有机化学 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1777-1785.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202401021 上一篇 下一篇
综述与进展
郭静, 李诗瑶, 姚欢*( ), 杨留攀*(
), 杨留攀*( ), 王力立*(
), 王力立*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-16
修回日期:2024-02-21
发布日期:2024-03-12
基金资助:
Jing Guo, Shiyao Li, Huan Yao*( ), Liupan Yang*(
), Liupan Yang*( ), Lili Wang*(
), Lili Wang*( )
)
Received:2024-01-16
Revised:2024-02-21
Published:2024-03-12
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:文章分享

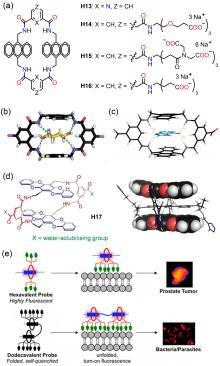
分子识别在自然界中广泛存在, 是许多生物过程以及超分子化学的核心. 水的极性环境会显著削弱特定的非共价相互作用(如氢键), 因此利用人工大环主体在水相中进行分子识别具有挑战性. 四内酰胺大环是一类疏水空腔内部具有极性结合位点的人工大环主体, 通过模仿生物受体的识别特性实现了水中亲水分子的识别, 在疏水效应以及氢键的协同作用下可以实现药物分子、糖类、染料、有机污染物及疾病标志物等物质的选择性识别. 总结了近三十年来四内酰胺大环在分子识别与应用方面的研究进展, 尤其是在水相中的分子识别与应用研究, 希望为今后四内酰胺大环的发展提供参考.
郭静, 李诗瑶, 姚欢, 杨留攀, 王力立. 四内酰胺大环的分子识别与应用研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(6): 1777-1785.
Jing Guo, Shiyao Li, Huan Yao, Liupan Yang, Lili Wang. Research Progress of Tetralactam Macrocycle-Based Molecular Recognition and Applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(6): 1777-1785.
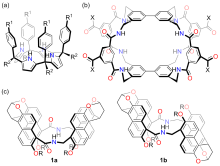
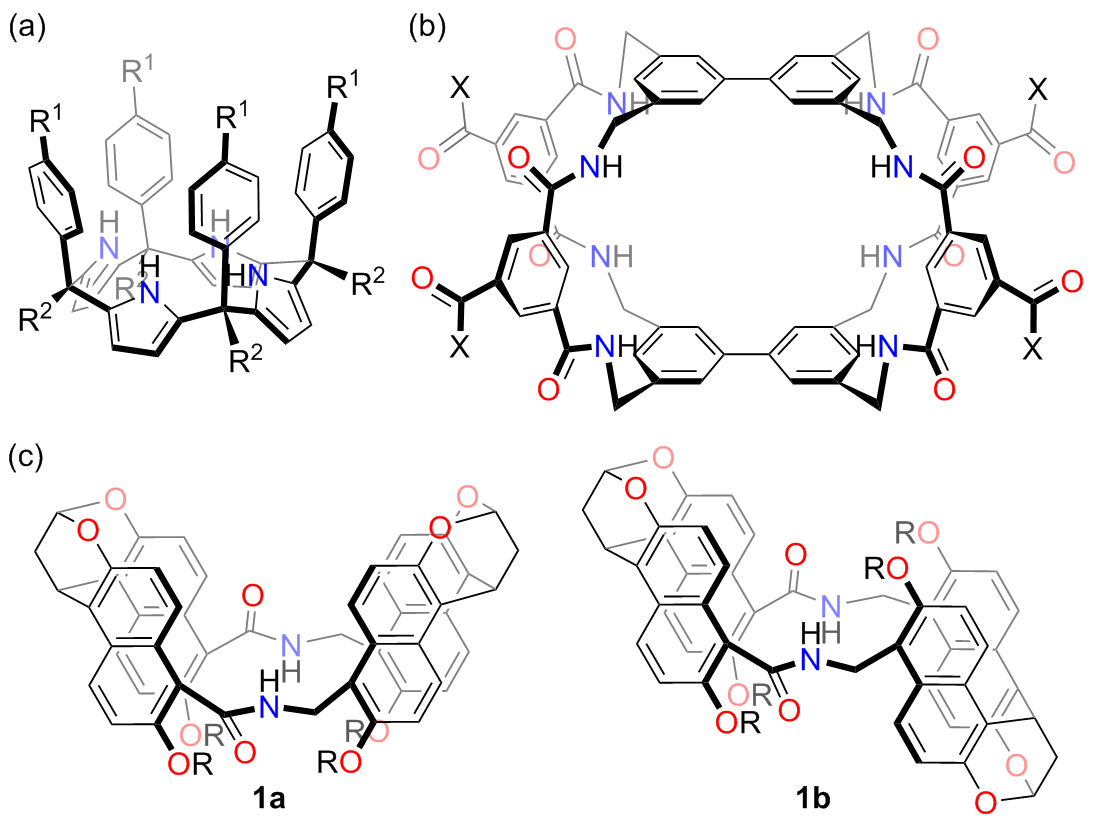
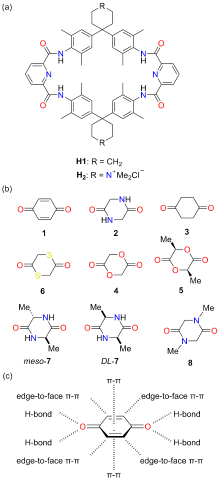
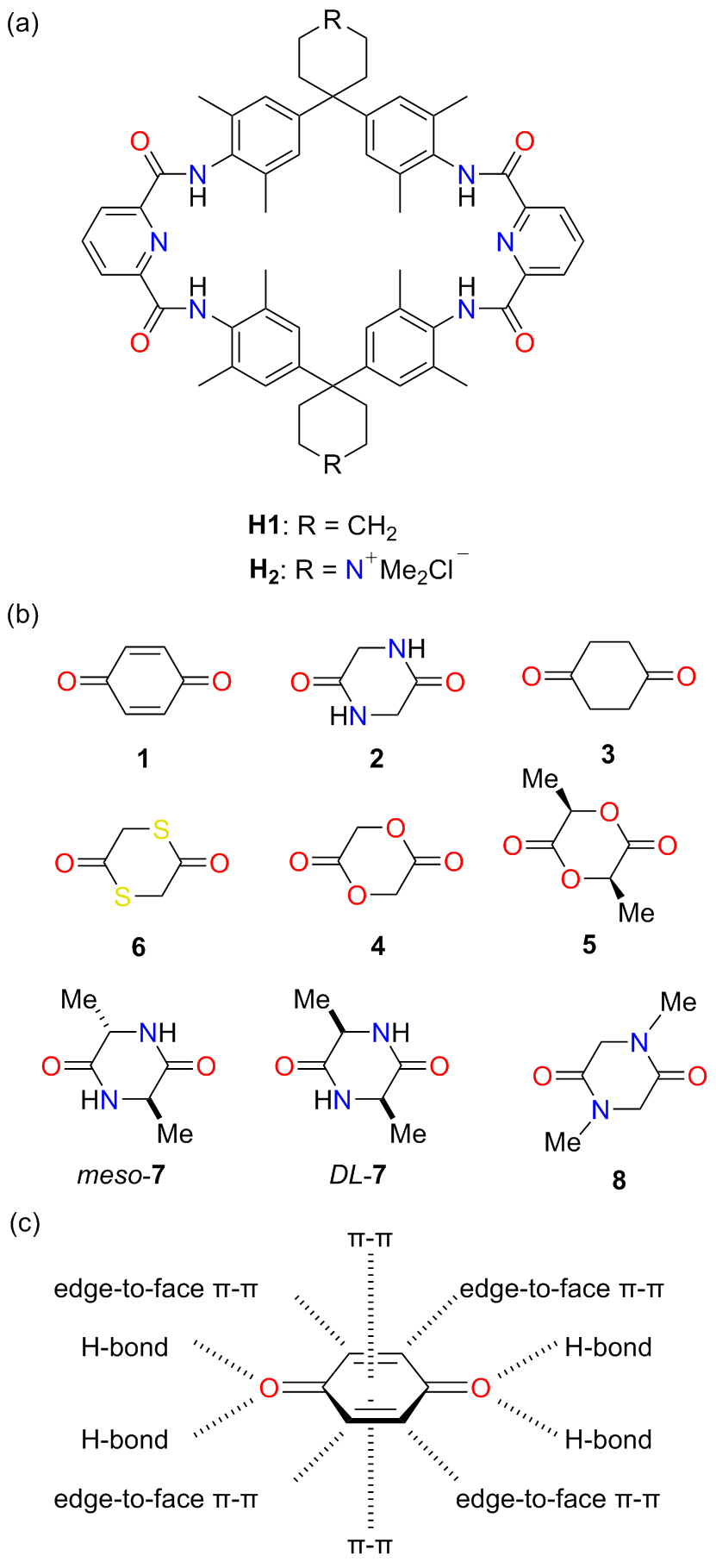




| [1] |
Wagner, B. D. Host-Guest Chemistry-Supramolecular Inclusion in Solution, De Gruyter, 2020.
|
| [2] |
Li, D.-H.; Smith, B. D. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1086.
|
| [3] |
Liu, W.; Samanta, S. K.; Smith, B. D.; Isaacs, L. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2391.
|
| [4] |
Luo, Q. H. Macrocyclic Chemistry-Host-Guest Compound and Supramolecular, Science Press, Beijing, 2009. (in Chinese)
|
|
(罗勤慧, 大环化学- -主-客体化合物和超分子, 科学出版社, 北京, 2009.)
|
|
| [5] |
Yazaki, K.; Sei, Y.; Akita, M.; Yoshizawa, M. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5179.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms6179 pmid: 25322998 |
| [6] |
Biedermann, F.; Schneider, H.-J. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5216.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00583 pmid: 27136957 |
| [7] |
Persch, E.; Dumele, O.; Diederich, F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3290.
|
| [8] |
Livnah, O.; Bayer, E. A.; Wilchek, M.; Sussman, J. L. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1993, 90, 5076.
|
| [9] |
Escobar, L.; Ballester, P. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 2445.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00522 pmid: 33472000 |
| [10] |
Yang, L.-P.; Wang, X.; Yao, H.; Jiang, W. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 53, 198.
|
| [11] |
Shen, Z.-Y.; Li, S.-Y.; Yang, L.-P.; Wang, L.-L.; Yao, H. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 44, 1151. (in Chinese)
|
|
(谌泽亚, 李诗瑶, 杨留攀, 王力立, 姚欢, 有机化学, 2024, 44, 1151.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202310017 |
|
| [12] |
Huang, G.; Chen, Z.; Wei, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhong, H.; Tan, M. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 614. (in Chinese)
|
|
(黄国保, 陈志林, 韦贤生, 陈钰, 李秀英, 仲辉, 谭明雄, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 614.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201909029 |
|
| [13] |
Purse, B. W.; Rebek, J. Jr, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2005, 102, 10777.
|
| [14] |
Adriaenssensa, L.; Ballester, P. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3261.
doi: 10.1039/c2cs35461f pmid: 23321897 |
| [15] |
Butterfield, S. M.; Rebek, J., Jr. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15366.
pmid: 17131990 |
| [16] |
Gassensmith, J. J.; Arunkumar, E.; Barr, L.; Baumes, J. M.; DiVittorio, K. M.; Johnson, J. R.; Noll, B. C.; Smith, B. D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 15054.
doi: 10.1021/ja075567v pmid: 17994746 |
| [17] |
Wang, Y.-F.; Wang, S.-M.; Zhang, X.; Nian, H.; Zheng, L.-S.; Wang, X.; Schreckenbach, G.; Jiang, W.; Yang, L.-P.; Wang, L.-L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202310115.
|
| [18] |
Allen, W. E.; Gale, P. A.; Brown, C. T.; Lynch, V. M.; Sessler, J. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 12471.
|
| [19] |
Escobar, L.; Sun, Q.; Ballester, P. Acc. Chem. Res. 2023, 56, 500.
|
| [20] |
Verdejo, B.; Gil-Ramírez, G.; Ballester, P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3178.
doi: 10.1021/ja900151u pmid: 19216565 |
| [21] |
Hernández-Alonso, D.; Zankowski, S.; Adriaenssens, L.; Ballester, P. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 13, 1022.
|
| [22] |
Peñuelas-Haro, G.; Ballester, P. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 2413.
doi: 10.1039/c8sc05034a pmid: 30931096 |
| [23] |
Xiong, Y.; Li, M.; Xiong, P.; Yang, M.; Qing, G.; Sun, T. Prog. Chem. 2014, 26, 48. (in Chinese)
|
|
(熊雨婷, 李闵闵, 熊鹏, 杨梦, 卿光焱, 孙涛垒, 化学进展, 2014, 26, 48.)
doi: 10.7536/PC130631 |
|
| [24] |
Klein, E.; Crump, M. P.; Davis, A. P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 298.
|
| [25] |
Shorthill, B. J.; Avetta, C. T.; Glass, T. E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12732.
pmid: 15469241 |
| [26] |
Ferrand, Y.; Crump, M. P.; Davis, A. P. Science 2007, 318, 619.
pmid: 17962557 |
| [27] |
Ríos, P.; Mooibroek, T. J.; Carter, T. S.; Williams, C.; Wilson, M. R.; Crump, M. P.; Davis, A. P. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 4056.
|
| [28] |
Davis, A. P. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 2531.
|
| [29] |
Tromans, R. A.; Samanta, S. K.; Chapman, A. M.; Davis, A. P. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 3223.
doi: 10.1039/c9sc05406e pmid: 34122828 |
| [30] |
Huang, G.-B.; Wang, S.-H.; Ke, H.; Yang, L.-P.; Jiang, W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 14550.
|
| [31] |
Wang, L.-L.; Chen, Z.; Liu, W.-E.; Ke, H.; Wang, S.-H.; Jiang, W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8436.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b05021 pmid: 28609613 |
| [32] |
Liu, W.-E.; Chen, Z.; Yang, L.-P.; Au-Yeung, H. Y.; Jiang, W. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 9797.
|
| [33] |
Yang, L. P.; Ke, H.; Yao, H.; Jiang, W. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 21404.
|
| [34] |
Li, S.-Y.; Wang, D.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, L.-L.; Yang, L.-P. Curr. Opin. Green Sustainable Chem. 2023, 40.
|
| [35] |
Yao, H.; Ke, H.; Zhang, X.; Pan, S.-J.; Li, M.; Yang, L.-P.; Schreckenbach, G.; Jiang, W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 13466.
|
| [36] |
Zhao, C.-D.; Yao, H.; Li, S.-Y.; Du, F.; Wang, L.-L.; Yang, L.-P. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 108879.
|
| [37] |
Hunter, C. A. J. Chem. Soc.,Chem. Commun. 1991, 749.
|
| [38] |
Johnston, A. G.; Leigh, D. A.; Pritchard, R. J.; Deegan, M. D. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 1995, 34, 1209.
|
| [39] |
Johnston, A. G.; Leigh, D. A.; Murphy, A.; Smart, J. P.; Deegan, M, D., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 10662.
|
| [40] |
Biscarini, F.; Cavallini, M.; Leigh, D. A.; León, S.; Teat, S. J.; Wong, J. K. Y.; Zerbetto, F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 225.
pmid: 11782174 |
| [41] |
Zhai, C.; Xu, C.; Cui, Y.; Wojtas, L.; Liu, W. Chem.-Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202300524.
|
| [42] |
Liu, W.; Oliver, A. G.; Smith, B. D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 6810.
|
| [43] |
Wang, L.-L.; Tu, Y.-K.; Yao, H.; Jiang, W. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1460.
|
| [44] |
Wang, L.-L.; Tu, Y.-K.; Valkonen, A.; Rissanen, K.; Jiang, W. Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 892.
|
| [45] |
Ke, C.; Destecroix, H.; Crump, M. P.; Davis, A. P. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 718.
|
| [46] |
Peck, E. M.; Liu, W.; Spence, G. T.; Shaw, S. K.; Davis, A. P.; Destecroix, H.; Smith, B. D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 8668.
|
| [47] |
Allott, C.; Adams, H.; Bernad, P. L. Jr; Hunter, C. A.; Rotgerc, C.; Thomasa, J. A. Chem. Commun. 1998, 2449.
|
| [48] |
Destecroix, H.; Renney, C. M.; Mooibroek, T. J.; Carter, T. S.; Stewart, P. F. N.; Crump, M. P.; Davis, A. P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2057.
|
| [49] |
Fernandes, A.; Viterisi, A.; Aucagne, V.; Leigh, D. A.; Papot, S. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 2083.
|
| [50] |
Dong, J.; Davis, A. P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 60, 8035.
|
| [51] |
Fiona, H. A.; Carver, J.; Hunter, C. A.; Osborne, N. J. Chem. Commun. 1996, 2529.
|
| [52] |
Fernandes, A.; Viterisi, A.; Coutrot, F.; Potok, S.; Leigh, D. A.; Aucagne, V.; Papot, S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6443.
|
| [53] |
Dempsey, J. M.; Zhai, C.; McGarraugh, H. H.; Schreiber, C. L.; Stoffel, S. E.; Johnson, A.; Smith, B. D. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 12793.
|
| [54] |
Zhang, H.; Wang, L.-L.; Pang, X.-Y.; Yang, L.-P.; Jiang, W. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 13724.
|
| [55] |
Li, S.-Y.; Yao, H.; Hu, H.; Chen, W.-J.; Yang, L.-P.; Wang, L.-L. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 7204.
|
| [56] |
Yao, H.; Li, S.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Pang, X.-Y.; Lu, J.-L.; Chen, C.; Jiang, W.; Yang, L.-P.; Wang, L.-L. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 5411.
|
| [57] |
Yao, H.; Qin, J.; Wang, Y.-F.; Wang, S.-M.; Yi, L.-H.; Li, S.-Y.; Du, F.; Yang, L.-P.; Wang, L.-L. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 109154.
|
| [58] |
Mandal, P. K.; Kauffmann, B.; Destecroix, H.; Ferrand, Y.; Davis, A. P.; Huc, I. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 9355.
|
| [59] |
Van Eker, D.; Samanta, S. K.; Davis, A. P. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 9268.
|
| [60] |
Liu, W.; Johnson, A.; Smith, B. D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 3361.
|
| [61] |
Federica, B.; Patrick, S.; Soumen, S.; Tiddo, M.; Thomas, H.-J.; Kejia, S.; Bradley, S.; Davis, A. P.; Balduzzi, F.; Stewart, P.; Samanta, S. K.; Mooibroek, T. J.; Hoeg-Jensen, T.; Shi, K.; Smith, B. D.; Davis, A. P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202314373.
|
| [62] |
Roland, F. M.; Peck, E. M.; Rice, D. R.; Smith, B. D. Bioconjugate Chem. 2017, 28, 1093.
|
| [63] |
Liu, W.; Gómez-Durán, C. F. A.; Smith, B. D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6390.
|
| [64] |
Shaw, S. K.; Liu, W.; Gómez Durán, C. F. A.; Schreiber, C. L.; Betancourt Mendiola, M. L.; Zhai, C.; Roland, F. M.; Padanilam, S. J.; Smith, B. D. Chem.-Eur. J. 2018, 24, 13821.
|
| [65] |
Dharmarwardana, M.; Dempsey, J. M.; Padilla-Coley, S.; Jarvis, T. S.; Shi, K.; Atkinson, K. M.; Smith, B. D. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 13518.
|
| [1] | 于蕾, 盛康, 李亭, 唐从辉. 多相铁催化环状醚C(sp3)—H键活化的芳基烯烃氧烷基化[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(6): 1978-1986. |
| [2] | 张晓, 胡密霞, 杜艳青, 梁凤英, 张笑迎, 额尔敦. 阴离子-π相互作用研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(4): 1181-1196. |
| [3] | 谌泽亚, 李诗瑶, 杨留攀, 王力立, 姚欢. 基于指示剂置换法的大环荧光传感平台的构建及应用研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(4): 1151-1159. |
| [4] | 付雅彤, 孙超凡, 张丹, 金成国, 陆居有. 巢式-碳硼烷硼氢键官能化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(2): 438-447. |
| [5] | 徐忠荣, 万结平, 刘云云. 基于热、光以及电化学过程的无过渡金属碳-氢键硫氰化和硒氰化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(7): 2425-2446. |
| [6] | 贾海瑞, 邱早早. 过渡金属催化硼-氢键活化合成含硼-杂原子键邻碳硼烷衍生物的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(3): 1045-1068. |
| [7] | 李芬, 刘传志, 户志远, 罗盼盼, 崔蓉铮, 黄彦珂, 刘新明, 刘澜涛, 吴玮. 分子间卤键和氢键控制的网络结构的组装[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(2): 705-711. |
| [8] | 鲁会名, 马拉毛草, 马恒昌. 超分子聚集诱导发光材料的研究进展及展望[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(12): 4075-4105. |
| [9] | 孙美娇, 谭晶, 谭玉, 彭进松, 陈春霞. 钯催化3-(2-氨基嘧啶-4-基)吲哚2位C—H键芳基化反应的研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(11): 3945-3959. |
| [10] | 谢吴成, 陈浒, 黎韵越, 林洁玲, 陈婉雯, 石君君. 导向碳氢键活化与不饱和分子的电氧化环化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(5): 1286-1306. |
| [11] | 刘文启, 沈振陆, 徐森苗. 三苯基砷/铱催化的非活化一级碳氢键的双硼化反应合成1,1-偕二硼烷[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(4): 1101-1110. |
| [12] | 李可欣, 杨庆远, 张鹏鹏, 张武元. 过氧化氢原位生成驱动过氧合酶催化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(3): 732-741. |
| [13] | 乐柏佟, 吴新鑫, 朱晨. 烯基自由基参与的分子内氢原子转移反应的新进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(2): 458-470. |
| [14] | 吴豪志, 罗田, 姜建文, 万结平. 碘化钾催化无保护8-氨基喹啉的选择性C(5)-芳基硫醚化和C(5),C(7)-双芳基硫醚化及吲哚C(2),C(3)-双芳基硫醚化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(11): 3721-3729. |
| [15] | 朱登, 陈志敏. 手性路易斯碱/布朗斯特酸协同催化策略在有机硫化物不对称合成中的应用[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(10): 3015-3032. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||