有机化学 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 3873-3884.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202502009 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
收稿日期:2025-02-10
修回日期:2025-04-14
发布日期:2025-05-06
Ying Lia, Shuozhen Hua, Wei Fangb, Xing Xiaob, Xinsheng Zhanga,*( )
)
Received:2025-02-10
Revised:2025-04-14
Published:2025-05-06
Contact:
文章分享

本研究旨在通过电化学方法氧化乙醇胺(MEA)合成甘氨酸(Gly). 对电解槽结构对反应效果的影响进行了研究, 发现无隔膜电解槽在提高Gly收率、Gly选择性、MEA转化率和电流效率等方面的效果优于隔膜电解槽. 通过一系列实验设计, 发现无隔膜电解槽电解效果高于隔膜电解槽的主要原因为阴极Pb发生了部分Pb(Ⅱ)溶出现象. 溶出的Pb(Ⅱ)迁移至阳极, 在阳极表面氧化生成PbO2并附着于阳极表面, PbO2与Pt协同催化氧化乙醇胺提高了甘氨酸的收率. 借助电化学原位红外光谱研究揭示了C—OH在Pt-PbO2电极表面具有较强吸附, 且Pt-PbO2可促进乙醇胺中的C—OH电氧化为C=O和COOH. 最后通过优化电解质种类和浓度、乙醇胺浓度等条件, 以90.54%的高收率获得甘氨酸, 甘氨酸选择性和乙醇胺转化率均超过90%. 重复性实验证明该电解法具有较好的重复性. 通过调节溶液pH、过滤、减压蒸馏、洗涤、干燥一系列操作得到Gly固体, Gly分离效率为88%.
李颖, 胡硕真, 方卫, 肖星, 张新胜. 乙醇胺电氧化合成甘氨酸的研究[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(10): 3873-3884.
Ying Li, Shuozhen Hu, Wei Fang, Xing Xiao, Xinsheng Zhang. Study on Synthesis of Glycine by Electrooxidation of Ethanolamine[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(10): 3873-3884.






| Anode | Gly yield/% | Gly selectivity/% | MEA conversion/% | Faraday efficiency/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | 27.02 | 45.40 | 59.52 | 21.62 |
| PbO2 | 70.28 | 78.50 | 89.54 | 56.25 |
| Pt-PbO2 | 80.99 | 81.45 | 99.43 | 64.81 |
| Anode | Gly yield/% | Gly selectivity/% | MEA conversion/% | Faraday efficiency/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | 27.02 | 45.40 | 59.52 | 21.62 |
| PbO2 | 70.28 | 78.50 | 89.54 | 56.25 |
| Pt-PbO2 | 80.99 | 81.45 | 99.43 | 64.81 |




| Acid-base environment | Gly yield/% | Gly selecti- vity/% | MEA con- version/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acidic media | 79.22 | 88.61 | 89.40 |
| Alkaline media | 3.09 | 5.25 | 58.99 |
| Acid-base environment | Gly yield/% | Gly selecti- vity/% | MEA con- version/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acidic media | 79.22 | 88.61 | 89.40 |
| Alkaline media | 3.09 | 5.25 | 58.99 |


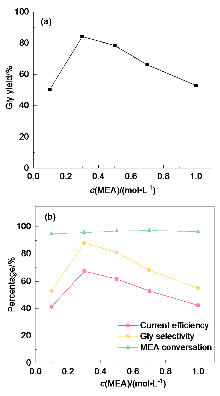



| Serial number | Gly yield/% | Gly selecti- vity/% | MEA con- version/% | Faraday efficiency/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 84.23 | 88.03 | 95.69 | 67.28 |
| 2 | 86.30 | 90.16 | 95.73 | 69.53 |
| 3 | 85.57 | 88.43 | 96.77 | 68.50 |
| Serial number | Gly yield/% | Gly selecti- vity/% | MEA con- version/% | Faraday efficiency/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 84.23 | 88.03 | 95.69 | 67.28 |
| 2 | 86.30 | 90.16 | 95.73 | 69.53 |
| 3 | 85.57 | 88.43 | 96.77 | 68.50 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
|
(郭浩, 钮东方, 胡硕真, 电化学, 2021, 27, 498.)
doi: 10.13208/j.electrochem.201203 |
|
| [5] |
|
|
(王振华, 马聪, 方萍, 徐海超, 梅天胜, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 1115.)
doi: 10.6023/A22060260 |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
|
(热孜古丽•玉努斯, 卡迪尔亚•阿布都外力, 罗时玮, 阿布都热西提•阿布力克木, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 843.)
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
(坎比努尔•努尔买买提, 王超, 罗时玮, 阿布都热西提•阿布力克木, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 582.)
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
|
(李娟, 姚玉妮, 中国饲料添加剂, 2010, (9), 26.)
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
(柯轲, 张紫微, 康会芳, 方热军, 孔祥峰, 饲料研究, 2017 (10), 20.)
|
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
|
(钱益斌, 杨利民, 安徽农业科学, 2009, 37, 5828.)
|
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
|
(程明立, 史建公, 张毅, 苑志伟, 袁立焕, 沈小宁, 中外能源, 2022, 27, 70.)
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
(黄平, 李云政, 张青山, 化学研究, 2004, 15, 77.)
|
|
| [22] |
|
|
(朱志华, 李燕, 赫崇衡, 于筛成, 徐佩若, 石油化工, 2005, 34, 279.)
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
|
(李鑫, 张伟, 赵广, 赫瑞元, 韩萌, 杨仁俊, 毋楠, 龚文照, 农药, 2019, 58, 788.)
|
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
|
(段正康, 杨运泉, 刘文英, 熊鹰, 李国龙, 精细化工, 2000, 17, 345.)
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
(卢祖国, 博士论文, 浙江大学, 杭州, 2003.)
|
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c05064 pmid: 38334492 |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1021/cr9000995 pmid: 19606907 |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
|
(曾燕真, 硕士论文, 福州大学, 福州, 2015.)
|
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [1] | 尤晓琴, 黄克金, 庄诗怡, 刘晨江, 金伟伟. 电化学促进的甘氨酸衍生物酯交换反应[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(4): 1360-1368. |
| [2] | 宣良明, 赵伟, 范润东, 严琼姣, 汪伟, 陈芬儿. 基于甘氨酸衍生物α-C(sp3)—H官能团化的催化体系研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(9): 2700-2721. |
| [3] | 何蔺恒, 夏稳, 周玉祥, 于贤勇. 电催化N-芳基甘氨酸和苯并[e][1,2,3]噁噻嗪-2,2-二氧化物的串联脱羧环化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(3): 997-1004. |
| [4] | 黄克金, 蔡金博, 王瑞革, 张永红, 王斌, 夏昱, 金伟伟, 李新勇, 刘晨江. 硼促进甘氨酸衍生物的电化学C(sp2)—H溴化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(3): 989-996. |
| [5] | 祝志强, 肖利金, 谢宗波, 乐长高. 甘氨酸衍生物α-C(sp3)-H键官能团化反应的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(9): 2345-2364. |
| [6] | 赵亮, 周圣斌, 童军华, 王江, 柳红. 不对称合成手性3,5-二取代脯氨酸及其衍生物[J]. 有机化学, 2018, 38(6): 1437-1446. |
| [7] | 陈金全, 康泰然, 刘敬林, 何龙, 刘全忠. 高选择性相转移催化原位产生不饱和亚胺参与的不对称Michael反应[J]. 有机化学, 2013, 33(07): 1483-1489. |
| [8] | 惠爱玲, 吴泽宇, 袁媛, 周安, 潘见. 银杏内酯衍生物和类似物的合成及PAFR和GlyR拮抗活性研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2013, 33(06): 1263-1272. |
| [9] | 金英学, 王家昌, 岳群峰, 曲凤玉, 魏树权, 谭广慧. N-(末端三甲基硅苄基甘氨酸肽链)-2,3-萘二甲酰亚胺的光诱导单电子转移成环反应[J]. 有机化学, 2012, 32(07): 1290-1295. |
| [10] | 王勇, 龙亚秋. 蛋白酪氨酸激酶小分子抑制剂的研究新进展[J]. 有机化学, 2011, 31(10): 1595-1595. |
| [11] | 周佳栋; 曹 飞*; 张小龙; 杨 颖; 应汉杰; 韦 萍. 一种基于共保护策略合成谷胱甘肽的新方法[J]. 有机化学, 2009, 29(08): 1272-1277. |
| [12] | 彭汝芳,金波,曹葵,舒远杰,楚士晋. 含能富勒烯吡咯烷衍生物的合成及工艺研究[J]. 有机化学, 2007, 27(02): 276-278. |
| [13] | 李振江,万红贵,韦萍,石玉瑚,欧阳平凯. 手性辅基法不对称合成特殊结构α-氨基酸——甘氨酸等当体途径[J]. 有机化学, 2005, 25(08): 881-892. |
| [14] | 张欣, 朱华玲, 徐海珍, 王瑾玲. 1-苯基-3-甲基-4-苯甲酰基-5-吡唑啉酮(HPMBP)缩甘氨酸甲酯的合成、表征和晶体结构[J]. 有机化学, 2004, 24(2): 195-198. |
| [15] | 杨大成,范莉,钟裕国. 全保护RGD三肽的合成方法研究[J]. 有机化学, 2003, 23(5): 493-498. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||