 | | 4.84 | — | 13.64 | — | 4.3 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Ⅱ-12 | 4-ClC6H4 | 2.44 | — | 2.17 | — | 0 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| 7I-19 | — | — | 48.48 | — | 0 | — | 4.44 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| 7I-20 | — | — | 2.41 | — | 46.51 | — | 0 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| 3 | — | — | 100 | 100 | 97.78 | 41.3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||||||
| Nitenpyram | — | — | 100 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Dinotefuran | — | — | — | 100 | 100 | 100 | — | — | 97.56 | ||||||||||||
| Spinosad | — | — | — | — | — | — | 100 | 100 | — | ||||||||||||
| DMF | — | — | 4.76 | 1.06 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.9 | 2.35 | ||||||||||||
| Compd. | Inhibition rate/% (50 μg/mL) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA | BC | RS | PC | CG | FG | MG | FO | FM | |
| Ⅰ-1 | 0.0±0.8 | 14.5±3.7 | 30.0±2.7 | 6.6±0.8 | 8.0±4.6 | 1.0±2.0 | 11.1±1.0 | 0.1±2.4 | 5.1±0.2 |
| Ⅰ-2 | 0.0±1.8 | 11.2±1.6 | 20.5±2.0 | 0.6±0.8 | 5.9±3.1 | 12.1±4.1 | 6.8±1.4 | 1.0±0.5 | 2.4±1.4 |
| Ⅰ-3 | 3.6±0.4 | 11.3±3.2 | 16.9±1.6 | 3.4±1.1 | 0.0±0.4 | 14.9±0.7 | 1.6±0.7 | 0.3±0.9 | 0.2±3.9 |
| Ⅰ-4 | 0.0±0.9 | 13.3±1.1 | 11.6±3.7 | 0.0±1.4 | 11.8±0.8 | 13.6±8.8 | 4.1±0.3 | 2.3±4.2 | 1.3±3.3 |
| Ⅰ-5 | 3.2±1.8 | 6.5±1.3 | 7.6±4.3 | 8.3±0.2 | 5.8±1.1 | 0.7±3.6 | 5.6±0.4 | 3.7±3.5 | 4.2±1.4 |
| Ⅰ-6 | 4.8±0.8 | 10.7±2.8 | 14.0±1.6 | 15.5±1.1 | 13.3±0.6 | 0.0±1.2 | 5.4±1.2 | 0.1±0.3 | 2.4±1.6 |
| Ⅰ-7 | 5.4±0.4 | 13.8±1.4 | 13.3±2.4 | 20.8±0.7 | 10.9±0.3 | 0.9±0.4 | 4.1±0.7 | 0.2±0.7 | 4.2±1.7 |
| Ⅰ-8 | 12.3±2.7 | 14.8±1.0 | 10.4±4.6 | 11.5±1.6 | 6.1±3.1 | 0.0±0.2 | 6.2±1.2 | 5.4±1.4 | 6.8±4.9 |
| Ⅰ-9 | 68.2±1.0 | 35.5±0.9 | 34.1±4.7 | 50.8±2.1 | 26.4±0.9 | 12.1±1.2 | 7.0±2.2 | 21.0±1.4 | 13.5±1.5 |
| Ⅰ-10 | 89.4±0.1 | 25.2±3.0 | 33.1±2.2 | 48.7±2.4 | 18.2±3.8 | 9.2±1.3 | 20.2±0.5 | 4.9±2.7 | 54.9±1.9 |
| Ⅰ-11 | 0.0±3.5 | 8.4±4.7 | 15.9±4.2 | 1.7±1.4 | 7.1±2.3 | 0.0±2.5 | 5.4±0.7 | 4.6±1.4 | 7.437±23 |
| Ⅰ-12 | 69.7±0.9 | 20.4±1.3 | 31.8±3.5 | 10.5±3.4 | 0.0±1.4 | 9.2±3.9 | 6.1±3.4 | 13.3±1.9 | 42.1±1.0 |
| Ⅰ-13 | 75.8±1.1 | 26.5±1.5 | 23.0±1.6 | 25.3±0.9 | 11.5±2.2 | 19.0±2.5 | 7.5±2.8 | 15.3±1.8 | 47.9±3.3 |
| Ⅰ-14 | 45.7±3.9 | 16.7±2.9 | 19.3±1.7 | 14.8±2.2 | 0.0±1.4 | 17.7±1.5 | 5.8±0.7 | 8.7±2.7 | 32.2±2.5 |
| Ⅰ-15 | 87.7±0.5 | 61.2±3.4 | 59.3±2.3 | 44.0±1.2 | 21.2±4.2 | 17.2±0.5 | 10.7±3.1 | 22.7±2.3 | 59.0±0.7 |
| Ⅰ-16 | 0.0±0.8 | 15.5±3.5 | 21.0±1.9 | 6.3±0.7 | 3.7±0.9 | 8.8±2.1 | 10.4±1.2 | 5.4±0.4 | 37.6±1.6 |
| Ⅰ-17 | 0.0±2.7 | 11.6±0.9 | 21.2±1.1 | 5.3±0.6 | 10.1±2.5 | 1.5±1.2 | 2.5±1.0 | 10.3±2.6 | 6.3±0.3 |
| Ⅰ-18 | 0.0±2.2 | 10.8±2.6 | 23.9±3.7 | 0.0±0.7 | 4.7±4.6 | 9.5±2.1 | 4.9±1.8 | 1.5±1.7 | 36.1±4.5 |
| Ⅱ-1 | 0.0±1.5 | 10.4±1.7 | 5.1±1.9 | 2.4±3.2 | 15.5±0.8 | 0.4±0.7 | 5.8±0.4 | 10.6±1.4 | 3.8±1.8 |
| Ⅱ-2 | 2.0±2.0 | 6.1±4.7 | 12.4±3.4 | 0.9±0.7 | 16.8±0.4 | 4.1±2.4 | 3.3±0.7 | 4.5±3.8 | 1.5±2.2 |
| Ⅱ-3 | 0.0±2.0 | 8.6±2.9 | 21.2±4.8 | 0.0±1.6 | 0.0±2.2 | 5.6±4.4 | 3.0±1.8 | 0.0±1.2 | 0.0±2.6 |
| Ⅱ-4 | 3.6±0.6 | 13.2±4.0 | 14.9±3.4 | 10.9±2.6 | 7.2±1.4 | 9.1±1.5 | 6.5±0.9 | 0.0±0.4 | 4.2±0.7 |
| Ⅱ-5 | 13.8±1.2 | 9.7±3.9 | 6.1±4.0 | 13.0±4.1 | 9.4±3.2 | 21.9±2.7 | 4.9±0.4 | 3.6±1.7 | 13.7±0.7 |
| Ⅱ-6 | 23.1±1.5 | 20.1±3.8 | 6.4±1.6 | 27.9±1.7 | 9.5±2.5 | 6.4±0.8 | 36.3±4.3 | 8.4±1.2 | 44.9±3.5 |
| Ⅱ-7 | 12.4±1.7 | 13.6±0.2 | 18.9±4.3 | 11.7±4.6 | 10.9±3.2 | 0.0±2.0 | 3.1±0.5 | 1.1±1.4 | 7.0±0.3 |
| Ⅱ-8 | 9.4±0.8 | 13.7±3.7 | 10.4±1.6 | 20.1±2.0 | 0.0±0.3 | 0.0±3.7 | 6.4±0.5 | 3.2±1.4 | 8.9±2.2 |
| Ⅱ-9 | 64.8±0.2 | 48.9±1.6 | 45.5±2.0 | 34.4±3.2 | 12.8±2.4 | 6.6±1.4 | 11.8±0.7 | 22.8±1.8 | 12.1±4.0 |
| Ⅱ-10 | 90.0±0.7 | 41.7±4.1 | 52.4±2.8 | 54.1±1.4 | 17.5±2.0 | 13.4±2.4 | 24.0±1.1 | 6.8±4.7 | 46.5±8.7 |
| Ⅱ-11 | 2.3±2.8 | 5.6±0.6 | 19.2±3.7 | 2.3±1.7 | 5.8±0.3 | 0.0±0.3 | 9.6±4.9 | 3.3±1.1 | 1.1±1.6 |
| Ⅱ-12 | 86.9±1.3 | 34.7±1.8 | 46.6±1.6 | 16.2±1.1 | 0.0±0.6 | 4.8±2.1 | 10.3±1.0 | 0.0±2.6 | 45.6±5.0 |
| 7Ⅰ-19 | 10.2±1..0 | 17.3±3.8 | 25.3±3.7 | 27.5±1.1 | 10.9±3.8 | 2.8±1.0 | 10.9±0.5 | 9.7±2.8 | 9.7±1.1 |
| 7Ⅰ-20 | 8.7±1.5 | 0.4±1.8 | 52.4±2.8 | 6.1±2.6 | 11.4±4.7 | 0.8±1.6 | 4.7±0.0 | 5.5±0.9 | 2.0±2.1 |
| 3 | 0.0±3.8 | 9.4±4.6 | 2.3±3.9 | 0.0±1.2 | 15.7±1.1 | 0.0±0.5 | 5.5±1.1 | 0.6±1.6 | 4.1±0.3 |
| Hymexazol | 100.0±0.0 | 50.4±1.9 | 25.8±2.0 | 1.5±1.2 | 37.5±0.4 | 41.4±0.7 | 43.0±1.3 | 51.6±0.3 | 36.4±2.0 |
| Compd. | Inhibition rate/% (50 μg/mL) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA | BC | RS | PC | CG | FG | MG | FO | FM | |
| Ⅰ-1 | 0.0±0.8 | 14.5±3.7 | 30.0±2.7 | 6.6±0.8 | 8.0±4.6 | 1.0±2.0 | 11.1±1.0 | 0.1±2.4 | 5.1±0.2 |
| Ⅰ-2 | 0.0±1.8 | 11.2±1.6 | 20.5±2.0 | 0.6±0.8 | 5.9±3.1 | 12.1±4.1 | 6.8±1.4 | 1.0±0.5 | 2.4±1.4 |
| Ⅰ-3 | 3.6±0.4 | 11.3±3.2 | 16.9±1.6 | 3.4±1.1 | 0.0±0.4 | 14.9±0.7 | 1.6±0.7 | 0.3±0.9 | 0.2±3.9 |
| Ⅰ-4 | 0.0±0.9 | 13.3±1.1 | 11.6±3.7 | 0.0±1.4 | 11.8±0.8 | 13.6±8.8 | 4.1±0.3 | 2.3±4.2 | 1.3±3.3 |
| Ⅰ-5 | 3.2±1.8 | 6.5±1.3 | 7.6±4.3 | 8.3±0.2 | 5.8±1.1 | 0.7±3.6 | 5.6±0.4 | 3.7±3.5 | 4.2±1.4 |
| Ⅰ-6 | 4.8±0.8 | 10.7±2.8 | 14.0±1.6 | 15.5±1.1 | 13.3±0.6 | 0.0±1.2 | 5.4±1.2 | 0.1±0.3 | 2.4±1.6 |
| Ⅰ-7 | 5.4±0.4 | 13.8±1.4 | 13.3±2.4 | 20.8±0.7 | 10.9±0.3 | 0.9±0.4 | 4.1±0.7 | 0.2±0.7 | 4.2±1.7 |
| Ⅰ-8 | 12.3±2.7 | 14.8±1.0 | 10.4±4.6 | 11.5±1.6 | 6.1±3.1 | 0.0±0.2 | 6.2±1.2 | 5.4±1.4 | 6.8±4.9 |
| Ⅰ-9 | 68.2±1.0 | 35.5±0.9 | 34.1±4.7 | 50.8±2.1 | 26.4±0.9 | 12.1±1.2 | 7.0±2.2 | 21.0±1.4 | 13.5±1.5 |
| Ⅰ-10 | 89.4±0.1 | 25.2±3.0 | 33.1±2.2 | 48.7±2.4 | 18.2±3.8 | 9.2±1.3 | 20.2±0.5 | 4.9±2.7 | 54.9±1.9 |
| Ⅰ-11 | 0.0±3.5 | 8.4±4.7 | 15.9±4.2 | 1.7±1.4 | 7.1±2.3 | 0.0±2.5 | 5.4±0.7 | 4.6±1.4 | 7.437±23 |
| Ⅰ-12 | 69.7±0.9 | 20.4±1.3 | 31.8±3.5 | 10.5±3.4 | 0.0±1.4 | 9.2±3.9 | 6.1±3.4 | 13.3±1.9 | 42.1±1.0 |
| Ⅰ-13 | 75.8±1.1 | 26.5±1.5 | 23.0±1.6 | 25.3±0.9 | 11.5±2.2 | 19.0±2.5 | 7.5±2.8 | 15.3±1.8 | 47.9±3.3 |
| Ⅰ-14 | 45.7±3.9 | 16.7±2.9 | 19.3±1.7 | 14.8±2.2 | 0.0±1.4 | 17.7±1.5 | 5.8±0.7 | 8.7±2.7 | 32.2±2.5 |
| Ⅰ-15 | 87.7±0.5 | 61.2±3.4 | 59.3±2.3 | 44.0±1.2 | 21.2±4.2 | 17.2±0.5 | 10.7±3.1 | 22.7±2.3 | 59.0±0.7 |
| Ⅰ-16 | 0.0±0.8 | 15.5±3.5 | 21.0±1.9 | 6.3±0.7 | 3.7±0.9 | 8.8±2.1 | 10.4±1.2 | 5.4±0.4 | 37.6±1.6 |
| Ⅰ-17 | 0.0±2.7 | 11.6±0.9 | 21.2±1.1 | 5.3±0.6 | 10.1±2.5 | 1.5±1.2 | 2.5±1.0 | 10.3±2.6 | 6.3±0.3 |
| Ⅰ-18 | 0.0±2.2 | 10.8±2.6 | 23.9±3.7 | 0.0±0.7 | 4.7±4.6 | 9.5±2.1 | 4.9±1.8 | 1.5±1.7 | 36.1±4.5 |
| Ⅱ-1 | 0.0±1.5 | 10.4±1.7 | 5.1±1.9 | 2.4±3.2 | 15.5±0.8 | 0.4±0.7 | 5.8±0.4 | 10.6±1.4 | 3.8±1.8 |
| Ⅱ-2 | 2.0±2.0 | 6.1±4.7 | 12.4±3.4 | 0.9±0.7 | 16.8±0.4 | 4.1±2.4 | 3.3±0.7 | 4.5±3.8 | 1.5±2.2 |
| Ⅱ-3 | 0.0±2.0 | 8.6±2.9 | 21.2±4.8 | 0.0±1.6 | 0.0±2.2 | 5.6±4.4 | 3.0±1.8 | 0.0±1.2 | 0.0±2.6 |
| Ⅱ-4 | 3.6±0.6 | 13.2±4.0 | 14.9±3.4 | 10.9±2.6 | 7.2±1.4 | 9.1±1.5 | 6.5±0.9 | 0.0±0.4 | 4.2±0.7 |
| Ⅱ-5 | 13.8±1.2 | 9.7±3.9 | 6.1±4.0 | 13.0±4.1 | 9.4±3.2 | 21.9±2.7 | 4.9±0.4 | 3.6±1.7 | 13.7±0.7 |
| Ⅱ-6 | 23.1±1.5 | 20.1±3.8 | 6.4±1.6 | 27.9±1.7 | 9.5±2.5 | 6.4±0.8 | 36.3±4.3 | 8.4±1.2 | 44.9±3.5 |
| Ⅱ-7 | 12.4±1.7 | 13.6±0.2 | 18.9±4.3 | 11.7±4.6 | 10.9±3.2 | 0.0±2.0 | 3.1±0.5 | 1.1±1.4 | 7.0±0.3 |
| Ⅱ-8 | 9.4±0.8 | 13.7±3.7 | 10.4±1.6 | 20.1±2.0 | 0.0±0.3 | 0.0±3.7 | 6.4±0.5 | 3.2±1.4 | 8.9±2.2 |
| Ⅱ-9 | 64.8±0.2 | 48.9±1.6 | 45.5±2.0 | 34.4±3.2 | 12.8±2.4 | 6.6±1.4 | 11.8±0.7 | 22.8±1.8 | 12.1±4.0 |
| Ⅱ-10 | 90.0±0.7 | 41.7±4.1 | 52.4±2.8 | 54.1±1.4 | 17.5±2.0 | 13.4±2.4 | 24.0±1.1 | 6.8±4.7 | 46.5±8.7 |
| Ⅱ-11 | 2.3±2.8 | 5.6±0.6 | 19.2±3.7 | 2.3±1.7 | 5.8±0.3 | 0.0±0.3 | 9.6±4.9 | 3.3±1.1 | 1.1±1.6 |
| Ⅱ-12 | 86.9±1.3 | 34.7±1.8 | 46.6±1.6 | 16.2±1.1 | 0.0±0.6 | 4.8±2.1 | 10.3±1.0 | 0.0±2.6 | 45.6±5.0 |
| 7Ⅰ-19 | 10.2±1..0 | 17.3±3.8 | 25.3±3.7 | 27.5±1.1 | 10.9±3.8 | 2.8±1.0 | 10.9±0.5 | 9.7±2.8 | 9.7±1.1 |
| 7Ⅰ-20 | 8.7±1.5 | 0.4±1.8 | 52.4±2.8 | 6.1±2.6 | 11.4±4.7 | 0.8±1.6 | 4.7±0.0 | 5.5±0.9 | 2.0±2.1 |
| 3 | 0.0±3.8 | 9.4±4.6 | 2.3±3.9 | 0.0±1.2 | 15.7±1.1 | 0.0±0.5 | 5.5±1.1 | 0.6±1.6 | 4.1±0.3 |
| Hymexazol | 100.0±0.0 | 50.4±1.9 | 25.8±2.0 | 1.5±1.2 | 37.5±0.4 | 41.4±0.7 | 43.0±1.3 | 51.6±0.3 | 36.4±2.0 |
| Compd. | Log P | Comd. | Log P | Compd. | Log P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ-1 | 2.56 | Ⅰ-9 | 5.64 | Ⅰ-13 | 5.06 |
| Ⅰ-3 | 3.81 | Ⅰ-10 | 6.55 | Ⅰ-14 | 4.78 |
| Ⅰ-6 | 4.72 | Ⅰ-12 | 5.26 | Ⅰ-15 | 6.52 |
| Compd. | Log P | Comd. | Log P | Compd. | Log P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ-1 | 2.56 | Ⅰ-9 | 5.64 | Ⅰ-13 | 5.06 |
| Ⅰ-3 | 3.81 | Ⅰ-10 | 6.55 | Ⅰ-14 | 4.78 |
| Ⅰ-6 | 4.72 | Ⅰ-12 | 5.26 | Ⅰ-15 | 6.52 |
| [1] |
Elbert, A.; Becker, B.; Hartwig, J.; Erdelen, C. Pflanzenschutz- Nachr. Bayer 1991, 44, 113.
|
| [2] |
Casida, J. E.; Quistad, G. B. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1998, 43, 1.
pmid: 9444749 |
| [3] |
Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R. Pest Manage. Sci. 2008, 64, 1084.
doi: 10.1002/ps.v64:11 |
| [4] |
Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J. E. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 260.
doi: 10.1021/ar800131p |
| [5] |
Casida, J. E. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2923.
doi: 10.1021/jf102438c |
| [6] |
Kagabu, S. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2887.
doi: 10.1021/jf101824y |
| [7] |
Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J. E. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2883.
doi: 10.1021/jf103856c |
| [8] |
Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R.; Beck, M. E. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9464.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v52.36 |
| [9] |
Leite, S. A.; Guedes, R. N. C.; da Costa, D. R.; Colmenarez, Y. C.; Matsumoto, S. N.; dos Santos, M. P.; Coelho, B. S.; Moreira, A. A.; Castellani, M. A. Pest Manage. Sci. 2022, 78, 2581.
doi: 10.1002/ps.v78.6 |
| [10] |
Alsafran, M.; Rizwan, M.; Usman, K.; Saleem, M. H.; Jabri, H. A. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108485.
doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2022.108485 |
| [11] |
Britt, E. E. Chem. Eng. News 2023, 101, 14.
|
| [12] |
Lourencetti, A. P. S.; Azevedo, P.; Miotelo, L.; Malaspina, O.; Nocelli, R. C. F. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120842.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120842 |
| [13] |
European Food Safety, A. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05178.
|
| [14] |
Demortain, D. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2021, 46, 78-82.
doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2021.02.017 pmid: 33737144 |
| [15] |
Onozaki, Y.; Horikoshi, R.; Ohno, I.; Kitsuda, S.; Durkin, K. A.; Suzuki, T.; Asahara, C.; Hiroki, N.; Komabashiri, R.; Shimizu, R.; Furutani, S.; Ihara, M.; Matsuda, K.; Mitomi, M.; Kagabu, S.; Uomoto, K.; Tomizawa, M. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7865.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02924 |
| [16] |
Xu, Y.; Yang, D. Y.; Zou, X. G.; Rui, C. H.; Zhou, Z. Y.; Ma, Y. Q.; Qin, Z. H. Pest Manage. Sci. 2017, 73, 1927.
doi: 10.1002/ps.2017.73.issue-9 |
| [17] |
Yang, S.; Lai, Q.; Lai, F.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, C.; Xu, H. Pest Manage. Sci. 2021, 77, 1013.
doi: 10.1002/ps.v77.2 |
| [18] |
Nauen, R.; Jeschke, P.; Velten, R.; Beck, M. E.; Ebbinghaus- Kintscher, U.; Thielert, W.; Wolfel, K.; Haas, M.; Kunz, K.; Raupach, G. Pest Manage. Sci. 2015, 71, 850.
doi: 10.1002/ps.2015.71.issue-6 |
| [19] |
Wernecke, A.; Eckert, J. H.; Forster, R.; Kurlemann, N.; Odemer, R. J. Plant Dis. Protect. 2021, 129, 93.
|
| [20] |
Tamburini, G.; Wintermantel, D.; Allan, M. J.; Dean, R. R.; Knauer, A.; Albrecht, M.; Klein, A. M. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146084.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146084 |
| [21] |
Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R.; Gutbrod, O.; Beck, M. E.; Matthiesen, S.; Haas, M.; Velten, R. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 121, 31.
doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2014.10.011 |
| [22] |
Zhu, C.; Li, G.; Xiao, K.; Shao, X.; Cheng, J.; Li, Z. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 255.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2018.05.013 |
| [23] |
Markussen, M. D. K.; Kristensen, M. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 98, 50.
doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2010.04.012 |
| [24] |
Kim, J.; Chon, K.; Kim, B.-S.; Oh, J.-A.; Yoon, C.-Y.; Park, H.-H. Pest Manage. Sci. 2022, 78, 5402.
doi: 10.1002/ps.v78.12 |
| [25] |
Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, T.; Wu, S.; Wu, Z.; Wu, S.; Song, R.; Song, B. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8598.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c01899 |
| [26] |
Sur, R. B. Insectol. 2003, 56, 35.
|
| [27] |
Nauen, R.; Tietjen, K.; Wagner, K.; Elbert, A. Pestic. Sci. 1998, 52, 53.
doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9063(199801)52:1【-逻*辑*与-】amp;lt;【-逻*辑*与-】amp;gt;1.0.CO;2-J |
| [28] |
Nauen, R.; Reckmann, U.; Armborst, S.; Stupp, H.-P.; Elbert, A. Pestic. Sci. 1999, 55, 265.
doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9063(199903)55:3【-逻*辑*与-】amp;lt;【-逻*辑*与-】amp;gt;1.0.CO;2-5 |
| [29] |
Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, F.; Wu, X.; Pan, X.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Y. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 3567.
doi: 10.1002/jssc.v45.18 |
| [30] |
Suchail, S.; Guez, D.; Belzunces, L. P. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 2482.
doi: 10.1897/1551-5028(2001)020【-逻*辑*与-】lt;2482:dbaact【-逻*辑*与-】gt;2.0.co;2 pmid: 11699773 |
| [31] |
Jayashree, B. S.; Nikhil, P. S.; Paul, S. Med. Chem. 2022, 18, 915-925.
doi: 10.2174/1573406418666220127124228 |
| [32] |
Kang, O.-Y.; Kim, E.; Lee, W. H.; Ryu, D. H.; Lim, H. J.; Park, S. J. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 2004.
doi: 10.1039/D2RA06988A |
| [33] |
Wu, H.; Maimaitijiang, A.; Tang, D.; Xie, B.; Niu, C.; Aisa, H. A. Heterocycles 2023, 106, 94.
doi: 10.3987/COM-22-14764 |
| [34] |
Guzel, E.; Acar Cevik, U.; Evren, A. E.; Bostanc, H. E.; Gul, U. D.; Kays, U.; Ozkay, Y.; Kaplanckl, Z. A. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 4369.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c07755 |
| [35] |
Li, J.; Zhang, J. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 41.
doi: 10.2174/1568026621666211111160332 |
| [36] |
Gupta, O.; Pradhan, T.; Chawla, G. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1274, 134487.
doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134487 |
| [37] |
Xie, R.; Mei, X.; Ning, J. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 67, 345.
doi: 10.1248/cpb.c18-00704 |
| [38] |
Li, B.; Yu, Y.; Duan, W.; Lin, G.; Wen, R.; Zhang, Z. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202200726.
doi: 10.1002/cbdv.v19.11 |
| [39] |
Zhao, F.; Singh, T.; Xiao, Y.; Su, W.; Yang, D.; Jia, C.; Li, J.-Q.; Qin, Z. Synthesis 2021, 53, 1901.
doi: 10.1055/a-1477-4630 |
| [40] |
Ouyang, Y.; Huang, J.-j.; Wang, Y.-L.; Zhong, H.; Song, B.-A.; Hao, G.-f. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 10761.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c01460 |
| [41] |
Chen, D.; Hao, G.; Song, B. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 10090.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c02757 |
| [42] |
Banerjee, P.; Eckert, A. O.; Schrey, A. K.; Preissner, R. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W257.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gky318 |
| [43] |
Cheng, F.; Li, W.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, J.; Wu, Z.; Liu, G.; Lee, P. W.; Tang, Y. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 3099.
doi: 10.1021/ci300367a |
| [44] |
Williams, A. J.; Grulke, C. M.; Edwards, J.; McEachran, A. D.; Mansouri, K.; Baker, N. C.; Patlewicz, G.; Shah, I.; Wambaugh, J. F.; Judson, R. S.; Richard, A. M. J. Cheminf. 2017, 9, 61/61-61/27.
|
| [45] |
Perez Santin, E.; Rodriguez Solana, R.; Gonzalez Garcia, M.; Garcia Suarez, M. D. M.; Blanco Diaz, G. D.; Cima Cabal, M. D.; Moreno Rojas, J. M.; Lopez Sanchez, J. I. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Comput. Mol. Sci. 2021, 11, e1516.
|
| [46] |
Han, Q.; Wu, N.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Zhang, R.-L.; Li, H.-L.; Jiang, Z.-Y.; Huang, J.-X.; Duan, H.-X.; Yang, Q. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 7387.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c02091 |
| [47] |
Zhao, P.-L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, M.-Z.; Liu, Z.-M.; Huang, W.; Yang, G.-F. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10767.
doi: 10.1021/jf802343p |
| [48] |
Su, W.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Rui, C.; Duan, H.; Qin, Z. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5028.
doi: 10.1021/jf300616x |
| [49] |
Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Du, S.; Han, X.; Li, J. Q.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Xu, L.; Qin, Z. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 111.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c05784 |
| [1] | 吴思敏, 唐嘉欣, 周于佳, 徐学涛, 张昊星, 王少华. 2β-Acetoxyferruginol去醋酸基骨架衍生物抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(2): 613-621. |
| [2] | 霍海波, 李桂霞, 王世军, 韩春, 师宝君, 李健. 新型γ-咔啉衍生物的合成及其抑菌活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(1): 204-215. |
| [3] | 王锋, 陈钰, 裴鸿艳, 张静, 张立新. 含哌啶的新型1,2,4-噁二唑类衍生物的设计合成及抗真菌活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(8): 2826-2836. |
| [4] | 张紫婵, 孙洋, 华晟, 徐宝琳, 张敏, 赵勤, 郑丹丹, 王杨, 鞠剑峰, 石玉军, 戴红. 新型含异噁唑单元的吡唑酰胺类衍生物的合成及杀虫活性[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(4): 1435-1443. |
| [5] | 徐欢, 吴鸿飞, 张晓鸣, 路星星, 孙腾达, 亓悦, 林誉凡, 杨新玲, 张莉, 凌云. 含1,2,3,4-四氢异喹啉片段磺酰肼和酰肼类化合物的设计、合成及生物活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(2): 725-733. |
| [6] | 孙昌兴, 张福豪, 张欢, 李鹏辉, 姜林. 新型2-(1-甲基-1H-吡唑-4-基)嘧啶-4-甲酰胺的设计、合成、杀菌活性及分子对接研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(1): 229-235. |
| [7] | 汪蕾, 于淑晶, 杨娜, 王宝雷. 新型含二氢喹唑啉酮的咖啡因衍生物的合成及生物活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(1): 299-307. |
| [8] | 李文娟, 张睿, 蔡志华, 韩小强, 何林, 代斌. 苯炔[3+2]环加成反应构建三氟甲基取代的苯并环状亚砜亚胺衍生物及其杀棉蚜活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(9): 2832-2839. |
| [9] | 王长凯, 孙腾达, 张学博, 杨新玲, 路星星, 徐欢, 石发胜, 张莉, 凌云. 新型含氟吡唑酰肼类化合物的设计合成与生物活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(5): 1527-1536. |
| [10] | 王秀, 段文贵, 林桂汕, 李宝谕, 张文静, 雷福厚. 含天然蒎烯结构的4-酰基-3-氨基-1,2,4-三唑-硫醚衍生物的合成、抑菌活性、三维定量构效关系及分子对接研究[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(3): 871-883. |
| [11] | 孔媛芳, 杨彬, 庄严, 张京玉, 孙德梅, 董春红. 基于二肽基肽酶4 (DPP-4)靶点设计的五种降糖活性杂环合成及构效关系研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(3): 770-784. |
| [12] | 曾艳, 聂礼飞, 牛超, 阿依提拉•麦麦提江, Khurshed Bozorov, 赵江瑜, 阿吉艾克拜尔•艾萨. 二氢噁唑并[5,4-d]吡咯并[1,2-a]嘧啶酮的合成及生物活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(2): 543-556. |
| [13] | 崔玉成, 陈美桦, 林桂汕, 段文贵, 李晴敏, 邹壬萱, 岑波. 含偕二甲基环丙烷结构的1,3,4-噻二唑-脲化合物的合成、抑菌活性及分子对接研究[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(11): 3784-3797. |
| [14] | 陈澍, 邵莹莹, 付欣豪, 陈庆悟, 杜晓华, 谭成侠. 吡啶联噻唑双酰胺类化合物的设计、合成及杀虫活性[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(11): 3870-3879. |
| [15] | 陈睿嘉, 周聪, 逄锡文, 刘佳君, 顾玉诚, 刘建文, 李忠. 以环丙烷限制构象的新型双酰胺的设计、合成、抗癌活性及计算分析[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(1): 277-292. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||