化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (12): 1673-1680.DOI: 10.6023/A23050263 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 庆祝《化学学报》创刊90周年合辑
研究论文
投稿日期:2023-06-01
发布日期:2023-08-14
作者简介:基金资助:
Chang Li, Zhendong Zheng, Jiangnan Zheng( ), Ruijun Tian(
), Ruijun Tian( )
)
Received:2023-06-01
Published:2023-08-14
Contact:
*E-mail: About author:Supported by:文章分享
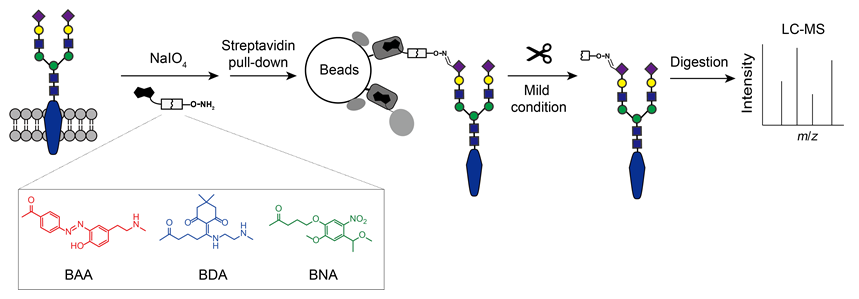
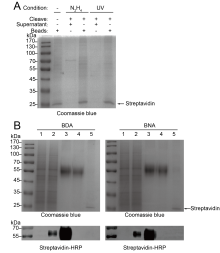
糖蛋白在细胞活动和疾病发生发展过程中发挥着重要作用. 然而, 在复杂的生物样本中, 糖蛋白的丰度往往较低, 因而在质谱分析前必须对其进行富集以实现高灵敏质谱分析. 目前, 已经发展出诸多糖蛋白富集方法, 其中肼化学法与肟点击化学法因对糖蛋白标记的普适性与无偏性受到了越来越多的关注. 然而, 由于这些方法以共价连接或者超高亲和力生物素结合的方式在固相载体上捕获糖蛋白, 因此无法选择性地洗脱被富集的糖蛋白. 传统的方法是在固相载体上直接进行酶解, 因此无法排除非特异性吸附蛋白、内源性生物素化蛋白、固相载体上的链霉亲和素等无关蛋白对糖蛋白质谱分析产生的背景干扰. 本工作设计并合成了三种可断裂的双功能探针[生物素-偶氮苯-氧胺(BAA)、生物素-N-1-(4,4-二甲基-2,6-二氧环亚己基)乙基-氧胺(BDA)、生物素-邻硝基苄基-氧胺(BNA)], 通过温和的方式从固相载体上释放糖蛋白, 从而排除非糖蛋白的干扰, 提高糖蛋白富集的选择性. 对三种探针的标记与富集效果、切割效率、蛋白回收率等性能进行了评估. 结果显示, 探针BDA与BNA的性能较为优越. 最后, 探针BNA被应用于细胞表面糖蛋白的分离富集与质谱鉴定中. 与传统的在固相载体上直接进行酶解的方法相比, 该方法中非糖蛋白数目从3564降到了2139, 降幅达到了40.0%, 糖蛋白的无标定量(LFQ)分析强度提升了104.2%. 此外, 切割方法极大降低了内源性生物素化蛋白的干扰. 上述结果表明, 可断裂双功能探针显著地提高了糖蛋白质谱鉴定的灵敏度与选择性, 为生物与医学等领域中糖蛋白的深度解析提供了新的工具.
李畅, 郑振东, 郑江南, 田瑞军. 基于可断裂双功能探针的糖蛋白分析★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(12): 1673-1680.
Chang Li, Zhendong Zheng, Jiangnan Zheng, Ruijun Tian. Glycoprotein Identification using Cleavable Bifunctional Probes★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(12): 1673-1680.







| [1] |
Pirro, M.; Schoof, E.; van Vliet, S. J.; Rombouts, Y.; Stella, A.; de Ru, A.; Mohammed, Y.; Wuhrer, M.; van Veelen, P. A.; Hensbergen, P. J. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 1125.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00796 |
| [2] |
Kailemia, M. J.; Xu, G.; Wong, M.; Li, Q.; Goonatilleke, E.; Leon, F.; Lebrilla, C. B. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 208.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04202 pmid: 29049885 |
| [3] |
Venkatakrishnan, V.; Packer, N. H.; Thaysen-Andersen, M. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2013, 7, 553.
doi: 10.1586/17476348.2013.837752 |
| [4] |
Shi, Y.; Gao, W.; Lytle, N. K.; Huang, P.; Yuan, X.; Dann, A. M.; Ridinger-Saison, M.; DelGiorno, K. E.; Antal, C. E.; Liang, G.; Atkins, A. R.; Erikson, G.; Sun, H.; Meisenhelder, J.; Terenziani, E.; Woo, G.; Fang, L.; Santisakultarm, T. P.; Manor, U.; Xu, R.; Becerra, C. R.; Borazanci, E.; Von Hoff, D. D.; Grandgenett, P. M.; Hollingsworth, M. A.; Leblanc, M.; Umetsu, S. E.; Collisson, E. A.; Scadeng, M.; Lowy, A. M.; Donahue, T. R.; Reya, T.; Downes, M.; Evans, R. M.; Wahl, G..M.; Pawson, T.; Tian, R.; Hunter, T. Nature 2019, 569, 131.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1130-6 |
| [5] |
Campos-da-Paz, M.; Dòrea, J. G.; Galdino, A. S.; Lacava, Z. G. M.; de Fatima Menezes Almeida Santos, M. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2018, 12, 269.
doi: 10.2174/1872208312666180731104244 pmid: 30062978 |
| [6] |
Saavedra, D.; Crombet, T. Front Immunol. 2017, 8, 269.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00269 pmid: 28348561 |
| [7] |
Riley, N. M.; Bertozzi, C. R.; Pitteri, S. J. Mol. Cell Proteomics 2021, 20, 100029.
doi: 10.1074/mcp.R120.002277 |
| [8] |
Suttapitugsakul, S.; Sun, F.; Wu, R. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 267.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04651 pmid: 31626732 |
| [9] |
Zhang, L.; Du, X.; Zeng, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 149 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A15090584 |
|
(张丽霞, 杜秀芳, 曾盈, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 149.)
doi: 10.6023/A15090584 |
|
| [10] |
Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Lu, H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 705 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A21020048 |
|
(李月悦, 彭叶, 陆豪杰, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 705.)
doi: 10.6023/A21020048 |
|
| [11] |
Bao, H.; Xie, L.; Lu, H. Se Pu 2016, 34, 1145 (in Chinese).
|
|
(包慧敏, 谢力琦, 陆豪杰, 色谱, 2016, 34, 1145.)
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2016.09003 |
|
| [12] |
Liu, L.; Qin, H.; Ye, M. Se Pu 2021, 39, 1045 (in Chinese).
|
|
(刘璐瑶, 秦洪强, 叶明亮, 色谱, 2021, 39, 1045.)
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.06011 |
|
| [13] |
Xiong, Y.; Cheng, M.; Lu, H. Fenxi Huaxue 2021, 49, 1597 (in Chinese).
|
|
(熊莹莹, 程孟霞, 陆豪杰, 分析化学, 2021, 49, 1597)
|
|
| [14] |
Duan, L.; Zangiabadi, M.; Zhao, Y. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 10199.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC02892D |
| [15] |
Shu, Q.; Li, M.; Shu, L.; An, Z.; Wang, J.; Lv, H.; Yang, M.; Cai, T.; Hu, T.; Fu, Y.; Yang, F. Mol. Cell Proteomics. 2020, 19, 672.
doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA119.001791 |
| [16] |
Xiao, H.; Chen, W.; Smeekens, J. M.; Wu, R. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1692.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04081-3 |
| [17] |
Zeng, Y.; Ramya, T. N.; Dirksen, A.; Dawson, P. E.; Paulson, J. C. Nat. Methods. 2009, 6, 207.
|
| [18] |
Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Zhang, C.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Lu, H. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7920.
doi: 10.1021/ac5018666 pmid: 25062325 |
| [19] |
Szychowski, J.; Mahdavi, A.; Hodas, J. J.; Bagert, J. D.; Ngo, J. T.; Landgraf, P.; Dieterich, D. C.; Schuman, E. M.; Tirrell, D. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18351.
doi: 10.1021/ja1083909 pmid: 21141861 |
| [20] |
Yang, Y.; Hahne, H.; Kuster, B.; Verhelst, S. H. Mol. Cell Proteomics 2013, 12, 237.
doi: 10.1074/mcp.M112.021014 |
| [21] |
Beard, H. A.; Korovesis, D.; Chen, S.; Verhelst, S. H. L. Mol. Omics 2021, 17, 197.
doi: 10.1039/D0MO00181C |
| [22] |
Eom, T.; Khan, A. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 420.
doi: 10.1039/C9OB02515D |
| [23] |
Mnatsakanyan, R.; Markoutsa, S.; Walbrunn, K.; Roos, A.; Verhelst, S. H. L.; Zahedi, R. P. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2195.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10182-4 pmid: 31097712 |
| [24] |
Chang, T. C.; Adak, A. K.; Lin, T. W.; Li, P. J.; Chen, Y. J.; Lai, C. H.; Liang, C. F.; Chen, Y. J.; Lin, C. C. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 1216.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.01.050 |
| [25] |
Chen, W.; Wang, S.; Adhikari, S.; Deng, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Ke, M., Yang, P.; Tian, R. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4864.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b00631 |
| [26] |
Gao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Su, Y.; Huang, P.; Lu, X.; Gong, Q.; Chen, W.; Xu, R.; Tian, R. Analyst 2020, 145, 6441.
doi: 10.1039/D0AN01149E |
| [27] |
Pace, C. L.; Muddiman, D. C. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 10, 1021.
|
| [28] |
Frankenfield, A. M.; Fernandopulle, M. S.; Hasan, S.; Ward, M. E.; Hao, L. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 15437.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03107 pmid: 33201688 |
| [29] |
Chu, B.; He, A.; Tian, Y.; He, W.; Chen, P.; Hu, J.; Xu, R.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, M.; Yang, P.; Li, S. S. C.; Sun, Y.; Li, P.; Hunter, T.; Tian, R. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2018, 92, E8863.
|
| [1] | 张娜娜, 于恺然, 李际婷, 张嘉宁, 刘宇博. 化学生物学解析疾病中O-GlcNAc糖基化功能: 研究工具与策略[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 843-856. |
| [2] | 成受明, 周波. 基于超高分辨质谱的溶解性有机质分子转化机理分析[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1106-1114. |
| [3] | 闫续, 屈贺幂, 常烨, 段学欣. 金属有机框架在气体预富集、预分离及检测中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1183-1202. |
| [4] | 陈玉宛, 周雯, 李欣蔚, 杨开广, 梁振, 张丽华, 张玉奎. 基于液质联用技术的蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用研究进展※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 817-826. |
| [5] | 李月悦, 彭叶, 陆豪杰. N-糖链唾液酸连接异构体的质谱分析方法研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 705-715. |
| [6] | 邵阳, 杨国胜, 张继龙, 罗敏, 马玲玲, 徐殿斗. 人工放射性核素236U的分析方法进展及其应用[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 716-728. |
| [7] | 阮曼, 赵艳霞, 何圣贵. 纳米尺寸氧化钇团簇阴离子与正丁烷反应的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 490-499. |
| [8] | 刘吉林, 于凯, 张洪, 姜杰. 质谱离子源技术用于电化学反应机理研究的进展[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(6): 504-515. |
| [9] | 李威, 冉铁成, 张瑜, 何威, 马继飞, 汪启胜, 张继超, 诸颖. SiO2介导的5 nm金颗粒的高效富集及其催化活性研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(2): 170-176. |
| [10] | 李亚男, 季伙燕, 王天一, 沈蕾, 施秀英, 王建新. 血清肌钙蛋白I液相色谱串联质谱法建立及优化[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(6): 539-544. |
| [11] | 任响, 张小平, 王雨芬, 曹静瑜, 程媛媛, 冯守华, 陈焕文. 倍硫磷的甲基在分子内和分子间迁移的质谱研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(4): 358-364. |
| [12] | 汪泽, 黄漪铃, 任娟, 陈相峰, 陈德华. 电子捕获裂解质谱研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(2): 130-142. |
| [13] | 夏海伦, 华鑫, 龙亿涛. 电位调控电解质迁移过程的ToF-SIMS可视化研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(11): 1164-1167. |
| [14] | 顾天航, 石君明, 滑熠龙, 刘静, 王伟, 张伟贤. 应用纳米零价铁富集银的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(10): 991-997. |
| [15] | 张丽霞, 杜秀芳, 曾盈. 糖蛋白/糖肽分离富集中的化学[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(2): 149-154. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||