化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (5): 488-497.DOI: 10.6023/A25010031 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
曾玥, 唐笑*( ), 周于芝, 李艳虹, 荆川, 凌发令, 杨红梅, 周贤菊
), 周于芝, 李艳虹, 荆川, 凌发令, 杨红梅, 周贤菊
投稿日期:2025-01-25
发布日期:2025-03-10
基金资助:
Yue Zeng, Xiao Tang*( ), Yuzhi Zhou, Yanhong Li, Chuan Jing, Faling Ling, Hongmei Yang, Xianju Zhou
), Yuzhi Zhou, Yanhong Li, Chuan Jing, Faling Ling, Hongmei Yang, Xianju Zhou
Received:2025-01-25
Published:2025-03-10
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:文章分享
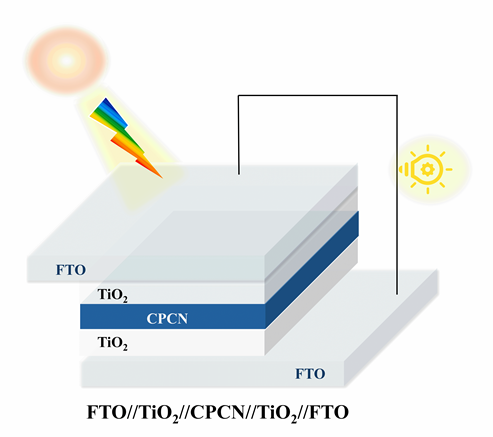
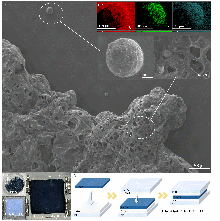
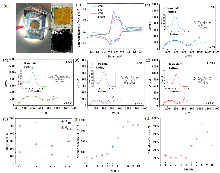
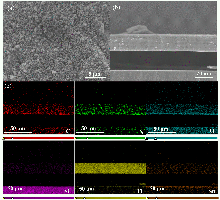
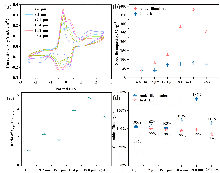
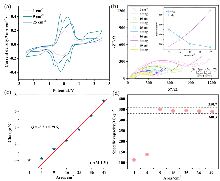
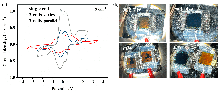
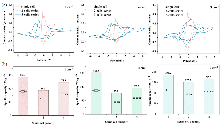
储能技术对于稳定未来智能电网尤为重要. 全固态储能技术仍是推动储能系统发展的关键挑战. 本工作利用富碳氮化碳(CPCN)本征具有光吸收和电荷存储的双重功能和TiO2高介电性制备出不含电解质的全固态光超级电容器. 为提高富碳氮化碳全固态光超级电容器的光生电荷存储容量, 对其性能影响因素进行研究. 通过延长CPCN熟化时间、提高TiO2介孔薄膜的厚度、增大TiO2/CPCN电极面积使光生电荷存储容量显著增加. 并且串联模式下可以有效增大电压窗口, 并联模式下可以进一步减少电子损失, 光生电荷存储容量达到412.8 C•g-1.
曾玥, 唐笑, 周于芝, 李艳虹, 荆川, 凌发令, 杨红梅, 周贤菊. 富碳氮化碳全固态光超级电容器性能影响因素研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(5): 488-497.
Yue Zeng, Xiao Tang, Yuzhi Zhou, Yanhong Li, Chuan Jing, Faling Ling, Hongmei Yang, Xianju Zhou. Study on Factors Affecting Performance of C-Rich Carbon Nitride-based All-Solid-State Photo-Supercapacitor[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(5): 488-497.








| [1] |
|
|
(朱宪国, 博士论文, 华北电力大学, 北京, 2022.)
|
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30707-z pmid: 30111783 |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.202011930 pmid: 33022857 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
|
(何利蓉, 唐笑, 张灵, 李艳虹, 相国涛, 周贤菊, 凌发令, 姚璐, 蒋浩, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 506.)
doi: 10.6023/A20120575 |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
|
(李梅, 钟淑英, 胡军平, 孙宝珍, 徐波, 物理学报, 2024, 73, 138201.)
|
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
|
(马超, 武佳炜, 朱琳, 韩晓霞, 阮伟东, 宋薇, 王旭, 赵冰, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 1024.)
doi: 10.6023/A19050191 |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [1] | 张林, 张慧, 朱从潭, 郭学益, 杨英. CsPbIBr2钙钛矿太阳能电池湿度稳定机制研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(9): 971-978. |
| [2] | 陈宇波, 郑德旭, 王楠, 刘吉双, 于凤阳, 吴飒建, 刘生忠, 李智鹏. 旋涂两步法甲脒铅基钙钛矿太阳能电池近期研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(9): 987-1000. |
| [3] | 江雪, 涂开槐, 段泰男, 肖泽云. 添加剂在有机太阳能电池中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(5): 551-564. |
| [4] | 张雨琦, 占辰, 贡祎, 陆峰, 范曲立. 聚乙二醇化介孔二氧化硅包裹共轭聚合物用于近红外光学诊疗[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(12): 1226-1233. |
| [5] | 贾凌轩, 詹泽庞, 贺紫晗, 狄重安, 朱道本. 面向神经电子接口器件的有机材料进展与展望★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1175-1186. |
| [6] | 孙博, 琚雯雯, 王涛, 孙晓军, 赵婷, 卢晓梅, 陆峰, 范曲立. 高分散共轭聚合物-金属有机框架纳米立方体的制备及抗肿瘤应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 757-762. |
| [7] | 查汉, 房进, 闫翎鹏, 杨永珍, 马昌期. 有机太阳能电池热失效机制及三元共混提升其热稳定性研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 131-145. |
| [8] | 李东旭, 徐翔, 宋佳鸽, 梁松挺, 付予昂, 路新慧, 邹应萍. 轮烷结构优化聚合物太阳能电池光伏性能★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1500-1507. |
| [9] | 齐子朋, 高冬, 朱志成, 贺志远, 白国英. 聚乙烯醇调控水溶性共轭聚噻吩的光学性质[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 921-928. |
| [10] | 祁育, 章福祥. 太阳能光催化分解水制氢※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 827-838. |
| [11] | 闫彬, 薛丁江, 胡劲松. 硒化亚锗薄膜太阳能电池研究进展※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 797-804. |
| [12] | 林文源, 朱清哲, 马云龙, 王鹏, 万硕, 郑庆东. 理性调控聚合物给体-非富勒烯受体的混溶性制备高效率有机太阳能电池※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 724-733. |
| [13] | 周静, 田雪迎, 王斌凯, 张沙沙, 刘宗豪, 陈炜. 低温原子层沉积封装技术在OLED上的应用及对有机、钙钛矿太阳能电池封装的启示[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(3): 395-422. |
| [14] | 王志琴, 项博, 黄晓宇, 陆国林, 冯纯. 磷钨酸对对苯撑乙烯撑寡聚物-b-聚(2-乙烯基吡啶)自晶种行为的影响※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(3): 297-302. |
| [15] | 安攀, 张庆慧, 杨状, 武佳星, 张佳颖, 王雅君, 李宇明, 姜桂元. 双碳目标下太阳能制氢技术的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(12): 1629-1642. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||