化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (3): 331-337.DOI: 10.6023/A20100459 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
黄靖1, 王超1, 林敏刚1, 曾钫1,*( ), 吴水珠1,*(
), 吴水珠1,*( )
)
投稿日期:2020-10-06
发布日期:2020-11-17
通讯作者:
曾钫, 吴水珠
作者简介:基金资助:
Jing Huang1, Chao Wang1, Mingang Lin1, Fang Zeng1,*( ), Shuizhu Wu1,*(
), Shuizhu Wu1,*( )
)
Received:2020-10-06
Published:2020-11-17
Contact:
Fang Zeng, Shuizhu Wu
Supported by:文章分享

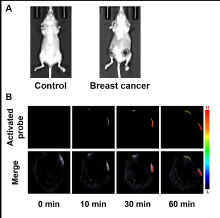
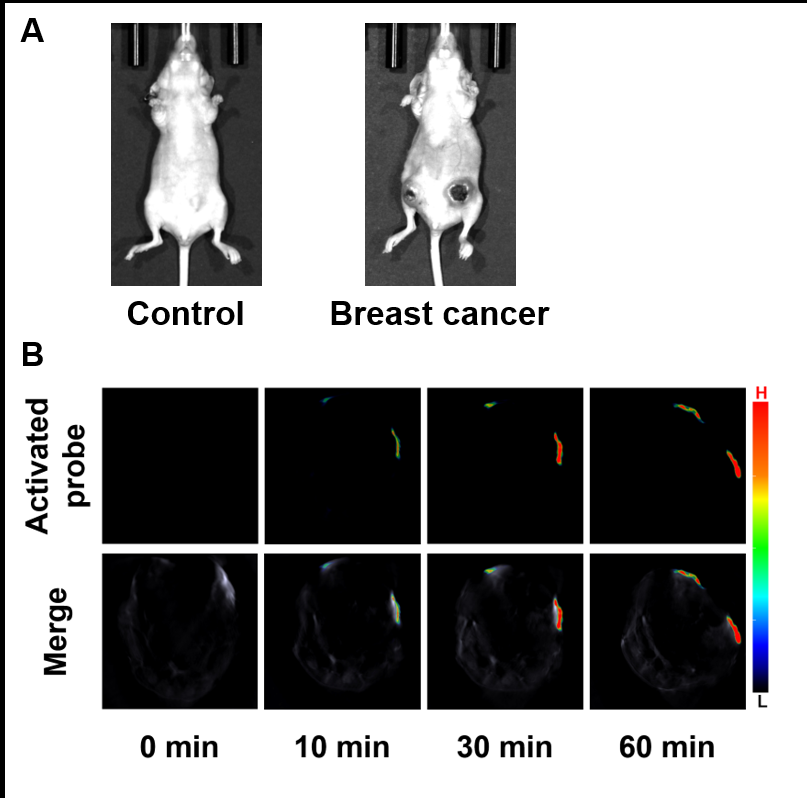
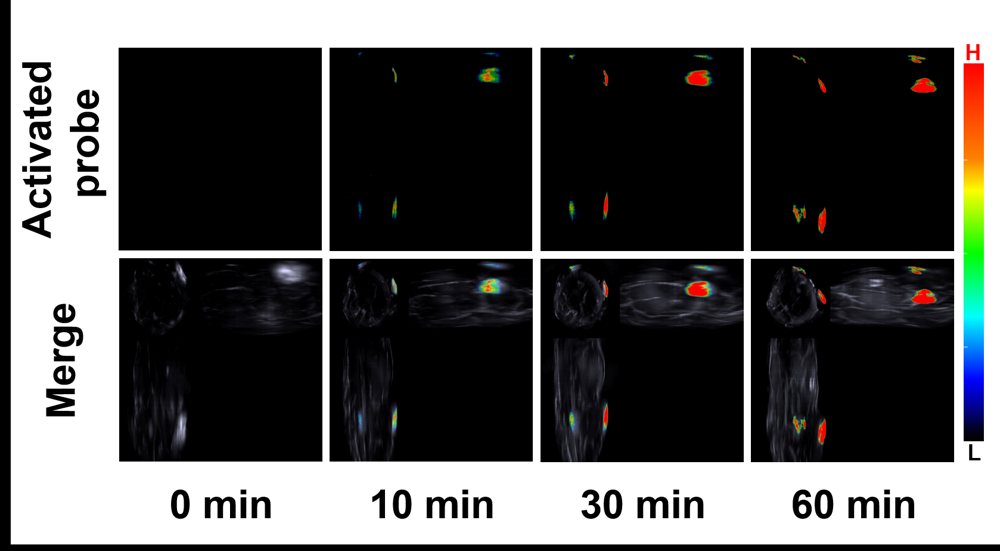
醌氧化还原酶(NQO1)是生物体内的一种双电子还原反应的专性催化还原酶. 在一些疾病如乳腺癌中NQO1过度表达, 因此NQO1可作为生物标志物以观察乳腺癌肿瘤的产生和发展. 目前已有一些文献报导用于NQO1检测和荧光成像的荧光探针, 但大部分这些探针具有吸收波长较短、背景干扰较强、组织穿透深度较低等不足. 为克服荧光探针成像的上述缺陷, 我们构建出一种具有推拉电子结构的可对NQO1响应的新型近红外光声探针TPA-X-Q. 实验结果表明, 该探针可在生物体内和体外对NQO1进行专一性的增强型光声检测和成像, 并可提供高分辨率的实时光声信号图像. 此外, 这种新型的光声探针能够成功应用于乳腺癌小鼠模型, 对乳腺癌肿瘤中过量表达的NQO1进行灵敏准确的光声检测与成像, 借助多光谱光声断层扫描技术(MSOT)的三维光声图像重建功能, 可实现肿瘤病灶区域的定位.
黄靖, 王超, 林敏刚, 曾钫, 吴水珠. 醌氧化还原酶响应型光声探针的合成及其对乳腺癌的成像[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(3): 331-337.
Jing Huang, Chao Wang, Mingang Lin, Fang Zeng, Shuizhu Wu. Synthesis of NQO1-activatable Optoacoustic Probe and Its Imaging of Breast Cancer[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(3): 331-337.





| [1] |
Asher, G.; Reuven, N.; Shaul, Y. BioEssays 2006, 28,844.
doi: 10.1002/bies.20447 pmid: 16927316 |
| [2] |
Clavería-Gimeno, R.; Velazquez-Campoy, A.; Pey, A. L. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 636,17.
doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2017.10.020 pmid: 29100982 |
| [3] |
Pey, A. L. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126,1223.
pmid: 30615965 |
| [4] |
Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, B.; Zhou, Y. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38,714.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v38.7 |
| [5] |
Wang, N.; Zhao, J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 26,775. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1614-7065 |
|
( 王乃兴, 赵嘉, 有机化学, 2006, 26,775.) 83d27848-ce6f-4042-bcec-2202ef50c36e
|
|
| [6] |
Mizumoto, A.; Ohashi, S.; Kamada, M.; Saito, T.; Nakai, Y.; Baba, K.; Hirohashi, K.; Mitani, Y.; Kikuchi, O.; Matsubara, J.; Yamada, A.; Takahashi, T.; Lee, H.; Okuno, Y.; Kanai, M.; Muto, M. J. Gastroenterol 2019, 54,687.
pmid: 30737573 |
| [7] |
Luo, S.; Lei, K.; Xiang, D.; Ye, K. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longevity 2018, 2018,1.
|
| [8] |
Sies, H.; Berndt, C.; Jones, D. P. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86,715.
pmid: 28441057 |
| [9] |
Sabharwal, S. S.; Schumacker, P. T. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14,709.
doi: 10.1038/nrc3803 pmid: 25342630 |
| [10] |
Hayes, J. D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A. T.; Tew, K. D. Cancer Cell 2020, 38,167.
pmid: 32649885 |
| [11] |
Sharma, C.; Wang, H.-X.; Li, Q.; Knoblich, K.; Reisenbichler, E. S.; Richardson, A. L.; Hemler, M. E. Cancer Res. 2017, 77,6880.
pmid: 29055014 |
| [12] |
Danson, S.; Ward, T. H.; Butler, J.; Ranson, M. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2004, 30,437.
pmid: 15245776 |
| [13] |
Dinkova-Kostova, A. T.; Talalay, P. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 501,116.
doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2010.03.019 pmid: 20361926 |
| [14] |
Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, T.; Men, J.; Lin, Z.; Qi, P.; Piao, Y.; Yan, G.. BMC Cancer 2015, 15,207.
pmid: 25880877 |
| [15] |
Li, L.-S.; Reddy, S.; Lin, Z.-H.; Liu, S.; Park, H.; Chun, S. G.; Bornmann, W. G.; Thibodeaux, J.; Yan, J.; Chakrabarti, G.; Xie, X.; Sumer, B. D.; Boothman, D. A.; Yordy, J. S. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15,1757.
pmid: 27196777 |
| [16] |
Pani, G.; Giannoni, E.; Galeotti, T.; Chiarugi, P. Antioxid. Redox Signaling 2009, 11,2791.
doi: 10.1089/ars.2009.2739 |
| [17] |
Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Cui, X.; Lin, Z.; Liu, S.; Chen, L. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 33,14.
doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-33-14 pmid: 24499631 |
| [18] |
Fagerholm, R.; Hofstetter, B.; Tommiska, J.; Aaltonen, K.; Vrtel, R.; Syrjäkoski, K.; Kallioniemi, A.; Kilpivaara, O.; Mannermaa, A.; Kosma, V.-M.; Uusitupa, M.; Eskelinen, M.; Kataja, V.; Aittomäki, K.; von Smitten, K.; Heikkilä, P.; Lukas, J.; Holli, K.; Bartkova, J.; Blomqvist, C.; Bartek, J.; Nevanlinna, H. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40,844.
pmid: 18511948 |
| [19] |
Jamshidi, M.; Bartkova, J.; Greco, D.; Tommiska, J.; Fagerholm, R.; Aittomäki, K.; Mattson, J.; Villman, K.; Vrtel, R.; Lukas, J.; Heikkilä, P.; Blomqvist, C.; Bartek, J.; Nevanlinna, H. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 132,955.
doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1629-5 pmid: 21706157 |
| [20] |
Qi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, B.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90,1014.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04407 pmid: 29182316 |
| [21] |
Xiong, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, F. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77,1239. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19080305 pmid: 73282259-D05E-4539-8A88-A678B317D50D |
|
( 熊麟, 凡勇, 张凡, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 1239.)
pmid: 73282259-D05E-4539-8A88-A678B317D50D |
|
| [22] |
Niu, H.; Tang, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, Y. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56,7710.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC02668A |
| [23] |
Specht, E. A.; Braselmann, E.; Palmer, A. E. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79,93.
pmid: 27860833 |
| [24] |
Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zeng, F.; Huang, S.; Huang, J.; Xie, H.; Yu, C.; Wu, S. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8,1511.
pmid: 26701212 |
| [25] |
Chang, Y.; Li, B.; Guo, M.; Cai, Y.; Xu, K. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 39,2485. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201903010 |
|
( 常永新, 李白, 郭淼, 蔡永红, 徐括喜, 有机化学, 2019, 39,2485.) ce3fcf14-0b02-4e50-a864-d4e0aa974467
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201903010 |
|
| [26] |
Christensen, P. R.; Wolf, M. O. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26,8471.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v26.46 |
| [27] |
Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, L.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74,910. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A16070342 pmid: 038E5B9E-3975-4E43-99F1-BAB63AF9C904 |
|
( 王俊, 武英龙, 孙立和, 曾钫, 吴水珠, 化学学报, 2016, 74,910.) 6d05ea64-37bd-41b8-8490-f1e8f5c3f335
doi: 10.6023/A16070342 pmid: 038E5B9E-3975-4E43-99F1-BAB63AF9C904 |
|
| [28] |
Liu, P.; Xu, J.; Yan, D.; Zhang, P.; Zeng, F.; Li, B.; Wu, S. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51,9567.
doi: 10.1039/C5CC02149A |
| [29] |
Yang, Q.; Wen, Y.; Xu, J.; Shao, S. Talanta 2020, 216,120982.
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120982 pmid: 32456908 |
| [30] |
Yuan, Z.; Xu, M.; Wu, T.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Ernest, U.; Gui, L.; Wang, F.; He, Q.; Chen, H. Talanta 2019, 198,323.
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.02.009 pmid: 30876568 |
| [31] |
Shen, Z.; Prasai, B.; Nakamura, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Jackson, M. S.; McCarley, R. L. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12,1121.
pmid: 28240865 |
| [32] |
Hettiarachchi, S. U.; Prasai, B.; McCarley, R. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136,7575. e701d009-6c49-4c13-aed7-52d3b59ac8c3
doi: 10.1021/ja5030707 |
| [33] |
Pan, D.; Luo, F.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, F.; Kuang, Y.-Q.; Jiang, J.-H. Analyst 2017, 142,2624.
pmid: 28608874 |
| [34] |
Cheng, Z.; Valença, W. O.; Dias, G. G.; Scott, J.; Barth, N. D.; de Moliner, F.; Souza, G. B. P.; Mellanby, R. J.; Vendrell, M.; da Silva Júnior, E.N. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27,3938.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2019.07.017 pmid: 31327676 |
| [35] |
Ovsepian, S. V.; Olefir, I.; Westmeyer, G.; Razansky, D.; Ntziachristos, V. Neuron 2017, 96,966.
doi: S0896-6273(17)30990-X pmid: 29216459 |
| [36] |
Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. Theranostics 2019, 9,7313.
pmid: 31695770 |
| [37] |
Ouyang, J.; Sun, L.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, C.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.Eng. 2020, 59,10111.
|
| [38] |
Reber, J.; Willershäuser, M.; Karlas, A.; Paul-Yuan, K.; Diot, G.; Franz, D.; Fromme, T.; Ovsepian, S. V.; Bézière, N.; Dubikovskaya, E.; Karampinos, D. C.; Holzapfel, C.; Hauner, H.; Klingenspor, M.; Ntziachristos, V. Cell Metab. 2018, 27,689.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.02.002 pmid: 29514074 |
| [39] |
Zhan, C.; Huang, Y.; Lin, G.; Huang, S.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. Small 2019, 15,1900309.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v15.33 |
| [40] |
Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, L.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29,1807960.
|
| [41] |
Diot, G.; Metz, S.; Noske, A.; Liapis, E.; Schroeder, B.; Ovsepian, S. V.; Meier, R.; Rummeny, E.; Ntziachristos, V. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23,6912.
pmid: 28899968 |
| [42] |
Ntziachristos, V.; Razansky, D. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110,2783.
doi: 10.1021/cr9002566 pmid: 20387910 |
| [43] |
Luís Dean-Ben, X.; Razansky, D. Light: Sci. Appl. 2018, 7,18004.
|
| [44] |
Gujrati, V.; Mishra, A.; Ntziachristos, V. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53,4653.
doi: 10.1039/C6CC09421J |
| [45] |
Schellenberg, M. W.; Hunt, H. K. Photoacoustics 2018, 11,14.
doi: 10.1016/j.pacs.2018.07.001 pmid: 30073147 |
| [46] |
Song, X.; Bian, H.; Wang, C.; Hu, M.; Li, N.; Xiao, Y. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15,8091.
pmid: 28905964 |
| [47] |
Kim, H.; Lee, M.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Yoon, J. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37,1465.
doi: 10.1039/b802497a pmid: 18648672 |
| [48] |
Han, J.; Burgess, K.; Chem. Rev. 2010, 110,2709.
pmid: 19831417 |
| [49] |
Mendoza, M. F.; Hollabaugh, N. M.; Hettiarachchi, S. U.; McCarley, R. L. Biochemistry 2012, 51,8014.
pmid: 22989153 |
| [50] |
Wu, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9,3983.
pmid: 30266905 |
| [1] | 王海朋, 蔡文生, 邵学广. 抗冻剂抗冻机制的近红外光谱与分子模拟研究★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1167-1174. |
| [2] | 武虹乐, 郭锐, 迟涵文, 唐永和, 宋思睿, 葛恩香, 林伟英. 喹啉基粘度荧光探针的合成及其检测应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 905-911. |
| [3] | 郑文山, 高冠斌, 邓浩, 孙涛垒. Ag2Se@Ag2S核壳量子点的室温合成及其近红外荧光性能优化[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 763-770. |
| [4] | 李兰英, 陶晴, 闻艳丽, 王乐乐, 郭瑞妍, 刘刚, 左小磊. 多聚腺嘌呤DNA探针及其生物传感应用★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 681-690. |
| [5] | 吕鑫, 吴仪, 张勃然, 郭炜. 过氧化氢激活型近红外氟硼二吡咯光敏剂的设计、合成及光动力治疗研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(4): 359-370. |
| [6] | 李畅, 郑振东, 郑江南, 田瑞军. 基于可断裂双功能探针的糖蛋白分析★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(12): 1673-1680. |
| [7] | 贺晓梦, 袁方, 张素雅, 张健健. 基于尼罗红类ONOO–近红外荧光探针的开发及其成像应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1515-1521. |
| [8] | 赵珂, 程夏宇, 马雪雪, 耿明慧. 含哌嗪基团锌离子探针的双光子吸收增强机理[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1371-1378. |
| [9] | 孙丽, 王亚静, 李涛, 郭英姝, 张书圣. 金纳米笼探针用于线粒体成像和光热损伤细胞★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1301-1310. |
| [10] | 宋思睿, 唐永和, 孙良广, 郭锐, 姜冠帆, 林伟英. 基于香豆素荧光团的新型极性检测荧光探针的开发及其成像应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1217-1222. |
| [11] | 刘巴蒂, 王承俊, 钱鹰. 噻吩基氟硼二吡咯近红外光敏染料的合成、双光子荧光成像及光动力治疗研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1071-1083. |
| [12] | 张沛森, 荆莉红. 肿瘤病理可视化纳米探针的研究进展※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 805-816. |
| [13] | 廉纬, 方泽铠, 涂大涛, 李嘉尧, 韩思远, 李仁富, 商晓颖, 陈学元. 模板法控制合成AgInSe2:Zn2+近红外荧光量子点及其生物标记应用※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(5): 625-632. |
| [14] | 吴志芬, 柯建熙, 刘永升, 孙蓬明, 洪茂椿. 稀土近红外二区纳米荧光影像探针及其生物医学应用※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 542-552. |
| [15] | 张景荣, 黄得财, 黄聪聪, 梁思思, 朱浩淼. In2BP3O12:Cr3+宽带近红外荧光粉的发光性能及应用研究※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 453-459. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||