Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (9): 1097-1106.DOI: 10.6023/A21050219 Previous Articles Next Articles
Special Issue: 分子探针、纳米生物学与生命分析化学
Review
潘立祥a, 黄艳琴a,*( ), 盛况a, 张瑞a,c, 范曲立a, 黄维a,b,*(
), 盛况a, 张瑞a,c, 范曲立a, 黄维a,b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2021-05-17
发布日期:2021-09-17
通讯作者:
黄艳琴, 黄维
作者简介: |
潘立祥, 男, 汉族, 1997年出生于江苏, 2019年本科毕业于盐城工学院, 随后加入南京邮电大学黄艳琴课题组攻读硕士学位, 研究方向为基于近红外有机共轭材料的纳米诊疗剂及其生物应用. |
 |
黄艳琴, 南京邮电大学教授, 2006年获复旦大学博士学位, 2006年7月起就职于南京邮电大学信息材料与纳米技术研究院. 主要研究方向是有机/聚合物光电材料及其在化学与生物传感、生物成像与诊疗中的应用. 承担和参与国家省部级各类项目6项, 在Biosensors and Bioelectronics、ACS Appl. Mater. & Interfaces、Polymer Chemistry、Langmuir等国际期刊上发表SCI论文30余篇. 2016年获江苏省科学技术奖二等奖, 2009年获江苏省科技进步奖二等奖. |
 |
盛况, 男, 汉族, 1996年出生于江苏, 2018年本科毕业于南京工业大学, 随后加入南京邮电大学黄艳琴课题组攻读硕士学位, 研究方向为水溶性共轭材料生物成像和光疗试剂设计、合成与应用. |
 |
张瑞, 2001年7月起就职于东南大学附属中大医院, 从事眼科临床与教学工作, 2019年获得东南大学博士学位. 主要研究方向是眼科新型药物研发及激光在眼科的临床应用. 承担和参与国家自然科学基金、有机电子与信息显示国家重点实验室开放研究基金等科研项目. |
 |
范曲立, 南京邮电大学教授, 2003年于新加坡国立大学获得博士学位, 2003年至2006年在复旦大学工作, 2006年8月起就职于南京邮电大学. 主要研究方向是面向纳米生物医学领域有机半导体材料的制备与临床前的应用研究, 近五年来以第一或通讯作者在Nature Communications、 Journal of the American Chemical Society、 Advanced Materials、 ACS Nano 等国际期刊发表SCI论文80余篇; 承担和参与国家省部级各类项目10余项, 2012年获国家优秀青年科学基金, 2013年获国家自然科学二等奖(排名第四), 2014年入选国家百千万人才工程, 2019年入选国家万人计划中青年科技创新领军人才. |
 |
黄维, 教授, 博导, 有机电子、塑料电子、印刷电子、生物电子及柔性电子学家, 中国科学院院士、俄罗斯科学院外籍院士、亚太材料科学院院士、东盟工程与技术科学院外籍院士、巴基斯坦科学院外籍院士. 历任复旦大学先进材料研究院院长, 南京邮电大学副校长、党委常委, 南京工业大学校长、党委副书记, 2017任西北工业大学党委常委、常务副校长. 曾两次获得国家自然科学奖二等奖、三次获得高等学校科学研究优秀成果奖(科学技术)自然科学奖一等奖、多次获得江苏省科学技术奖一等奖和二等奖, 以及何梁何利基金“科学与技术进步奖”. |
基金资助:
Lixiang Pana, Yanqin Huanga( ), Kuang Shenga, Rui Zhanga,c, Quli Fana, Wei Huanga,b(
), Kuang Shenga, Rui Zhanga,c, Quli Fana, Wei Huanga,b( )
)
Received:2021-05-17
Published:2021-09-17
Contact:
Yanqin Huang, Wei Huang
Supported by:Share
Lixiang Pan, Yanqin Huang, Kuang Sheng, Rui Zhang, Quli Fan, Wei Huang. Applications of Hyaluronic Acid Nanomaterials in Fluorescence/Photoacoustic Imaging and Phototherapy[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(9): 1097-1106.
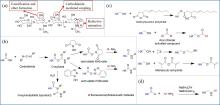
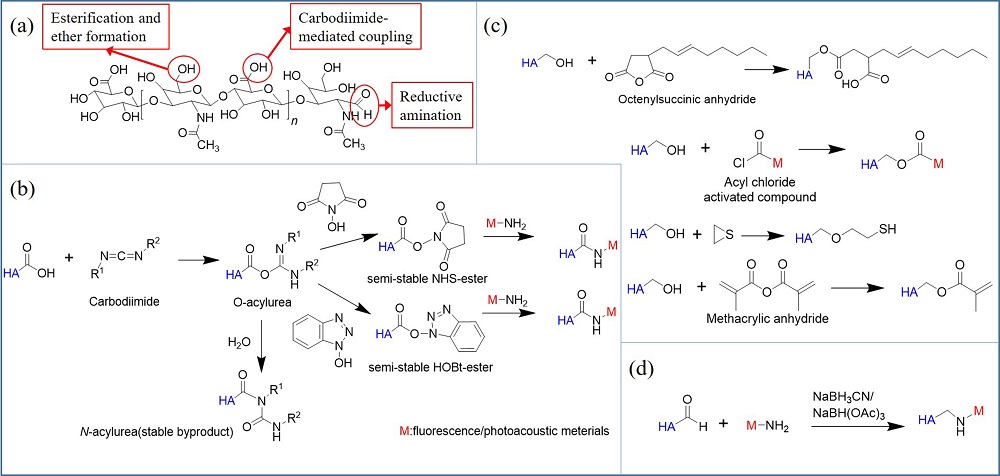
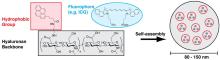
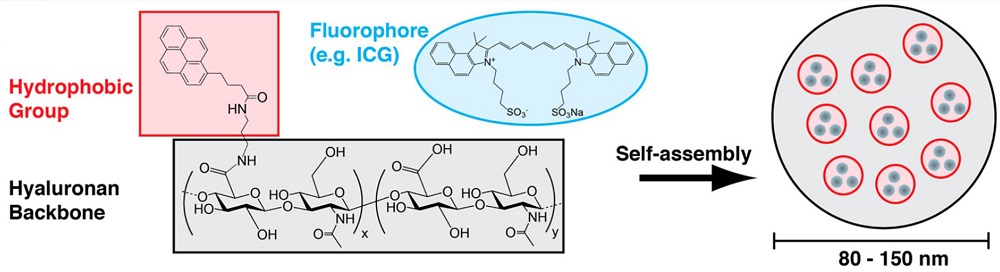
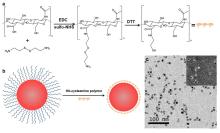


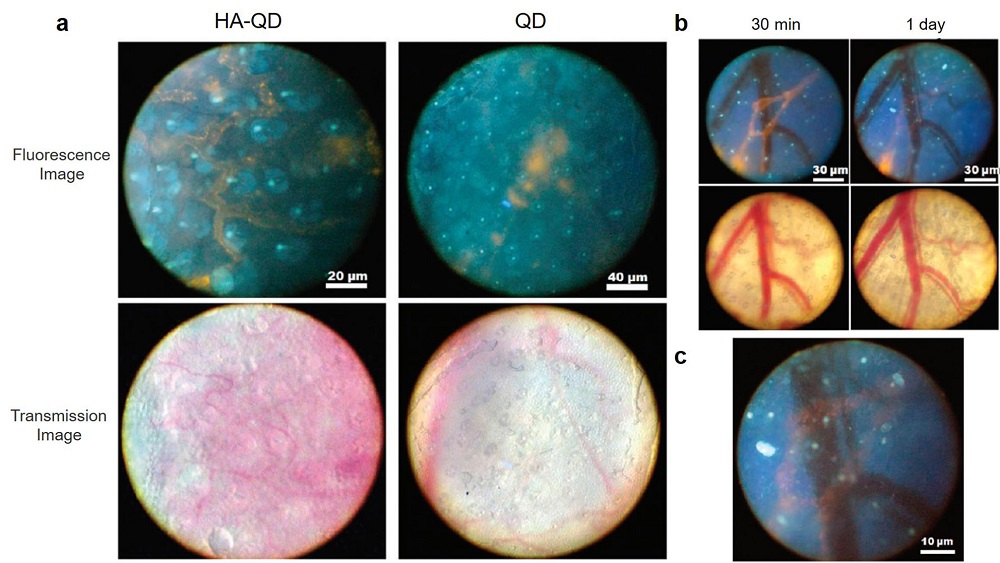
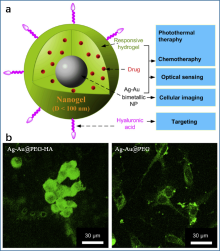

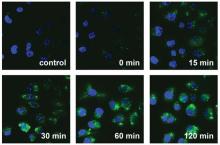

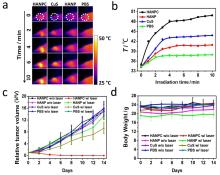

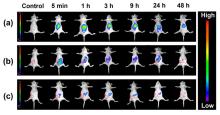


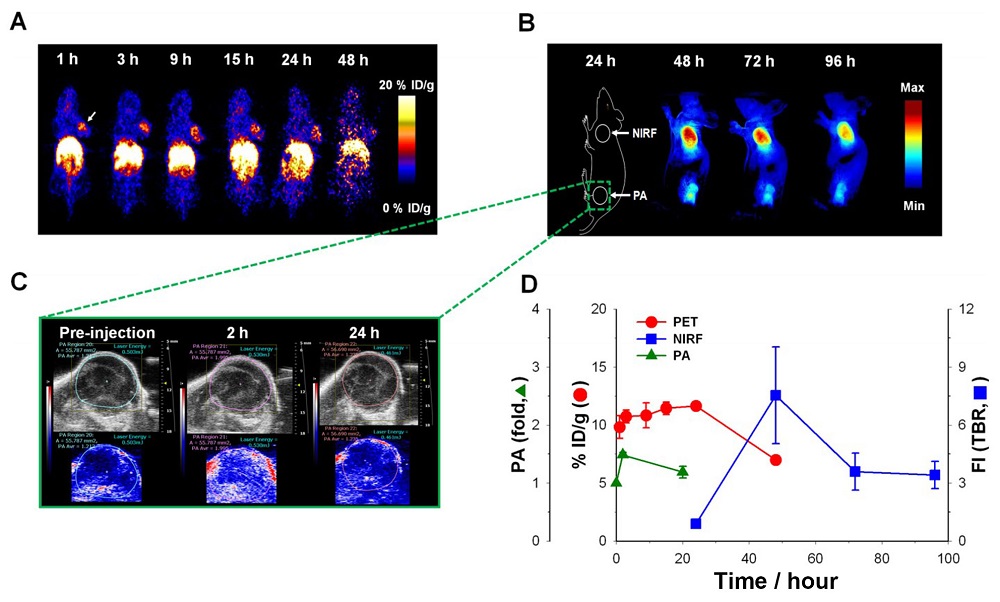
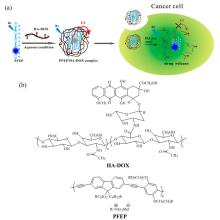


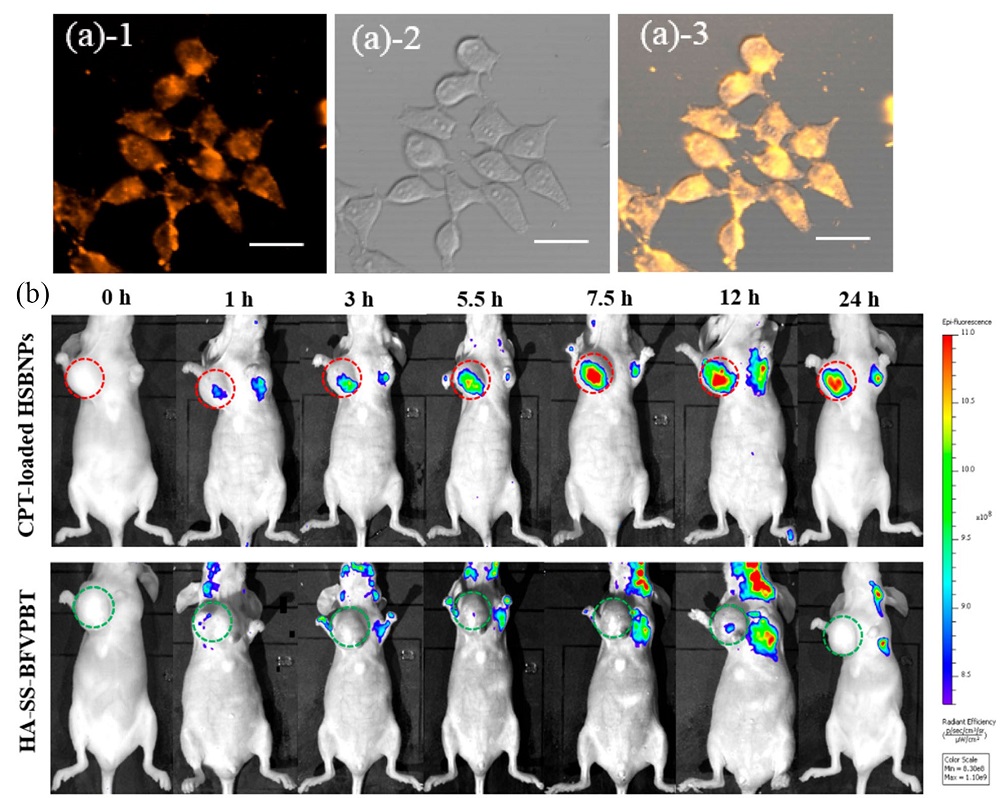
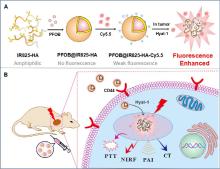

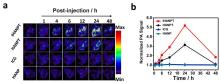

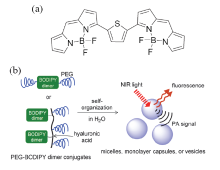

| [1] |
Torre, L. A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R. L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21262 |
| [2] |
Chen, W. Q.; Zheng, R. S.; Baade, P. D.; Zhang, S. W.; Zeng, H. M.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A.; Yu, X. Q.; He, J. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 115.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21338 |
| [3] |
Kobayashi, H.; Ogawa, M.; Alford, R.; Choyke, P. L.; Urano, Y. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2620.
doi: 10.1021/cr900263j pmid: 20000749 |
| [4] |
Kim, D.; Ryu, H. G.; Ahn, K. H. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 4550.
doi: 10.1039/C4OB00431K |
| [5] |
Wang, X.; Xie, X.; Ku, G.; Wang, L. V. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006, 11, 024015.
doi: 10.1117/1.2192804 |
| [6] |
Luo, S. L.; Zhang, E. L.; Su, Y. P.; Cheng, T. M.; Shi, C. M. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 7127.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.06.024 |
| [7] |
Lu, X. M.; Chen, P. F.; Hu, W. B.; Tang, Y. F.; Huang, W.; Fan, Q. L. Prog. Chem. 2017, 29, 119.
|
| [8] |
Gao, P.; Pan, W.; Li, N.; Tang, B. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 6035.
doi: 10.1039/C9SC01652J |
| [9] |
Antaris, A. L.; Chen, H.; Diao, S.; Ma, Z. R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, S. J.; Wang, J.; Lozano, A. X.; Fan, Q. L.; Chew, L. L.; Zhu, M.; Cheng, K.; Hong, X. C.; Dai, H. J.; Cheng, Z. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 11.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00022-8 |
| [10] |
Ren, X. J.; Lu, X. M.; Fan, Q. L.; Huang, W. Prog. Chem. 2013, 25, 1739.
|
| [11] |
Sang, R. Y.; Xu, X. P.; Wang, Q.; Fan, Q. L.; Huang, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 901.
doi: 10.6023/A20050190 |
| [12] |
Ren, T. B.; Wang, Z. Y.; Xiang, Z.; Lu, P.; Lai, H. H.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X. B.; Tan, W. H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 800.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v60.2 |
| [13] |
Lei, Z. H.; Zhang, F. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 16294.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v60.30 |
| [14] |
Song, K. H.; Stein, E. W.; Margenthaler, J. A.; Wang, L. V. J. Biomed. Opt. 2008, 13, 054033.
doi: 10.1117/1.2976427 |
| [15] |
Pu, K. Y.; Shuhendler, A. J.; Jokerst, J. V.; Mei, J. G.; Gambhir, S. S.; Bao, Z. N.; Rao, J. H. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 233.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2013.302 |
| [16] |
Fan, Q. L.; Cheng, K.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, R. P.; Yang, M.; Hu, X.; Ma, X. W.; Bu, L. H.; Lu, X. M.; Xiong, X. X.; Huang, W.; Zhao, H.; Cheng, Z. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 843.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v27.5 |
| [17] |
Yang, Z.; Dai, Y. L.; Yin, C.; Fan, Q. L.; Zhang, W. S.; Song, J.; Yu, G. C.; Tang, W.; Fan, W. P.; Yung, B. C.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Li, X. C.; Tang, Y. F.; Huang, W.; Song, J. B.; Chen, X. Y. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 8.
|
| [18] |
Liu, Y. J.; Bhattarai, P.; Dai, Z. F.; Chen, X. Y. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2053.
doi: 10.1039/C8CS00618K |
| [19] |
Hu, W. B.; He, T. C.; Jiang, R. C.; Yin, J.; Li, L.; Lu, X. M.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, L.; Huang, L.; Sun, H. D.; Huang, W.; Fan, Q. L. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 1680.
doi: 10.1039/C6CC09473B |
| [20] |
Wang, Q.; Dai, Y. N.; Xu, J. Z.; Cai, J.; Niu, X. R.; Zhang, L.; Chen, R. F.; Shen, Q. M.; Huang, W.; Fan, Q. L. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 12.
|
| [21] |
Li, J.; Jiang, R. C.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Hu, X. M.; Yuan, Y.; Lu, X. M.; Wang, W. J.; Huang, W.; Fan, Q. L. Biomaterials 2019, 217, 9.
|
| [22] |
Wang, Q.; Xia, B.; Xu, J. Z.; Niu, X. R.; Cai, J.; Shen, Q. M.; Wang, W. J.; Huang, W.; Fan, Q. L. Mat. Chem. Front. 2019, 3, 650.
|
| [23] |
Xie, N.; Feng, K.; Chen, B.; Zhao, M.; Peng, S.; Zhang, L. P.; Tung, C. H.; Wu, L. Z. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 502.
doi: 10.1039/C3TB21251C |
| [24] |
Garland, M.; Yim, J. J.; Bogyo, M. Cell Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 122.
doi: S2451-9456(15)00469-9 pmid: 26933740 |
| [25] |
Li, K.; Liu, B. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6570.
doi: 10.1039/C4CS00014E |
| [26] |
Yan, T.; Liu, Z. H.; Song, X. Y.; Zhang, S. S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 657.
doi: 10.6023/A20040132 |
| [27] |
Toole, B. P. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 528.
doi: 10.1038/nrc1391 |
| [28] |
Tripodo, G.; Trapani, A.; Torre, M. L.; Giammona, G.; Trapani, G.; Mandracchia, D. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 97, 400.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.03.032 |
| [29] |
Saravanakumar, G.; Deepagan, V. G.; Jayakumar, R.; Park, J. H. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 17.
pmid: 24724496 |
| [30] |
Jiang, G.; Park, K.; Kim, J.; Kim, K. S.; Hahn, S. K. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 727.
doi: 10.1021/mp800176t |
| [31] |
Luo, Y.; Prestwich, G. D. Bioconjugate Chem. 1999, 10, 755.
pmid: 10502340 |
| [32] |
Luo, Y.; Prestwich, G. D. Bioconjugate Chem. 2001, 12, 1085.
pmid: 11716704 |
| [33] |
Shi, H. X.; Sun, W. C.; Liu, C. B.; Gu, G. Y.; Ma, B.; Si, W. L.; Fu, N. N.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, W.; Dong, X. C. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 113.
doi: 10.1039/C5TB02041G |
| [34] |
Bhang, S. H.; Won, N.; Lee, T. J.; Jin, H.; Nam, J.; Park, J.; Chung, H.; Park, H. S.; Sung, Y. E.; Hahn, S. K.; Kim, B. S.; Kim, S. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1389.
doi: 10.1021/nn900138d pmid: 19476339 |
| [35] |
Hill, T. K.; Abdulahad, A.; Kelkar, S. S.; Marini, F. C.; Long, T. E.; Provenzale, J. M.; Mohs, A. M. Bioconjugate Chem. 2015, 26, 294.
doi: 10.1021/bc5005679 |
| [36] |
Yoon, H. Y.; Koo, H.; Choi, K. Y.; Lee, S. J.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I. C.; Leary, J. F.; Park, K.; Yuk, S. H.; Park, J. H.; Choi, K. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3980.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.02.016 |
| [37] |
Jalani, G.; Naccache, R.; Rosenzweig, D. H.; Lerouge, S.; Haglund, L.; Vetrone, F.; Cerruti, M. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11255.
doi: 10.1039/C5NR02482J |
| [38] |
Wang, H. N.; Sun, H. F.; Wei, H.; Xi, P.; Nie, S. M.; Ren, Q. S. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 13.
|
| [39] |
Huang, Y. Q.; Yao, X.; Zhang, R.; Lang, O. Y.; Jiang, R. C.; Liu, X. F.; Song, C. X.; Zhang, G. W.; Fan, Q. L.; Wang, L. H.; Huang, W. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 19144.
doi: 10.1021/am505113p |
| [40] |
Huang, Y. Q.; Song, C. X.; Li, H. C.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, R. C.; Liu, X. F.; Zhang, G. W.; Fan, Q. L.; Wang, L. H.; Huang, W. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 21529.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b06799 |
| [41] |
Wu, W. T.; Shen, J.; Banerjee, P.; Zhou, S. Q. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7555.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.06.030 |
| [42] |
Lee, H.; Lee, K.; Kim, I. K.; Park, T. G. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1884.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v19:12 |
| [43] |
Lee, H.; Lee, K.; Kim, I. K.; Park, T. G. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4709.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.08.038 |
| [44] |
Jeong, E. H.; Jung, G.; Hong, C. A.; Lee, H. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 53.
doi: 10.1007/s12272-013-0273-5 pmid: 24214174 |
| [45] |
Zhang, L. W.; Gao, S.; Zhang, F.; Yang, K.; Ma, Q. J.; Zhu, L. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12250.
doi: 10.1021/nn506130t |
| [46] |
Wang, X.; Chen, J. T.; Zhu, H. M.; Chen, X. Y.; Yan, X. P. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10225.
doi: 10.1021/ac401934p pmid: 24074184 |
| [47] |
Chen, Z. W.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z. H.; Ju, E. G.; Gao, N.; Zhou, L.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Biomaterials 2015, 39, 15.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.10.066 |
| [48] |
Gong, H.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1951.
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2013.10.002 |
| [49] |
Mani, V.; Chen, S. M.; Lou, B. S. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 11641.
|
| [50] |
Lim, S. Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Q. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362.
doi: 10.1039/C4CS00269E |
| [51] |
Hou, L.; Yang, X. M.; Ren, J. X.; Wang, Y. C.; Zhang, H. J.; Feng, Q. H.; Shi, Y. Y.; Shan, X. N.; Yuan, Y. J.; Zhang, Z. Z. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 607.
|
| [52] |
Xie, L. S.; Wang, G. H.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, F.; Guo, Z. D.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X. Z.; Zhu, L. Biomaterials 2016, 103, 219.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.06.058 |
| [53] |
Liu, S. Y.; Zhao, N.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, H. G. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6836.
doi: 10.1039/C5NR00070J |
| [54] |
Abdullah-Al, N.; Lee, J. E.; Jeong, J. H.; Park, S. Y. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 4082.
doi: 10.1021/bm4012166 pmid: 24106989 |
| [55] |
Swierczewska, M.; Choi, K. Y.; Mertz, E. L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, L.; Yoon, H. Y.; Park, J. H.; Bhirde, A.; Lee, S.; Chen, X. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3613.
doi: 10.1021/nl301309g pmid: 22694219 |
| [56] |
Zhu, C. L.; Liu, L. B.; Yang, Q.; Lv, F. T.; Wang, S. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4687.
doi: 10.1021/cr200263w |
| [57] |
Song, W.; Yin, C.; Jiang, R.; Lu, X.; Quan, Y.; Tian, C.; Li, J.; Hu, W.; Sun, P.; Deng, W.; Fan, Q.; Huang, W. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 5295.
doi: 10.1039/C5PY00633C |
| [58] |
Huang, Y. Q.; Sun, L. J.; Zhang, R.; Hu, J.; Liu, X. F.; Jiang, R. C.; Fan, Q. L.; Wang, L. H.; Huang, W. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 2421.
doi: 10.1021/acsabm.9b00130 |
| [59] |
Wang, Y. F.; Zhang, W. S.; Sun, P. F.; Cai, Y.; Xu, W. G.; Fan, Q. L.; Hu, Q. G.; Han, W. Theranostics 2019, 9, 391.
doi: 10.7150/thno.30268 |
| [60] |
Huang, Y. Q.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, Y. K.; Chen, H.; Jiang, R. C.; Liu, X. F.; Fan, Q. L.; Wang, L. H.; Huang, W. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 4998.
doi: 10.1039/C6NJ04128K |
| [61] |
Wang, X. C.; Chang, G.; Cao, R. J.; Meng, L. J. Prog. Chem. 2015, 27, 794.
|
| [62] |
Cho, H. J.; Yoon, H. Y.; Koo, H.; Ko, S. H.; Shim, J. S.; Cho, J. H.; Park, J. H.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I. C.; Kim, D.-D. J. Controlled Release 2012, 162, 111.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.06.011 |
| [63] |
Liang, X. L.; Fang, L.; Li, X. D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F. Biomaterials 2017, 132, 72.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.04.006 |
| [64] |
Sun, W.; Guo, S. G.; Hu, C.; Fan, J. L.; Peng, X. J. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7768.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00001 |
| [65] |
Mok, H.; Jeong, H.; Kim, S. J.; Chung, B. H. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8628.
doi: 10.1039/c2cc33555g |
| [66] |
Kim, J.; Chong, Y.; Mok, H. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 881.
doi: 10.1002/mabi.201300511 |
| [67] |
Park, H. S.; Lee, J. E.; Cho, M. Y.; Hong, J. H.; Cho, S. H.; Lim, Y. T. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2012, 33, 1549.
doi: 10.1002/marc.201200246 |
| [68] |
Miki, K.; Inoue, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nakano, K.; Matsuoka, H.; Yamauchi, F.; Yano, T.; Ohe, K. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 219.
doi: 10.1021/bm501438e |
| [69] |
Wang, G.; Zhang, F.; Tian, R.; Zhang, L.; Fu, G.; Yang, L.; Zhu, L. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5608.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b12400 |
| [70] |
Zhang, H. J.; Pei, Y. M.; Zhang, X. G.; Zhu, L.; Hou, L.; Chang, J. B.; Zhang, Z. Z. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 15.
|
| [71] |
Yu, F.; Zhu, M. S.; Li, N. N.; Ao, M. T.; Li, Y.; Zhong, M. Y.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, H. Y.; Fan, Z. X.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Z. Q.; Qi, Z. Q.; Shen, Y. M.; Chen, X. D. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 12.
|
| [72] |
Boens, N.; Leen, V.; Dehaen, W. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1130.
doi: 10.1039/c1cs15132k pmid: 21796324 |
| [73] |
Miki, K.; Enomoto, A.; Inoue, T.; Nabeshima, T.; Saino, S.; Shimizu, S.; Matsuoka, H.; Ohe, K. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 249.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.6b01568 |
| [74] |
Sun, H.; Benjaminsen, R. V.; Almdal, K.; Andresen, T. L. Bioconjugate Chem. 2012, 23, 2247.
doi: 10.1021/bc300349n |
| [75] |
Baier, G.; Fichter, M.; Kreyes, A.; Klein, K.; Maeilaender, V.; Gehring, S.; Landfester, K. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 148.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.5b01279 pmid: 26629829 |
| [76] |
Song, Y. C.; Wang, Z.; Li, L. H.; Shi, W.; Li, X. H.; Ma, H. M. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15696.
doi: 10.1039/C4CC07565J |
| [77] |
Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y. M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J. T.; Liu, Y. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 10.
|
| [1] | Feida Che, Xiaoming Zhao, Xin Zhang, Qi Ding, Xin Wang, Ping Li, Bo Tang. Fluorescence Imaging of Active Molecules Associated with Depression★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(9): 1255-1264. |
| [2] | Yuan Zhang, Beining Zheng, Meichun Fu, Shouhua Feng. Research Progress in the Application of Spinel Oxides in Tumor Therapy★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(8): 949-954. |
| [3] | Hongyue Wu, Rui Guo, Hanwen Chi, Yonghe Tang, Sirui Song, Enxiang Ge, Weiying Lin. Viscosity Fluorescent Probes Based on Quinoline Group and Its Applications [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(8): 905-911. |
| [4] | Xin Lv, Yi Wu, Boran Zhang, Wei Guo. Design, Synthesis and Photodynamic Therapy of a H2O2-Activatable Near Infrared Borondipyrromethene (BODIPY) Photosensitizer [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(4): 359-370. |
| [5] | Yanqin Huang, Lijun Li, Shupei Yang, Rui Zhang, Xingfen Liu, Quli Fan, Wei Huang. HA-AuNPs/FDF for Highly Sensitive Detection of Hyaluronidase, Tumor-targeting Fluorescence Cell Imaging and Phototherapy [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(12): 1687-1694. |
| [6] | Yinghong Yan, Pingzhao Liang, Yang Zou, Lin Yuan, Xiaojun Peng, Jiangli Fan, Xiaobing Zhang. Structure and Properties Regulation of Organic Photosensitizers and Application in Photodiagnosis and Treatment★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(11): 1642-1662. |
| [7] | Li Sun, Yajing Wang, Tao Li, Yingshu Guo, Shusheng Zhang. Au Nanocages Probes for Mitochondrial Imaging and Photothermal Damage Cells★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(10): 1301-1310. |
| [8] | He Xu, Pengbo Han, Anjun Qin, Ben Zhong Tang. Recent Advances and Application Prospects in Photothermal Materials★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(10): 1420-1437. |
| [9] | Sirui Song, Yonghe Tang, Liangguang Sun, Rui Guo, Guanfan Jiang, Weiying Lin. Development of a Novel Fluorescent Probe Based on Coumarin Fluorophore for Polarity Detection and Its Imaging Applications [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(9): 1217-1222. |
| [10] | Badi Liu, Chengjun Wang, Ying Qian. Synthesis, Two-photon Fluorescence Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy of Near Infrared Thienyl-BODIPY Photosensitizer [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(8): 1071-1083. |
| [11] | Shen Zhang, Shan Feng, Longyu Ma, Yingying Yang, Chaoqun Liu, Ningning Song, Yanwei Yang. Research of Synergistic Photothermal Antibacterial Strategy Based on Polymeric Guanidine Derivative Grafted on Mesoporous Carbon Nanospheres [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 265-271. |
| [12] | Yanran Li, Zigui Wang, Zhaohui Tang. Water Soluble IR-780 Polymer for Mitochondria-Targeted Photodynamic Therapy※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 291-296. |
| [13] | Qi Wang, Hui Xia, Yanwei Xiong, Xinmin Zhang, Jie Cai, Chong Chen, Yicong Gao, Feng Lu, Quli Fan. Simple Preparation of Near-infrared-II Organic Small Molecule-based Phototheranostics by Manipulation of the Electron-donating Unit [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(11): 1485-1493. |
| [14] | Ju Huang, Zhen Li, Zhihong Liu. Functionalized Upconversion Nanoparticles for Disassembly of β‑Amyloid Aggregation with Near-Infrared Excitation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(8): 1049-1057. |
| [15] | Tingwen Wei, Long Jiang, Yahui Chen, Xiaoqiang Chen. Recent Progress of Photocage Molecules and Materials [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(1): 58-70. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||