化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (8): 1043-1051.DOI: 10.6023/A23040144 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 庆祝《化学学报》创刊90周年合辑
综述
投稿日期:2023-04-19
发布日期:2023-09-14
作者简介: |
陈其文, 武汉大学博士后, 合作导师为张先正教授. 分别于2015年、2018年在西北农林科技大学获得学士及硕士学位; 2021年在武汉大学获得博士学位, 同年在武汉大学进行博士后研究工作. 主要研究方向为构建微生物基活性生物材料用于疾病治疗. |
 |
张先正, 武汉大学教授, 1994、1997、2000年相继于武汉大学获学士、硕士和博士学位. 2000年9月~2001年8月新加坡材料研究所Research Associate. 2001年9月~2004年8月美国康奈尔大学博士后. 自2004年9月起在武汉大学化学与分子科学学院任教授, 主要从事生物医用高分子材料的研究. |
基金资助:Received:2023-04-19
Published:2023-09-14
Contact:
*E-mail: xz-zhang@whu.edu.cn
About author:Supported by:文章分享

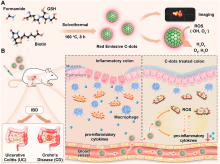
近年来, 炎性肠道疾病(Inflammatory bowel diseases, IBD)的发病率越来越高, 给全球的公共健康带来了沉重的负担. 目前, 人们主要使用抗炎药、抗生素、生物抗体及免疫调节剂等药物来抑制炎症反应治疗IBD, 但疗效并不理想. 生物酶具有高效、专一的催化活性, 在炎性疾病诊疗领域引起了广泛的研究兴趣. 但生物酶纯化困难、在生物体内易失活, 限制了其进一步应用. 相比于生物酶, 纳米酶制备简单、结构稳定、类酶催化活性高, 近年来将纳米酶应用于生物医药领域受到了广泛的关注, 如抗癌、抗菌、抗炎等. 本综述总结了近年来纳米酶在IBD治疗方面的研究进展, 重点介绍了所用纳米酶的组成、合成方法、催化特性及治疗机制. 文中进一步讨论了目前用于IBD治疗纳米酶的应用限制, 并对未来用于IBD治疗的纳米酶的构建进行了展望.
陈其文, 张先正. 纳米酶介导的炎性肠道疾病治疗研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 1043-1051.
Qiwen Chen, Xianzheng Zhang. Reserach Advances on Nanozyme-Guided Therapy of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(8): 1043-1051.
| Nanozymes | Catalytic activity | Anti-inflammation application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pt NPs | SOD, CAT, POD-like | Human Cerebral Cavernous Malformation (CCM) disease | [34] |
| PVP-IrNPs | CAT, POD-like | Cell protection | [35] |
| Rh-PEG NDs | SOD, CAT-lile, and •OH, ONOO−,•NO scavenging activity | IBD therapy | [36] |
| Single-atom Fe-N4 | SOD-like, CAT-like | Cell protection | [37] |
| Mo NPs | N-Acetyl cysteine-like | Anti-tumor cell | [38] |
| Fe3O4 NPs | CAT-like | Anti-aging | [39] |
| MnO2 NPs | SOD, CAT-like | Cell protection | [40] |
| Mn3O4 NPs | SOD, CAT, GPx-like, and •OH scavenging activity | Parkinson’s disease | [41] |
| CeO2 NPs | SOD, CAT-like | Neuroprotective effect | [42] |
| MoS2 NPs | SOD, CAT-like | Osteoarthritis | [43] |
| CuxO NPs | SOD, CAT, and GPx-like | Parkinson’s disease | [44] |
| CuTA | SOD-like, CAT-like, and •OH scavenging activity | Lung destruction | [45] |
| NiCo2O4@PVP | •OH, $\mathrm{O}_{2}^{-}$ and H2O2 scavenging activity | IBD therapy | [46] |
| PtPdMo trim | POD, CAT-like, and •OH, 1O2, •NO scavenging activities | Brain injury | [47] |
| Carbogenic nanozyme | SOD, CAT-like •NO and ONOO-scavenging activities | Traumatic brain injury | [48] |
| C-dots nanozyme | SOD-like | IBD therapy | [49] |
| Melanin NPs | SOD-like | Ischemic stroke | [50] |
| Se-CQDs | •OH scavenging activity | Cell protection | [51] |
| Se@Pda | GPx-like | Anti-inflammation | [52] |
| Nanozymes | Catalytic activity | Anti-inflammation application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pt NPs | SOD, CAT, POD-like | Human Cerebral Cavernous Malformation (CCM) disease | [34] |
| PVP-IrNPs | CAT, POD-like | Cell protection | [35] |
| Rh-PEG NDs | SOD, CAT-lile, and •OH, ONOO−,•NO scavenging activity | IBD therapy | [36] |
| Single-atom Fe-N4 | SOD-like, CAT-like | Cell protection | [37] |
| Mo NPs | N-Acetyl cysteine-like | Anti-tumor cell | [38] |
| Fe3O4 NPs | CAT-like | Anti-aging | [39] |
| MnO2 NPs | SOD, CAT-like | Cell protection | [40] |
| Mn3O4 NPs | SOD, CAT, GPx-like, and •OH scavenging activity | Parkinson’s disease | [41] |
| CeO2 NPs | SOD, CAT-like | Neuroprotective effect | [42] |
| MoS2 NPs | SOD, CAT-like | Osteoarthritis | [43] |
| CuxO NPs | SOD, CAT, and GPx-like | Parkinson’s disease | [44] |
| CuTA | SOD-like, CAT-like, and •OH scavenging activity | Lung destruction | [45] |
| NiCo2O4@PVP | •OH, $\mathrm{O}_{2}^{-}$ and H2O2 scavenging activity | IBD therapy | [46] |
| PtPdMo trim | POD, CAT-like, and •OH, 1O2, •NO scavenging activities | Brain injury | [47] |
| Carbogenic nanozyme | SOD, CAT-like •NO and ONOO-scavenging activities | Traumatic brain injury | [48] |
| C-dots nanozyme | SOD-like | IBD therapy | [49] |
| Melanin NPs | SOD-like | Ischemic stroke | [50] |
| Se-CQDs | •OH scavenging activity | Cell protection | [51] |
| Se@Pda | GPx-like | Anti-inflammation | [52] |
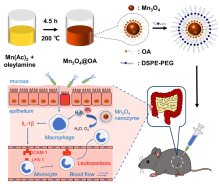

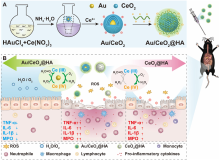



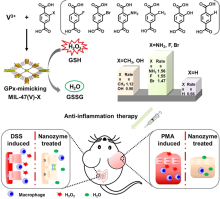

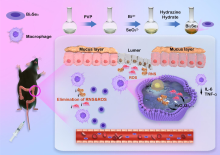


| [1] |
Ng S. C.; Shi H. Y.; Hamidi N.; Underwood F. E.; Tang W.; Benchimol E. I.; Panaccione R.; Ghosh S.; Wu J. C. Y.; Chan F. K. L.; Sung J. J. Y.; Kaplan G. G. Lancet 2017, 390, 2769.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32448-0 |
| [2] |
Rogler G.; Singh A.; Kavanaugh A.; Rubin D. T. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1118.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.07.042 |
| [3] |
Zhao M.; Gonczi L.; Lakatos P. L.; Burisch J. J. Crohns Colitis 2021, 15, 1573.
doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjab029 |
| [4] |
Friedrich M. J. JAMA, J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2018, 319, 648.
|
| [5] |
Kaplan G. G.; Ng S. C. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 307.
doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(16)30077-2 |
| [6] |
Crowley E.; Warner N.; Pan J.; Khalouei S.; Elkadri A.; Fiedler K.; Foong J.; Turinsky A. L.; Bronte-Tinkew D.; Zhang S.; Hu J.; Tian D.; Li D.; Horowitz J.; Siddiqui I.; Upton J.; Roifman C. M.; Church P. C.; Wall D. A.; Ramani A. K.; Kotlarz D.; Klein C.; Uhlig H.; Snapper S. B.; Gonzaga-Jauregui C.; Paterson A. D.; McGovern D. P. B.; Brudno M.; Walters T. D.; Griffiths A. M.; Muise A. M. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 2208.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.023 |
| [7] |
Grivennikov S. I.; Wang K.; Mucida D.; Stewart C. A.; Schnabl B.; Jauch D.; Taniguchi K.; Yu G.-Y.; Oesterreicher C. H.; Hung K. E.; Datz C.; Feng Y.; Fearon E. R.; Oukka M.; Tessarollo L.; Coppola V.; Yarovinsky F.; Cheroutre H.; Eckmann L.; Trinchieri G.; Karin M. Nature 2012, 491, 254.
doi: 10.1038/nature11465 |
| [8] |
Helmink B. A.; Khan M. A. W.; Hermann A.; Gopalakrishnan V.; Wargo J. A. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 377.
doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0377-7 |
| [9] |
Xavier R. J.; Podolsky D. K. Nature 2007, 448, 427.
doi: 10.1038/nature06005 |
| [10] |
Scaldaferri F.; Fiocchi C. J. Digest. Dis. 2007, 8, 171.
doi: 10.1111/cdd.2007.8.issue-4 |
| [11] |
Allez M.; Modigliani R. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2000, 16, 329.
doi: 10.1097/00001574-200007000-00007 |
| [12] |
West N. R.; Hegazy A. N.; Owens B. M. J.; Bullers S. J.; Linggi B.; Buonocore S.; Coccia M.; Goertz D.; This S.; Stockenhuber K.; Pott J.; Friedrich M.; Ryzhakov G.; Baribaud F.; Brodmerkel C.; Cieluch C.; Rahman N.; Mueller-Newen G.; Owens R. J.; Kuehl A. A.; Maloy K. J.; Plevy S. E.; Keshav S.; Travis S. P. L.; Powrie F.; Oxford I. B. D. C. I. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 579.
doi: 10.1038/nm.4307 |
| [13] |
Larabi A.; Barnich N.; Nguyen H. T. T. Autophagy 2020, 16, 38.
doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1635384 |
| [14] |
Neurath M. F. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 269.
doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.208 |
| [15] |
Baumgart D. C.; Le Berre C. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1302.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1907607 |
| [16] |
He H.; Xie M.; Zhang M.; Zhang H.; Zhu H.; Fang Y.; Shen Z.; Wang R.; Zhao Z.; Zhu L.; Qian X.; Li H. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 2625.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v40.22 |
| [17] |
Lee Y.; Sugihara K.; Gillilland M. G., III; Jon S.; Kamada N.; Moon J. J. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 118.
doi: 10.1038/s41563-019-0462-9 |
| [18] |
Dammes N.; Goldsmith M.; Ramishetti S.; Dearling J. L. J.; Veiga N.; Packard A. B.; Peer D. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 1030.
doi: 10.1038/s41565-021-00928-x |
| [19] |
Zhou J.; Li M.; Chen Q.; Li X.; Chen L.; Dong Z.; Zhu W.; Yang Y.; Liu Z.; Chen Q. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3432.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31171-0 |
| [20] |
Zhang S.; Langer R.; Traverso G. Nano Today 2017, 16, 82.
doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2017.08.006 |
| [21] |
Cao M.; Dai X.; Chen B.; Zhao N.; Xu F.-J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 1054. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20070295 |
|
( 曹萌轩, 代晓光, 陈贝贝, 赵娜娜, 徐福建, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1054.)
|
|
| [22] |
Chen Q.-W.; Cao M.-W.; Qiao J.-Y.; Li Q.-R.; Zhang X.-Z. Nanoscale Horiz. 2023, 8, 489.
doi: 10.1039/D2NH00572G |
| [23] |
Ianiro G.; Tilg H.; Gasbarrini A. Gut 2016, 65, 1906.
doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312297 |
| [24] |
Cross R. K.; Lapshin O.; Finkelstein J. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 42, 244.
doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e31802f19af |
| [25] |
Mair S.; Atabay Y.; Mayer K.; Petersen A.; Schmid R. M.; Huber W. J. Crohns Colitis 2014, 8, S255.
|
| [26] |
Liang X.; Wen K.; Chen Y.; Fang G.; Yang S.; Li Q. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 4843.
doi: 10.2147/IJN.S378073 |
| [27] |
Liang W.; Wied P.; Carraro F.; Sumby C. J.; Nidetzky B.; Tsung C.-K.; Falcaro P.; Doonan C. J. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1077.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01029 |
| [28] |
Zhou Z.; Vazquez-Gonzalez M.; Willner I. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 4541.
doi: 10.1039/D0CS01030H |
| [29] |
Cheng C.; Zhao S.; Cheng Y.; Liu Y.; Wei H. Sci. China: Life Sci. 2021, 64, 1368.
|
| [30] |
Wu J.; Wang X.; Wang Q.; Lou Z.; Li S.; Zhu Y.; Qin L.; Wei H. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1004.
doi: 10.1039/C8CS00457A |
| [31] |
Wei H.; Wang E. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6060.
doi: 10.1039/c3cs35486e |
| [32] |
Fan L.; Jiang Q.; Pan M.; Wang W.; Zhang L.; Liu X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 419. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20030079 |
|
( 樊蕾, 江群英, 潘敏, 王文晓, 张丽, 刘晓庆, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 419.)
|
|
| [33] |
Wu Y.; Chen Q.; Liu S.; Xiao H.; Zhang M.; Zhang X. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 2186.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2019.08.014 |
| [34] |
Moglianetti M.; De Luca E.; Pedone D.; Marotta R.; Catelani T.; Sartori B.; Amenitsch H.; Retta S. F.; Pompa P. P. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3739.
doi: 10.1039/C5NR08358C |
| [35] |
Su H.; Liu D.-D.; Zhao M.; Hu W.-L.; Xue S.-S.; Cao Q.; Le X.-Y.; Ji L.-N.; Mao Z.-W. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8233.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b01271 |
| [36] |
Miao Z.; Jiang S.; Ding M.; Sun S.; Ma Y.; Younis M. R.; He G.; Wang J.; Lin J.; Cao Z.; Huang P.; Zha Z. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 3079.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b05035 |
| [37] |
Ma W.; Mao J.; Yang X.; Pan C.; Chen W.; Wang M.; Yu P.; Mao L.; Li Y. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 159.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC08116F |
| [38] |
Akhtar M. J.; Ahamed M.; Alhadlaq H. A.; Alshamsan A.; Khan M. A. M.; Alrokayan S. A. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 457, 370.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2015.07.034 |
| [39] |
Zhang Y.; Wang Z.; Li X.; Wang L.; Yin M.; Wang L.; Chen N.; Fan C.; Song H. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1387.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v28.7 |
| [40] |
Li W.; Liu Z.; Liu C.; Guan Y.; Ren J.; Qu X. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 13661.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.44 |
| [41] |
Singh N.; Savanur M. A.; Srivastava S.; D'Silva P.; Mugesh G. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14267.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.45 |
| [42] |
Zeng F.; Wu Y.; Li X.; Ge X.; Guo Q.; Lou X.; Cao Z.; Hu B.; Long N. J.; Mao Y.; Li C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5808.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201802309 |
| [43] |
Chen T.; Zou H.; Wu X.; Chen Y.; Bo S.; Zheng L.; Yang G. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 3079.
doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b00372 |
| [44] |
Hao C.; Qu A.; Xu L.; Sun M.; Zhang H.; Xu C.; Kuang H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 1091.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b11856 |
| [45] |
Lin S.; Cheng Y.; Zhang H.; Wang X.; Zhang Y.; Zhang Y.; Miao L.; Zhao X.; Wei H. Small 2020, 16, 1902123.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v16.27 |
| [46] |
Zhao N.; Yang F.-E.; Zhao C.-Y.; Lv S.-W.; Wang J.; Liu J.-M.; Wang S. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2021, 10, 2101618.
doi: 10.1002/adhm.v10.23 |
| [47] |
Mu X.; Wang J.; Li Y.; Xu F.; Long W.; Ouyang L.; Liu H.; Jing Y.; Wang J.; Dai H.; Liu Q.; Sun Y.; Liu C.; Zhang X.-D. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1870.
|
| [48] |
Mu X.; He H.; Wang J.; Long W.; Li Q.; Liu H.; Gao Y.; Ouyang L.; Ren Q.; Sun S.; Wang J.; Yang J.; Liu Q.; Sun Y.; Liu C.; Zhang X.-D.; Hu W. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 4527.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b01333 |
| [49] |
Ma Y.; Zhao J.; Cheng L.; Li C.; Yan X.; Deng Z.; Zhang Y.; Liang J.; Liu C.; Zhang M. Carbon 2023, 204, 526.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2023.01.006 |
| [50] |
Liu Y.; Ai K.; Ji X.; Askhatova D.; Du R.; Lu L.; Shi J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 856.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b11013 |
| [51] |
Li F.; Li T.; Sun C.; Xia J.; Jiao Y.; Xu H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9910.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.33 |
| [52] |
Huang Y.; Liu Z.; Liu C.; Zhang Y.; Ren J.; Qu X. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 10224.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v24.40 |
| [53] |
Dickinson B. C.; Chang C. J. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 504.
doi: 10.1038/nchembio.607 |
| [54] |
Nathan C.; Cunningham-Bussel A. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 349.
doi: 10.1038/nri3423 |
| [55] |
Chen Q.; He S.; Zhang F.; Cui F.; Liu J.; Wang M.; Wang D.; Jin Z.; Li C. Sci. China Mater. 2021, 64, 510.
doi: 10.1007/s40843-020-1431-5 |
| [56] |
Hu X.; Wang N.; Guo X.; Liang Z.; Sun H.; Liao H.; Xia F.; Guan Y.; Lee J.; Ling D.; Li F. Nano Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 101.
doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00848-y |
| [57] |
Wang J.; Fang L.; Li P.; Ma L.; Na W.; Cheng C.; Gu Y.; Deng D. Nano Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 74.
|
| [58] |
Li Z.; Chen J.; Tian H.; Chen X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 668. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21120615 |
|
( 李真, 陈杰, 田华雨, 陈学思, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 668.)
|
|
| [59] |
Gao L.; Zhuang J.; Nie L.; Zhang J.; Zhang Y.; Gu N.; Wang T.; Feng J.; Yang D.; Perrett S.; Yan X. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 577.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2007.260 |
| [60] |
Huang Y.; Ren J.; Qu X. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4357.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00672 |
| [61] |
Zeng J.; Wang X.; Zhang X.; Zhuo R. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 1156. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19070259 |
|
( 曾锦跃, 王小双, 张先正, 卓仁禧, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 1156.)
|
|
| [62] |
Kwon H. J.; Kim D.; Seo K.; Kim Y. G.; Han S. I.; Kang T.; Soh M.; Hyeon T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9408.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.30 |
| [63] |
Yan R.; Sun S.; Yang J.; Long W.; Wang J.; Mu X.; Li Q.; Hao W.; Zhang S.; Liu H.; Gao Y.; Ouyang L.; Chen J.; Liu S.; Zhang X.-D.; Ming D. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 11552.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b05075 |
| [64] |
Ding J.; Lin J.; Chen L. M.; Guo Z. J. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 17, 305. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 丁隽, 林骏, 陈兰明, 郭子建, 无机化学学报, 2001, 17, 305.)
|
|
| [65] |
Yang B.-W.; Chen Y.; Shi J.-L. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 45, 237.
|
| [66] |
Zhang Y.; Khalique A.; Du X.; Gao Z.; Wu J.; Zhang X.; Zhang R.; Sun Z.; Liu Q.; Xu Z.; Midgley A. C.; Wang L.; Yan X.; Zhuang J.; Kong D.; Huang X. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006570.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v33.9 |
| [67] |
Huang Y.; Liu Z.; Liu C.; Ju E.; Zhang Y.; Ren J.; Qu X. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6646.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201600868 |
| [68] |
Yang X.; Yang Y.; Gao F.; Wei J.-J.; Qian C.-G.; Sun M.-J. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 4334.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b00934 |
| [69] |
Cai Z.; Zhang Y.; Jiang L.; Zhu J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 481. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20120583 |
|
( 蔡政, 张颖雯, 姜立萍, 朱俊杰, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 481.)
|
|
| [70] |
Cheng Y.; Cheng C.; Yao J.; Yu Y.; Liu Y.; Zhang H.; Miao L.; Wei H. Adv. Therap. 2021, 4, 2100081.
doi: 10.1002/adtp.v4.9 |
| [71] |
Qiu H.; Gong H.; Bao Y.; Jiang H.; Tong W. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 457.
doi: 10.1039/D1BM01525G |
| [72] |
Liu Y.; Cheng Y.; Zhang H.; Zhou M.; Yu Y.; Lin S.; Jiang B.; Zhao X.; Miao L.; Wei C.-W.; Liu Q.; Lin Y.-W.; Du Y.; Butch C. J.; Wei H. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb2695.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb2695 |
| [73] |
Lin S.; Zhao H.; Xu C.; Zhang P.; Mei X.; Jiang D. Mater. Design 2023, 225, 111465.
|
| [74] |
Ma Y.; Tian Z.; Zhai W.; Qu Y. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 10328.
doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4666-y |
| [75] |
Zeng F.; Shi Y.; Wu C.; Liang J.; Zhong Q.; Briley K.; Xu B.; Huang Y.; Long M.; Wang C.; Chen J.; Tang Y.; Li X.; Jiang M.; Wang L.; Xu Q.; Yang L.; Chen P.; Duan S.; Xie J.; Li C.; Wu Y. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 107.
doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01319-7 |
| [76] |
Cheng C.; Cheng Y.; Zhao S.; Wang Q.; Li S.; Chen X.; Yang X.; Wei H. Bioconjugate Chem. 2022, 33, 248.
doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.1c00583 |
| [77] |
Zhang S.; Ermann J.; Succi M. D.; Zhou A.; Hamilton M. J.; Cao B.; Korzenik J. R.; Glickman J. N.; Vemula P. K.; Glimcher L. H.; Traverso G.; Langer R.; Karp J. M. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 300ra12.
|
| [78] |
Li M.; Liu J.; Shi L.; Zhou C.; Zou M.; Fu D.; Yuan Y.; Yao C.; Zhang L.; Qin S.; Liu M.; Cheng Q.; Wang Z.; Wang L. Bioactive Mater. 2023, 25, 95.
|
| [79] |
Zhao S.; Li Y.; Liu Q.; Li S.; Cheng Y.; Cheng C.; Sun Z.; Du Y.; Butch C. J.; Wei H. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004692.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v30.45 |
| [80] |
Naha P. C.; Hsu J. C.; Kim J.; Shah S.; Bouche M.; Si-Mohamed S.; Rosario-Berrios D. N.; Douek P.; Hajfathalian M.; Yasini P.; Singh S.; Rosen M. A.; Morgan M. A.; Cormode D. P. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 10187.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c03457 |
| [81] |
Liang M.; Yan X. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2190.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00140 |
| [82] |
Zhang Z.; Zhang X.; Liu B.; Liu J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5412.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b00601 |
| [83] |
Ji S.; Jiang B.; Hao H.; Chen Y.; Dong J.; Mao Y.; Zhang Z.; Gao R.; Chen W.; Zhang R.; Liang Q.; Li H.; Liu S.; Wang Y.; Zhang Q.; Gu L.; Duan D.; Liang M.; Wang D.; Yan X.; Li Y. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 407.
doi: 10.1038/s41929-021-00609-x |
| [84] |
Gao L.; Fan K.; Yan X. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3207.
doi: 10.7150/thno.19738 |
| [85] |
Yuan R.; Li Y.; Han S.; Chen X.; Chen J.; He J.; Gao H.; Yang Y.; Yang S.; Yang Y. ACS Cent. Sci. 2022, 8, 10.
doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.1c00866 |
| [86] |
Fan K.; Wang H.; Xi J.; Liu Q.; Meng X.; Duan D.; Gao L.; Yan X. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 424.
doi: 10.1039/C6CC08542C |
| [87] |
Liu Y.; Xu B.; Lu M.; Li S.; Guo J.; Chen F.; Xiong X.; Yin Z.; Liu H.; Zhou D. Bioactive Mater. 2022, 12, 246.
|
| [88] |
Xu B.; Li S.; Zheng L.; Liu Y.; Han A.; Zhang J.; Huang Z.; Xie H.; Fan K.; Gao L.; Liu H. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107088.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v34.15 |
| [89] |
Singh B.; Gawande M. B.; Kute A. D.; Varma R. S.; Fornasiero P.; McNeice P.; Jagadeesh R. V.; Beller M.; Zboril R. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 13620.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00158 |
| [90] |
Jiang B.; Liang M. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 174.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v39.1 |
| [91] |
Zhao J.; Cai X.; Gao W.; Zhang L.; Zou D.; Zheng Y.; Li Z.; Chen H. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 26108.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b10345 |
| [92] |
Zhao J.; Gao W.; Cai X.; Xu J.; Zou D.; Li Z.; Hu B.; Zheng Y. Theranostics 2019, 9, 2843.
doi: 10.7150/thno.33727 |
| [93] |
Fan L.; Sun P.; Huang Y.; Xu Z.; Lu X.; Xi J.; Han J.; Guo R. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 1147.
doi: 10.1021/acsabm.9b01079 |
| [94] |
Lu N.; Yan X.; Gu Y.; Zhang T.; Liu Y.; Song Y.; Xu Z.; Xing Y.; Li X.; Zhang Z.; Zhai S. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 395, 139197.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.139197 |
| [95] |
Sun W.; Wang N.; Zhou X.; Sheng Y.; Su X. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 363.
doi: 10.1007/s00604-022-05446-8 |
| [96] |
Liang X.; Han L. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2001933.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v30.28 |
| [97] |
Ma C.-B.; Xu Y.; Wu L.; Wang Q.; Zheng J.-J.; Ren G.; Wang X.; Gao X.; Zhou M.; Wang M.; Wei H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202116170.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v61.25 |
| [98] |
Li W.; Song Y.; Liang X.; Zhou Y.; Xu M.; Lu Q.; Wang X.; Li N. Biomaterials 2021, 276, 121063.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121063 |
| [99] |
Sun L.; Li W.; Liu Z.; Zhou Z.; Feng Y. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139870.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.139870 |
| [100] |
Zhang C.; Wang H.; Yang X.; Fu Z.; Ji X.; Shi Y.; Zhong J.; Hu W.; Ye Y.; Wang Z.; Ni D. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabp9882.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abp9882 |
| [101] |
Wu J.; Yu Y.; Cheng Y.; Cheng C.; Zhang Y.; Jiang B.; Zhao X.; Miao L.; Wei H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 1227.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v60.3 |
| [102] |
Song J. H.; Yoon T.; Lee S.-M.; Mun C. H.; Kim D.; Han J.; Kim J.-W.; Bae Y.; Kim T.; Park Y. N.; Cho M.-H.; Park Y.-B.; Yoo K.-H. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2107433.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v32.2 |
| [103] |
Tejwan N.; Saini A. K.; Sharma A.; Singh T. A.; Kumar N.; Das J. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 132.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.12.023 |
| [104] |
Yuxin X.; Laipeng S.; Kang L.; Haipeng S.; Zonghua W.; Wenjing W. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 5857.
doi: 10.1007/s00216-022-04149-6 |
| [105] |
Zhuo S.; Fang J.; Li M.; Wang J.; Zhu C.; Du J. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 745.
doi: 10.1007/s00604-019-3887-6 |
| [106] |
Cong W.; Bai R.; Li Y.-F.; Wang L.; Chen C. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 34725.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b12319 |
| [107] |
Maity S.; Dhar B. B. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 1296.
doi: 10.1039/D1CY02224E |
| [108] |
Huang Y.; Su E.; Ren J.; Qu X. Nano Today 2021, 38, 101205.
doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2021.101205 |
| [109] |
Tian R.; Ma H.; Ye W.; Li Y.; Wang S.; Zhang Z.; Liu S.; Zang M.; Hou J.; Xu J.; Luo Q.; Sun H.; Bai F.; Yang Y.; Liu J. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2204025.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v32.36 |
| [110] |
Huang Y.; Liu C.; Pu F.; Liu Z.; Ren J.; Qu X. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 3082.
doi: 10.1039/C7CC00045F |
| [111] |
Zhang Z.; Yan A.; Xu Z.; Tian R.; Hou C.; Luo Q.; Sun H.; Xu J.; Yu S.; Wang T.; Liu J. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140165.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.140165 |
| [112] |
Shi C.; Yue F.; Shi F.; Qin Q.; Wang L.; Wang G.; Mu L.; Liu D.; Li Y.; Yu T.; She J. J. Inflammation Res. 2021, 14, 85.
doi: 10.2147/JIR.S288412 |
| [113] |
Ala M.; Kheyri Z. Nutrition 2021, 85, 111153.
doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2021.111153 |
| [114] |
Zhang C.; Li Q.; Shan J.; Xing J.; Liu X.; Ma Y.; Qian H.; Chen X.; Wang X.; Wu L.-M.; Yu Y. Acta Biomater. 2023, 160, 252.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.02.016 |
| [115] |
Guo H.; Guo H.; Xie Y.; Chen Y.; Lu C.; Yang Z.; Zhu Y.; Ouyang Y.; Zhang Y.; Wang X. Redox Biol. 2022, 56, 102441.
doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102441 |
| [116] |
Zhu D.; Wu H.; Jiang K.; Xu Y.; Miao Z.; Wang H.; Ma Y. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2203160.
doi: 10.1002/adhm.v12.12 |
| [117] |
Wang X.; Wang H.; Zhou S. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 11751.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c03219 |
| [118] |
He D.; Yan M.; Sun P.; Sun Y.; Qu L.; Li Z. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2994.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2021.03.078 |
| [119] |
Lu J.; Mao Y.; Feng S.; Li X.; Gao Y.; Zhao Q.; Wang S. Acta Biomater. 2022, 148, 310.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.06.001 |
| [120] |
Gao W.; He J.; Chen L.; Meng X.; Ma Y.; Cheng L.; Tu K.; Gao X.; Liu C.; Zhang M.; Fan K.; Pang D.-W.; Yan X. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 160.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-35828-2 |
| [121] |
Liu C.; Fan W.; Cheng W.-X.; Gu Y.; Chen Y.; Zhou W.; Yu X.-F.; Chen M.; Zhu M.; Fan K.; Luo Q.-Y. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213856.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v33.19 |
| [122] |
Gao W.; He J.; Chen L.; Meng X.; Ma Y.; Cheng L.; Tu K.; Gao X.; Liu C.; Zhang M.; Fan K.; Pang D.-W.; Yan X. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 160.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-35828-2 |
| [123] |
Guo X.; Huang H.; Cui R.; Wang D.; Liu J.; Wang D.; Liu S.; Zhao Y.; Dong J.; Sun B. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 3418.
doi: 10.1021/acsabm.2c00361 |
| [124] |
Ma W.; Xue Y.; Guo S.; Jiang Y.; Wu F.; Yu P.; Mao L. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 5115.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC01840F |
| [125] |
Ma Y.; Gao W.; Zhang Y.; Yang M.; Yan X.; Zhang Y.; Li G.; Liu C.; Xu C.; Zhang M. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 6358.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c21700 |
| [126] |
Huang Q.; Yang Y.; Zhu Y.; Chen Q.; Zhao T.; Xiao Z.; Wang M.; Song X.; Jiang Y.; Yang Y.; Zhang J.; Xiao Y.; Nan Y.; Wu W.; Ai K. Small 2023, 19, 2207350.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v19.19 |
| [1] | 殷雪旸, 顾恺, 邵正中. 载药蛋白质/聚苯硼酸复合纳米微球制备及其释药性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 116-123. |
| [2] | 税子怡, 何娜娜, 陈黎, 赵炜, 陈曦. 多孔钙钛矿型氧还原催化剂在柔性铝空气电池中的应用研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(6): 557-564. |
| [3] | 李威, 冉铁成, 张瑜, 何威, 马继飞, 汪启胜, 张继超, 诸颖. SiO2介导的5 nm金颗粒的高效富集及其催化活性研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(2): 170-176. |
| [4] | 楚婉怡, 唐笑, 李振, 林景诚, 钱觉时. 液相合成超薄TiO2纳米片微结构影响因素研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(7): 549-555. |
| [5] | 韩若冰, 芦姗, 王艳杰, 张雪华, 吴强, 贺涛. SO4-和I-共掺杂的聚苯胺对电极在染料敏化太阳电池中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(10): 1061-1068. |
| [6] | 梁滢, 俞瀚, 黄清明, 张新奇, 俞建长. 硅藻土辅助制备有序介孔碳及其电催化性能[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(18): 1939-1944. |
| [7] | 汤静, 何建平, 王涛, 郭云霞, 薛海荣. 石墨化的有序介孔碳的制备及其作为载体的Pt催化剂对甲醇的电催化氧化[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(15): 1751-1759. |
| [8] | 马雁. Ni3Al箔在甲烷重整反应中的催化性能[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(02): 122-126. |
| [9] | 任小娟,韩满意,李瀛,谢志翔. 3β-羟基-24-降胆-5-烯-23-酸的合成[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(14): 1700-1704. |
| [10] | 龙绘锦,4, 孟庆巨, 元晶, 杨文胜, 曹亚安. B离子掺杂TiO2催化剂(TiO2-xBx)光催化活性的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(6): 657-661. |
| [11] | 成旦红,洪亮铭,吕士银,姬学彬,印仁和. 电解煤浆制氢钛基阳极铂铁合金催化剂的制备及电催化活性研究[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(5): 511-514. |
| [12] | 雷雪飞,薛向欣. 不同复合体系对含钛高炉渣光催化还原Cr(VI)的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(22): 2539-2546. |
| [13] | 沈星灿,郭为民,梁宏,张来军,胡瑞祥,王卓渊. 微波载银对纳米二氧化钛相变及光催化性能的增效作用[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(1): 49-55. |
| [14] | 张伟, 罗云敬, 钟儒刚, 郑大威, 佘远斌. 四苯基钴卟啉化合物催化过亚硝酸根分解的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(6): 557-560. |
| [15] | 印仁和, 吕士银, 姬学彬, 洪亮铭, 曹为民, 张新胜. 电解煤浆制氢阳极的制备及电催化活性研究[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(24): 2847-2852. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
