有机化学 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 1786-1791.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202112004 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
收稿日期:2021-12-02
修回日期:2022-01-08
发布日期:2022-02-25
通讯作者:
张向阳, 唐裕才
基金资助:
Xiangyang Zhang( ), Qinglin Wu, Feifei Wang, Youming Shen, Yucai Tang(
), Qinglin Wu, Feifei Wang, Youming Shen, Yucai Tang( )
)
Received:2021-12-02
Revised:2022-01-08
Published:2022-02-25
Contact:
Xiangyang Zhang, Yucai Tang
Supported by:文章分享
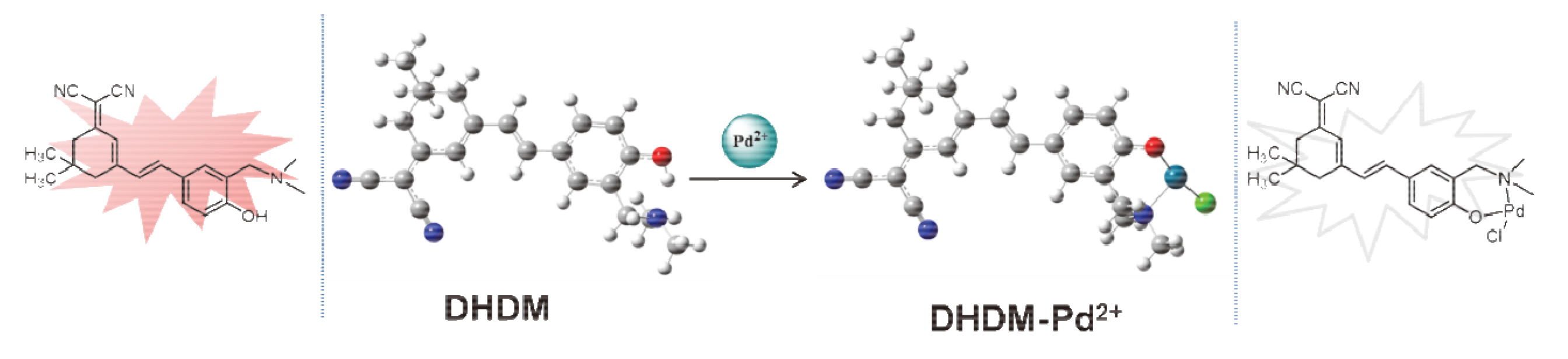
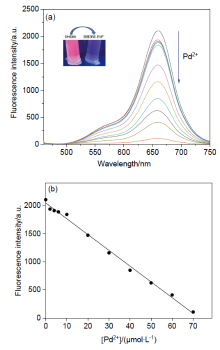
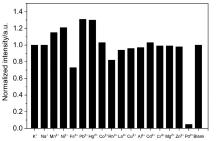
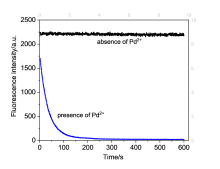
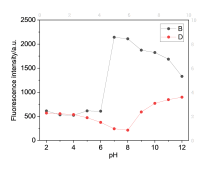
设计、合成了一种含有异佛尔酮骨架和2-羟基-N,N-二甲基苄胺的近红外荧光探针DHDM. 荧光探针DHDM可用于特异性地检测Pd2+, 具有良好的检测限(53 nmol/L)和斯托克斯位移(220 nm). 在0~70 μmol/L浓度范围内, 660 nm处的荧光发射强度与Pd2+呈现良好的线性关系. 根据高分辨质谱、红外光谱、对比实验以及DFT计算的结果, 提出了一种可能的识别机理. 最后, 成功地将荧光探针DHDM应用于细胞中Pd2+的荧光成像, 显示其在生物体系中潜在的应用. 这种以2-羟基-N,N-二甲基苄胺为识别基团的设计策略将为构建性能优异的其它荧光探针提供新思路.
张向阳, 吴庆林, 王菲菲, 申有名, 唐裕才. 一种以2-羟基-N,N-二甲基苄胺为新识别基团的钯离子近红外荧光探针及其细胞成像[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(6): 1786-1791.
Xiangyang Zhang, Qinglin Wu, Feifei Wang, Youming Shen, Yucai Tang. A Near-Infrared Fluorescent Probe with 2-Hydroxy-N,N-dimethyl- benzylamine as a New Recognition Fragment for Pd2+ Detection and Bioimaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(6): 1786-1791.








| [1] |
Wataha, J. C.; Hanks, C. T. J. Oral Rehabil. 1996, 23, 309.
pmid: 8736443 |
| [2] |
Kielhorn, J.; Melber, C.; Keller, D.; Mangelsdorf, I. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2002, 205, 417.
doi: 10.1078/1438-4639-00180 |
| [3] |
Hager, A.; Guimond, N.; Grunenberg, L.; Hanisch, C.; Steiger, S.; Preuss, A. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2020, 24, 2941.
doi: 10.1021/acs.oprd.0c00377 |
| [4] |
Filon, F. L.; Crosera, M.; Mauro, M.; Baracchini, E.; Bovenzi, M.; Montini, T.; Fornasiero, P.; Adamib, G. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 497.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.077 |
| [5] |
Hong, S.; Chung, S.; Park, J.; Hwang, J. P.; Lee, C. H.; Uhm, S.; Bong, S.; Lee, J. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 4722.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c03555 |
| [6] |
Park, S.-H.; Kwon, N.; Lee, J.-H.; Yoon, J.; Shin, I. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 143.
doi: 10.1039/C9CS00243J |
| [7] |
Li, H. L.; Fan, J. L.; Peng, X. J. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7943.
|
| [8] |
Saleem, M.; Lee, K. H. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 72150.
|
| [9] |
Park, S.-H.; Kwon, N.; Lee, J.-H.; Yoon, J.; Shin, I. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 143.
|
| [10] |
She, M. Y.; Wang, Z. H.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, Q.; Chen, P. F. L.; Zhang, S. Y.; Li, J. L. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 432, 213712.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213712 |
| [11] |
Zhu, J.-L.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y. Y.; Xu, L. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 6629.
|
| [12] |
Jin, T. X.; Huang, C.; Cui, M. Y.; Yang, Y. H.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, W. P.; Qian, X. H. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 10686.
doi: 10.1039/D0TB01829E |
| [13] |
Kaura, M.; Choi, D. H. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 58.
doi: 10.1039/C4CS00248B |
| [14] |
Murata, O.; Shindo, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Iwasawa, N.; Citterio, D.; Oka, K.; Hiruta, Y. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 966.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b03872 pmid: 31724392 |
| [15] |
Li, Z.; Xu, Y. Q.; Fu, J.; Zhu, H. L.; Qian, Y. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 888.
doi: 10.1039/C7CC08333E |
| [16] |
Kwon, J. Y.; Jang, Y. J.; Lee, Y. J.; Kim, K. M.; Seo, M. S.; Nam, W.; Yoon, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10107.
doi: 10.1021/ja051075b |
| [17] |
Peng, X. J.; Du, J. J.; Fan, J. L.; Wang, J. Y.; Wu, Y. K.; Zhao, J. Z.; Sun, S. G.; Xu, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1500.
doi: 10.1021/ja0643319 |
| [18] |
Kumar, V.; Kalitaa, A.; Mondal, B. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 16264.
doi: 10.1039/c3dt51642c |
| [19] |
Gharami, S.; Aich, K.; Ghosh, P.; Patra, L.; Murmu, N.; Mondal, T. K. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 187.
doi: 10.1039/C9DT04245H |
| [20] |
Huo, F. J.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Ning, P.; Meng, X. M.; Yin, C. X. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2798.
doi: 10.1039/C7TB00299H |
| [21] |
Chen, W.; Luo, N.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, L.-J.; Wang, F. L.; Jiang, J.-H. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 8664.
doi: 10.1039/D1CC03259C |
| [22] |
Guo, Z.; Park, S.; Yoon, J.; Shin, I. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 16.
|
| [23] |
Liu, J. S.; Xiong, Y. H.; Huang, Y. N.; Zhu, X. Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yan, J. W. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 18453.
doi: 10.1039/D1NJ02472H |
| [24] |
Wang, K.; Zhao, C.-X.; Leng, T.-H.; Wang, C.-Y.; Lu, Y.-X.; Zhu, W.-H. Dyes Pigm. 2018, 151, 194.
doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2017.12.039 |
| [25] |
Zanalettia, R.; Freccero, M. Chem. Commun. 2002, 17, 1908.
|
| [26] |
Zhang, M.-Z.; Han, H.-H.; Zhang, S.-Z.; Wang, C.-Y.; Lu, Y.-X.; Zhu, W.-H. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8780.
doi: 10.1039/C7TB02323E |
| [1] | 李焕清, 陈兆华, 陈祖佳, 邱琪雯, 张又才, 陈思鸿, 汪朝阳. 基于有机小分子的汞离子荧光探针研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(9): 3067-3077. |
| [2] | 刘甜甜, 张鸿鹏, 焦晓梦, 白银娟. 多信号同时检测生物硫醇荧光探针的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(6): 2081-2095. |
| [3] | 曲衍杰, 李亚军, 鲍红丽. 反应型氟离子探针的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(3): 809-825. |
| [4] | 陈志华, 胡艳, 马丽丽, 张子怡, 刘传祥. 基于氢化吡啶辅助氨基氧化策略的次氯酸根荧光探针的设计、合成及其性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(2): 718-724. |
| [5] | 马延慧, 武宇乾, 王晓旭, 高贵, 周欣. 基于1,3-二氯-7-羟基-9,9-二甲基-2(9H)-吖啶酮(DDAO)的近红外荧光探针研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(1): 94-111. |
| [6] | 卢辉旭, 唐永和, 周红梅, 林伟英. 一种荧光增强型甲醛荧光探针的合成及其性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(4): 1163-1169. |
| [7] | 陈思鸿, 陈淇, 罗时荷, 曹西颖, 杨国贤, 曾晓晴, 汪朝阳. 基于三苯胺的荧光探针设计、合成与应用研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(3): 919-933. |
| [8] | 陈曦, 高晨, 付超, 朱婷婷, 刘振江, 刘传祥. 基于氟引发串联释放的氟硼二吡咯类荧光探针的合成及其识别性能[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(1): 303-309. |
| [9] | 张继东, 詹妍, 李胡月雯, 齐怡, 王瑞鹏, 孟莉. 硒化合物荧光传感器研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(7): 1847-1859. |
| [10] | 曹西颖, 罗时荷, 杨崇岭, 肖颖, 李晓燕, 张钧如, 汪朝阳. 有机聚合物荧光传感器的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(12): 4046-4059. |
| [11] | 赵小龙, 李娜, 刘发玉, 高超, 丰久彪, 刘乐平, 关晓琳, 燕娜. 高选择性检测ONOO-的水溶性反应型氟硼二吡咯(BODIPY)荧光探针的合成与应用[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(12): 4339-4343. |
| [12] | 郑天骄, 陈炫颖, 朱亮亮, 王道累, 邹祺, 曾涛, 陈文博. 一种新型二氰基乙烯修饰的二呋喃环戊烯光开关:荧光性质、传感性能和生物应用[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(9): 2492-2498. |
| [13] | 常永新, 李白, 郭淼, 蔡永红, 徐括喜. 一种新型连续检测镉离子和焦磷酸阴离子的逻辑门荧光传感器及其细胞成像研究[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(9): 2485-2491. |
| [14] | 陈思鸿, 庞楚明, 陈孝云, 严智浩, 黄诗敏, 李香弟, 钟雅婷, 汪朝阳. 多功能荧光探针的设计、合成与应用研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(7): 1846-1857. |
| [15] | 石岩, 于有伟, 薛林, 王延风. 以苝二酰亚胺为发色团的荧光探针的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(12): 3414-3437. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||