化学学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 77 ›› Issue (11): 1177-1183.DOI: 10.6023/A19070276 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2019-07-26
发布日期:2019-09-24
通讯作者:
于淑君
E-mail:sjyu@ncepu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Shi Leia, Pang Hongweia, Wang Xiangxueb, Zhang Panb, Yu Shujuna*( )
)
Received:2019-07-26
Published:2019-09-24
Contact:
Yu Shujun
E-mail:sjyu@ncepu.edu.cn
文章分享

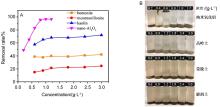
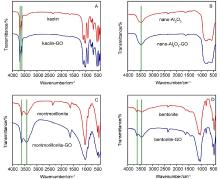
氧化石墨烯(GO)由于具有优异的物理化学性质,被广泛应用于能源化工、环境修复、纳米材料、液相催化等领域.与此同时,GO在应用的过程中不可避免会排放到自然界中,释放到环境中的毒性可能导致生物系统的不稳定性.因此,本文系统研究了几种常见阳离子(Na+、K+、Ca2+、Mg2+),阴离子(PO43-、SO42-、CO32-、HCO3-、Cl-)和粘土矿物(蒙脱石、高岭土、膨润土、纳米氧化铝)在不同浓度下对GO聚沉的影响,并以FTIR表征聚沉GO前后的粘土矿物.实验结果表明,阳离子具有较强的GO聚沉能力,且不同价态阳离子的聚沉能力有着较大差异.经分析,GO在水溶液中的电性为负,阳离子作为反离子,聚沉行为符合Schulze-Hardy规则,同价态阳离子间聚沉能力存在差异的主要原因是电负性和离子的水合作用.阴离子则起到增加GO水溶液稳定性的作用,且阳离子的聚沉作用高于阴离子的稳定作用.具有相同价态阴离子的钠盐聚沉GO的能力也存在差异,主要原因是HCO3-和CO32-的水解作用使得其负电荷数降低,稳定GO的能力下降.粘土矿物含有羟基和金属氧键,可与GO发生相互作用.根据粘土矿物最大聚沉效率的不同,聚沉能力为:纳米氧化铝>高岭土>膨润土>蒙脱土,主要影响因素为粘土矿物在水中的电性.本文有助于了解GO在不同水环境中的聚沉行为,对未来石墨烯工程应用于污染治理具有重要意义.
石磊, 庞宏伟, 王祥学, 张盼, 于淑君. 氧化石墨烯在水体中的迁移转化机制研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(11): 1177-1183.
Shi Lei, Pang Hongwei, Wang Xiangxue, Zhang Pan, Yu Shujun. Study on the Migration and Transformation Mechanism of Graphene Oxide in Aqueous Solutions[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2019, 77(11): 1177-1183.
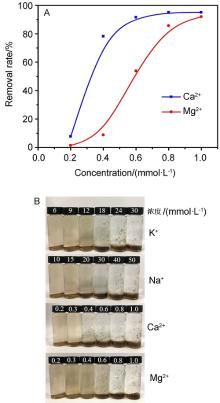
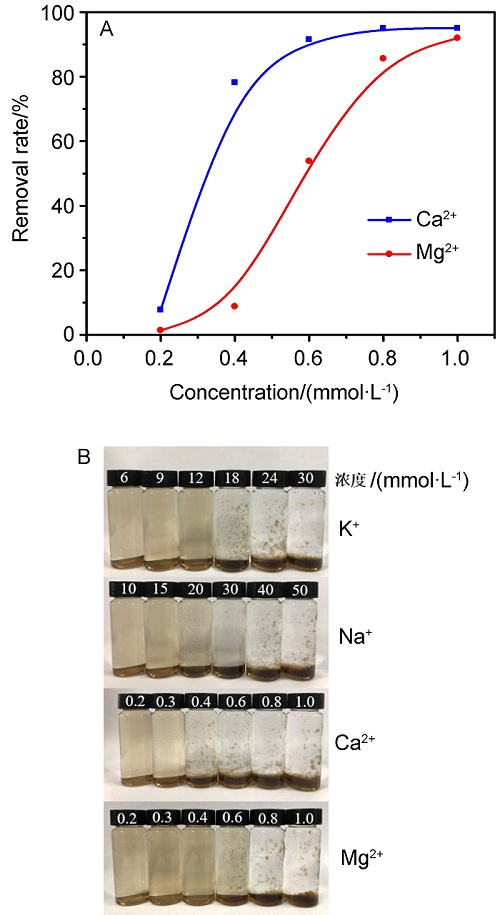
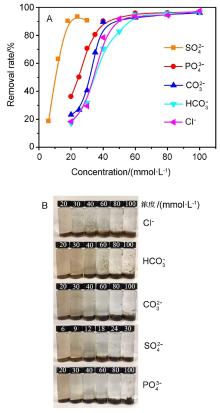
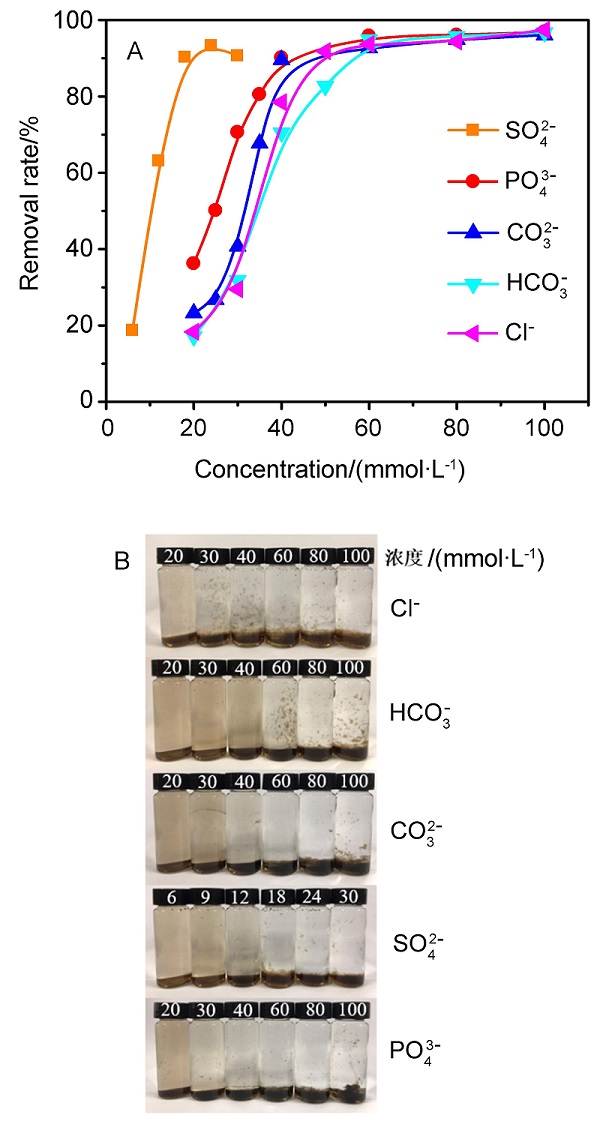


| [1] |
Loh K. P.; Bao Q. L.; Ang P. K.; Yang J. X. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 2277.
doi: 10.1039/b920539j |
| [2] |
Dreyer D. R.; Park S. J.; Bielawski C. W.; Ruoff R. S. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 228.
doi: 10.1039/B917103G |
| [3] |
Chen D.; Feng H.; Li J. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 6027.
doi: 10.1021/cr300115g |
| [4] |
Stoller M. D.; Park S. J.; Zhu Y. W.; An j.; Ruoff R. S. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3498.
doi: 10.1021/nl802558y |
| [5] |
Zhao K. L.; Hao Y.; Zhu M.; Cheng G. S. Acta Chim. Sinica. 2018, 76, 168.
doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB201707111 |
|
赵 克丽; 郝 莹; 朱 墨; 程 国胜 化学学报 2018, 76, 168.
doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB201707111 |
|
| [6] |
Zhang S. W.; Zhang J.; Wu S. D.; lv W.; Kang F. Y.; Yang Q. H. Acta. Chim. Sinica. 2017, 75, 163.
doi: 10.11862/CJIC.2017.023 |
|
张 思伟; 张 俊; 吴 思达; 吕 伟; 康 飞宇; 杨 全红 化学学报 2017, 75, 163.
doi: 10.11862/CJIC.2017.023 |
|
| [7] |
Zhong G. Y.; Wang H. J.; Yu H.; Peng F. Acta Chim. Sinica. 2017, 75, 943
doi: 10.6023/A17040183 |
|
钟 国玉; 王 红娟; 余 皓; 彭 峰 化学学报 2017, 75, 943
doi: 10.6023/A17040183 |
|
| [8] |
Wang X.; Li Y. B.; Du L. Y.; Gao F. J.; Wu Q.; Yang L. J.; Chen Q.; Wang X. J.; Hu Z. Acta Chim. Sinica. 2018, 76, 627.
doi: 10.11862/CJIC.2018.081 |
|
王 啸; 李 有彬; 杜 玲玉; 高 福杰; 吴 强; 杨 立军; 陈 强; 王 喜章; 胡 征 化学学报 2018, 76, 627.
doi: 10.11862/CJIC.2018.081 |
|
| [9] |
Lu J. H.; Tan S. Z.; Zhu Y. Q.; Li W.; Chen T. X.; Wang Y.; Liu C. Acta Chim. Sinica. 2019, 77, 253
doi: 10.6023/A18100433 |
|
卢 静荷; 谭 淑珍; 朱 雨清; 李 伟; 陈 天啸; 王 瑶; 刘 陈 化学学报 2019, 77, 253
doi: 10.6023/A18100433 |
|
| [10] |
Ma W. H.; Chang Y. Z.; Han G. Y.; Xiao Y. M.; Fu D. Y.; Chang Y. H. Chinese J. Chem. 2017, 35, 1844.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.201700398 |
| [11] |
Yang X. L.; Cai H. Y.; Bao M. Y.; Yu J. Q.; Lu J. R.; Li Y. M. Chinese J. Chem. 2017, 35, 1549.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.201700202 |
| [12] |
Li M. Y.; Liu R. Q.; Han G. Y.; Tian Y. N.; Chang Y. Z.; Xiao Y. M. Chinese J. Chem. 2017, 35, 1405.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.201700061 |
| [13] |
Song C. Y.; Sun X.; Ye K.; Zhu K.; Cheng H.; Yan J.; Cao D. X.; Wang G. L. Acta. Chim. Sinica. 2017, 75, 1003
doi: 10.6023/A17070298 |
|
宋 聪颖; 孙 逊; 叶 克; 朱 凯; 程 魁; 闫 俊; 曹 殿学; 王 贵领 化学学报 2017, 75, 1003
doi: 10.6023/A17070298 |
|
| [14] |
Liao K. H.; Lin Y. S.; Macosko C. W.; Haynes C. L. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2607.
doi: 10.1021/am200428v |
| [15] |
Gao Y.; Chen K.; Ren X. M.; Ahmed A.; Tasawar H.; Chen C. L. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12208.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b02234 |
| [16] |
Gao Y; Wu J. C.; Ren X. M.; Tan X. L. Tasawar H.; Ahmed A.; Cheng C.; Chen C. L. Environ. Sci.:Nano 2017, 4, 1016.
doi: 10.1039/C7EN00052A |
| [17] |
Gao Y.; Ren X. M.; Wu J. C.; Tasawar H.; Ahmed A.; Cheng C.; Chen C. l. Environ. Sci.:Nano 2018, 5, 362.
doi: 10.1039/C7EN01012E |
| [18] |
Wang J.; Yao W.; Gu P. C.; Yu S. J.; Wang X. X.; Du Y.; Wang H. Q.; Chen Z. S.; Hayat T.; Wang X. K. Cellulose 2016, 24, 85
doi: 10.1007/s10570-016-1117-5 |
| [19] |
Vallabani N. V. S.; Mittal S.; Shukla R. K.; Pandey A. K.; Dhakate S. R.; Pasricha R.; Dhawan A. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 106.
doi: 10.1166/jbn.2011.1224 |
| [20] |
Akhavan O.; Ghaderi E. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5731.
doi: 10.1021/nn101390x |
| [21] |
Hu J.; Zhang C. X.; Jiang L.; Fang S. D.; Zhang X. D.; Wang X. K.; Meng Y. D. J. Power Sources 2014, 248, 831.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.09.099 |
| [22] |
Zaghouane-Boudiaf H.; Boutahala M.; Arab L. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 187, 142.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.112 |
| [23] |
Wang J.; Wang X. X.; Tan L. Q.; Chen Y. T.; Hayat T.; Hu J.; Alsaedi A.; Ahmad B.; Guo W.; Wang X. K. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 297, 106.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.012 |
| [24] |
Meunier N.; Drogui P.; Montane C.; Hausler R.; Mercier G.; Blais J. F. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 581.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.02.050 |
| [25] |
Qiang S. R.; Wang M. Y.; Liang J. J.; Zhao X. L.; Fan Q. H.; Geng R. Y.; Luo D. X.; Li Z. B.; Zhang L. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 122016.
doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122016 |
| [26] |
Yang K. J.; Chen B. L.; Zhu X. Y.; Xing B. S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11066.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b04235 |
| [27] |
Chowdhury I.; Mansukhani N. D.; Guiney L. M.; Hersam M. C.; Bouchard D. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10886.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b01866 |
| [28] |
Zeng Z. Y.; Wang Y. L.; Zhou Q. B.; Yang K.; Lin D. H. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 366.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.112 |
| [29] |
Zhao J.; Liu F. F.; Wang Z. Y.; Cao X. S.; Xing B. S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2849.
doi: 10.1021/es505605w |
| [30] |
Liang J. J.; Li P.; Zhao X. L.; Liu Z. Y.; Fan Q. H.; Li Z.; Wang D. Q. Nanoscale 2018, 3, 1383
doi: 10.1039/c0nr00814a |
| [31] |
Park C. M.; Chu K. H.; Heo J.; Her N.; Jang M.; Son A.; Yoon Y. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 309, 133.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.02.006 |
| [32] | Li N.; Ma J. Z.; Bao Y. Chem. Res. 2009, 20, 98 |
| 李 娜; 马 建中; 鲍 艳 化学研究 2009, 20, 98 | |
| [33] |
Huang G. X.; Guo H. Y.; Zhao J.; Liu Y. H.; Xing B. S. Water Res. 2012, 102, 313
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.06.050 |
| [34] |
Anirudhan T. S.; Ramachandran M. Proc. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 95, 215.
doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2015.03.003 |
| [35] |
Chowdhury I.; Duch M. C.; Mansukhani N. D.; Hersam M. C.; Bouchard D. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6288.
doi: 10.1021/es400483k |
| [36] |
Wu L.; Liu L.; Gao B.; Muñoz-Carpena R.; Zhang M.; Chen H.; Zhou Z. H.; Wang H. Langmuir 2013, 29, 15174.
doi: 10.1021/la404134x |
| [37] |
Ma J. C.; Dougherty D. A. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 1303.
doi: 10.1021/cr9603744 |
| [38] |
Trivedi P.; Axe L.; Dyer J. Colloids Surf. A 2001, 191, 107.
doi: 10.1016/S0927-7757(01)00768-3 |
| [39] |
Raza G.; Amjad M.; Kaur I.; Wen D. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8462.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b05746 |
| [40] |
Volkov A. G.; Paula D. W.; Dreamer D. W. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1997, 42, 153.
doi: 10.1016/S0302-4598(96)05097-0 |
| [41] |
Tansel B.; Sager J.; Rector T.; Garland J.; Strayer R. F.; Levine L. F.; Roberts M.; Hummerick M.; Bauer J. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 51, 40.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2005.12.020 |
| [42] |
Abdelmeguid A. E.; Aboelfetoh E. F.; Ebeid E. M. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 738.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.04.137 |
| [43] |
Tahir S. S.; Rauf N. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 1842.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.10.033 |
| [44] |
Hummers W. S.; Offeman R. E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339.
doi: 10.1021/ja01539a017 |
| [1] | 侯威, 么艳彩, 张礼知. 电化学还原去除水中含氧酸根离子研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 979-989. |
| [2] | 刘稳, 王昱捷, 杨慧琴, 李成杰, 吴娜, 颜洋. 离子液体非共价诱导制备碳纳米管/石墨烯集流体用于钠金属负极[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1379-1386. |
| [3] | 廉纬, 方泽铠, 涂大涛, 李嘉尧, 韩思远, 李仁富, 商晓颖, 陈学元. 模板法控制合成AgInSe2:Zn2+近红外荧光量子点及其生物标记应用※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(5): 625-632. |
| [4] | 邱凯, 严铭霞, 赵守旺, 安胜利, 王玮, 贾桂霄. Al掺杂的锂离子电池层状正极材料Li(Li0.17Ni0.17Al0.04Fe0.13Mn0.49)O2结构稳定性及氧离子氧化的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(9): 1146-1153. |
| [5] | 韩旭, 张留伟, 张强, 睢晞航, 钱明, 陈麒先, 王静云. 活性氧响应的新型阳离子共聚物构建及其基因递送性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 794-802. |
| [6] | 李宛飞, 李鑫, 范海燕, 肖建华, 刘倩倩, 程淼, 胡敬, 魏涛, 吴正颖, 凌云, 刘波, 张跃钢. 非亲核镁硫电池电解液的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(5): 628-640. |
| [7] | 董雪, 曹鸿, 徐雷, 王志鹏, 陈靖, 徐超. 镎和钚与环境中无机阴离子的配位化学研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(12): 1415-1424. |
| [8] | 余梦, 张子俊, 朱国委, 谷振华, 段玉霖, 余良翀, 高冠斌, 孙涛垒. Ag2S基近红外II区荧光量子点的水相合成优化探究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(10): 1281-1285. |
| [9] | 马明昊, 徐明, 刘思金. 氧化石墨烯的表面化学修饰及纳米-生物界面作用机理[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(9): 877-887. |
| [10] | 黄荣谊, 沈琼, 张超, 张少勇, 徐衡. 过渡金属催化有机腈和叠氮酸钠反应机理的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(6): 565-571. |
| [11] | 宋光捷, 武调弟, 刘福鑫, 张彬雁, 刘秀辉. 壳聚糖/氮掺杂还原氧化石墨烯修饰电极对黄嘌呤的检测及尿酸抑制的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(1): 82-88. |
| [12] | 宋学霞, 李继成, 李朝晖, 李喜飞, 丁燕怀, 肖启振, 雷钢铁. 钾掺杂对钒酸钠纳米片储钠性能的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(7): 625-633. |
| [13] | 卢静荷, 谭淑珍, 朱雨清, 李伟, 陈天啸, 王瑶, 刘陈. 荧光核酸适配体功能化氧化石墨烯生物传感器用于快速检测氯霉素[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(3): 253-256. |
| [14] | 李琦, 贾怡, 李峻柏. 二苯丙氨酸短肽手性结构的可控组装[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(11): 1173-1176. |
| [15] | 王英辉, 节家龙, 赵红梅, 白羽, 秦佩萱, 宋迪. 实验与理论研究G-四链体中鸟嘌呤自由基阳离子脱质子反应[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(6): 475-482. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||