化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (7): 716-724.DOI: 10.6023/A25030091 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2025-03-24
发布日期:2025-07-28
基金资助:
Chaofan Guo, jinzhan Su*( ), Liejin Guo
), Liejin Guo
Received:2025-03-24
Published:2025-07-28
Contact:
*E-mail: j.su@mail.xjtu.edu.cn
Supported by:文章分享

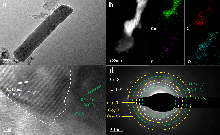
在能源危机和可持续发展的背景下, 具有零碳排放特性的氮还原合成氨(NRR)方法具有很好的前景. 开发具有高氨产率和法拉第效率(FE)的高效电催化剂对提高合成氨效率至关重要. 通过界面工程和空位工程来调节电子结构是提高电催化剂性能的一种新途径, 制备了具备核壳异质界面结构和硫空位的Cu2S@Co3S4/CF催化剂, 该催化剂表现出122 μg•h-1•cm-2的氨产率, 法拉第反应效率为34.6%, 并且经过6次循环测试后性能没有发生衰减, 优于大多数已报道的催化剂, 结合实验和表征可以发现, 该催化剂的高性能归因于Cu2S核可以通过均匀界面向表面Co3S4提供丰富的电子, 促进氮还原加氢反应, 并限制了*H耦合形成氢气, 抑制了竞争的析氢反应(HER), 有助于在氨产量和法拉第效率之间的更理想的平衡, 并且硫空位的引入进一步促进了N2的吸附和活化. 此外, Cu2S@Co3S4/CF作为阴极电催化剂应用于锌-氮气电池中表现出14.6 mW•cm-2的出色功率密度, 能够在电化学合成NH3的同时实现储能, 这项工作展示了一种很有前途的开发高效电催化剂的方法, 对解决能源危机和促进向低碳经济的转变具有重要意义.
郭超凡, 苏进展, 郭烈锦. 具有内置电场效应的Cu2S@Co3S4/CF核壳异质结催化剂氮还原性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(7): 716-724.
Chaofan Guo, jinzhan Su, Liejin Guo. Nitrogen Reduction Properties of Cu2S@Co3S4/CF Core-shell Heterojunction Catalysts with Built-in Electric Field Effect[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(7): 716-724.















| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b02501 pmid: 31701745 |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
|
(王亚飞, 徐良晨, 姚向昱, 闫霆, 潘卫国, 当代化工研究, 2024, 15.)
|
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [1] |
|
|
(郭烈锦, 科技导报, 2021, 39, 1.)
|
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.6023/A22010057 |
|
(张谭, 余钟亮, 余嘉祺, 万慧凝, 包成宇, 涂文强, 杨颂, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 788.)
doi: 10.6023/A22010057 |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.6023/A20090412 |
|
(詹溯, 章福祥, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 146.)
doi: 10.6023/A20090412 |
|
| [9] |
|
|
(张晓方, 甘汶, 纪之骄, 许明, 李初福, 何广利, 化工进展, 2025, 44, 809.)
doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2024-0198 |
|
| [10] |
|
|
(熊昆, 陈伽瑶, 杨娜, 蒋尚坤, 李莉, 魏子栋, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1138.)
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
|
(姚嫣, 付年凯, 有机化学, 2025, 45, 1.)
|
|
| [14] |
|
|
(叶增辉, 刘华清, 张逢质, 有机化学, 2024, 44, 840.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202310034 |
|
| [15] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
|
(应霞薇, 浮建军, 曾敏, 刘文, 张天宇, 沈培康, 张信义, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 503.)
doi: 10.6023/A21120562 |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [1] | 徐梦鑫, 杨智健, 孙径, 邹文强, 徐忠宁, 郭国聪. Pd/Pr-CeO2催化剂载体氧空位调控CO酯化制碳酸二甲酯选择性[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(7): 655-660. |
| [2] | 张娜娜, 李静. 氧空位增强PdNi/HfO2催化剂在乙二醇电催化氧化中的活性[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(7): 709-715. |
| [3] | 罗雅玲, 庄展洋, 范峰滔, 李灿. Al掺杂SrTiO3的合成调控及其光催化全分解水性能[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(6): 608-615. |
| [4] | 刘珊珊, 董微微, 李珍珍, 张瑶瑶, 李超, 焦林郁. 离子液体调控的串联脱氢环化反应多样性合成生物质基氮杂环[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(5): 479-487. |
| [5] | 胡博, 肖霞, 王鹏, 束小龙, 卞梦琪, 王健捷, 赵震. 二氧化碳加氢制低碳烯烃Fe基催化剂研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(5): 535-550. |
| [6] | 田野, 张博尧, 陈俊宇, 姬梦鑫, 任浩, 匙玉华. MoSi2N4/ZrS2(HfS2) II型异质结调节电子传输用于光催化制氢的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(5): 498-509. |
| [7] | 杨雪, 刘妍伶, 陈霞, 周晓玉, 王爱玲, 刘海龙. 草酰单胺配体促进的低剂量钯催化水相Suzuki偶联反应[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(4): 354-359. |
| [8] | 卢一林, 董盛杰, 崔方超, 薄婷婷, 毛卓. 希托夫紫磷烯/SnS2范德华异质结作为直接全解水光催化剂的理论构建[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(4): 377-389. |
| [9] | 孙伟, 辛国祥, 刘飞, 鞠藤, 程宇通, 宋金玲, 包金小, 布林朝克. 三维石墨烯/富含氧空位Fe2O3复合材料的构建实现超级电容器超高能量密度[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 张宇, 张睿, 王子健, 汪啸, 宋术岩, 张洪杰. 固体酸催化剂的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(2): 152-169. |
| [11] | 佟浩, 邓玉雪, 李磊, 陶铮, 申来法, 张校刚. 高载量ZnO@C@NiCo-LDH异质结构电极的制备及其超电容性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(2): 110-118. |
| [12] | 王帅, 宋华. 氮修饰Ni2P-Nx/SiO2催化剂设计合成及间甲酚加氢脱氧性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(9): 979-986. |
| [13] | 张帆帆, 蔡元韬, 陶剑波, 常国菊, 郭欣辰, 郝仕油. Zn, C引入量和煅烧温度对ZnO/C/CeO2光催化还原Cu2+效率的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(8): 871-878. |
| [14] | 付祎帅, 王文亮, 苗晖, 陈育彤, 崔洋怡, 王紫薇, 潘佳文, 肖国伟. 微波响应型CMF@CoS2/MoS2催化剂的制备及其用于木质素蒸气的催化重整[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(6): 596-603. |
| [15] | 刘浩, 徐旭莉, 郭勇, 刘晓晖, 王艳芹. Ru/NiPOx高效电催化醛还原胺化反应的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(5): 477-485. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||