有机化学 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 732-741.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202108052 上一篇 下一篇
综述与进展
李可欣a, 杨庆远a,*( ), 张鹏鹏b, 张武元b,*(
), 张鹏鹏b, 张武元b,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-08-28
修回日期:2021-09-30
发布日期:2021-10-21
通讯作者:
杨庆远, 张武元
基金资助:
Kexin Lia, Qingyuan Yanga( ), Pengpeng Zhangb, Wuyuan Zhangb(
), Pengpeng Zhangb, Wuyuan Zhangb( )
)
Received:2021-08-28
Revised:2021-09-30
Published:2021-10-21
Contact:
Qingyuan Yang, Wuyuan Zhang
Supported by:文章分享
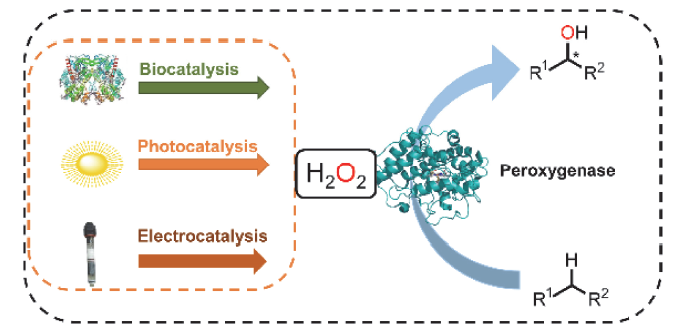
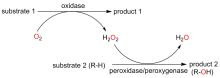
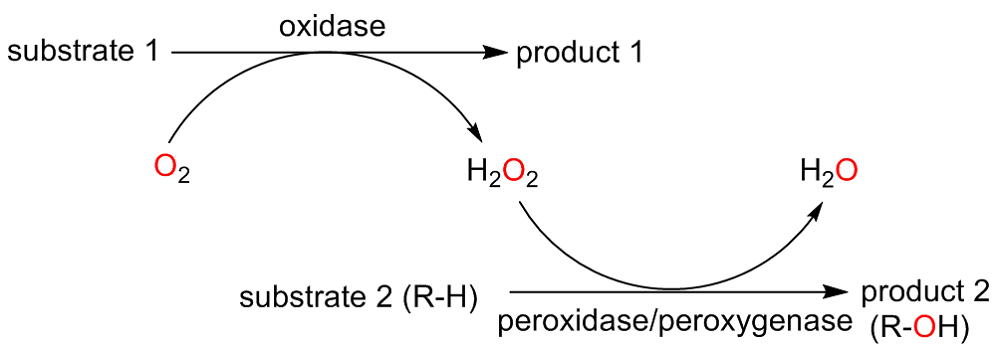
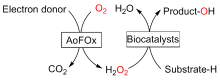
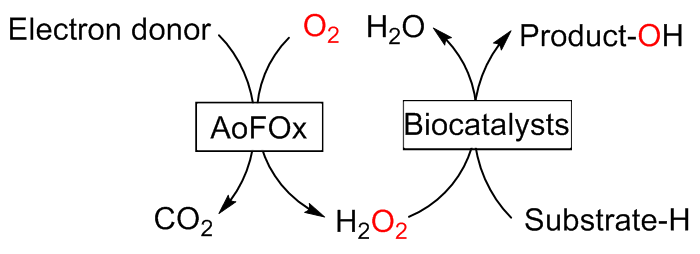
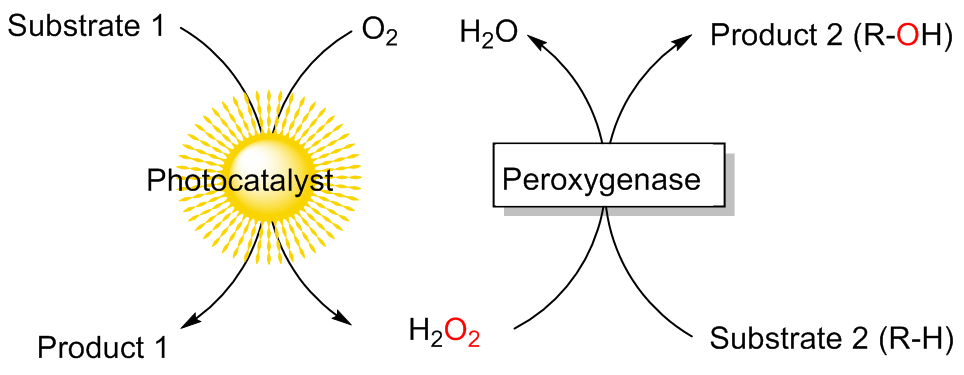
C—H键的选择性催化氧官能团化反应是有机化学中非常具有挑战的一类反应. 与贵金属络合物催化剂相比, 生物酶在选择性和活性等方面表现出一定优势. 其中, 过氧合酶(peroxygenase)作为近年来研究热点, 能够直接利用过氧化氢(H2O2)作为共底物催化C—H键的氧官能团化反应. 过氧合酶结合了P450单加氧酶的催化多功能性且无须依赖辅酶及其再生体系, 因此在有机合成中引起越来越多的重视. 但是, 过氧合酶在实际应用中存在一个瓶颈: 即过氧合酶对其催化所必须的H2O2浓度敏感, 当反应体系中H2O2浓度过高时, 会引起过氧合酶中的亚铁血红素氧化分解, 从而导致酶失活. 为突破该瓶颈, 调控反应体系中H2O2的浓度对于高效应用过氧合酶来说格外重要. 概括了近年来多种原位生成H2O2驱动过氧合酶催化的方法. 从酶催化、光催化、电催化原位生成H2O2角度出发, 全面分析了近年来开发的高原子经济性H2O2原位生成技术驱动过氧合酶催化体系的优缺点, 为促进该酶在有机合成中的应用提供参考.
李可欣, 杨庆远, 张鹏鹏, 张武元. 过氧化氢原位生成驱动过氧合酶催化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(3): 732-741.
Kexin Li, Qingyuan Yang, Pengpeng Zhang, Wuyuan Zhang. Research Progress of Peroxygenase-Catalyzed Reactions Driven by in-situ Generation of H2O2[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(3): 732-741.
| 年份 | 原位生成H2O2方式 | 催化剂/电极 | 酶 | 底物 | 产物 | eea/% | TON/TTNb | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 葡萄糖氧化酶 | CPO (氯过氧化物 Chloroperoxidase) | 硫代苯甲醚 | (R)-苯甲基亚砜 | 99 | 250000 | [ | |
| 2002 | D-氨基酸 | CiP (来自灰盖鬼伞菌的过氧合酶, peroxidase from Coprinus cinereus) | (三种)芳香甲基 硫化物 | (三种)芳甲基亚砜 | 97 | >500 | [ | |
| 2007 | 甲醇氧化酶 | CiP | 硫代苯甲醚 | (R)-苯甲基亚砜 | 75左右 | >700 | [ | |
| 2014 | 甲酸脱氢酶、 NADH氧化酶 | HRP (辣根过氧合酶, peroxidase from horseradish) | 乙苯 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 | — | 6785 | [ | |
| 2015 | 酶催化 | 甲醇氧化酶、 甲醛歧化酶、 NADH氧化酶、 甲酸脱氢酶、 3-羟基苯甲酸- 6-羟化酶 | AaeUPO (真菌过加氧酶, The unspecific peroxygenase from Agrocybe aegerita) | 乙苯 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 | >99 | 294700 | [ |
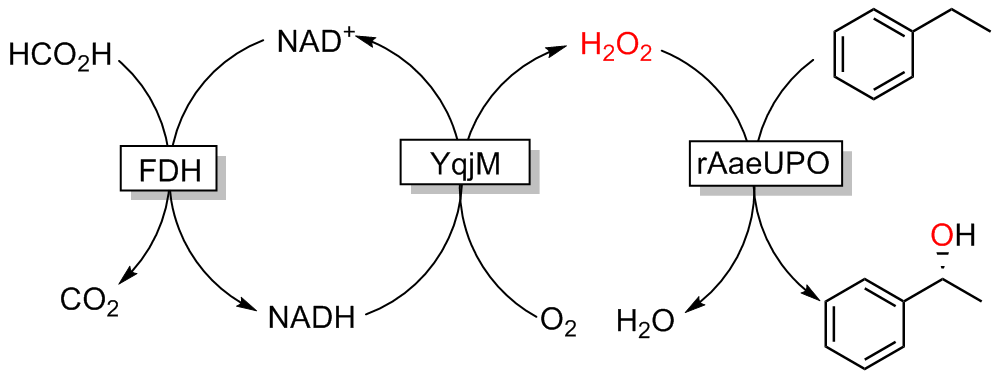
| 2018 | NADH氧化酶、 YqjM | rAaeUPO (重组真菌过加氧酶, recombinant peroxygenase from Agrocybe aegerita) | 乙苯 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 | >96 | 390000 | [ | |
| 2020 | 甲酸氧化酶 | rAaeUPO | 乙苯 环己烷 顺式β-甲基苯乙烯 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 环己醇 (1R,2S)-顺-β- 甲基苯乙烯 | 97.5 | 49000 | [ | |
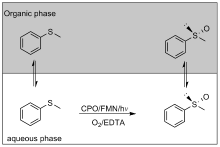
| 2009 | 黄素单核苷酸 | CPO | 硫代苯甲醚 | (R)-苯甲基亚砜 | <99 | 22000 | [ | |
| 2013 | 黄素单核苷酸 | CPO | 硫代苯甲醚 | (R)-苯甲基亚砜 | >96 | 12600 | [ | |
| 2017 | Au-TiO2 | rAaeUPO | 乙苯 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 | >98 | >71000 | [ | |
| 2019 | 光催化 | 石墨相氮化碳g-C3N4 | rAaeUPO | 乙苯 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 | >97.8 | 60000 | [ |
| 2019 | 酚藏红花、 亚甲基蓝、 黄素单核苷酸 | rAaeUPO | 乙苯 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 | >95 | 100000 | [ | |
| 2020 | 水溶性蒽醌 磺酸钠 | CiVCPO; rAaeUPO | 百里香酚 乙苯 环己烷 苯乙烯 4-戊烯酸 | 卤化百里香酚 (R)-1-苯乙醇 环己醇, 环己酮 1-苯基-2-溴乙醇 氧化苯乙烯 4-溴甲基环戊内酯 | 34 | 318000; 177000 | [ | |
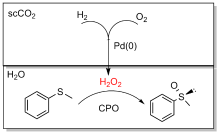
| 2004 | 碳基电极 | CPO | 硫代苯甲醚 | (R)-苯甲基亚砜 | >98.5 | 95000 | [ | |
| 2006 | 碳基电极 | CPO | 三种底物 | 三种产物 | 93、99 | 58900 64400 7000 | [ | |
| 2007 | 碳基电极 | CPO | 硫代苯甲醚 | (R)-苯甲基亚砜 | 98.5 | 145000 | [ | |
| 2011 | 电催化 | GDE电极 | CPO | 单氯二甲醚 硫代苯甲醚 吲哚 | 二氯二甲醚 (R)-苯甲基亚砜 羟吲哚 | — | 203100 83600 39000 | [ |
| 2014 | GDE电极 | CPO | 一氯二甲酮 | 二氯二甲酮 | — | 1150000 | [ | |
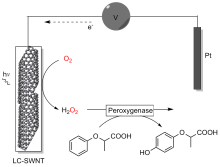
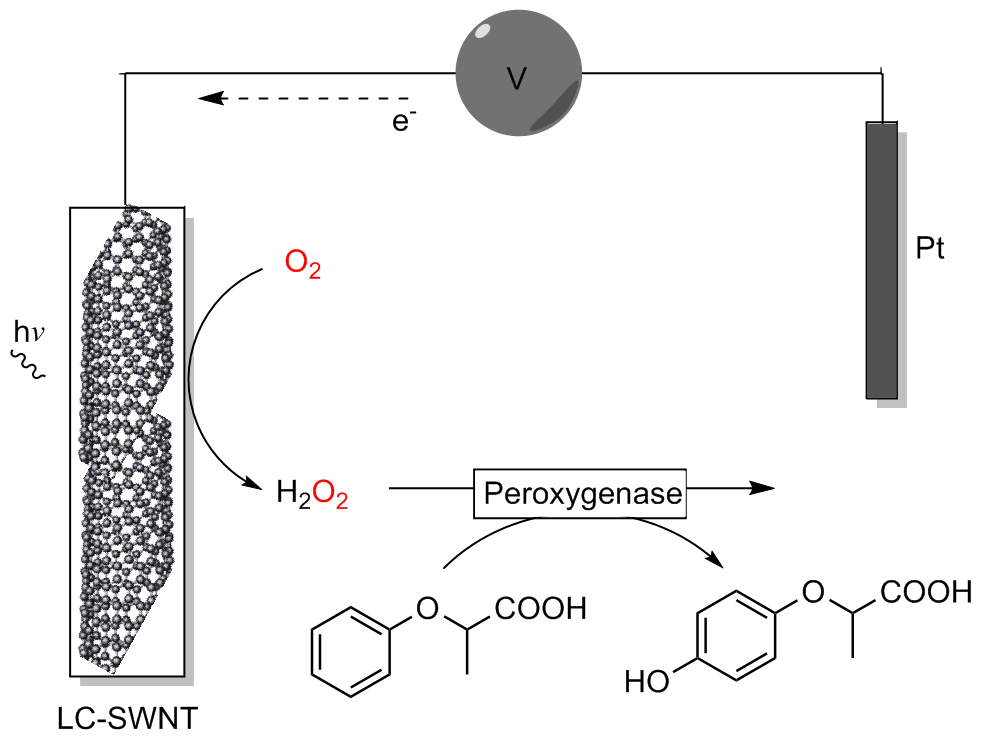
| 2017 | 黄素-SWNT 电极 | AaeUPO | 乙苯 2-苯氧基丙酸 吲哚 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 | 95% | 123900±7290 5900±210 4900±340 | [ | |
| 2019 | 氧化碳纳米管 | CiVCPO | 4-戊烯酸 | 溴内酯 | — | — | [ |
| 年份 | 原位生成H2O2方式 | 催化剂/电极 | 酶 | 底物 | 产物 | eea/% | TON/TTNb | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 葡萄糖氧化酶 | CPO (氯过氧化物 Chloroperoxidase) | 硫代苯甲醚 | (R)-苯甲基亚砜 | 99 | 250000 | [ | |
| 2002 | D-氨基酸 | CiP (来自灰盖鬼伞菌的过氧合酶, peroxidase from Coprinus cinereus) | (三种)芳香甲基 硫化物 | (三种)芳甲基亚砜 | 97 | >500 | [ | |
| 2007 | 甲醇氧化酶 | CiP | 硫代苯甲醚 | (R)-苯甲基亚砜 | 75左右 | >700 | [ | |
| 2014 | 甲酸脱氢酶、 NADH氧化酶 | HRP (辣根过氧合酶, peroxidase from horseradish) | 乙苯 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 | — | 6785 | [ | |
| 2015 | 酶催化 | 甲醇氧化酶、 甲醛歧化酶、 NADH氧化酶、 甲酸脱氢酶、 3-羟基苯甲酸- 6-羟化酶 | AaeUPO (真菌过加氧酶, The unspecific peroxygenase from Agrocybe aegerita) | 乙苯 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 | >99 | 294700 | [ |
| 2018 | NADH氧化酶、 YqjM | rAaeUPO (重组真菌过加氧酶, recombinant peroxygenase from Agrocybe aegerita) | 乙苯 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 | >96 | 390000 | [ | |
| 2020 | 甲酸氧化酶 | rAaeUPO | 乙苯 环己烷 顺式β-甲基苯乙烯 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 环己醇 (1R,2S)-顺-β- 甲基苯乙烯 | 97.5 | 49000 | [ | |
| 2009 | 黄素单核苷酸 | CPO | 硫代苯甲醚 | (R)-苯甲基亚砜 | <99 | 22000 | [ | |
| 2013 | 黄素单核苷酸 | CPO | 硫代苯甲醚 | (R)-苯甲基亚砜 | >96 | 12600 | [ | |
| 2017 | Au-TiO2 | rAaeUPO | 乙苯 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 | >98 | >71000 | [ | |
| 2019 | 光催化 | 石墨相氮化碳g-C3N4 | rAaeUPO | 乙苯 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 | >97.8 | 60000 | [ |
| 2019 | 酚藏红花、 亚甲基蓝、 黄素单核苷酸 | rAaeUPO | 乙苯 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 | >95 | 100000 | [ | |
| 2020 | 水溶性蒽醌 磺酸钠 | CiVCPO; rAaeUPO | 百里香酚 乙苯 环己烷 苯乙烯 4-戊烯酸 | 卤化百里香酚 (R)-1-苯乙醇 环己醇, 环己酮 1-苯基-2-溴乙醇 氧化苯乙烯 4-溴甲基环戊内酯 | 34 | 318000; 177000 | [ | |
| 2004 | 碳基电极 | CPO | 硫代苯甲醚 | (R)-苯甲基亚砜 | >98.5 | 95000 | [ | |
| 2006 | 碳基电极 | CPO | 三种底物 | 三种产物 | 93、99 | 58900 64400 7000 | [ | |
| 2007 | 碳基电极 | CPO | 硫代苯甲醚 | (R)-苯甲基亚砜 | 98.5 | 145000 | [ | |
| 2011 | 电催化 | GDE电极 | CPO | 单氯二甲醚 硫代苯甲醚 吲哚 | 二氯二甲醚 (R)-苯甲基亚砜 羟吲哚 | — | 203100 83600 39000 | [ |
| 2014 | GDE电极 | CPO | 一氯二甲酮 | 二氯二甲酮 | — | 1150000 | [ | |
| 2017 | 黄素-SWNT 电极 | AaeUPO | 乙苯 2-苯氧基丙酸 吲哚 | (R)-1-苯乙醇 | 95% | 123900±7290 5900±210 4900±340 | [ | |
| 2019 | 氧化碳纳米管 | CiVCPO | 4-戊烯酸 | 溴内酯 | — | — | [ |






| [1] |
Dong, J.-J.; Fernández-Fueyo, E.; Hollmann, F.; Paul, C. E.; Pasic, M.; Schmidt, S.; Wang, Y.-H.; Younes, S.; Zhang, W.-Y. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9238.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201800343 |
| [2] |
Zeng, Z.-G.; Sang, X.-K.; Yuan, B.; Wu, M.-H.; Zhang, W.-Y. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 41, 959. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202009007 |
|
(曾志刚, 桑贤轲, 袁波, 吴鸣虎, 张武元, 有机化学, 2021, 41, 959.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202009007 |
|
| [3] |
Bormann, S.; Baraibar, A. G.; Ni, Y.; Holtmann, D.; Hollmann, F. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 2038.
doi: 10.1039/C4CY01477D |
| [4] |
Ullrich, R.; Nüske, J.; Scheibner, K.; Spantzel, J.; Hofrichter, M. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 4575.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.8.4575-4581.2004 |
| [5] |
Hofrichter, M.; Ullrich, R. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 71, 276.
pmid: 16628447 |
| [6] |
Zhang, W.-Y.; Hollmann, F. Synthesis of Vinyl Polymers via Enzymatic Oxidative Polymerisation, Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd, Singapore, 2019, p. 343.
|
| [7] |
Peter, S.; Kinne, M.; Wang, X.-S.; Ullrich, R.; Kayser, G.; Groves, J. T.; Hofrichter, M. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 3667.
doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08285.x |
| [8] |
Lucas, F.; Babot, E. D.; Cañellas, M.; del Río, J. C.; Kalum, L.; Ullrich, R.; Hofrichter, M.; Guallar, V.; Martínez, A. T.; Gutiérrez, A. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 288.
doi: 10.1039/C5CY00427F |
| [9] |
Kinne, M.; Ullrich, R.; Hammel, K. E.; Scheibner, K.; Hofrichter, M. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 5950.
doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.07.152 |
| [10] |
de Santons, P. G.; Cañellas, M.; Tieves, F.; Younes, S. H. H.; Molina-Espeja, P.; Hofrichter, M.; Hollmann, F.; Guallar, V.; Alcalde, M. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 4789.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b01004 |
| [11] |
Molina-Espeja, P.; Cañellas, M.; Plou, F. J.; Hofrichter, M.; Lucas, F.; Guallar, V.; Alcalde, M. ChemBioChem 2016, 17, 341.
doi: 10.1002/cbic.201500493 pmid: 26677801 |
| [12] |
Thiel, D.; Doknić, D.; Deska, J. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5278.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms6278 |
| [13] |
Valderrama, B.; Ayala, M.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R. Chem. Biol. 2002, 9, 555.
doi: 10.1016/S1074-5521(02)00149-7 |
| [14] |
van de Velde, F.; Lourenco, N. D.; Bakker, M.; van Rantwijk, F.; Sheldon, R. A. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 69, 286.
pmid: 10861408 |
| [15] |
Bakker, M.; van de Velde, F.; van Rantwijk, F.; Sheldon, R. A. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 70, 342.
pmid: 10992238 |
| [16] |
Okrasa, K.; Guibé-Jampel, E.; Therisod, M. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 2000, 7, 1077.
|
| [17] |
Ribitsch, D.; Karl, W.; Wehrschütz-Sigl, E.; Tutz, S.; Remler, P.; Weber, H. J.; Gruber, K.; Stehr, R.; Bessler, C.; Hoven, N.; Sauter, K.; Schwab, H. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 81, 875.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-008-1661-5 pmid: 18787818 |
| [18] |
Okrasa, K.; Falcimaigne, A.; Guibé-Jampel, E.; Therisod, M. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2002, 13, 519.
doi: 10.1016/S0957-4166(02)00142-8 |
| [19] |
Pezzotti, F.; Okrasa, K.; Therisod, M. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2005, 16, 2681.
doi: 10.1016/j.tetasy.2005.07.004 |
| [20] |
Pezzotti, F.; Therisod, M. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2007, 18, 701.
doi: 10.1016/j.tetasy.2007.03.010 |
| [21] |
Rocha-Martin, J.; Velasco-Lozano, S.; Guisán, J. M.; López- Gallego, F. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 303.
doi: 10.1039/C3GC41456F |
| [22] |
Jung, D.; Streb, C.; Hartmann, M. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 113, 523.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2007.12.009 |
| [23] |
Ni, Y.; Fernández-Fueyo, E.; Baraibar, A. G.; Ullrich, R.; Hofrichter, M.; Yanase, H.; Alcalde, M.; van Berkel, W. J. H.; Hollmann, F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 55, 798.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201507881 |
| [24] |
Chang, A.; Scheer, M.; Grote, A.; Schomburg, I.; Schomburg, D. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D588.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn820 |
| [25] |
Pesic, M; Willot, S. J. P.; Fernández-Fueyo, E.; Tieves, F.; Alcalde, M.; Hollamnn, F. Z. Naturforsch., C: J. Biosci. 2018, 74, 100.
|
| [26] |
Tieves, F.; Willot, S. J. P.; van Schie, M. M. C. H.; Rauch, M. C. R.; Younes, S. H. H.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Dong, J.-J.; de Santos, P. G.; Robbins, J. M.; Bommarius, B.; Alcalde, M.; Bommarius, A. S.; Hollmann, F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7873.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.23 |
| [27] |
Willot, S. J. P.; Hoang, M. D.; Paul, C. E.; Alcalde, M.; Arends, I. W. C. E.; Bommarius, A. S.; Bommarius, B.; Hollmann, F. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 2713.
doi: 10.1002/cctc.v12.10 |
| [28] |
Li, Y.-Y.; Yuan, B.; Sun, Z.-T.; Zhang, W.-Y. Green Synth. Catal. 2021, 2, 267.
|
| [29] |
Perez, D. I.; Grau, M. M.; Arends, I. W. C. E.; Hollmann, F. Chem. Commun. 2009, 41, 6848.
|
| [30] |
Churakova, E.; Kluge, M.; Ullrich, R.; Arends, I.; Hofrichter, M.; Hollmann, F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 10716.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201105308 |
| [31] |
Churakova, E.; Arends, I. W. C. E.; Hollmann, F. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 565.
doi: 10.1002/cctc.201200490 |
| [32] |
Zhang, W.-Y.; Burek, B. O.; Fernández-Fueyo, E.; Alcalde, M.; Bloh, J. Z.; Hollmann, F. Angew. Chem. 2017, 56, 15451.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201708668 |
| [33] |
Zhang, W.-Y.; Fernández-Fueyo, E.; Ni, Y.; van Schie, M.; Gacs, J.; Renirie, R.; Wever, R.; Mutti, F. G.; Rother, D. R.; Alcalde, M.; Hollmann, F. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 55.
doi: 10.1038/s41929-017-0001-5 |
| [34] |
Teranishi, M.; Hoshino, R.; Naya, S.; Tada, H. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 12965.
doi: 10.1002/ange.201606734 |
| [35] |
van Schie, M. M. C. H.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Tieves, F.; Choi, D. S.; Park, C. B.; Burek, B. O.; Bloh, J. Z.; Arends, I. W. C. E.; Paul, C. E.; Alcalde, M.; Hollmann, F. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 7409.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b01341 |
| [36] |
Willot, S. J. P.; Fernández-Fueyo, E.; Tieves, F.; Pesic, M.; Alcalde, M.; Arends, I. W. C. E.; Park, C. B.; Hollmann, F. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 890.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b03752 |
| [37] |
Yuan, B.; Mahor, D.; Fei, Q.; Wever, R.; Alcalde, M.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Hollmann, F. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 8277.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c01958 pmid: 32802571 |
| [38] |
Zhang, W.-Y.; Liu, H.-H.; van Schie, M. M. C. H.; Hagedoorn, P. L.; Alcalde, M.; Denkova, A. G.; Djanashvili, K.; Hollmann, F. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 14195.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c03059 |
| [39] |
Lvtz, S.; Steckhan, E.; Liese, A. Electrochem. Commun. 2004, 6, 583.
doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2004.04.009 |
| [40] |
Kohlmann, C.; Lvtz, S. Eng. Life Sci. 2006, 6, 170.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1618-2863 |
| [41] |
Lvtz, S.; Vuorilehto, K.; Liese, A. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 98, 525.
doi: 10.1002/bit.v98:3 |
| [42] |
Horst, A. E. M.; Mangold, K. M.; Holtmann, D. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 260.
doi: 10.1002/bit.25698 |
| [43] |
Krieg, T.; Hvttmann, S.; Mangold, K. M.; Schrader, J.; Holtmann, D. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2686.
doi: 10.1039/c1gc15391a |
| [44] |
Holtmann, D.; Krieg, T.; Getrey, L.; Schrader, J. Catal. Commun. 2014, 51, 82.
doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2014.03.033 |
| [45] |
Horst, A. E. W.; Bormann, S.; Meyer, J.; Steinhagen, M.; Ludwig, R.; Drews, A.; Ansorge-Schumacher, M.; Holtmann, D. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2016, 133, S137.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcatb.2016.12.008 |
| [46] |
Choi, D. S.; Ni, Y.; Fernández-Fueyo, E.; Lee, M.; Hollmann, F.; Park, C. B. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 1563.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b03453 |
| [47] |
Kim, H. W.; Ross, M. B.; Kornienko, N.; Zhang, L.; Guo, J.-H.; Yang, P.-D.; McCloskey, B. D. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 282.
doi: 10.1038/s41929-018-0044-2 |
| [48] |
Bormann, S.; van Schie, M. M. C. H.; De Almeida, T. P.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Stöckl, M.; Ulber, R.; Hollmann, F.; Holtmann, D. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 4759.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.v12.21 |
| [49] |
Karmee, S. K.; Roosen, C.; Kohlmann, C.; Lvtz, S.; Greiner, L.; Leitner, W. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1052.
doi: 10.1039/b820606f |
| [50] |
Edwards, J. K.; Freakley, S. J.; Carley, A. F.; Kiely, C. J.; Hutchings, G. J. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 845.
doi: 10.1021/ar400177c |
| [51] |
Freakley, S. J.; Kochius, S.; van Marwijk, J.; Fenner, C.; Lewis, R. J.; Baldenius, K.; Marais, S. S.; Opperman, D. J.; Harrison, S. T. L.; Alcalde, M.; Smit, M. S.; Hutchings, G. J. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07882-8 |
| [52] |
Yoon, J.; Kim, J.; Tieves, F.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Alcalde, M.; Hollmann, F.; Park, C. B. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 5236.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c00188 |
| [1] | 李路瑶, 贺忠文, 张振国, 贾振华, 罗德平. 三芳基碳正离子在有机合成中的应用[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(2): 421-437. |
| [2] | 赵茜帆, 陈永正, 张世明. 碳基非金属催化剂在有机合成领域的应用及机理研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(1): 137-147. |
| [3] | 周然, 袁春梅, 张桃, 毛飘, 刘燚, 孟开妮, 幸惠, 薛伟. 含喹唑啉酮的查尔酮衍生物的设计、合成及生物活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(9): 3196-3209. |
| [4] | 胡慧娟, 闫巧丽, 卢晓刚, 杨启帆, 裴承新, 王红梅, 高润利. 猪胰脂肪酶催化外消旋P-手性α-羟基磷酸酯类化合物的动力学拆分[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(8): 2815-2825. |
| [5] | 徐光利, 许静, 徐海东, 崔香, 舒兴中. 过渡金属催化烯烃和炔烃合成1,3-共轭二烯化合物研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(6): 1899-1933. |
| [6] | 窦谦, 汪太民, 房丽晶, 翟宏斌, 程斌. 光诱导铁催化在有机合成中的应用研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(4): 1386-1415. |
| [7] | 白林盛, 洪鹏, 应安国. 功能化聚丙烯腈纤维促进有机反应的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(4): 1241-1270. |
| [8] | 莫百川, 陈春霞, 彭进松. 木质素及其衍生物负载金属催化剂在有机合成中的应用研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(4): 1215-1240. |
| [9] | 马彪, 章淼淼, 李占宇, 彭进松, 陈春霞. 无过渡金属催化的Suzuki-Type交叉偶联反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(2): 455-470. |
| [10] | 陈泗林, 杨芸辉, 陈超, 王从洋. 过渡金属催化的酮羰基导向C—H键官能化反应进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(1): 1-16. |
| [11] | 高润烨, 左玲玲, 王芳, 李传莹, 蒋华江, 李品华, 王磊. 无外加光催化剂下可见光促进的可控有机反应进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(7): 1883-1903. |
| [12] | 黄卫春, 丁欣宇, 訾由. 乙烯基/芳基鏻盐在有机合成中的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(2): 471-486. |
| [13] | 杨少慧, 宋敬城, 董道青, 杨昊, 周梦宇, 张会淑, 王祖利. N-胺基吡啶盐作为氮自由基前体在可见光诱导碳氮键形成反应中的进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(12): 4099-4110. |
| [14] | 马姣丽, 郭鹏虎, 李静, 廖新成, 程辉成. 含1,3,4-噻二唑和吡唑的酰胺衍生物的合成和抗肿瘤活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(8): 3214-3222. |
| [15] | 张永红, 唐承宗, 刘永红, 刘晨江. 芳基三氮烯作为芳基前体和芳基偶氮前体在有机合成中的应用研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(7): 2587-2600. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||