化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (5): 625-632.DOI: 10.6023/A21120606 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 中国科学院青年创新促进会合辑
研究论文
廉纬a,b, 方泽铠a,b, 涂大涛a,b,c,*( ), 李嘉尧a,b, 韩思远b, 李仁富b,c, 商晓颖b,c, 陈学元a,b,c,*(
), 李嘉尧a,b, 韩思远b, 李仁富b,c, 商晓颖b,c, 陈学元a,b,c,*( )
)
投稿日期:2021-12-30
发布日期:2022-05-31
通讯作者:
涂大涛, 陈学元
作者简介:基金资助:
Wei Liana,b, Zekai Fanga,b, Datao Tua,b,c( ), Jiayao Lia,b, Siyuan Hanb, Renfu Lib,c, Xiaoying Shangb,c, Xueyuan Chena,b,c(
), Jiayao Lia,b, Siyuan Hanb, Renfu Lib,c, Xiaoying Shangb,c, Xueyuan Chena,b,c( )
)
Received:2021-12-30
Published:2022-05-31
Contact:
Datao Tu, Xueyuan Chen
About author:Supported by:文章分享

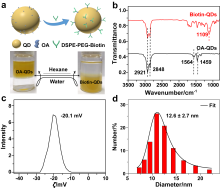
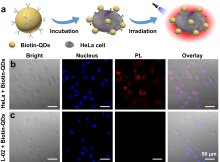
AgInSe2 (AISe)量子点具有带隙小、斯托克斯位移大、荧光寿命长且不含重金属有毒元素等特性, 使其在生物医学领域具有重要研究价值. 同时, AISe量子点的光学性质对尺寸和组成具有强烈的依赖关系, 然而传统的直接合成法很难实现对AISe量子点形貌和组分的精准调控, 从而极大限制了其发光效率. 对此, 作者提出了温和条件(75 ℃)下以In2Se3:Zn2+量子点为模板, 离子交换法控制合成AISe近红外荧光量子点的策略, 所合成的AISe量子点很好地维持了In2Se3:Zn2+模板的形貌, 进一步通过系统调节Ag/In投料物质的量比控制离子交换程度, AISe量子点的实际Ag/In组分比实现了从0.26~1.09宽范围调节; 最高绝对量子产率可达42.5%, 这一数值远高于通过直接合成法所得到的AISe量子点. 通过稳态、瞬态和低温光谱等手段对不同组分AISe量子点的发光行为进行了系统的光谱学研究, 揭示了其发光机理. 另外, 利用AISe量子点高效的近红外发光和良好的生物安全性, 实现了基于AISe近红外量子点探针的肿瘤细胞靶向成像, 展示出AISe量子点在生物成像和疾病的早期诊疗等领域具有很好的应用潜力.
廉纬, 方泽铠, 涂大涛, 李嘉尧, 韩思远, 李仁富, 商晓颖, 陈学元. 模板法控制合成AgInSe2:Zn2+近红外荧光量子点及其生物标记应用※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(5): 625-632.
Wei Lian, Zekai Fang, Datao Tu, Jiayao Li, Siyuan Han, Renfu Li, Xiaoying Shang, Xueyuan Chen. Template-Based Controlled Synthesis and Bioapplication of AgInSe2:Zn2+ Near-Infrared Luminescent Quantum Dots※[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(5): 625-632.

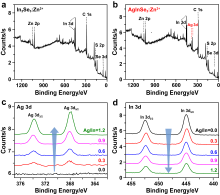
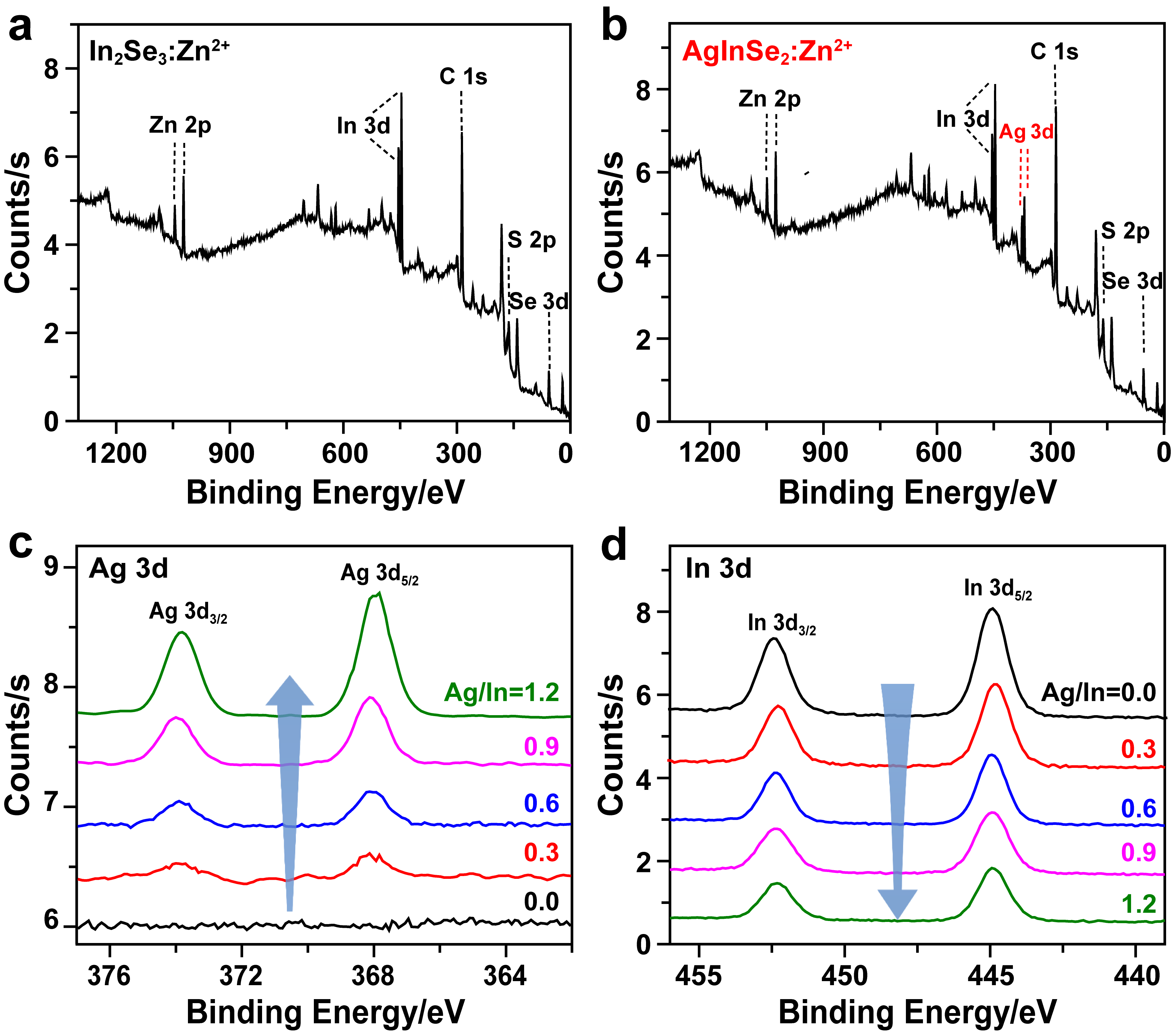


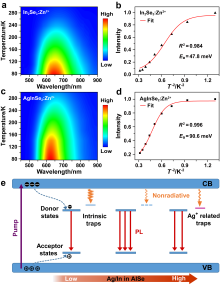



| [1] |
Yoffe, A. D. Adv. Phys. 2001, 50, 1.
|
| [2] |
Dai, X. L.; Zhang, Z. X.; Jin, Y. Z.; Niu, Y.; Cao, H. J.; Liang, X. Y.; Chen, L. W.; Wang, J. P.; Peng, X. G. Nature 2014, 515, 96.
doi: 10.1038/nature13829 |
| [3] |
Liu, Y. H.; Zhang, D. X.; Mao, B. D.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Tan, H. Q.; Kang, Z. H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 1349. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20060274 |
|
(刘艳红, 张东旭, 毛宝东, 黄慧, 刘阳, 谭华桥, 康振辉, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1349.)
doi: 10.6023/A20060274 |
|
| [4] |
Xiong, R.; Yu, S. T.; Smith, M. J.; Zhou, J.; Krecker, M.; Zhang, L. J.; Nepal, D.; Bunning, T. J.; Tsukruk, V. V. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 9074.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b03305 pmid: 31381316 |
| [5] |
Medintz, I. L.; Uyeda, H. T.; Goldman, E. R.; Mattoussi, H. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 435.
pmid: 15928695 |
| [6] |
Li, Y.; Li, J. H.; Xu, L. M.; Chen, J. W.; Song, J. Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 126. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20080386 |
|
(李严, 李金航, 许蕾梦, 陈嘉伟, 宋继中, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 126.)
doi: 10.6023/A20080386 |
|
| [7] |
Meinardi, F.; McDaniel, H.; Carulli, F.; Colombo, A.; Velizhanin, K. A.; Makarov, N. S.; Simonutti, R.; Klimov, V. I.; Brovelli, S. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 878.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.178 |
| [8] |
Yu, M.; Zhang, Z. J.; Zhu, G. W.; Gu, Z. H.; Duan, Y. L.; Yu, L. C.; Gao, G. B.; Sun, T. L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1281. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21070333 |
|
(余梦, 张子俊, 朱国委, 谷振华, 段玉霖, 余良翀, 高冠斌, 孙涛垒, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1281.)
doi: 10.6023/A21070333 |
|
| [9] |
Niu, Y.; Pu, C. D.; Lai, R. C.; Meng, R. Y.; Lin, W. Z.; Qin, H. Y.; Peng, X. G. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 1149.
doi: 10.1007/s12274-016-1287-3 |
| [10] |
Fan, G. Y.; Wang, C. Y.; Fang, J. Y. Nano Today 2014, 9, 69.
doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2014.02.007 |
| [11] |
Chen, Y. Y.; Li, S. J.; Huang, L. J.; Pan, D. C. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 7819.
doi: 10.1021/ic400083w |
| [12] |
Li, Q.; Zhang, T.; Gu, H. W.; Ding, F. Z.; Qu, F.; Peng, X. Y.; Wang, H. Y.; Wu, Z. P. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 929. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A13010052 |
|
李谦, 张腾, 古宏伟, 丁发柱, 屈飞, 彭星煜, 王洪艳, 吴战鹏, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 929.)
doi: 10.6023/A13010052 |
|
| [13] |
Xie, R. G.; Rutherford, M.; Peng, X. G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5691.
doi: 10.1021/ja9005767 |
| [14] |
Regulacio, M. D.; Han, M. Y. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 511.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00535 |
| [15] |
Jain, S.; Bharti, S.; Bhullar, G. K.; Tripathi, S. K. J. Lumin. 2020, 219, 116912.
doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2019.116912 |
| [16] |
Feng, L.; Liang, X. J.; Yang, F.; Zhong, J. S.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, W. D. Acta Chim. Sinica 2011, 69, 2870. (in Chinese)
|
|
(冯丽, 梁晓娟, 杨帆, 钟家松, 王芸, 向卫东, 化学学报, 2011, 69, 2870.)
doi: 10.6023/A1106213 |
|
| [17] |
Zhong, H. Z.; Bai, Z. L.; Zou, B. S. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 3167.
doi: 10.1021/jz301345x |
| [18] |
Pathak, D.; Wagner, T.; Subrt, J.; Kupcik, J. Can. J. Phys. 2014, 92, 789.
doi: 10.1139/cjp-2013-0546 |
| [19] |
Yarema, O.; Yarema, M.; Wood, V. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 1446.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b04710 |
| [20] |
Kameyama, T.; Douke, Y.; Shibakawa, H.; Kawaraya, M.; Segawa, H.; Kuwabata, S.; Torimoto, T. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 29517.
doi: 10.1021/jp508769f |
| [21] |
Zacharia, A.; Papagiorgis, P.; Yarema, O.; Moser, A.; Othonos, A.; Luisier, M.; Wood, V.; Yarema, M.; Itskos, G. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 11239.
doi: 10.1021/acsanm.1c02685 |
| [22] |
Deng, D. W.; Qu, L. Z.; Gu, Y. Q. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 7077.
doi: 10.1039/C4TC01147C |
| [23] |
De Trizio, L.; Manna, L. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10852.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00739 pmid: 26891471 |
| [24] |
Gu, J.; Ding, Y.; Ke, J.; Zhang, Y. W.; Yan, C. H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 360. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A12121014 |
|
(顾均, 丁祎, 柯俊, 张亚文, 严纯华, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 360.)
doi: 10.6023/A12121014 |
|
| [25] |
Tappan, B. A.; Horton, M. K.; Brutchey, R. L. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 2935.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b05163 |
| [26] |
Langevin, M. A.; Ritcey, A. M.; Ni Allen, C. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3476.
doi: 10.1021/nn406439w |
| [27] |
Zhou, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhu, Y. H.; Cho, Y. J.; He, Q.; Yang, X.; Herrera, K.; Chu, Z. D.; Han, Y.; Downer, M. C.; Peng, H. L.; Lai, K. J. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 5508.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b02198 pmid: 28841328 |
| [28] |
Han, G.; Chen, Z. G.; Drennan, J.; Zou, J. Small 2014, 10, 2747.
doi: 10.1002/smll.201400104 |
| [29] |
Chen, B. K.; Chang, S.; Li, D. Y.; Chen, L. L.; Wang, Y. T.; Chen, T.; Zou, B. S.; Zhong, H. Z.; Rogach, A. L. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 5949.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b01971 |
| [30] |
Li, X.; Tu, D. T.; Yu, S. H.; Song, X. R.; Lian, W.; Wei, J. J.; Shang, X. Y.; Li, R. F.; Chen, X. Y. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 1804.
doi: 10.1007/s12274-019-2435-3 |
| [31] |
Yao, J. K.; Lifante, J.; Rodriguez-Sevilla, P.; de la Fuente-fernandez, M.; Sanz-Rodriguez, F.; Ortgies, D. H.; Calderon, O. G.; Melle, S.; Ximendes, E.; Jaque, D.; Marin, R. Small 2021, 17, 2103505.
doi: 10.1002/smll.202103505 |
| [32] |
Sousa, F. L. N.; Souza, B. A. S.; Jesus, A. C. C.; Azevedo, W. M.; Mansur, H. S.; Freitas, D. V.; Navarro, M. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 1239.
doi: 10.1039/C9GC03647D |
| [33] |
Kang, X. J.; Yang, Y. C.; Huang, L. J.; Tao, Y.; Wang, L.; Pan, D. C. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4482.
doi: 10.1039/C5GC00908A |
| [34] |
Luo, H.; Guo, S. H.; Zhang, Y. B.; Bu, K. J.; Lin, H. R.; Wang, Y. Q.; Yin, Y. F.; Zhang, D. Z.; Jin, S. Y.; Zhang, W. Q.; Yang, W. G.; Ma, B. W.; Lu, X. J. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2100786.
doi: 10.1002/advs.202100786 |
| [35] |
Lian, W.; Tu, D. T.; Hu, P.; Song, X. R.; Gong, Z. L.; Chen, T.; Song, J. B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X. Y. Nano Today 2020, 35, 100943.
doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2020.100943 |
| [36] |
Hamanaka, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Tsuzuki, M.; Kuzuya, T. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 1786.
doi: 10.1021/jp110409q |
| [37] |
Hu, J. H.; Song, J. L. Q.; Tang, Z. S.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Zhou, R. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 5821.
doi: 10.1039/D0TC00014K |
| [38] |
Knowles, K. E.; Hartstein, K. H.; Kilburn, T. B.; Marchioro, A.; Nelson, H. D.; Whitham, P. J.; Gamelin, D. R. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10820.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00048 |
| [39] |
Gao, Y.; Li, R. F.; Zheng, W.; Shang, X. Y.; Wei, J. J.; Zhang, M. R.; Xu, J.; You, W. W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X. Y. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 5452.
doi: 10.1039/c9sc01321k pmid: 31293727 |
| [1] | 王海朋, 蔡文生, 邵学广. 抗冻剂抗冻机制的近红外光谱与分子模拟研究★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1167-1174. |
| [2] | 郑文山, 高冠斌, 邓浩, 孙涛垒. Ag2Se@Ag2S核壳量子点的室温合成及其近红外荧光性能优化[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 763-770. |
| [3] | 吕鑫, 吴仪, 张勃然, 郭炜. 过氧化氢激活型近红外氟硼二吡咯光敏剂的设计、合成及光动力治疗研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(4): 359-370. |
| [4] | 贺晓梦, 袁方, 张素雅, 张健健. 基于尼罗红类ONOO–近红外荧光探针的开发及其成像应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1515-1521. |
| [5] | 李奎琛, 郑开元, 何静嘉, 金泽浩, 何秋, 王丽丽. 单相硫化锌量子点制作白光发光二极管(WQLEDs)[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1327-1333. |
| [6] | 刘巴蒂, 王承俊, 钱鹰. 噻吩基氟硼二吡咯近红外光敏染料的合成、双光子荧光成像及光动力治疗研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1071-1083. |
| [7] | 刘若湄, 冯艳辉, 李卓, 卢珊, 关天用, 李幸俊, 刘䶮, 陈卓, 陈学元. 基于cypate光裂解的新型近红外光响应稀土上转换纳米载药系统※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 423-427. |
| [8] | 吴志芬, 柯建熙, 刘永升, 孙蓬明, 洪茂椿. 稀土近红外二区纳米荧光影像探针及其生物医学应用※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 542-552. |
| [9] | 张景荣, 黄得财, 黄聪聪, 梁思思, 朱浩淼. In2BP3O12:Cr3+宽带近红外荧光粉的发光性能及应用研究※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 453-459. |
| [10] | 王文涛, 赵高崇, 杨柳, 周意诚, 丁黎明. 基于磁响应光子晶体与量子点的多重变色防伪研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(12): 1576-1582. |
| [11] | 王其, 夏辉, 熊炎威, 张新敏, 蔡杰, 陈冲, 高逸聪, 陆峰, 范曲立. 调控供电子策略简易制备近红外二区有机小分子光学诊疗试剂[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(11): 1485-1493. |
| [12] | 王旭生, 杨胥, 陈春辉, 李红芳, 黄远标, 曹荣. 石墨烯量子点/铁基金属-有机骨架复合材料高效光催化二氧化碳还原※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(1): 22-28. |
| [13] | 黄菊, 李贞, 刘志洪. 近红外光激发功能化上转换纳米颗粒用于解聚Aβ聚集体[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(8): 1049-1057. |
| [14] | 黄靖, 王超, 林敏刚, 曾钫, 吴水珠. 醌氧化还原酶响应型光声探针的合成及其对乳腺癌的成像[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(3): 331-337. |
| [15] | 高贺麒, 焦迪, 欧翰林, 章经天, 丁丹. 高性能聚集诱导发光纳米探针用于肿瘤切除手术导航[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(3): 319-325. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||