化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (2): 216-222.DOI: 10.6023/A20090435 上一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2020-09-21
发布日期:2020-11-06
通讯作者:
张欣
作者简介:基金资助:
Si Wang1, Jialing Ma1, Lifang Chen1, Xin Zhang1,*( )
)
Received:2020-09-21
Published:2020-11-06
Contact:
Xin Zhang
Supported by:文章分享

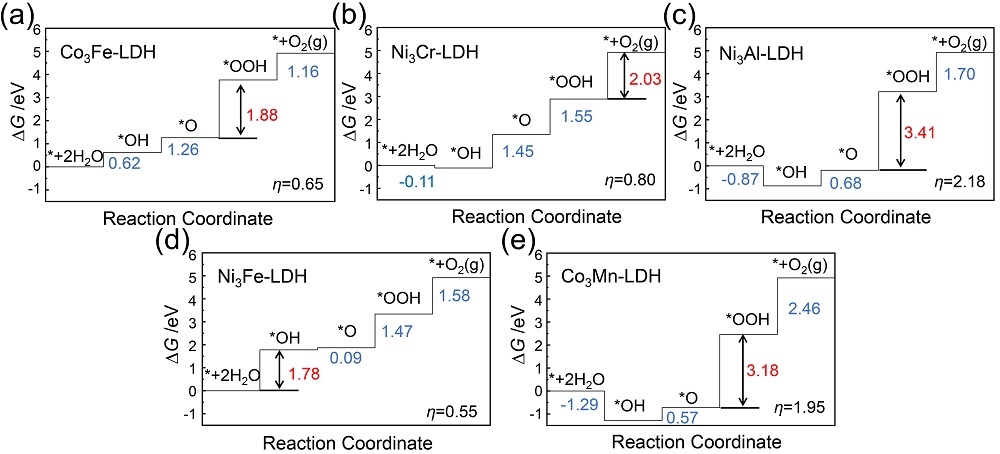
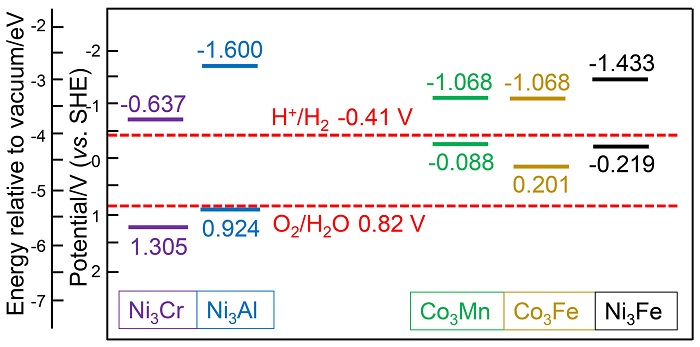
双金属氢氧化物(LDH)是催化析氧反应(OER)活性最佳的一类催化剂, 其中揭示双金属位点的协同作用是进一步提升其电催化、光催化性能的关键. 本工作采用密度泛函方法, 从理论计算角度探究了五种MN3+-LDH (M2+= Co2+、Ni2+, N3+=Al3+、Cr3+、Mn3+、Fe3+)在催化OER中的反应机制和双金属位点的协同作用. 研究结果表明, 在电催化OER中, 氧物种以桥连的方式同时吸附在双金属位点上, 双位点协同作用降低了OER中的电势决定步骤的自由能变, 并有效降低了电催化OER的过电位. Ni3Fe-LDH在五种LDH中具有最高的电催化OER活性. 在光催化OER中, 双金属协同作用影响了LDH的带隙、功函数及驱动力, 进而决定了LDH光催化OER的能力. 所研究的五种LDH均为可见光响应, 其中Ni3Cr-LDH由于其驱动力大于过电位而被预测为良好的OER光催化剂.
王思, 马嘉苓, 陈利芳, 张欣. 双金属氢氧化物催化析氧反应的协同机制研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 216-222.
Si Wang, Jialing Ma, Lifang Chen, Xin Zhang. Role of Synergistic Effect in Oxygen Evolution Reaction over Layered Double Hydroxide[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(2): 216-222.
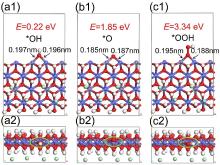


| 双金属氢氧化物 | 原子 | (100)晶面 | (100)-O | (100)-OH | (100)-OOH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co3Mn-LDH | Co | 0.47 | 0.75(0.28) | 0.70(0.23) | 0.69(0.22) |
| Mn | 0.64 | 0.90(0.26) | 0.92(0.28) | 0.83(0.19) | |
| Co3Fe-LDH | Co | 0.49 | 0.78(0.29) | 0.71(0.22) | 0.69(0.20) |
| Fe | 0.61 | 0.90(0.29) | 0.84(0.23) | 0.85(0.24) | |
| Ni3Fe-LDH | Ni | 0.53 | 0.72(0.19) | 0.64(0.11) | 0.68(0.15) |
| Fe | 0.67 | 1.04(0.37) | 0.97(0.30) | 0.94(0.27) |
| 双金属氢氧化物 | 原子 | (100)晶面 | (100)-O | (100)-OH | (100)-OOH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co3Mn-LDH | Co | 0.47 | 0.75(0.28) | 0.70(0.23) | 0.69(0.22) |
| Mn | 0.64 | 0.90(0.26) | 0.92(0.28) | 0.83(0.19) | |
| Co3Fe-LDH | Co | 0.49 | 0.78(0.29) | 0.71(0.22) | 0.69(0.20) |
| Fe | 0.61 | 0.90(0.29) | 0.84(0.23) | 0.85(0.24) | |
| Ni3Fe-LDH | Ni | 0.53 | 0.72(0.19) | 0.64(0.11) | 0.68(0.15) |
| Fe | 0.67 | 1.04(0.37) | 0.97(0.30) | 0.94(0.27) |
| 双金属氢氧化物 | Eg/eV | k-vector of VBM | k-vector of CBM | W/eV | EVBM/eV | ECBM/eV | Edf/eV | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni3Cr-LDH | 1.943 | 0.893 | 0.286 | 4.834 | –5.805 | –3.862 | 0.485 | ||
| Ni3Al-LDH | 2.525 | 0.000 | 0.892 | 4.162 | –5.424 | –2.899 | 0.104 | ||
| Co3Mn-LDH | 1.705 | 0.785 | 0.000 | 3.922 | –4.774 | –3.069 | –0.545 | ||
| Co3Fe-LDH | 1.554 | 1.000 | 0.214 | 3.924 | –4.701 | –3.147 | –0.619 | ||
| Ni3Fe-LDH | 1.214 | 0.892 | 0.000 | 3.674 | 4.281 | –3.067 | –1.039 | ||
| 双金属氢氧化物 | Eg/eV | k-vector of VBM | k-vector of CBM | W/eV | EVBM/eV | ECBM/eV | Edf/eV | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni3Cr-LDH | 1.943 | 0.893 | 0.286 | 4.834 | –5.805 | –3.862 | 0.485 | ||
| Ni3Al-LDH | 2.525 | 0.000 | 0.892 | 4.162 | –5.424 | –2.899 | 0.104 | ||
| Co3Mn-LDH | 1.705 | 0.785 | 0.000 | 3.922 | –4.774 | –3.069 | –0.545 | ||
| Co3Fe-LDH | 1.554 | 1.000 | 0.214 | 3.924 | –4.701 | –3.147 | –0.619 | ||
| Ni3Fe-LDH | 1.214 | 0.892 | 0.000 | 3.674 | 4.281 | –3.067 | –1.039 | ||

| LDH | 有效质量 | |
|---|---|---|
| me*/m0 | mh*/m0 | |
| Co3Fe-LDH | 6.01 | 3.62 |
| Ni3Cr-LDH | 2.61 | 8.22 |
| Ni3Al-LDH | 20.55 | 14.17 |
| Ni3Fe-LDH | 46.48 | 79.21 |
| Co3Mn-LDH | 7.96 | 4.98 |
| LDH | 有效质量 | |
|---|---|---|
| me*/m0 | mh*/m0 | |
| Co3Fe-LDH | 6.01 | 3.62 |
| Ni3Cr-LDH | 2.61 | 8.22 |
| Ni3Al-LDH | 20.55 | 14.17 |
| Ni3Fe-LDH | 46.48 | 79.21 |
| Co3Mn-LDH | 7.96 | 4.98 |
| [1] |
Meng X.; Yang Y.; Chen L.; Xu M.; Zhang X.; Wei M. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 4226.
|
| [2] |
Yu J.; Yang Y.; Wei M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 1129. (in Chinese)
|
|
余俊, 杨宇森, 卫敏, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 1129.
|
|
| [3] |
Gu P.; Song S.; Zhang S.; Wei B.; Wen T.; Wang X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 701. (in Chinese)
|
|
顾鹏程, 宋爽, 张塞, 韦犇犇, 文涛, 王祥科, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 701.
|
|
| [4] |
Bing W.; Zheng L.; He S.; Rao D.; Xu M.; Zheng L.; Wang B.; Wang Y.; Wei M. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 656.
|
| [5] |
Li X.; Jiang P.; Lu Y.; Zhang W.; Dong Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 544. (in Chinese)
|
|
李小磊, 蒋平平, 卢云, 张伟杰, 董玉明, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 544.
|
|
| [6] |
Wang N.; Pang H.; Yu S.; Gu P.; Song S.; Wang H.; Wang X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 143. (in Chinese)
|
|
王宁, 庞宏伟, 于淑君, 顾鹏程, 宋爽, 王宏青, 王祥科, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 143.
|
|
| [7] |
Xu S.-M. Ph. D. Dissertation, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 2017 (in Chinese).
|
|
徐思民 , 博士论文, 北京化工大学, 北京, 2017.
|
|
| [8] |
Gong M.; Li Y.; Wang H.; Liang Y.; Wu J.; Zhou J.; Wang J.; Regier T.; Wei F.; Dai H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8452.
|
| [9] |
Song F.; Hu X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16481.
|
| [10] |
Corrigan D.A. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1987, 18, 377.
|
| [11] |
Ma W.; Ma R.Z.; Wang C.H.; Liang J.B.; Liu X.H.; Zhou K.C.; Sasaki T. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 1977.
|
| [12] |
Trotochaud L.; Young S.L.; Ranney J.K.; Boettcher S.W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6744.
|
| [13] |
Chen J.Y.C.; Dang L.; Liang H.; Bi W.; Gerken J.B.; Jin S.; Alp A.E.; Stahl S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15090.
|
| [14] |
Ahn H.S.; Bard A.J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 313.
|
| [15] |
Görlin M.; Chernev P.; Araújo J.F.; Reier T.; Dresp S.; Paul B.; Krähnert R.; Dau H.; Strasser P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 5603.
|
| [16] |
Dionigi F.; Zeng Z.; Sinev I.; Merzdorf T.; Deshpande S.; Lopez M.B.; Kunze S.; Zegkinoglou I.; Sarodnik H.; Fan D.; Bergmann A.; Drnec J.; Araujo J.F.; Gliech M.; Teschner D.; Zhu J.; Li W.-X.; Greeley J.; Cuenya B.R.; Strasser P. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2522.
|
| [17] |
Segall M.D.; Lindan P.J.D.; Probert M.J.; Pickard C.J.; Hasnip P.J.; Clark S.J.; Payne M.C. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 2717.
|
| [18] |
Perdew J.P.; Burke K.; Ernzerhof M. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865.
|
| [19] |
Liao P.; Keith J.A.; Carter E.A. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 13296.
|
| [20] |
Alidoust N.; Toroker M.C.; Carter E.A. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 7963.
|
| [21] |
Bajdich M.; García-Mota M.; Vojvodic A.; Nørskov J.K.; Bell A.T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13521.
|
| [22] |
Mosey N.J.; Liao P.; Carter E.A. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 155123.
|
| [23] |
Kronawitter C.X.; Riplinger C.; He X.; Zahl P.; Carter E.A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13283.
|
| [24] |
Kanan D.K.; Carter E.A. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 9876.
|
| [25] |
Anglada J.M.; Bofill J.M. J. Comput. Chem. 2015, 19, 349.
|
| [26] |
Trasatti S. Pure Appl. Chem. 1986, 58, 955.
|
| [27] |
Xu S.-M.; Pan T.; Dou Y.; Yan H.; Zhang S.; Ning F.; Shi W.; Wei M. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 1509.
|
| [28] |
Wang Z.; Zhao J.; Cai Q. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 23113.
|
| [29] |
Kittel C.; Holcomb D.F. Introduction to Solid State Physics, Wiley, New Jersey, 1976.
|
| [30] |
Nozik A.J. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2003, 29, 189.
|
| [31] |
Mom R.V.; Cheng J.; Koper M.T.M.; Sprik M. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 4095.
|
| [32] |
Rossmeisl J.; Qu Z.W.; Zhu H.; Kroes G.J.; Nørskov J.K. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2007, 607, 83.
|
| [33] |
Valdés Á.; Qu Z.; Kroes G . J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 9872.
|
| [34] |
Man I.C.; Su H.Y.; Calle-Vallejo F.; Hansen H.A.; Martinez J.L.; Inoglu N.G.; Kitchin J.; Jaramillo T.F.; Nørskov J.K.; Rossmeisl J. ChemCatChem 2011, 3, 1159.
|
| [35] |
Cavani F.; Trifiro F.; Vaccari A. Catal. Today 1991, 11, 173.
|
| [36] |
Wang L.; Yu Q.; Feng C.; Zhang Y.; Hu J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 39, 1787. (in Chinese)
|
|
王力耕, 余琴, 冯春, 张岩, 胡军, 有机化学, 2019, 39, 1787.
|
|
| [37] |
Bi Y.; Cai Z.; Zhou D.; Tian Y.; Zhang Q.; Zhang Q.; Kuang Y.; Li Y.; Sun X.; Duan X. J. Catal. 2018, 358, 100.
|
| [38] |
Zhang J.; Ma D.; Wei X.; Gong P.; Dai K. Journal of Mudanjiang Normal University. 2017, 2, 52 (in Chinese).
|
|
张金锋, 马东, 韦学玉, 公丕锋, 代凯 , 牡丹江师范学院学报(自然科学版), 2017, 2, 52.
|
|
| [39] |
Zhang J.-F. Ph. D. Dissertation, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, 2016 (in Chinese).
|
|
张金峰 , 博士论文, 武汉理工大学, 武汉, 2016.)
|
| [1] | 王晓, 王星文, 肖乐辉. 单分子荧光成像研究单颗粒纳米催化机制[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 1002-1014. |
| [2] | 王娟, 肖华敏, 谢丁, 郭元茹, 潘清江. 铜掺杂与氮化碳复合氧化锌材料结构和二氧化氮气体传感性质的密度泛函理论计算[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1493-1499. |
| [3] | 马雪璐, 李蒙, 雷鸣. 三核过渡金属配合物在催化反应中的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(1): 84-99. |
| [4] | 田钊炜, 达伟民, 王雷, 杨宇森, 卫敏. 第二代生物柴油制备的多相催化剂的结构设计及研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1322-1337. |
| [5] | 柴贤丹, 陈文发, 闫秋楠, 刘彬文, 姜小明, 郭国聪. Rb2MGe3S8 (M=Zn, Cd): [MGe3S8]2–单元构型变换导致化合物从中心到非心的转变※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(5): 633-639. |
| [6] | 张丹琪, 邵英博, 郑汉良, 周碧莹, 薛小松. 双齿氮配体螯合五价碘试剂介导的苯酚氧化去芳构化机理的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(11): 1394-1400. |
| [7] | 赵彦武, 李星, 张富强, 张祥. 同手性金属有机框架(MOFs)维度的精准调控及荧光性质的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(11): 1409-1414. |
| [8] | 白子昂, 陈瑞兴, 庞宏伟, 王祥学, 宋刚, 于淑君. 硫化纳米零价铁对水中U(VI)的高效去除研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(10): 1265-1272. |
| [9] | 赵晶晶, 张正中, 陈小浪, 王蓓, 邓近远, 张蝶青, 李和兴. 微波诱导组装CuS@MoS2核壳纳米管及其光催化类芬顿反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(9): 961-967. |
| [10] | 薄一凡, 刘玉玉, 常永正, 李银祥, 张效霏, 宋春元, 许卫锋, 曹洪涛, 黄维. 环状芴基张力半导体拉曼光谱理论与实验研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(5): 442-446. |
| [11] | 王宁, 庞宏伟, 于淑君, 顾鹏程, 宋爽, 王宏青, 王祥科. 层状双金属氢氧化物及复合材料对放射性元素铀的吸附及机理研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(2): 143-152. |
| [12] | 杨波, 张永丽. 非均相芬顿体系协同去除复合双污染物: 化学转化, pH影响和机理分析[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(10): 1017-1023. |
| [13] | 王艺霖, 王敏杰, 李静, 魏子栋. 铁镍合金纳米颗粒镶嵌的多级孔氮掺杂碳催化剂的制备及析氧性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(1): 84-89. |
| [14] | 朱纯, 曹泽星. 高效金属双卟啉染料的计算设计及其敏化TiO2半导体复合体系的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(11): 1527-1534. |
| [15] | 严琳, 孔惠, 李在均. 3D石墨烯/镍铝层状双金属氢氧化物的制备及超级电容性能[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(05): 822-828. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||