化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (2): 242-256.DOI: 10.6023/A23120542 上一篇
综述
投稿日期:2024-01-04
发布日期:2024-02-04
作者简介: |
郭建荣, 中科院理化技术研究所特别研究助理. 2022年获得中国科学院理化技术研究所理学博士学位. 主要研究兴趣为环境污染物防治功能材料与技术、生物基可降解材料的制备及应用. 以第一作者已在Chem. Eng. J., Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp.等国际核心刊物发表论文5篇, 授权专利4项. |
 |
张书玉, 1999年出生, 东北林业大学材料科学与工程学院在读硕士研究生, 目前在中国科学院理化技术研究所进行生物基可降解材料的制备及应用方面的研究. |
 |
贺军辉, 中科院理化技术研究所研究员、博士生导师、微纳材料与技术研究中心主任、功能纳米材料研究组组长. 主要研究兴趣为功能纳米结构的创制、性能和应用; 功能纳米结构薄膜/涂层的设计、制备和性能; 功能纳米结构器件的设计、制备和性能; 功能纳米材料在绿色能源、节能环保及环境分析和治理中的应用. 在国内外核心刊物上发表论文380余篇, 被引用11000余次, 申请国内外专利100余项, 出版中文专著1部, 英文专著3部. |
 |
任世学, 博士, 教授, 博士生导师/硕士生导师. 一直从事植物多酚降解活化、化学改性和应用研究, 主持参加多项国家级及省部级课题. 主要研究方向有: 木质素降解活化及化学改性研究, 木质素的高值化应用研究, 植物多酚的定向解聚研究, 图像精准智能识别在林业工程领域的应用等. 出版专著及教材2部, 参加编著2部; 发表论文30余篇. |
基金资助:
Jianrong Guoa, Shuyu Zhanga,b, Junhui Hea( ), Shixue Renb
), Shixue Renb
Received:2024-01-04
Published:2024-02-04
Contact:
E-mail: About author:Supported by:文章分享

石油基塑料制品加工性好、低成本等优点在各行各业中需求量大且应用广泛, 为人类生活带来了极大便利, 促进了人类社会发展. 然而在使用之后常以焚烧与填埋等处理方式直接排放到自然环境中, 塑料在环境中难以降解, 这将对环境与生命健康造成严重威胁, 产生日益严重的“微塑料”问题. 在当前“禁塑令”以及“碳达峰、碳中和”的背景下, 开发生物质可降解材料取代石油基塑料已成为人们关注的焦点. 生物质种类丰富, 源于自然植物, 产量高, 可再生, 完全生物可降解, 生物相容性好, 环境友好, 是完美的石油基塑料替代品. 然而, 经调研发现, 从生物质原材料出发制备与石油基塑料具有类似性能的生物可降解材料也面临很多技术挑战, 例如复杂的加工过程、成型差、机械强度较低、透明度差等. 因此本综述重点聚焦于基于不同类型生物质原料制备可降解薄膜材料研究进展, 分别从淀粉、果胶与壳聚糖直接生物质原料, 秸秆、果壳与木材间接生物质原料出发, 从生物质原料来源、组成、结构与提取, 以及薄膜制备方法, 包括溶剂铸造法、吹塑法、挤压法、静电纺丝等, 并对所获得生物基薄膜的性能与应用进行综述. 最后, 梳理了当前基于生物质所制备可降解薄膜存在的不足之处和面临的挑战, 并对生物质可降解薄膜材料未来的研究进行了展望.
郭建荣, 张书玉, 贺军辉, 任世学. 基于生物质可降解薄膜的制备与应用[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 242-256.
Jianrong Guo, Shuyu Zhang, Junhui He, Shixue Ren. Preparation and Application of Biodegradable Films Based on Biomass[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 242-256.
| 淀粉样品 | 直链淀粉含量/% |
|---|---|
| 糯玉米淀粉 | 2.9~7.5 |
| 玉米淀粉 | 27~33 |
| 高直链玉米淀粉 | 68~82 |
| 蜡制甘薯淀粉 | 1.29~2.21 |
| 甘薯淀粉 | 18.98~21.68 |
| 高直链甘薯淀粉 | 37.94~44.72 |
| 高粱淀粉 | 24~33 |
| 大麦淀粉 | 3~46 |
| 小麦淀粉 | 3~31 |
| 淀粉样品 | 直链淀粉含量/% |
|---|---|
| 糯玉米淀粉 | 2.9~7.5 |
| 玉米淀粉 | 27~33 |
| 高直链玉米淀粉 | 68~82 |
| 蜡制甘薯淀粉 | 1.29~2.21 |
| 甘薯淀粉 | 18.98~21.68 |
| 高直链甘薯淀粉 | 37.94~44.72 |
| 高粱淀粉 | 24~33 |
| 大麦淀粉 | 3~46 |
| 小麦淀粉 | 3~31 |


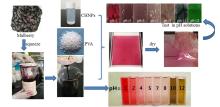

| 稻草 | 麦草 | 玉米 秸秆 | 油菜 秸秆 | 棉花 秸秆 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纤维 素/% | 36.21~48.88 | 25.03~50.56 | 31.57~48.65 | 30.41~51.96 | 31.54~51.80 |
| 半纤维素/% | 9.98~23.70 | 13.80~30.40 | 9.63~26.46 | 8.93~19.53 | 9.49~21.65 |
| 木质 素/% | 11.59~26.70 | 15.13~27.90 | 14.66~30.02 | 12.07~25.47 | 22.09~33.03 |
| 稻草 | 麦草 | 玉米 秸秆 | 油菜 秸秆 | 棉花 秸秆 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纤维 素/% | 36.21~48.88 | 25.03~50.56 | 31.57~48.65 | 30.41~51.96 | 31.54~51.80 |
| 半纤维素/% | 9.98~23.70 | 13.80~30.40 | 9.63~26.46 | 8.93~19.53 | 9.49~21.65 |
| 木质 素/% | 11.59~26.70 | 15.13~27.90 | 14.66~30.02 | 12.07~25.47 | 22.09~33.03 |
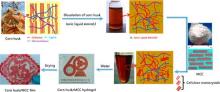
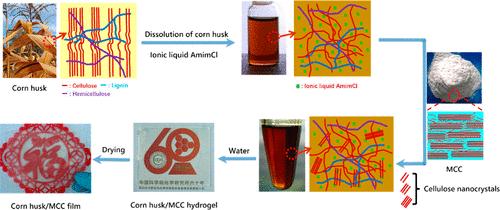
| 纤维素/% | 半纤维素/% | 木质素/% | 苯醇抽出物/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 油茶壳 | 16.46 | 29.36 | 27.20 | 5.15 |
| 椰子壳 | 34.12 | 22.36 | 28.04 | 10.34 |
| 油桐壳 | 48.42 | 18.56 | 26.18 | 5.70 |
| 核桃壳 | 36.38 | 27.85 | 43.70 | 2.57 |
| 板栗壳 | 21.47 | 16.28 | 36.58 | 12.67 |
| 开心果壳 | 43.08 | 25.30 | 16.33 | 8.17 |
| 腰果壳 | 26.66 | 9.67 | 13.65 | 26.66 |
| 花生壳 | 49.4 | 8.1 | 33.1 | 9.4 |
| 纤维素/% | 半纤维素/% | 木质素/% | 苯醇抽出物/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 油茶壳 | 16.46 | 29.36 | 27.20 | 5.15 |
| 椰子壳 | 34.12 | 22.36 | 28.04 | 10.34 |
| 油桐壳 | 48.42 | 18.56 | 26.18 | 5.70 |
| 核桃壳 | 36.38 | 27.85 | 43.70 | 2.57 |
| 板栗壳 | 21.47 | 16.28 | 36.58 | 12.67 |
| 开心果壳 | 43.08 | 25.30 | 16.33 | 8.17 |
| 腰果壳 | 26.66 | 9.67 | 13.65 | 26.66 |
| 花生壳 | 49.4 | 8.1 | 33.1 | 9.4 |
| 纤维素/% | 半纤维素/% | 木质素/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 松木 | 39.94 | 12.89 | 22.97 |
| 桉木 | 41.72 | 13.21 | 23.99 |
| 杨木 | 44.08 | 21.1 | 24.12 |
| 柚木 | 44.31 | 29.74 | 32.2 |
| 纤维素/% | 半纤维素/% | 木质素/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 松木 | 39.94 | 12.89 | 22.97 |
| 桉木 | 41.72 | 13.21 | 23.99 |
| 杨木 | 44.08 | 21.1 | 24.12 |
| 柚木 | 44.31 | 29.74 | 32.2 |
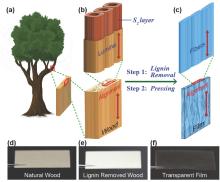
| [1] |
Singh, J.; Samuel, J.; Hurley, R. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 803551.
doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2021.803551 |
| [2] |
Henderson, L.; Green, C. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 152, 110908.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.110908 |
| [3] |
Tu, Z. X.; Zhong, Y. L.; Hu, H. Z.; Shao, D.; Haag, R.; Schirner, M.; Lee, J.; Sullenger, B.; Leong, K. W. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 557.
doi: 10.1038/s41578-022-00426-z |
| [4] |
Horton, A. A. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126885.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126885 |
| [5] |
Rivas, M. L.; Albion, I.; Bernal, B.; Handcock, R. N.; Heatwole, S. J.; Parrott, M. L.; Piazza, K. A.; Deschaseaux, E. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157555.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157555 |
| [6] |
Schmaltz, E.; Melvin, E. C.; Diana, Z.; Gunady, E. F.; Rittschof, D.; Somarelli, J. A.; Virdin, J.; Dunphy-Daly, M. M. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 106067.
doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106067 |
| [7] |
Horejs, C. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 641.
doi: 10.1038/s41578-020-00237-0 |
| [8] |
McDonough, W. Nature 2016, 539, 349.
doi: 10.1038/539349a |
| [9] |
Chen, L.; Msigwa, G.; Yang, M.; Osman, A. I.; Fawzy, S.; Rooney, D. W.; Yap, P.-S. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2277.
doi: 10.1007/s10311-022-01435-8 |
| [10] |
Mora Rollo, A.; Rollo, A.; Mora, C. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 332.
doi: 10.1038/s43017-020-0069-3 |
| [11] |
Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Carbon Energy 2022, 4, 1021.
doi: 10.1002/cey2.v4.6 |
| [12] |
Sun, X.; Xie, M.; Mai, L.; Zeng, E. Y. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129037.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129037 |
| [13] |
Shen, X.; Zhang, C.; Han, B.; Wang, F. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 1608.
doi: 10.1039/D1CS00908G |
| [14] |
Zhao, K. L.; Hao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Cheng, G. S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 168. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A17110499 |
|
(赵克丽, 郝莹, 朱墨, 程国胜, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 168.)
doi: 10.6023/A17110499 |
|
| [15] |
Chen, W.-H.; Lin, B.-J.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Chu, Y.-S.; Ubando, A. T.; Show, P. L.; Ong, H. C.; Chang, J.-S.; Ho, S.-H.; Culaba, A. B.; Pétrissans, A.; Pétrissans, M. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2021, 82, 100887.
doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2020.100887 |
| [16] |
Karahan, H. E.; Ji, M.; Pinilla, J. L.; Han, X.; Mohamed, A.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, S.; Montoya, A.; Beyenal, H.; Chen, Y. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 9668.
doi: 10.1039/D0TB01027H |
| [17] |
Mousa, E.; Wang, C.; Riesbeck, J.; Larsson, M. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2016, 65, 1247.
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.07.061 |
| [18] |
Adams, V. M.; Asamoah, E. F.; Maina, J. M.; Niu, S. L.; Panoutsou, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, B.; Yuan, X. Z.; You, S. M.; Ok, Y.; Niinemets, Ü. One Earth 2022, 5, 3.
doi: 10.1016/j.oneear.2021.12.018 |
| [19] |
Zhang, T. Science 2020, 367, 1305.
doi: 10.1126/science.abb1463 pmid: 32193311 |
| [20] |
Dhepe, P.; Tomishige, K.; Wu, K. C. W. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 2613.
doi: 10.1002/cctc.v9.14 |
| [21] |
Niu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Lei, Y.; Liu, S.; Liang, Y.; Wang, D.; Hui, S. e. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2019, 115, 109395.
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2019.109395 |
| [22] |
Shah, U.; Naqash, F.; Gani, A.; Masoodi, F. A. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F. 2016, 15, 568.
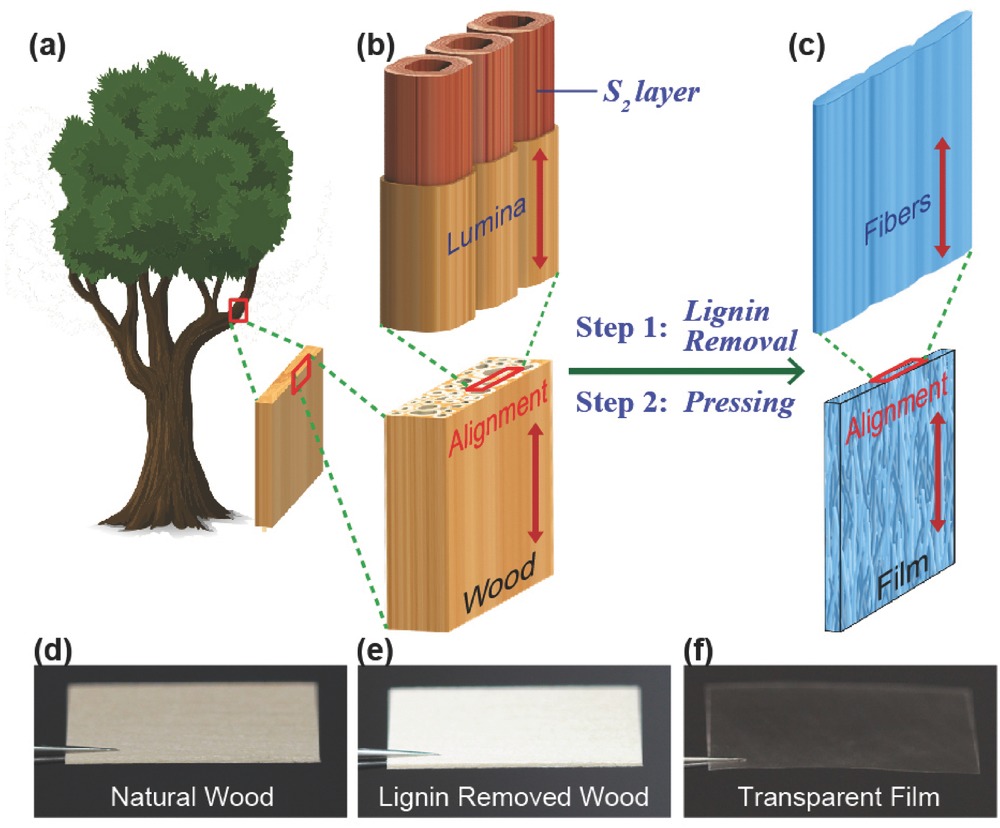
doi: 10.1111/crf3.2016.15.issue-3 |
| [23] |
Vamadevan, V.; Bertoft, E. Food Hydrocolloids 2020, 103, 105663.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105663 |
| [24] |
Cao, P.; Wu, G.; Yao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, E.; Yu, S.; Liu, Q.; Gilbert, R. G.; Li, S. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 296, 119959.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119959 |
| [25] |
Meimoun, J.; Wiatz, V.; Saint-Loup, R.; Parcq, J.; Favrelle, A.; Bonnet, F.; Zinck, P. Starch - Stärke. 2018, 70, 1600351.
doi: 10.1002/star.v70.1-2 |
| [26] |
Singh, G. P.; Bangar, S. P.; Yang, T.; Trif, M.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, D. Ploymers 2022, 10, 1987.
|
| [27] |
Su, C.-y.; Li, D.; Wang, L.-j.; Wang, Y. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 6923.
doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2036097 |
| [28] |
Chen, D.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Prakash, S.; Wan, J. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 228, 207.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.133 |
| [29] |
Guo, K.; Zhang, L.; Bian, X.; Cao, Q.; Wei, C. Food Hydrocolloids 2020, 98, 105279.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105279 |
| [30] |
Oseguera-Toledo, M. E.; Contreras-Jiménez, B.; Hernández-Becerra, E.; Rodriguez-Garcia, M. E. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 95, 103069.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2020.103069 |
| [31] |
Abral, H.; Soni Satria, R.; Mahardika, M.; Hafizulhaq, F.; Affi, J.; Asrofi, M.; Handayani, D.; Sapuan, S. M.; Stephane, I.; Sugiarti, E.; Muslimin, A. N. Starch. 2019, 71, 1800224.
|
| [32] |
Cui, C.; Ji, N.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 116, 854.
doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.08.024 |
| [33] |
Wang, R.; Liu, P.; Cui, B.; Kang, X.; Yu, B. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 34.
doi: S0141-8130(18)34975-4 pmid: 30472268 |
| [34] |
Lopes, J.; Gonçalves, I.; Nunes, C.; Teixeira, B.; Mendes, R.; Ferreira, P.; Coimbra, M. A. Food Packaging Shelf 2021, 28, 100644.
|
| [35] |
Mantovan, J.; Bersaneti, G. T.; Faria-Tischer, P. C. S.; Celligoi, M. A. P. C.; Mali, S. Food Packaging Shelf 2018, 18, 31.
|
| [36] |
Silva, O. A.; Pellá, M. G.; Pellá, M. G.; Caetano, J.; Simões, M. R.; Bittencourt, P. R. S.; Dragunski, D. C. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 290.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.132 |
| [37] |
Nouraddini, M.; Esmaiili, M.; Mohtarami, F. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1639.
doi: S0141-8130(18)32741-7 pmid: 30248421 |
| [38] |
Yıldırım-Yalçın, M.; Şeker, M.; Sadıkoğlu, H. Food Chem. 2019, 292, 6.
doi: S0308-8146(19)30655-7 pmid: 31054693 |
| [39] |
Wu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Lin, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, W.; Pu, S. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 569.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.071 |
| [40] |
Herniou-Julien, C.; Mendieta, J. R.; Gutiérrez, T. J. Food Hydrocolloids 2019, 89, 67.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.10.024 |
| [41] |
Collazo-Bigliardi, S.; Ortega-Toro, R.; Chiralt, A. Food Packaging Shelf 2019, 22, 100383.
|
| [42] |
Menzel, C.; González-Martínez, C.; Vilaplana, F.; Diretto, G.; Chiralt, A. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 976.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.222 |
| [43] |
Gao, W.; Dong, H.; Hou, H.; Zhang, H. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 321.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.12.011 |
| [44] |
Zhu, J.; Gao, W.; Wang, B.; Kang, X.; Liu, P.; Cui, B.; Abd El-Aty, A. M. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 1371.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.118 |
| [45] |
Dang, K. M.; Yoksan, R. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 188, 290.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.027 |
| [46] |
Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Jia, R.; Dai, Y.; Dong, H.; Hou, H.; Guo, Q. Food Hydrocolloids 2018, 79, 534.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.12.013 |
| [47] |
Zhou, X.; Yang, R.; Wang, B.; Chen, K. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 114912.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.05.042 |
| [48] |
Farrag, Y.; Ide, W.; Montero, B.; Rico, M.; Rodríguez-Llamazares, S.; Barral, L.; Bouza, R. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 2201.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.07.087 |
| [49] |
Li, W.; Yu, Y.; Dai, Z.; Peng, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z. J. Food Process. Pres. 2021, 45, e15237.
|
| [50] |
Freitas, C. M.; Coimbra, J. S.; Souza, V. G.; Sousa, R. C. Coatings 2021, 11, 11080922.
|
| [51] |
Yue, F.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Lü, X. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 825.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.073 |
| [52] |
Luis, A. S.; Briggs, J.; Zhang, X.; Farnell, B.; Ndeh, D.; Labourel, A.; Baslé, A.; Cartmell, A.; Terrapon, N.; Stott, K.; Lowe, E. C.; McLean, R.; Shearer, K.; Schückel, J.; Venditto, I.; Ralet, M.-C.; Henrissat, B.; Martens, E. C.; Mosimann, S. C.; Abbott, D. W.; Gilbert, H. J. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 210.
doi: 10.1038/s41564-017-0079-1 pmid: 29255254 |
| [53] |
Hachem, K.; Benabdesslem, Y.; Ghomari, S.; Hasnaoui, O.; Kaid-Harche, M. Heliyon. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 2, e00076.
|
| [54] |
Marenda, F. R. B.; Mattioda, F.; Demiate, I. M.; de Francisco, A.; de Oliveira Petkowicz, C. L.; Canteri, M. H. G.; de Mello Castanho Amboni, R. D. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 549.
doi: 10.1007/s10924-018-1355-8 |
| [55] |
Cui, J.; Zhao, C.; Feng, L.; Han, Y.; Du, H.; Xiao, H.; Zheng, J. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 39.
doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.01.077 |
| [56] |
Belkheiri, A.; Forouhar, A.; Ursu, A. V.; Dubessay, P.; Pierre, G.; Delattre, C.; Djelveh, G.; Abdelkafi, S.; Hamdami, N.; Michaud, P. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 985.
doi: 10.3390/app14030985 |
| [57] |
Belkheiri, A.; Forouhar, A.; Ursu, A. V.; Dubessay, P.; Pierre, G.; Delattre, C.; Djelveh, G.; Abdelkafi, S.; Hamdami, N.; Michaud, P. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6596.
doi: 10.3390/app11146596 |
| [58] |
Zoghi, A.; Vedadi, S.; Esfahani, Z. H.; Gavlighi, H. A.; Khosravi-Darani, K. Biomass Convers. Bior. 2023, 13, 5577.
|
| [59] |
Colodel, C.; Petkowicz, C. L. d. O. Food Hydrocolloids 2019, 86, 193.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.06.013 |
| [60] |
Maran, J. P.; Priya, B.; Al-Dhabi, N. A.; Ponmurugan, K.; Moorthy, I. G.; Sivarajasekar, N. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 35, 204.
doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.09.019 |
| [61] |
Panwar, D.; Panesar, P. S.; Chopra, H. K. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2024, 14, 159.
doi: 10.1007/s13399-021-02127-z |
| [62] |
Picot-Allain, M. C. N.; Ramasawmy, B.; Emmambux, M. N. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38, 282.
doi: 10.1080/87559129.2020.1733008 |
| [63] |
Cui, J.; Ren, W.; Zhao, C.; Gao, W.; Tian, G.; Bao, Y.; Lian, Y.; Zheng, J. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115524.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115524 |
| [64] |
Yu, M.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, M.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 258, 117662.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117662 |
| [65] |
Maxwell, E. G.; Colquhoun, I. J.; Chau, H. K.; Hotchkiss, A. T.; Waldron, K. W.; Morris, V. J.; Belshaw, N. J. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 923.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.09.063 |
| [66] |
Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Pi, F.; Zhang, T.; Ai, C.; Yu, S. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 759.
doi: S0141-8130(20)33765-X pmid: 32650011 |
| [67] |
Bayar, N.; Friji, M.; Kammoun, R. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 127.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.08.051 |
| [68] |
Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hu, D.; Xiao, K.; Wu, J.-Y. Food Hydrocolloids 2018, 79, 189.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.11.051 |
| [69] |
Wu, D.; Chen, S.; Ye, X.; Zheng, X.; Ahmadi, S.; Hu, W.; Yu, C.; Cheng, H.; Linhardt, R. J.; Chen, J. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132387.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132387 |
| [70] |
Espitia, P. J. P.; Du, W.-X.; Avena-Bustillos, R. d. J.; Soares, N. d. F. F.; McHugh, T. H. Food Hydrocolloids 2014, 35, 287.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.06.005 |
| [71] |
Kaczmarek, H.; Da¸browska, A.; Vuković-Kwiatkowska, I. J. Appl. Polym. 2011, 122, 1936.
doi: 10.1002/app.v122.3 |
| [72] |
Bagliotti Meneguin, A.; Stringhetti Ferreira Cury, B.; Evangelista, R. C. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 140.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.07.077 |
| [73] |
Jovanović, J.; Ćirković, J.; Radojković, A.; Mutavdžić, D.; Tanasijević, G.; Joksimović, K.; Bakić, G.; Branković, G.; Branković, Z. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 158, 106349.
|
| [74] |
Mendes, J. F.; Norcino, L. B.; Manrich, A.; Pinheiro, A. C. M.; Oliveira, J. E.; Mattoso, L. H. C. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 2905.
doi: 10.1007/s10924-020-01829-1 |
| [75] |
Norcino, L. B.; Mendes, J. F.; Natarelli, C. V. L.; Manrich, A.; Oliveira, J. E.; Mattoso, L. H. C. Food Hydrocolloids 2020, 106, 105862.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105862 |
| [76] |
de Oliveira, A. C. S.; Ferreira, L. F.; de Oliveira Begali, D.; Ugucioni, J. C.; de Sena Neto, A. R.; Yoshida, M. I.; Borges, S. V. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 2546.
doi: 10.1007/s10924-021-02054-0 |
| [77] |
Gurram, R.; Souza Filho, P. F.; Taherzadeh, M. J.; Zamani, A. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 4282.
doi: 10.1007/s10924-018-1300-x |
| [78] |
Jindal, M.; Kumar, V.; Rana, V.; Tiwary, A. K. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 52, 77.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.10.020 |
| [79] |
Gaona-Sánchez, V. A.; Calderón-Domínguez, G.; Morales-Sánchez, E.; Chanona-Pérez, J. J.; Arzate-Vázquez, I.; Terrés-Rojas, E. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43779.
|
| [80] |
Freitas, C. M.; Coimbra, J. S.; Souza, V. G.; Sousa, R. C. Coatings 2021, 11, 922.
doi: 10.3390/coatings11080922 |
| [81] |
Ma, X.; Chen, W.; Yan, T.; Wang, D.; Hou, F.; Miao, S.; Liu, D. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125501.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125501 |
| [82] |
Celus, M.; Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Kyomugasho, C.; Maes, I.; Van Loey, A. M.; Grauwet, T.; Hendrickx, M. E. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 86.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.08.056 |
| [83] |
Sun, D.; Chen, X.; Zhu, C. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 1239.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.052 |
| [84] |
Douglas, T. E. L.; Hempel, U.; Żydek, J.; Vladescu, A.; Pietryga, K.; Kaeswurm, J. A. H.; Buchweitz, M.; Surmenev, R. A.; Surmeneva, M. A.; Cotrut, C. M.; Koptyug, A. V.; Pamuła, E. Mater. Lett. 2018, 227, 225.
doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.05.060 |
| [85] |
Jindal, M.; Kumar, V.; Rana, V.; Tiwary, A. K. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 93, 386.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.12.012 |
| [86] |
Sucheta; Chaturvedi, K.; Sharma, N.; Yadav, S. K. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 284.
doi: S0141-8130(19)31761-1 pmid: 31004632 |
| [87] |
Hwang, S. W.; Shin, J. S. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 18, 2071071.
|
| [88] |
Ullah, K.; Sohail, M.; Buabeid, M. A.; Murtaza, G.; Ullah, A.; Rashid, H.; Khan, M. A.; Khan, S. A. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118557.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118557 |
| [89] |
Naqash, F.; Masoodi, F. A.; Rather, S. A.; Wani, S. M.; Gani, A. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 168, 227.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.03.058 |
| [90] |
López-Mata, M. A.; Gastelum-Cabrera, M.; Valbuena-Gregorio, E.; Zamudio-Flores, P. B.; Burruel-Ibarra, S. E.; Morales-Figueroa, G. G.; Quihui-Cota, L.; Juárez-Onofre, J. E. Iran Polym. J. 2018, 27, 545.
doi: 10.1007/s13726-018-0631-8 |
| [91] |
Martău, G. A.; Mihai, M.; Vodnar, D. C. Polymers 2019, 11, 1837.
doi: 10.3390/polym11111837 |
| [92] |
Iqbal, M. W.; Riaz, T.; Yasmin, I.; Leghari, A. A.; Amin, S.; Bilal, M.; Qi, X. Starch. 2021, 73, 2100088.
doi: 10.1002/star.v73.11-12 |
| [93] |
Kou, S.; Peters, L. M.; Mucalo, M. R. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 85.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.005 |
| [94] |
Zhang, X.; Ismail, B. B.; Cheng, H.; Jin, T. Z.; Qian, M.; Arabi, S. A.; Liu, D.; Guo, M. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118616.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118616 |
| [95] |
Antaby, E.; Klinkhammer, K.; Sabantina, L. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3390.
doi: 10.3390/app11083390 |
| [96] |
Ren, L.; Yan, X.; Zhou, J.; Tong, J.; Su, X. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1636.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.02.008 |
| [97] |
Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Lu, R.; Xu, J.; Hu, K.; Liu, Y. Foods 2019, 8, 423.
doi: 10.3390/foods8090423 |
| [98] |
Valencia-Sullca, C.; Vargas, M.; Atarés, L.; Chiralt, A. Food Hydrocolloids 2018, 75, 107.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.09.008 |
| [99] |
Rodriguez Llanos, J. H.; Tadini, C. C.; Gastaldi, E. J. Food Eng. 2021, 290, 110224.
doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2020.110224 |
| [100] |
Elsabee, M. Z.; Abdou, E. S. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1819.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2013.01.010 |
| [101] |
Qiao, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Yao, J. Food Chem. 2017, 235, 45.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.05.045 |
| [102] |
Uranga, J.; Puertas, A. I.; Etxabide, A.; Dueñas, M. T.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. Food Hydrocolloids 2019, 86, 95.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.02.018 |
| [103] |
Haghighi, H.; Biard, S.; Bigi, F.; De Leo, R.; Bedin, E.; Pfeifer, F.; Siesler, H. W.; Licciardello, F.; Pulvirenti, A. Food Hydrocolloids 2019, 95, 33.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.04.019 |
| [104] |
Benbettaïeb, N.; Chambin, O.; Assifaoui, A.; Al-Assaf, S.; Karbowiak, T.; Debeaufort, F. Food Hydrocolloids 2016, 56, 266.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.12.026 |
| [105] |
Treenate, P.; Monvisade, P. Macromol. Symp. 2017, 372, 147.
doi: 10.1002/masy.v372.1 |
| [106] |
Wang, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zou, X.; Shi, J. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 2843.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.10.063 |
| [107] |
Tao, F.; Cheng, Y.; Tao, H.; Jin, L.; Wan, Z.; Dai, F.; Xiang, W.; Deng, H. Mater. Des. 2020, 194, 108849.
doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108849 |
| [108] |
Mujtaba, M.; Morsi, R. E.; Kerch, G.; Elsabee, M. Z.; Kaya, M.; Labidi, J.; Khawar, K. M. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 889.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.109 |
| [109] |
Rezaei, F. S.; Sharifianjazi, F.; Esmaeilkhanian, A.; Salehi, E. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118631.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118631 |
| [110] |
Halloub, A.; Raji, M.; Essabir, H.; Chakchak, H.; boussen, R.; Bensalah, M.-o.; Bouhfid, R.; Qaiss, A. e. k. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 296, 119972.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119972 |
| [111] |
Flórez, M.; Guerra-Rodríguez, E.; Cazón, P.; Vázquez, M. Food Hydrocolloids 2022, 124, 107328.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107328 |
| [112] |
Zhou, Y.; Trabelsi, A.; El Mankibi, M. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 330, 127215.
doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127215 |
| [113] |
Charitha, V.; Athira, V. S.; Jittin, V.; Bahurudeen, A.; Nanthagopalan, P. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 285, 122851.
doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122851 |
| [114] |
Dafiqurrohman, H.; Safitri, K. A.; Setyawan, M. I. B.; Surjosatyo, A.; Aziz, M. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 366, 132926.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132926 |
| [115] |
Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, G.; Xiao, W.; Han, L. Waste Manage. 2020, 110, 87.
doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2020.05.018 |
| [116] |
Liu, J. F.; Cao, Y.; Yang, M. H.; Li, H. Q.; Xing, J. M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 1950. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A12050221 |
|
(刘建飞, 曹妍, 杨茂华, 李会泉, 邢建民, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 1950.)
doi: 10.6023/A12050221 |
|
| [117] |
Khan, R.; Jolly, R.; Fatima, T.; Shakir, M. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2022, 33, 2069.
doi: 10.1002/pat.v33.7 |
| [118] |
Abdulkhani, A.; Hosseinzadeh, J.; Ashori, A.; Esmaeeli, H. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 13.
doi: 10.1002/pc.v38.1 |
| [119] |
Ilangovan, M.; Guna, V.; Prajwal, B.; Jiang, Q.; Reddy, N. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 115996.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115996 |
| [120] |
Manian, A. P.; Cordin, M.; Pham, T. Cellulose 2021, 28, 8275.
doi: 10.1007/s10570-021-04051-x |
| [121] |
Acharya, S.; Liyanage, S.; Parajuli, P.; Rumi, S. S.; Shamshina, J. L.; Abidi, N. Polymers (Basel). 2021, 13, 4344.
doi: 10.3390/polym13244344 |
| [122] |
Lou, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, A.; Liu, Y. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 1208.
doi: 10.1039/D1RA07513F |
| [123] |
Wang, G.; Chen, H. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 93.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2015.11.036 |
| [124] |
Yang, M.; Rehman, M. S. U.; Yan, T.; Khan, A. U.; Oleskowicz-Popiel, P.; Xu, X.; Cui, P.; Xu, J. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 737.
doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.055 |
| [125] |
Isogai, A.; Zhou, Y. Curr. Opin. Solid St. M. 2019, 23, 101.
doi: 10.1016/j.cossms.2019.01.001 |
| [126] |
Ang, S.; Haritos, V.; Batchelor, W. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 234, 115900.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115900 |
| [127] |
Huang, S.; Zhou, L.; Li, M.-C.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, D. Materials 2017, 10, 80.
doi: 10.3390/ma10010080 |
| [128] |
Oun, A. A.; Rhim, J.-W. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 150, 187.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.05.020 |
| [129] |
Li, Y.; Song, X.; Xu, W.; Duan, X.; Shi, J.; Li, X. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 104001.
|
| [130] |
Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Mi, Q.; Jia, F.; Wu, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115057.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115057 |
| [131] |
Zhang, J.; Luo, N.; Wan, J.; Xia, G.; Yu, J.; He, J.; Zhang, J. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5127.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00488 |
| [132] |
Bian, H.; Yang, Y.; Tu, P.; Chen, J. Y. Membranes 2022, 12, 3390.
|
| [133] |
Cui, B.; Xie, H.; Sun, H.; Ji, T.; Li, S.; Jia, X.; Wang, W. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 12968.
doi: 10.1039/D2TA01204A |
| [134] |
Çavdaroğlu, E.; Büyüktaş, D.; Farris, S.; Yemenicioğlu, A. Food Hydrocolloids 2023, 135, 108136.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.108136 |
| [135] |
Lang, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Chen, H. Materials 2022, 15, 5170.
doi: 10.3390/ma15155170 |
| [136] |
Azeredo, H. M. C.; Kontou-Vrettou, C.; Moates, G. K.; Wellner, N.; Cross, K.; Pereira, P. H. F.; Waldron, K. W. Food Hydrocolloids 2015, 50, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.04.005 |
| [137] |
Shao, X.; Sun, H.; Jiang, R.; Qin, T.; Ma, Z. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 5639.
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2018.98.issue-15 |
| [138] |
Tessaro, L.; Lourenço, R. V.; Martelli-Tosi, M.; do Amaral Sobral, P. J. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 328.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.039 |
| [139] |
Guo, S. P. Ph.D. Dissertation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 2009. (in Chinese)
|
|
(郭仕鹏, 博士论文,中国科学院大学, 北京, 2009.)
|
|
| [140] |
Liu, Y. X. Ph.D. Dissertation, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, Changsha, 2019. (in Chinese)
|
|
(刘艳新, 博士论文,中南林业科技大学, 长沙, 2019.)
|
|
| [141] |
Wang, B.; Li, D. Compos. Part A-Appl. S. 2015, 79, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.08.029 |
| [142] |
Bano, S.; Negi, Y. S. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1041.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.10.069 |
| [143] |
Tamilselvi, A.; Jayakumar, G. C.; Sri Charan, K.; Sahu, B.; Deepa, P. R.; Kanth, S. V.; Kanagaraj, J. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 694.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.401 |
| [144] |
Gupta, H.; Kumar, H.; Gehlaut, A. K.; Singh, S. K.; Gaur, A.; Sachan, S.; Park, J.-W. J. Mater. Cycles Waste 2022, 24, 569.
doi: 10.1007/s10163-021-01343-z |
| [145] |
Kaewprachu, P.; Jaisan, C.; Rawdkuen, S.; Tongdeesoontorn, W.; Klunklin, W. Food Hydrocolloids 2022, 124, 107277.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107277 |
| [146] |
Halloub, A.; Raji, M.; Essabir, H.; Chakchak, H.; boussen, R.; Bensalah, M.-o.; Bouhfid, R.; Qaiss, A. e. k. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 296, 119972.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119972 |
| [147] |
Roldi-Oliveira, M.; Diniz, L. M.; Elias, A. L.; Luz, S. M. Polymers 2022, 14, 3390.
doi: 10.3390/polym14163390 |
| [148] |
Zhang, X.; Lian, H.; Shi, J.; Meng, W.; Peng, Y. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 1242.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.108 |
| [149] |
Meng, W.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Lian, H.; Wang, Q.; Peng, Y. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 137.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.235 |
| [150] |
Vasconcelos, L.; de Souza, M.; de Oliveira, J.; Silva Filho, E.; Silva, A.; Mazzetto, S. E.; Pereira, E. S.; Oliveira, R. L.; Bezerra, L. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1378.
doi: 10.3390/antiox10091378 |
| [151] |
Ma, Q.; Ren, Y.; Gu, Z.; Wang, L. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 851.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.08.099 |
| [152] |
Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Yong, H.; Qin, Y.; Liu, J.; Jin, C. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 1129.
doi: S0141-8130(19)37265-4 pmid: 31730981 |
| [153] |
Hanani, Z. A. N.; Yee, F. C.; Nor-Khaizura, M. A. R. Food Hydrocolloids 2019, 89, 253.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.10.007 |
| [154] |
Popescu, C.-M.; Navi, P.; Placencia Peña, M. I.; Popescu, M.-C. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2018, 191, 405.
doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2017.10.045 |
| [155] |
Xu, S.; Zeng, F. S.; Zhao, X. T.; Zhan, Y. G. Northwest Forestry University 2016, 31, 234. (in Chinese)
|
|
(徐速, 曾凡锁, 赵兴堂, 詹亚光, 西北林学院学报, 2016, 31, 234.)
|
|
| [156] |
Yang, X.; Berglund, L. A. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2001118.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v33.28 |
| [157] |
Maceda, A.; Soto-Hernández, M.; Peña-Valdivia, C. B.; Terrazas, T. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1700574.
doi: 10.1002/cbdv.v15.4 |
| [158] |
Almeida, R. O.; Ramos, A.; Alves, L.; Potsi, E.; Ferreira, P. J. T.; Carvalho, M. G. V. S.; Rasteiro, M. G.; Gamelas, J. A. F. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 188, 1003.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.015 pmid: 34371043 |
| [159] |
Lu, H.; Zhang, L.; Yan, M.; Wang, K.; Jiang, J. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118897.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118897 |
| [160] |
Yang, Y.; Li, N.; Lv, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Dong, K.; Cao, S.; Chen, T. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 1718.
doi: 10.1039/D2NA00097K |
| [161] |
Liu, W.; Zhang, S.; Liu, K.; Yang, H.; Lin, Q.; Xu, T.; Song, X.; Du, H.; Bai, L.; Yao, S.; Si, C. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 384, 135582.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135582 |
| [162] |
Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Xu, L.; Jia, C.; Dai, J.; Song, J.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Henderson, D.; Luo, W.; Li, H.; Minus, M. L.; Li, T.; Hu, L. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606284.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.21 |
| [163] |
Huang, K.; Maltais, A.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102177.
doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2022.102177 |
| [164] |
Song, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, S.; Xu, F. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 49340.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c14948 |
| [165] |
Rajan, K.; Kim, K.; Elder, T. J.; Naskar, A. K.; Labbé, N. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 8835.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c01741 |
| [1] | 何文, 王波, 冯晗俊, 孔祥如, 李桃, 肖睿. CO2捕集膜分离的Pebax基材料研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 226-241. |
| [2] | 刘露杰, 张建, 王亮, 肖丰收. 生物质基多元醇的多相催化选择性氢解★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 533-547. |
| [3] | 于璐瑶, 任祯, 杨宇森, 卫敏. 生物基聚酯单体的定向催化制备[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 175-190. |
| [4] | 伏成玉, 周星宇, 杨鹏. 基于蛋白质类淀粉样聚集的表面功能化★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1566-1576. |
| [5] | 王洁, 叶雨晴, 李源, 马小杰, 王博. 基于无机纳米材料的抗菌抗病毒功能涂层和薄膜[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1338-1350. |
| [6] | 田钊炜, 达伟民, 王雷, 杨宇森, 卫敏. 第二代生物柴油制备的多相催化剂的结构设计及研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1322-1337. |
| [7] | 张琪, 江梦云, 刘天一, 曾意迅, 石胜伟. 可蒸镀自旋交叉配合物的薄膜与器件[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1351-1363. |
| [8] | 孙嘉贤, 刘禹廷, 尹志刚, 郑庆东. 基于吸收互补有机半导体本体复合薄膜的高性能柔性光突触晶体管[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 936-945. |
| [9] | 曹琳安, 魏敏. 电子导电金属有机框架薄膜的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 1042-1056. |
| [10] | 闫彬, 薛丁江, 胡劲松. 硒化亚锗薄膜太阳能电池研究进展※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 797-804. |
| [11] | 舒恒, 包义德日根, 那永. CdS基纳米管光催化氧化5-羟甲基糠醛选择性生成2,5-呋喃二甲醛[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(5): 607-613. |
| [12] | 张蒙茜, 冯霄. 共轭微孔聚合物膜的制备策略及其分离应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(2): 168-179. |
| [13] | 孙稷, 易玖琦, 程龙玖. 定向Monte Carlo格点搜索算法用于氧化铝团簇(Al2O3)n (n=1~50)的结构搜索[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(9): 1154-1163. |
| [14] | 董锦辉, 李进杰, 王赫, 刘彬秀, 彭博, 陈健壮, 林绍梁. 呼吸图法制备基于准聚轮烷的响应性薄膜[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 803-808. |
| [15] | 吴峰, 苏倩倩, 周乐乐, 许鹏飞, 董傲, 钱卫平. 基于二氧化硅胶体晶体薄膜和反射干涉光谱的蛋白冠监测方法[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(3): 338-343. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||